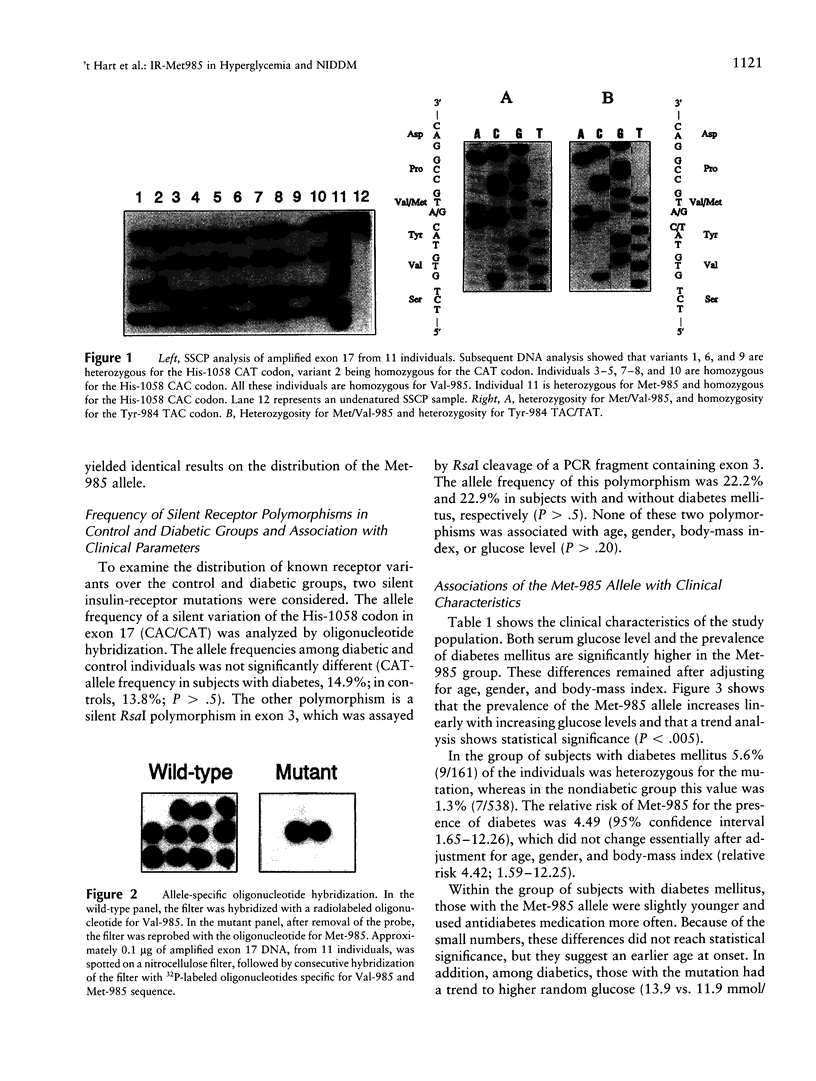
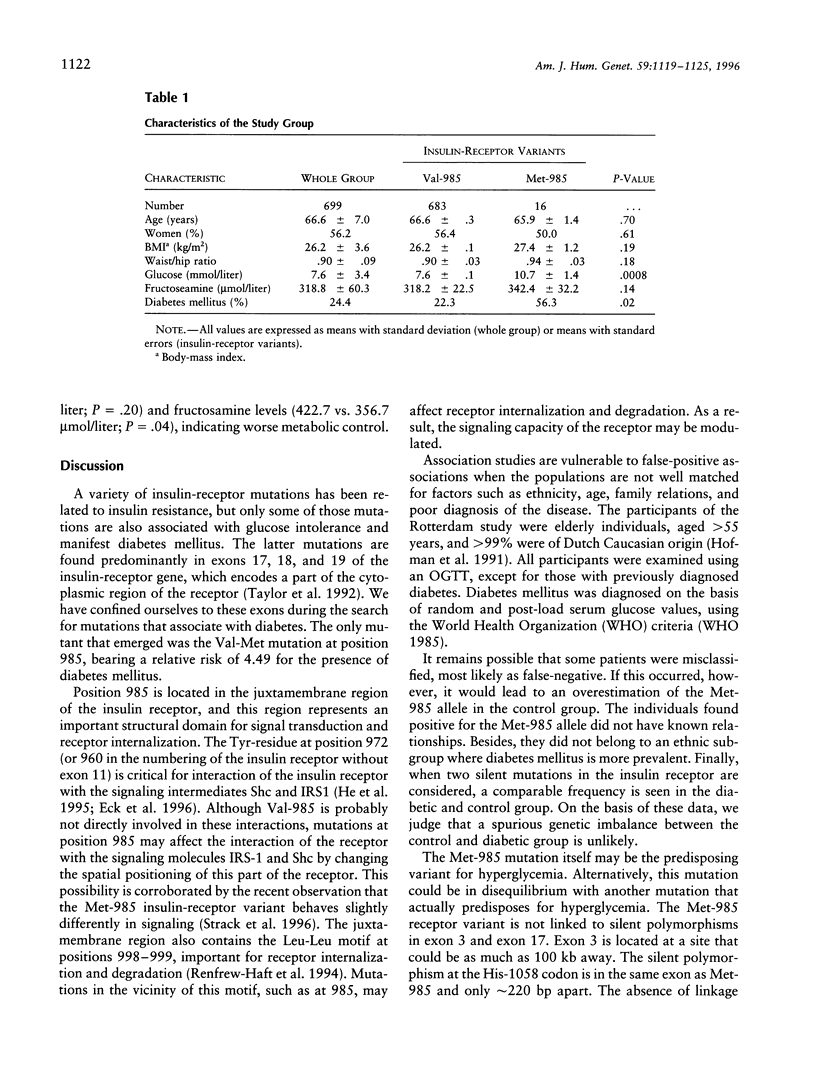
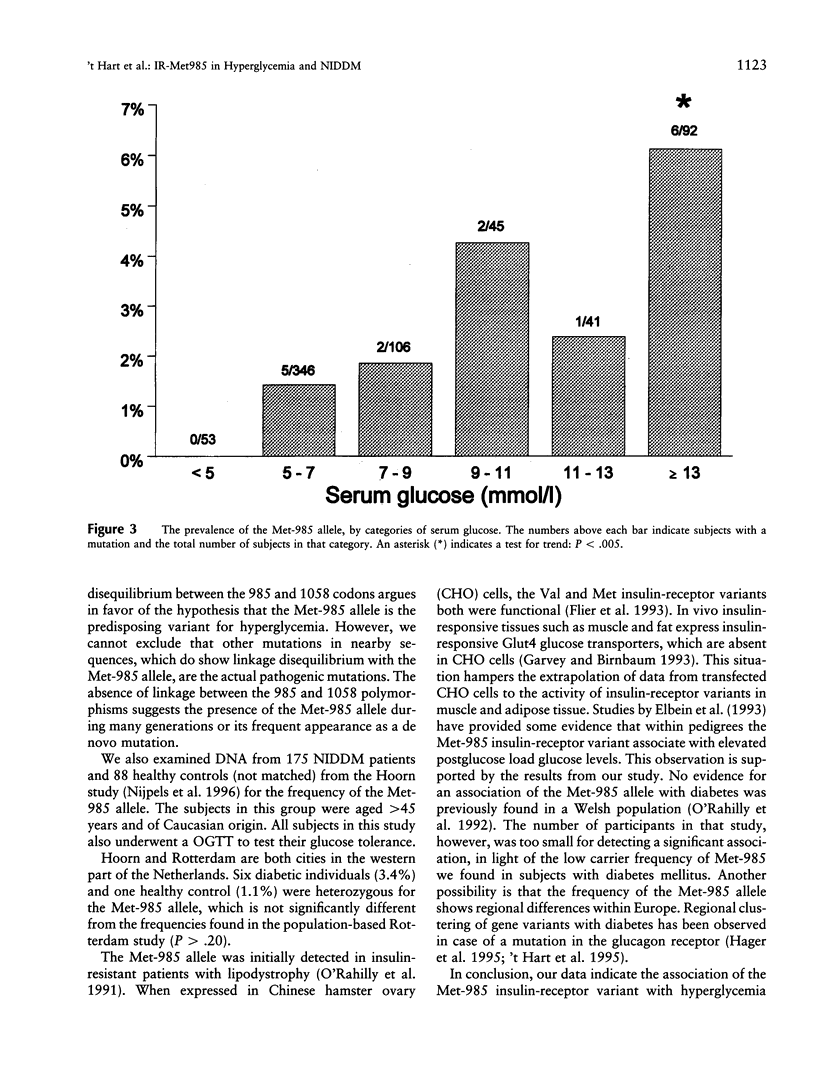
Abstract
One of the characteristics of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) is the presence of insulin resistance. Most NIDDM patients have a normal sequence of the insulin receptor, indicating that, if insulin-receptor mutations contribute to the development of NIDDM, they will be present only in a minor fraction of the NIDDM population. The goal of the present study was to examine whether insulin-receptor mutations contribute to the development of NIDDM. We examined 161 individuals with NIDDM and 538 healthy controls from the population-based Rotterdam study for the presence of mutations in the insulin-receptor gene by SSCP. A heterozygous mutation changing valine-985 into methionine was detected in 5.6% of diabetic subjects and in 1.3% of individuals with normal oral glucose tolerance test. Adjusted for age, gender, and body-mass index, this revealed a relative risk for diabetes of 4.49 (95% confidence interval 1.59-12.25) for Met-985 carriers. When the total study group was analyzed, the prevalence of the mutation increased with increasing serum glucose levels (test for trend P < .005). We conclude that the Met-985 insulin-receptor variant associates with hyperglycemia and represents a risk factor for NIDDM.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck-Nielsen H., Groop L. C. Metabolic and genetic characterization of prediabetic states. Sequence of events leading to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):1714–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI117518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Dhe-Paganon S., Trüb T., Nolte R. T., Shoelson S. E. Structure of the IRS-1 PTB domain bound to the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):695–705. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein S. C., Sorensen L. K., Schumacher M. C. Methionine for valine substitution in exon 17 of the insulin receptor gene in a pedigree with familial NIDDM. Diabetes. 1993 Mar;42(3):429–434. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J., Franssila-Kallunki A., Ekstrand A., Saloranta C., Widén E., Schalin C., Groop L. Early metabolic defects in persons at increased risk for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 10;321(6):337–343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908103210601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feskens E. J., Loeber J. G., Kromhout D. Diet and physical activity as determinants of hyperinsulinemia: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Aug 15;140(4):350–360. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Moller D. E., Moses A. C., O'Rahilly S., Chaiken R. L., Grigorescu F., Elahi D., Kahn B. B., Weinreb J. E., Eastman R. Insulin-mediated pseudoacromegaly: clinical and biochemical characterization of a syndrome of selective insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jun;76(6):1533–1541. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.6.8388881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Birnbaum M. J. Cellular insulin action and insulin resistance. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Oct;7(4):785–873. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(05)80237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haft C. R., Klausner R. D., Taylor S. I. Involvement of dileucine motifs in the internalization and degradation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26286–26294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager J., Hansen L., Vaisse C., Vionnet N., Philippi A., Poller W., Velho G., Carcassi C., Contu L., Julier C. A missense mutation in the glucagon receptor gene is associated with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):299–304. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart L. M., Stolk R. P., Jansen J. J., Grobbee D. E., Lemkes H. H., Maassen J. A. Absence of the Gly40-Ser mutation in the glucagon receptor among diabetic patients in the Netherlands. Diabetes Care. 1995 Oct;18(10):1400–1401. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.10.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley A. T., Turner R. C., Permutt M. A., Patel P., Tanizawa Y., Chiu K. C., O'Rahilly S., Watkins P. J., Wainscoat J. S. Linkage of type 2 diabetes to the glucokinase gene. Lancet. 1992 May 30;339(8805):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91958-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W., O'Neill T. J., Gustafson T. A. Distinct modes of interaction of SHC and insulin receptor substrate-1 with the insulin receptor NPEY region via non-SH2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23258–23262. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman A., Grobbee D. E., de Jong P. T., van den Ouweland F. A. Determinants of disease and disability in the elderly: the Rotterdam Elderly Study. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Jul;7(4):403–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00145007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Takata Y., Sasaoka T., Takada Y., Morioka H., Haruta T., Sawa T., Iwanishi M., Hu Y. G., Suzuki Y. Two naturally occurring mutations in the kinase domain of insulin receptor accelerate degradation of the insulin receptor and impair the kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):31019–31027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krook A., Kumar S., Laing I., Boulton A. J., Wass J. A., O'Rahilly S. Molecular scanning of the insulin receptor gene in syndromes of insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1994 Mar;43(3):357–368. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Kadowaki T. Maternally inherited diabetes and deafness: a new diabetes subtype. Diabetologia. 1996 Apr;39(4):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00400668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Flier J. S. Normal insulin-receptor cDNA sequence in Pima Indians with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1496–1500. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijpels G., Popp-Snijders C., Kostense P. J., Bouter L. M., Heine R. J. Fasting proinsulin and 2-h post-load glucose levels predict the conversion to NIDDM in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance: the Hoorn Study. Diabetologia. 1996 Jan;39(1):113–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00400421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S., Choi W. H., Patel P., Turner R. C., Flier J. S., Moller D. E. Detection of mutations in insulin-receptor gene in NIDDM patients by analysis of single-stranded conformation polymorphisms. Diabetes. 1991 Jun;40(6):777–782. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S., Krook A., Morgan R., Rees A., Flier J. S., Moller D. E. Insulin receptor and insulin-responsive glucose transporter (GLUT 4) mutations and polymorphisms in a Welsh type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic population. Diabetologia. 1992 May;35(5):486–489. doi: 10.1007/BF02342449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Bell G. I. Human insulin-receptor gene. Partial sequence and amplification of exons by polymerase chain reaction. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):123–128. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Cama A., Accili D., Barbetti F., Quon M. J., de la Luz Sierra M., Suzuki Y., Koller E., Levy-Toledano R., Wertheimer E. Mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):566–595. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaag A., Henriksen J. E., Beck-Nielsen H. Decreased insulin activation of glycogen synthase in skeletal muscles in young nonobese Caucasian first-degree relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):782–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI115656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vionnet N., Stoffel M., Takeda J., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Zouali H., Lesage S., Velho G., Iris F., Passa P. Nonsense mutation in the glucokinase gene causes early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):721–722. doi: 10.1038/356721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warram J. H., Martin B. C., Krolewski A. S., Soeldner J. S., Kahn C. R. Slow glucose removal rate and hyperinsulinemia precede the development of type II diabetes in the offspring of diabetic parents. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Dec 15;113(12):909–915. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-12-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H. Pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1994 Jan 8;343(8889):91–95. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90821-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland J. M., Lemkes H. H., Ruitenbeek W., Sandkuijl L. A., de Vijlder M. F., Struyvenberg P. A., van de Kamp J. J., Maassen J. A. Mutation in mitochondrial tRNA(Leu)(UUR) gene in a large pedigree with maternally transmitted type II diabetes mellitus and deafness. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):368–371. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vorm E. R., van der Zon G. C., Möller W., Krans H. M., Lindhout D., Maassen J. A. An Arg for Gly substitution at position 31 in the insulin receptor, linked to insulin resistance, inhibits receptor processing and transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]