Abstract
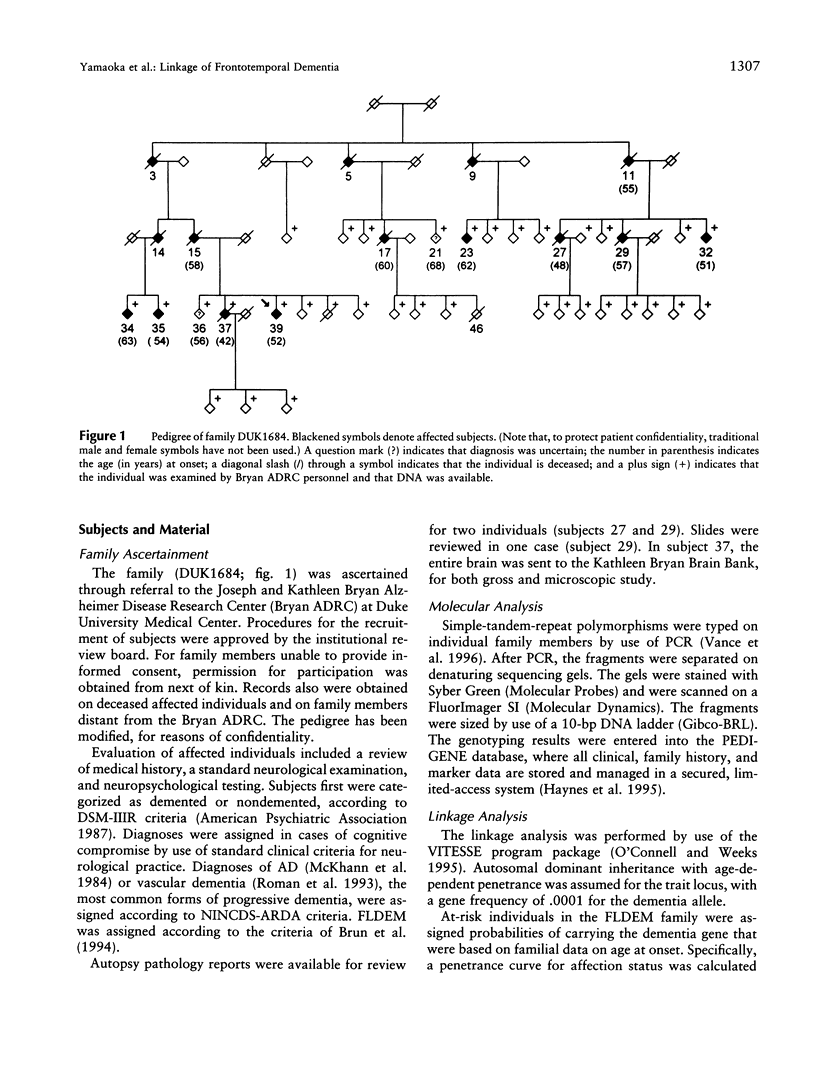
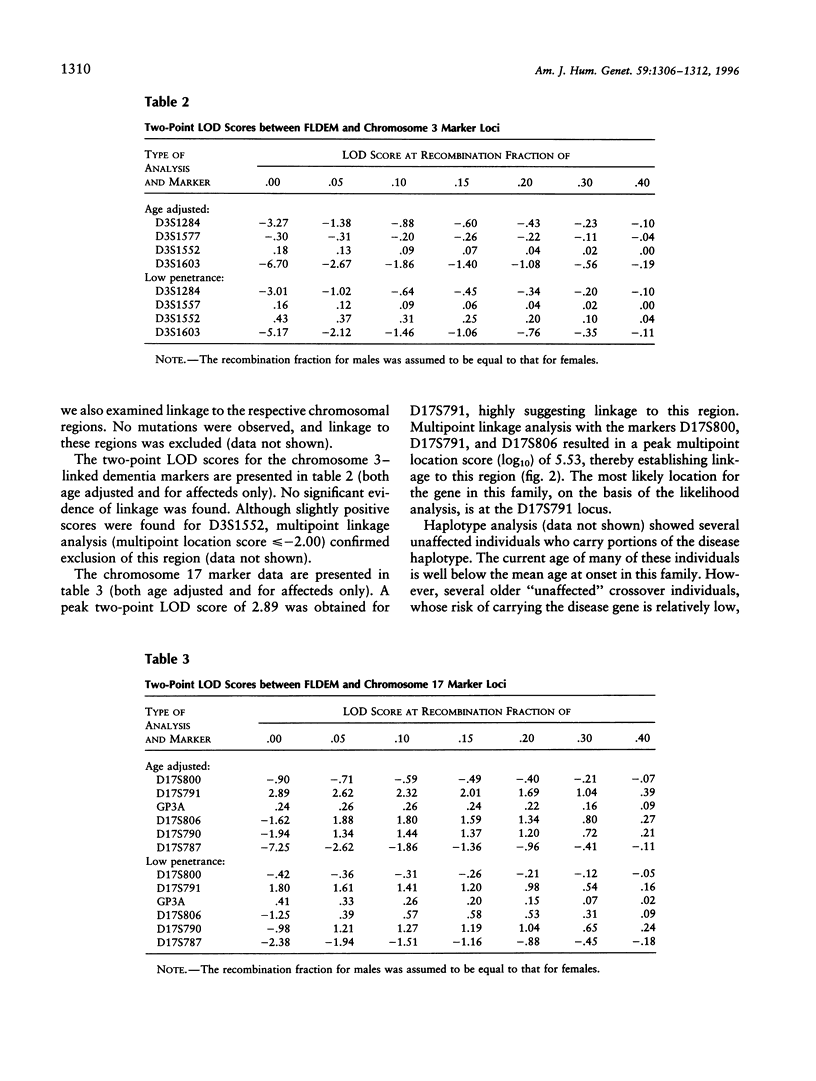
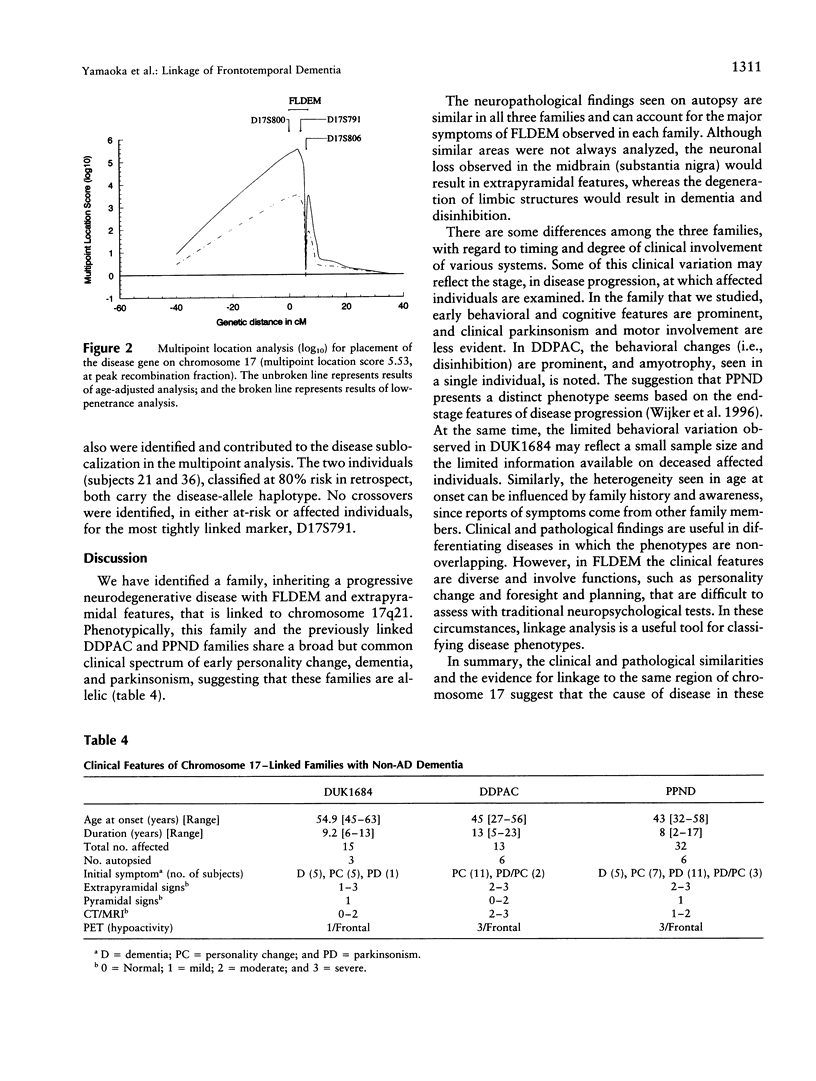
Frontotemporal dementia is a behavioral disorder of insidious onset and variable progression. Clinically, its early features reflect frontal lobe dysfunction characterized by personality change, deterioration in memory and executive functions, and stereotypical and perseverative behaviors. Pathologically, there is degeneration of the neocortex and subcortical nuclei, without distinctive features such as plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, or Pick or Lewy bodies. Within-family variation in neuropathology and clinical phenotype is observed. In cases where family aggregation is observed, it is inherited as an autosomal dominant, age-dependent disorder. Family studies recently have identified two dementia loci: chromosome 17 for disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophic complex and pallido-ponto-nigral degeneration and chromosome 3 for familial nonspecific dementia. We describe a family (DUK1684) with clinically and neuropathologically confirmed, autosomal dominant, non-Alzheimer disease dementia. Linkage analysis of this family showed evidence for linkage to chromosome 17q21, with a multipoint location score (log10) of 5.52. A comparison of the clinical and pathological features in DUK1684 with those of the other chromosome 17-linked families, together with the linkage data, suggests that these families are allelic. These studies emphasize that genetic linkage analysis remains a useful tool for differentiating disease loci in clinically complex traits.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J., Ashworth A., Gydesen S., Sorensen A., Rossor M., Hardy J., Collinge J. Familial non-specific dementia maps to chromosome 3. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1625–1628. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and neuropathological criteria for frontotemporal dementia. The Lund and Manchester Groups. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Apr;57(4):416–418. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.4.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gydesen S., Hagen S., Klinken L., Abelskov J., Sørensen S. A. Neuropsychiatric studies in a family with presenile dementia different from Alzheimer and Pick disease. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1987 Sep;76(3):276–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1987.tb02896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Lahad E., Wasco W., Poorkaj P., Romano D. M., Oshima J., Pettingell W. H., Yu C. E., Jondro P. D., Schmidt S. D., Wang K. Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer's disease locus. Science. 1995 Aug 18;269(5226):973–977. doi: 10.1126/science.7638622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch T., Sano M., Marder K. S., Bell K. L., Foster N. L., Defendini R. F., Sima A. A., Keohane C., Nygaard T. G., Fahn S. Clinical characteristics of a family with chromosome 17-linked disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophy complex. Neurology. 1994 Oct;44(10):1878–1884. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.10.1878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J. R., Weeks D. E. The VITESSE algorithm for rapid exact multilocus linkage analysis via genotype set-recoding and fuzzy inheritance. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):402–408. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Horwitz B., Grady C. L., Haxby J. V., DeCarli C., Schapiro M. B. Abnormal brain glucose metabolism in Alzheimer's disease, as measured by position emission tomography. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;291:231–248. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5931-9_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román G. C., Tatemichi T. K., Erkinjuntti T., Cummings J. L., Masdeu J. C., Garcia J. H., Amaducci L., Orgogozo J. M., Brun A., Hofman A. Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology. 1993 Feb;43(2):250–260. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. M., Jonasson F., Lennon F., Sarrica J., Damji K. F., Stauffer J., Pericak-Vance M. A., Klintworth G. K. Linkage of a gene for macular corneal dystrophy to chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;58(4):757–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh K. A., Butters N., Hughes J. P., Mohs R. C., Heyman A. Detection and staging of dementia in Alzheimer's disease. Use of the neuropsychological measures developed for the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease. Arch Neurol. 1992 May;49(5):448–452. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530290030008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijker M., Wszolek Z. K., Wolters E. C., Rooimans M. A., Pals G., Pfeiffer R. F., Lynch T., Rodnitzky R. L., Wilhelmsen K. C., Arwert F. Localization of the gene for rapidly progressive autosomal dominant parkinsonism and dementia with pallido-ponto-nigral degeneration to chromosome 17q21. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jan;5(1):151–154. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Lynch T., Pavlou E., Higgins M., Nygaard T. G. Localization of disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophy complex to 17q21-22. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;55(6):1159–1165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


