Abstract
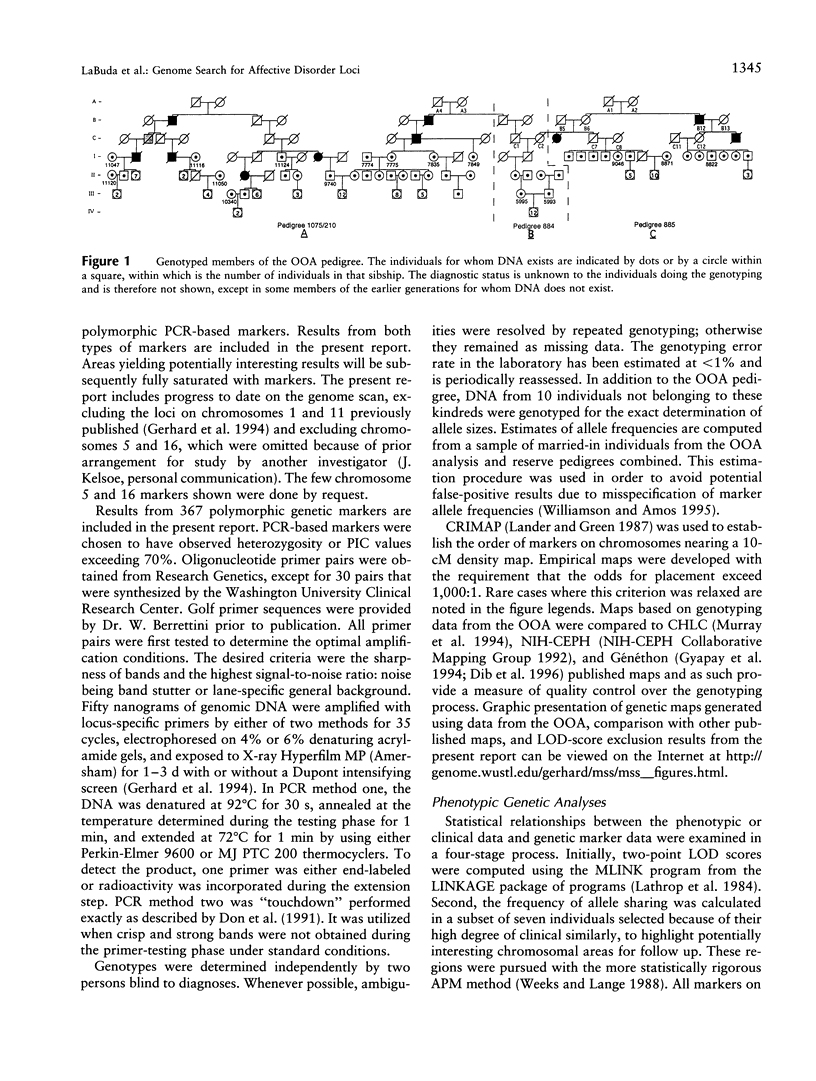
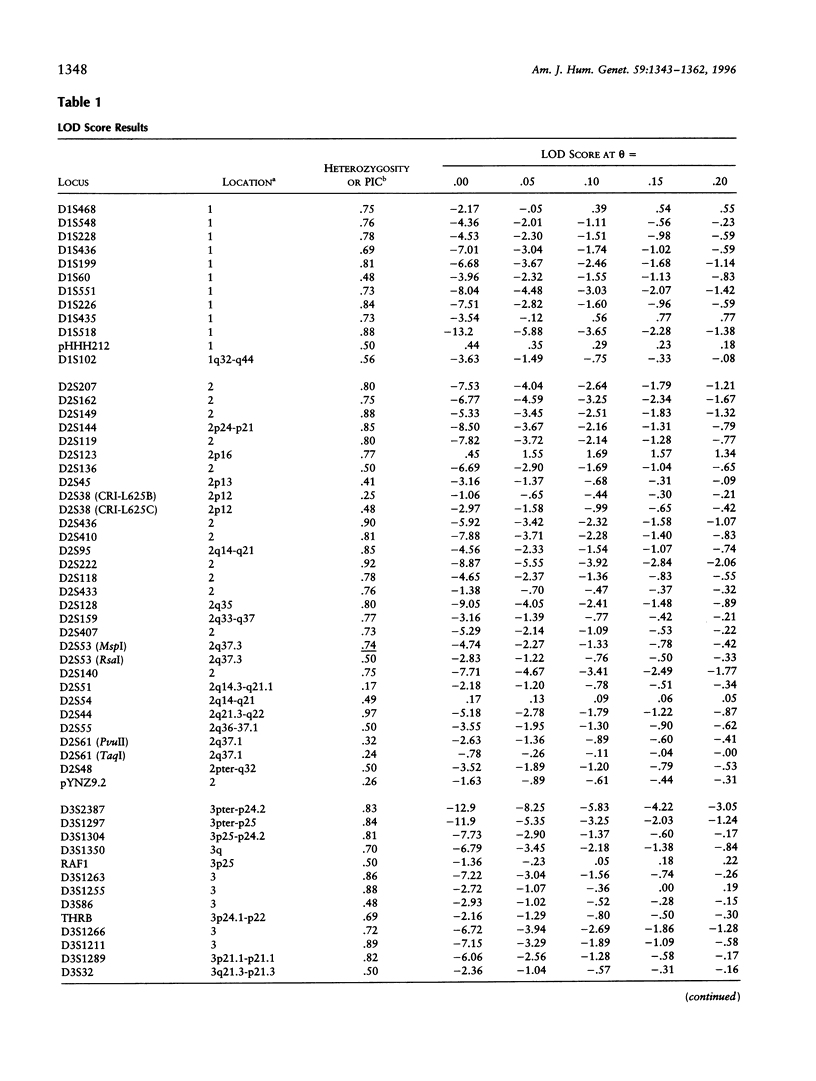
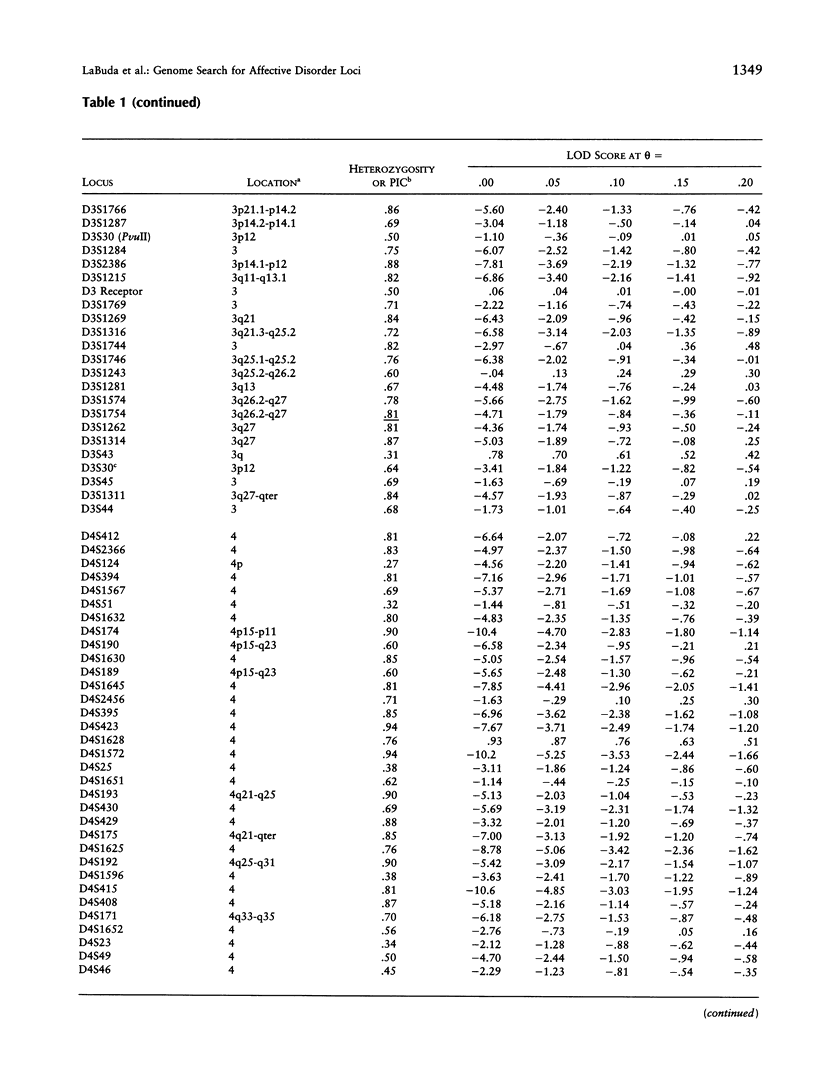
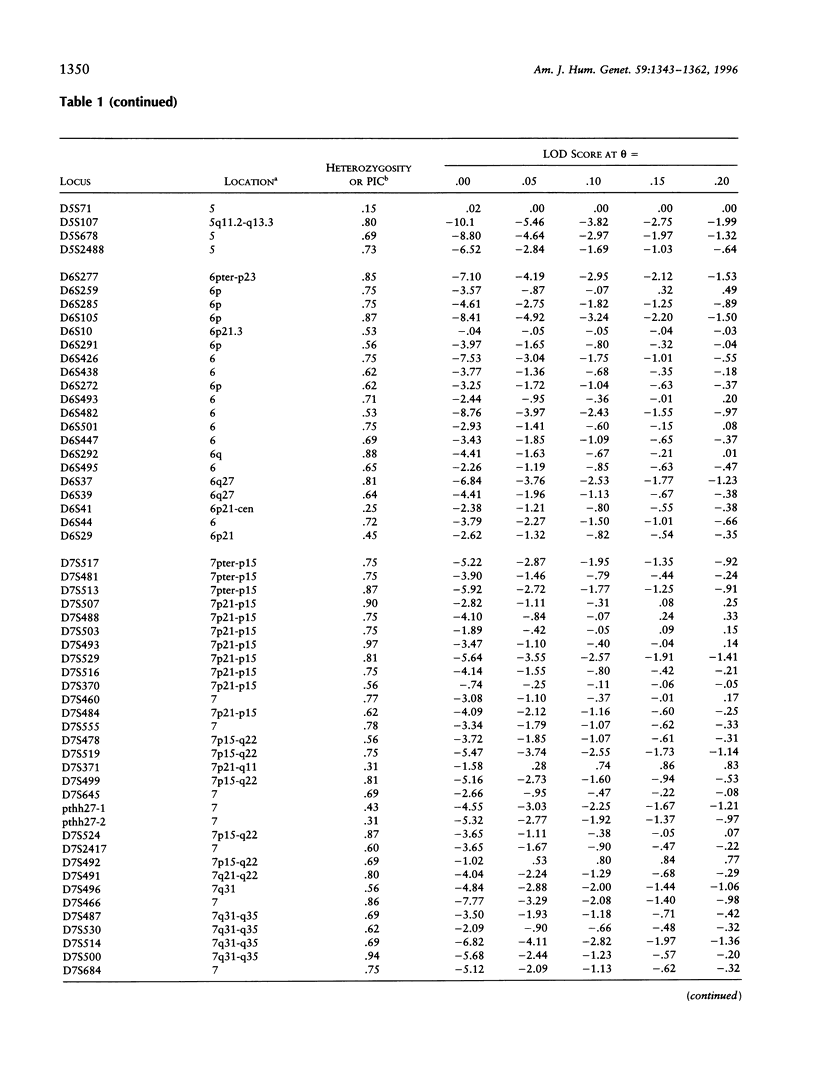
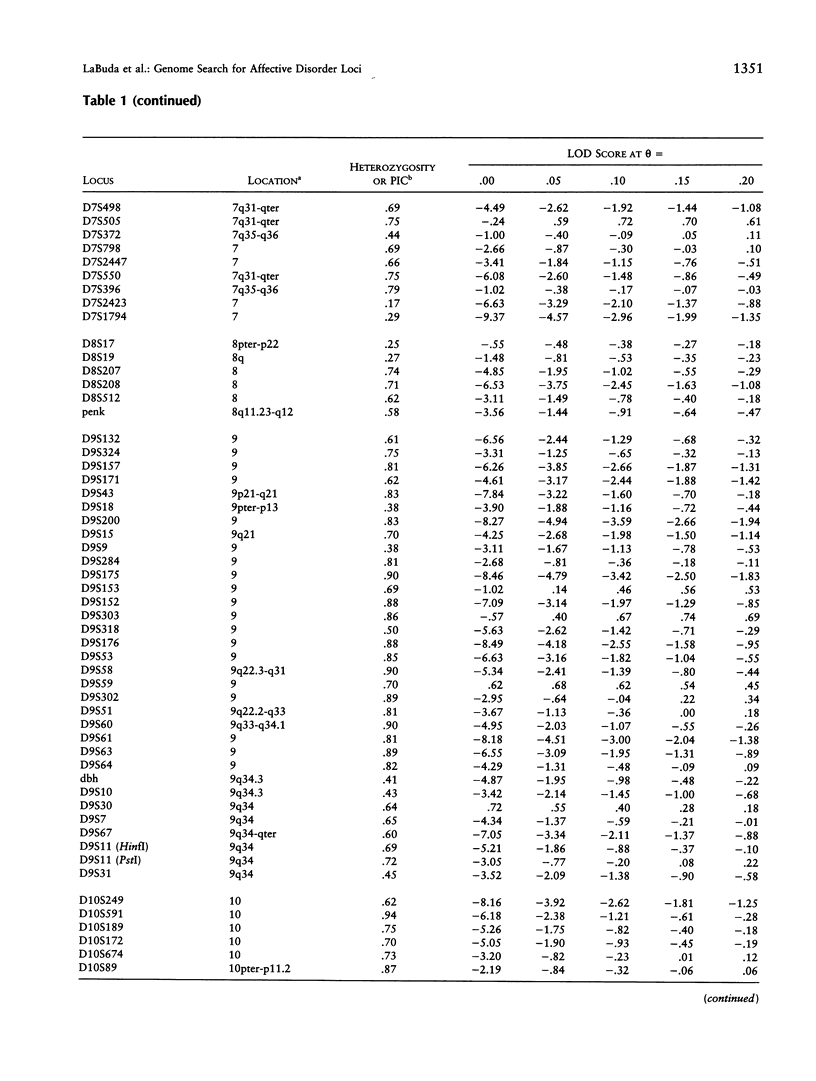
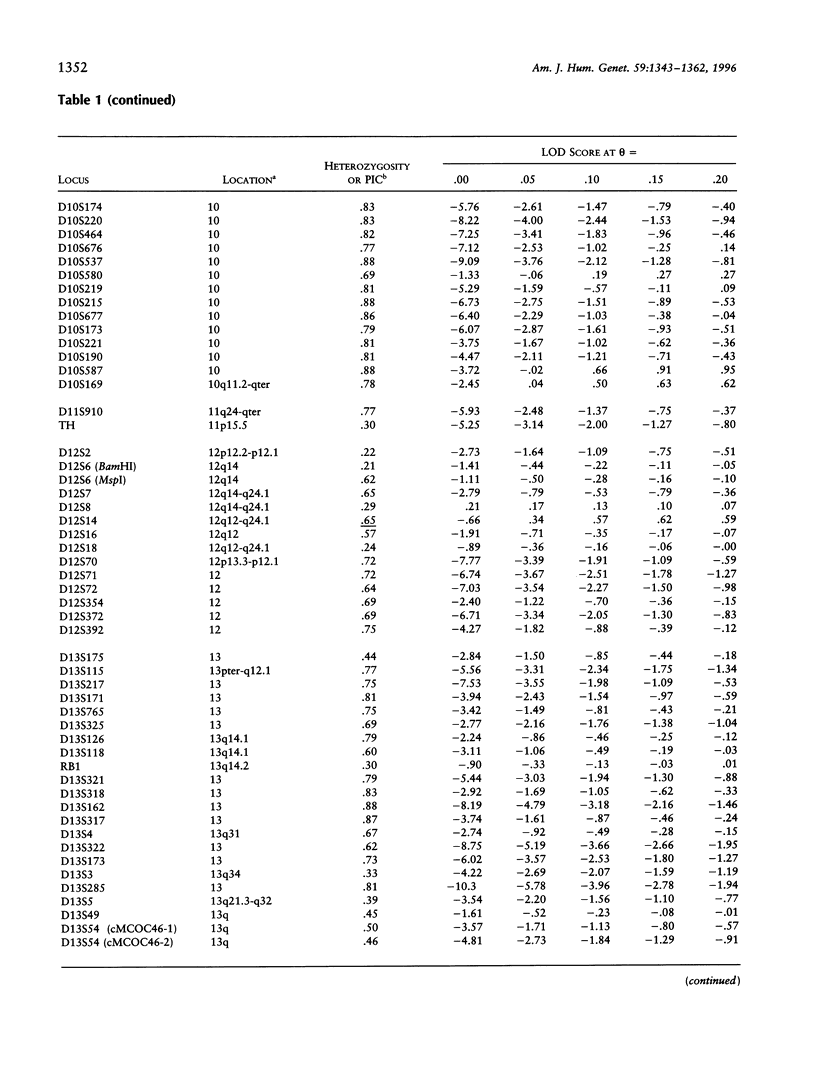
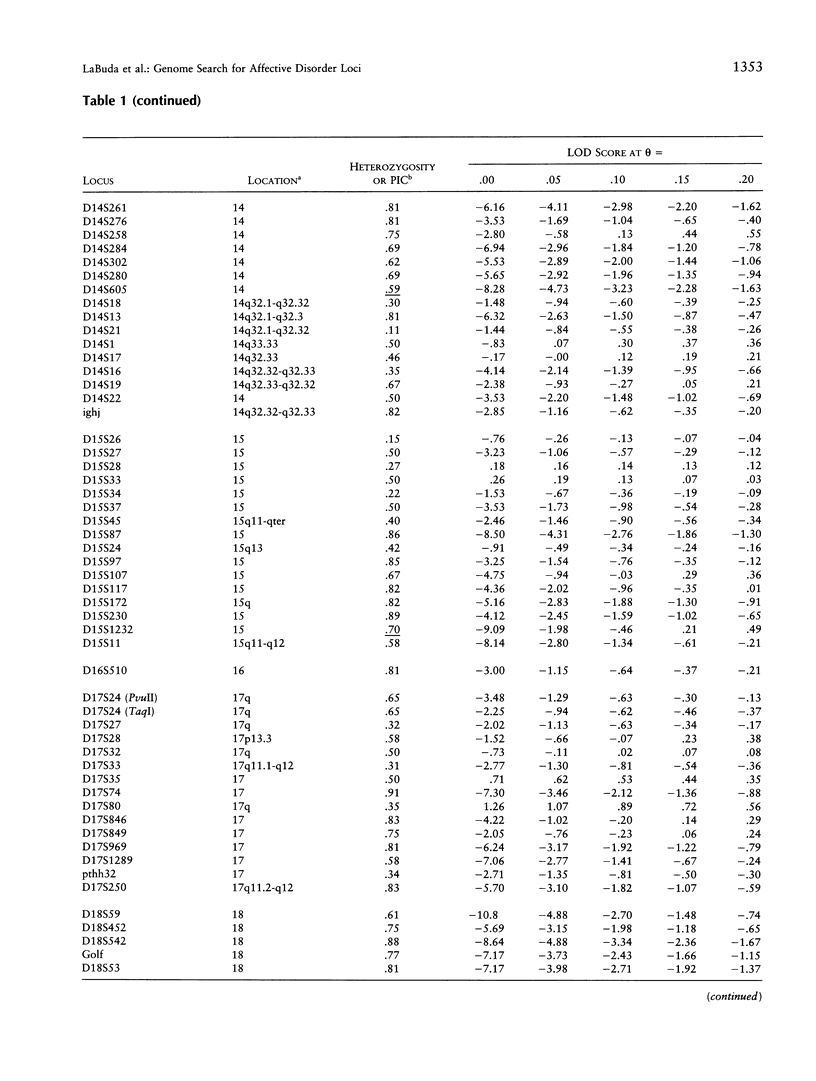
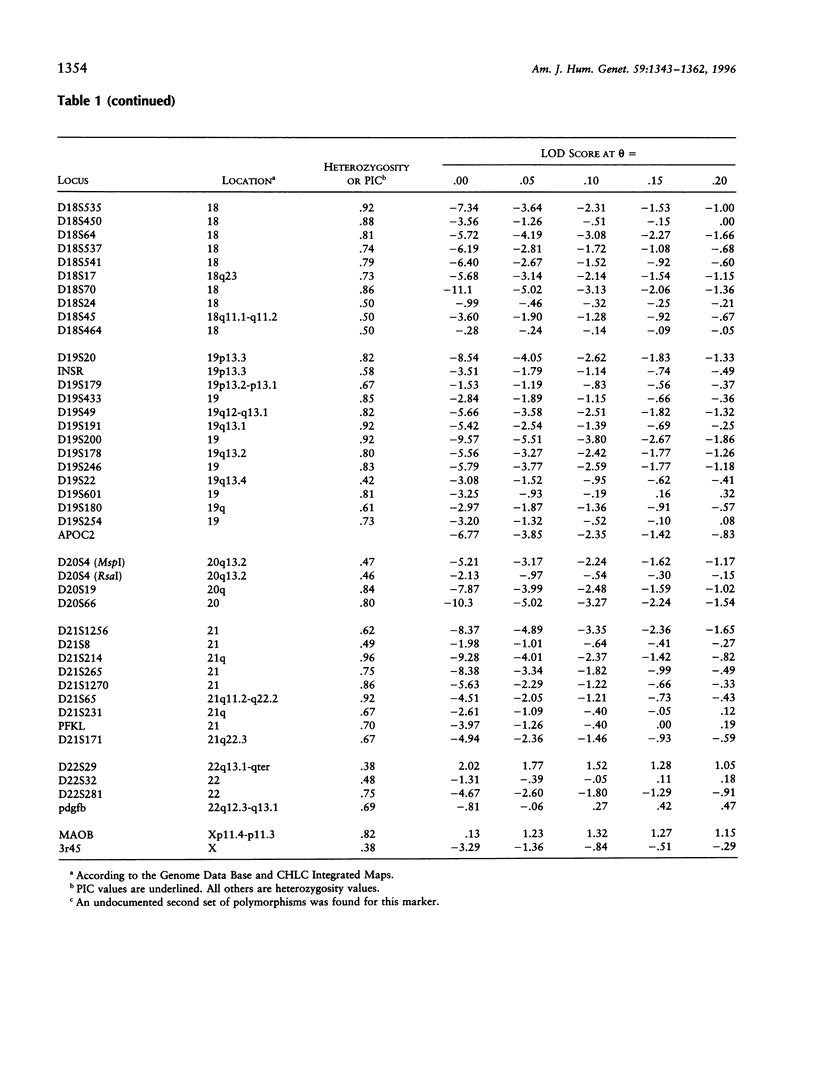
Progress of a full-genome scan for predisposition loci for affective disorder in the Old Order Amish is reported. LOD-score results have been previously published for 51 loci on chromosomes 1 and 11, collectively. The present report contains results for an additional 367 loci throughout the genome with extensive coverage on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 13, 14, 18, 19, and 21 (average marker density for these chromosomes = 10.7 cM). Analyses were conducted in a four-stage process: (1) two-point LOD scores were calculated for all loci under a dominant model with reduced penetrance, consistent with results of segregation analyses of these pedigrees; (2) a screen for the sharing of alleles in similarly affected individuals was used to highlight areas potentially important for further analysis; (3) the preceding areas and markers on densely covered chromosomes were analyzed using the affected-pedigree-member (APM) method; and (4) the sharing of extended haplotypes in affected individuals was examined in areas showing apparent clustering of significant allele sharing as assessed by the APM method. Of the 367 markers analyzed, no statistically significant LOD scores resulted. Some degree (P < .05) of allele sharing was found at 74 loci, and 3.8% of all markers analyzed (N = 14) passed more stringent significance criteria suggestive of linkage (P < or = .001 for at least one of the weighting functions). Multilocus APM and detailed exploration of extended haplotype sharing in areas highlighted by the APM analyses provided methods for more informative exploration of potentially suggestive results but did not identify areas clearly involved in the etiology of affective disorder in this population.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron M., Freimer N. F., Risch N., Lerer B., Alexander J. R., Straub R. E., Asokan S., Das K., Peterson A., Amos J. Diminished support for linkage between manic depressive illness and X-chromosome markers in three Israeli pedigrees. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):49–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Risch N., Hamburger R., Mandel B., Kushner S., Newman M., Drumer D., Belmaker R. H. Genetic linkage between X-chromosome markers and bipolar affective illness. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):289–292. doi: 10.1038/326289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrettini W. H., Ferraro T. N., Goldin L. R., Weeks D. E., Detera-Wadleigh S., Nurnberger J. I., Jr, Gershon E. S. Chromosome 18 DNA markers and manic-depressive illness: evidence for a susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5918–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood D. H., He L., Morris S. W., McLean A., Whitton C., Thomson M., Walker M. T., Woodburn K., Sharp C. M., Wright A. F. A locus for bipolar affective disorder on chromosome 4p. Nat Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):427–430. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H., Hoff M., Holik J., Hadley D., Fang N., Reimherr F., Wender P., Byerley W. Analysis of chromosome 18 DNA markers in multiplex pedigrees with manic depression. Biol Psychiatry. 1996 Apr 15;39(8):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(95)00292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H., Jensen S., Hoff M., Holik J., Plaetke R., Reimherr F., Wender P., Leppert M., Byerley W. A genome-wide search for genes predisposing to manic-depression, assuming autosomal dominant inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1234–1249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock N., Daniels J., Roberts E., Rees M., McGuffin P., Owen M. J. No evidence for allelic association between bipolar disorder and monoamine oxidase A gene polymorphisms. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Aug 14;60(4):322–324. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
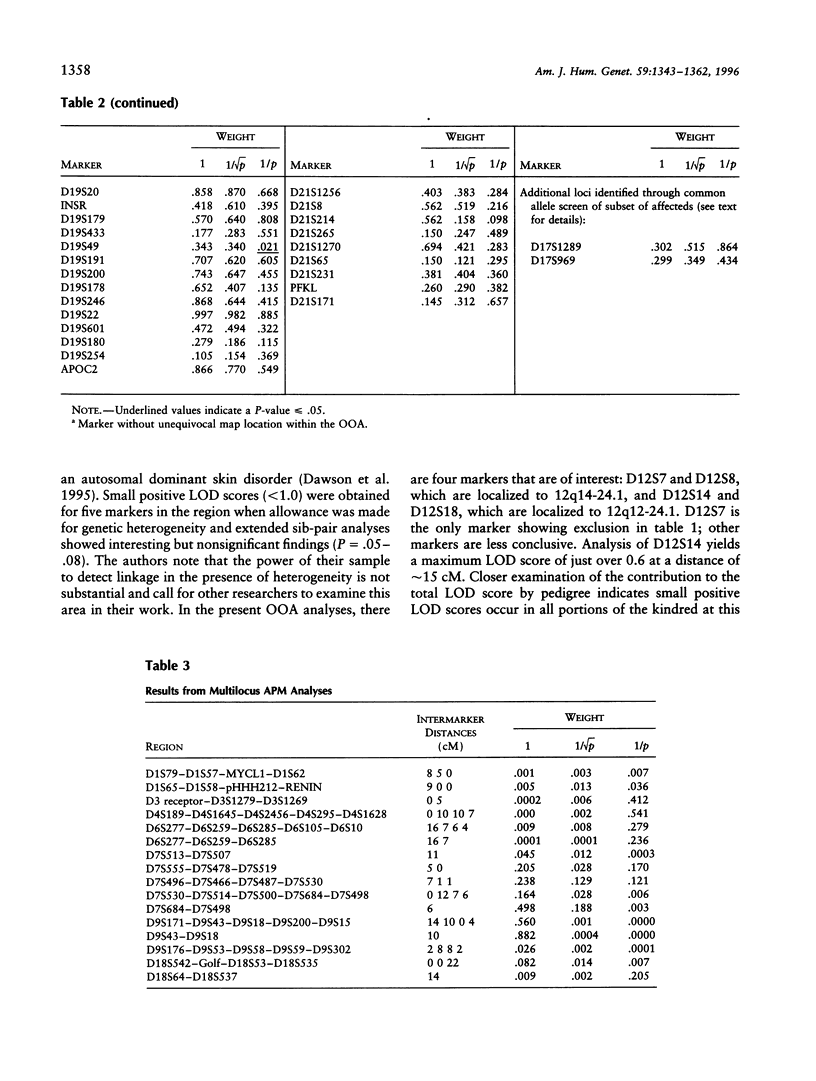
- Dawson E., Parfitt E., Roberts Q., Daniels J., Lim L., Sham P., Nöthen M., Propping P., Lanczik M., Maier W. Linkage studies of bipolar disorder in the region of the Darier's disease gene on chromosome 12q23-24.1. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 24;60(2):94–102. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De bruyn A., Raeymaekers P., Mendelbaum K., Sandkuijl L. A., Raes G., Delvenne V., Hirsch D., Staner L., Mendlewicz J., Van Broeckhoven C. Linkage analysis of bipolar illness with X-chromosome DNA markers: a susceptibility gene in Xq27-q28 cannot be excluded. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Dec 15;54(4):411–419. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320540423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De bruyn A., Souery D., Mendelbaum K., Mendlewicz J., Van Broeckhoven C. Linkage analysis of families with bipolar illness and chromosome 18 markers. Biol Psychiatry. 1996 Apr 15;39(8):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(95)00293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detera-Wadleigh S. D., Badner J. A., Goldin L. R., Berrettini W. H., Sanders A. R., Rollins D. Y., Turner G., Moses T., Haerian H., Muniec D. Affected-sib-pair analyses reveal support of prior evidence for a susceptibility locus for bipolar disorder, on 21q. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1279–1285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizier M. H., Babron M. C., Clerget-Darpoux F. Conclusion of LOD-score analysis for family data generated under two-locus models. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1338–1346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizier M. H., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Clerget-Darpoux F. Conclusions of segregation analysis for family data generated under two-locus models. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Dec;53(6):1338–1346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Cox P. T., Wainwright B. J., Baker K., Mattick J. S. 'Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4008–4008. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Pauls D. L., Sussex J. N., Kidd K. K., Allen C. R., Hostetter A. M., Housman D. E. Bipolar affective disorders linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):783–787. doi: 10.1038/325783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Hostetter A. M. Amish Study, I: Affective disorders among the Amish, 1976-1980. Am J Psychiatry. 1983 Jan;140(1):56–61. doi: 10.1176/ajp.140.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Ewald H., Mors O. Suggestion of linkage between manic-depressive illness and the enzyme phosphoglycolate phosphatase (PGP) on chromosome 16p. Clin Genet. 1993 Nov;44(5):254–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb03892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J., Spitzer R. L. A diagnostic interview: the schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Jul;35(7):837–844. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770310043002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimer N. B., Reus V. I., Escamilla M. A., McInnes L. A., Spesny M., Leon P., Service S. K., Smith L. B., Silva S., Rojas E. Genetic mapping using haplotype, association and linkage methods suggests a locus for severe bipolar disorder (BPI) at 18q22-q23. Nat Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):436–441. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., LaBuda M. C., Bland S. D., Allen C., Egeland J. A., Pauls D. L. Initial report of a genome search for the affective disorder predisposition gene in the old order Amish pedigrees: chromosomes 1 and 11. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Dec 15;54(4):398–404. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320540421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Ott J., Egeland J. A., Allen C. R., Fann C. S., Pauls D. L., Weissenbachoff J., Carulli J. P., Falls K. M., Keith T. P. A genome-wide search for chromosomal loci linked to bipolar affective disorder in the Old Order Amish. Nat Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):431–435. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Braden V. V., Fulton R. S., Lim R., Ueltzen M. S., Peluso D. C., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Idol J. R., Smith L. M., Chumakov I. A human chromosome 7 yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) resource: construction, characterization, and screening. Genomics. 1995 Jan 1;25(1):170–183. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heun R., Maier W. The distinction of bipolar II disorder from bipolar I and recurrent unipolar depression: results of a controlled family study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1993 Apr;87(4):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1993.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., Baharloo S., Blankenship K., Raeymaekers P., Juyn J., Sandkuijl L. A., Freimer N. B. Genome screening by searching for shared segments: mapping a gene for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1994 Dec;8(4):380–386. doi: 10.1038/ng1294-380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. B. Psychosocial aspects of depression and the role of psychotherapy. J Clin Psychiatry. 1990 Jun;51 (Suppl):26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawada Y., Hattori M., Dai X. Y., Nanko S. Possible association between monoamine oxidase A gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):335–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe J. R., Ginns E. I., Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Goldstein A. M., Bale S. J., Pauls D. L., Long R. T., Kidd K. K., Conte G. Re-evaluation of the linkage relationship between chromosome 11p loci and the gene for bipolar affective disorder in the Old Order Amish. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):238–243. doi: 10.1038/342238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Egeland J. A., Molthan L., Pauls D. L., Kruger S. D., Messner K. H. Amish study, IV: Genetic linkage study of pedigrees of bipolar probands. Am J Psychiatry. 1984 Sep;141(9):1042–1048. doi: 10.1176/ajp.141.9.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboyer M., Malafosse A., Boularand S., Campion D., Gheysen F., Samolyk D., Henriksson B., Denise E., des Lauriers A., Lepine J. P. Tyrosine hydroxylase polymorphisms associated with manic-depressive illness. Lancet. 1990 May 19;335(8699):1219–1219. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92738-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. C., Powell J. F., Murray R., Gill M. Monoamine oxidase A gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;54(6):1122–1124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. C., Powell J., Sham P., Castle D., Hunt N., Murray R., Gill M. Evidence for a genetic association between alleles of monoamine oxidase A gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Aug 14;60(4):325–331. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni R., Leboyer M., Bellivier F., Barbe B., Samolyk D., Allilaire J. F., Mallet J. Association of manic-depressive illness with tyrosine hydroxylase microsatellite marker. Lancet. 1995 Apr 8;345(8954):932–932. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Manion F., Quillen J., Sheffield V. C., Sunden S., Duyk G. M. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Cooperative Human Linkage Center (CHLC). Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2049–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8091227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nöthen M. M., Eggermann K., Albus M., Borrmann M., Rietschel M., Körner J., Maier W., Minges J., Lichtermann D., Franzek E. Association analysis of the monoamine oxidase A gene in bipolar affective disorder by using family-based internal controls. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Oct;57(4):975–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Bailey J. N., Carter A. S., Allen C. R., Egeland J. A. Complex segregation analyses of old order Amish families ascertained through bipolar I individuals. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Aug 14;60(4):290–297. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Gerhard D. S., Lacy L. G., Hostetter A. M., Allen C. R., Bland S. D., LaBuda M. C., Egeland J. A. Linkage of bipolar affective disorders to markers on chromosome 11p is excluded in a second lateral extension of Amish pedigree 110. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):730–736. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90081-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Morton L. A., Egeland J. A. Risks of affective illness among first-degree relatives of bipolar I old-order Amish probands. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;49(9):703–708. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820090031005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J., Reich T., Andreasen N. C., Endicott J., Van Eerdewegh M., Fishman R., Hirschfeld R. M., Klerman G. L. The familial transmission of bipolar illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 May;44(5):441–447. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800170063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., Botstein D. A manic depressive history. Nat Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):351–353. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah M., Coon H., Holik J., Hoff M., Helmer V., Panos P., Byerley W. Mutation scan of the D1 dopamine receptor gene in 22 cases of bipolar I disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 24;60(2):150–153. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. L., Endicott J., Robins E. Research diagnostic criteria: rationale and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Jun;35(6):773–782. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770300115013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine O. C., Xu J., Koskela R., McMahon F. J., Gschwend M., Friddle C., Clark C. D., McInnis M. G., Simpson S. G., Breschel T. S. Evidence for linkage of bipolar disorder to chromosome 18 with a parent-of-origin effect. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1384–1394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Lehner T., Luo Y., Loth J. E., Shao W., Sharpe L., Alexander J. R., Das K., Simon R., Fieve R. R. A possible vulnerability locus for bipolar affective disorder on chromosome 21q22.3. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):291–296. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Sobel E., O'Connell J. R., Lange K. Computer programs for multilocus haplotyping of general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1506–1507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. A., Amos C. I. Guess LOD approach: sufficient conditions for robustness. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(2):163–176. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


