Abstract
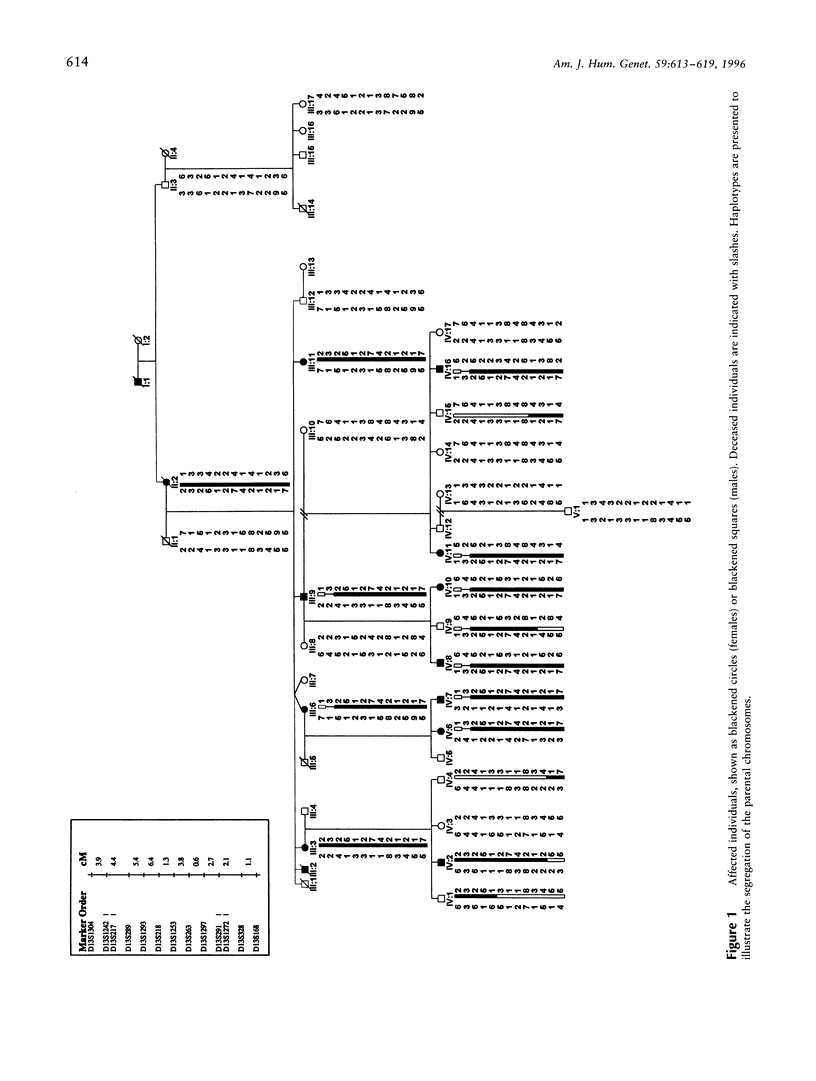
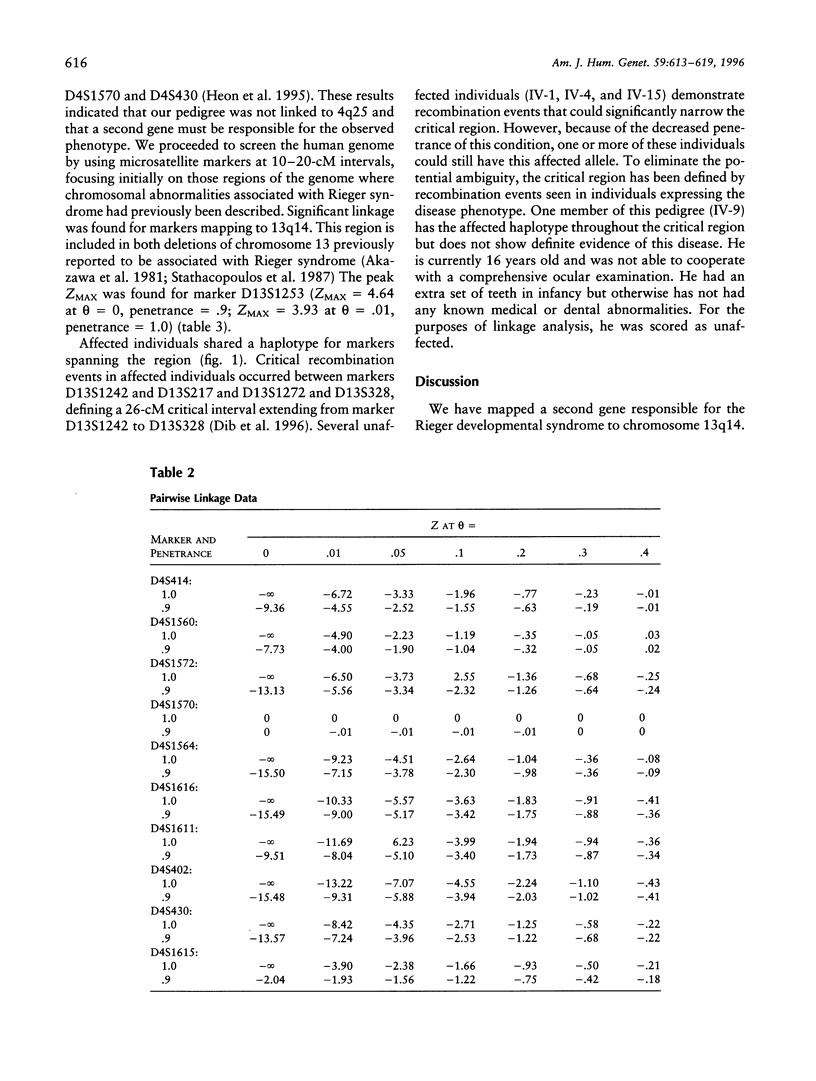
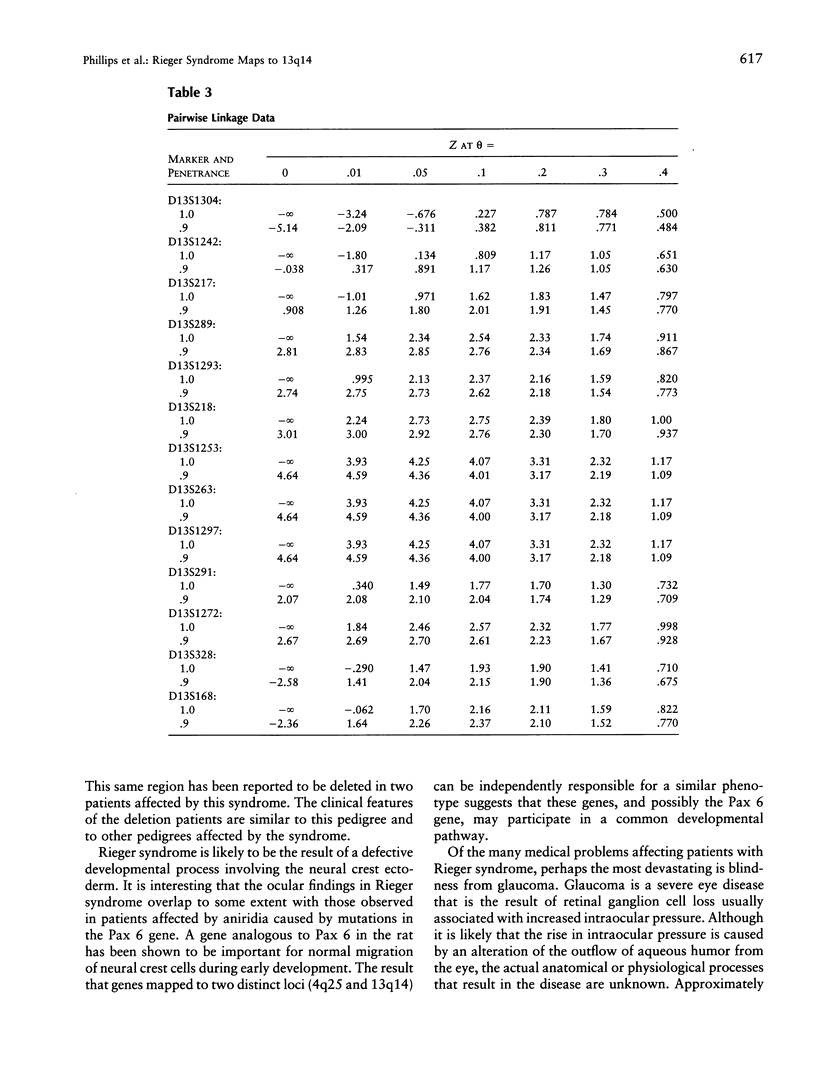
Rieger syndrome is a genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous disorder typically characterized by malformations of the eyes, teeth, and umbilicus. The syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait and exhibits significant variable expressivity. One locus associated with this disorder has been mapped to 4q25. Using a large four-generation pedigree, we have identified a second locus for Rieger syndrome located on chromosome 13q14.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breebaart A. C. A case of Rieger's anomaly with glaucoma--influence of sleep. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Dec;76(6):825–828. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.03850010827008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence D. E., Overdier D. G., Tao W., Qian X., Pani L., Lai E., Costa R. H. Identification of nine tissue-specific transcription factors of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead DNA-binding-domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3948–3952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté S., Preiss A., Haller J., Schuh R., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The gooseberry-zipper region of Drosophila: five genes encode different spatially restricted transcripts in the embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2793–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch N., Kaback M. The Axenfeld syndrome and the Rieger syndrome. J Med Genet. 1978 Feb;15(1):30–34. doi: 10.1136/jmg.15.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili N., Davis R. J., Fredericks W. J., Mukhopadhyay S., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Barr F. G. Fusion of a fork head domain gene to PAX3 in the solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):230–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann M. H., Breg R., Cotlier E. Rieger's syndrome with pericentric inversion of chromosome 6. Br J Ophthalmol. 1979 Jan;63(1):40–44. doi: 10.1136/bjo.63.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervé J., Warnet J. F., Jeaneau-Bellego E., Portnoi M. F., Taillemitte J. L., Hervé F. Monosomie partielle du bras court d'un chromosome 10, associée à un syndrome de Rieger et à undéficit immunitaire partiel, type Di George. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1984 Jan;31(1):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häcker U., Grossniklaus U., Gehring W. J., Jäckle H. Developmentally regulated Drosophila gene family encoding the fork head domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héon E., Sheth B. P., Kalenak J. W., Sunden S. L., Streb L. M., Taylor C. M., Alward W. L., Sheffield V. C., Stone E. M. Linkage of autosomal dominant iris hypoplasia to the region of the Rieger syndrome locus (4q25). Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Aug;4(8):1435–1439. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.8.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judisch G. F., Phelps C. D., Hanson J. Rieger's syndrome. A case report with a 15-year follow-up. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979 Nov;97(11):2120–2122. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1979.01020020438004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Hiemisch H., Luckow B., Schütz G. The HNF-3 gene family of transcription factors in mice: gene structure, cDNA sequence, and mRNA distribution. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):377–385. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., de Die-Smulders C. E., Verbraak F., Habex H., Decorte R., Marynen P., Fryns J. P., Cassiman J. J. Genetic heterogeneity in Rieger eye malformation. J Med Genet. 1994 Apr;31(4):340–341. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.4.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligutić I., Brecević L., Petković I., Kalogjera T., Rajić Z. Interstitial deletion 4q and Rieger syndrome. Clin Genet. 1981 Nov;20(5):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. M., Gallegos M. E., Morisseau B. A., Kim S. K. lin-31, a Caenorhabditis elegans HNF-3/fork head transcription factor homolog, specifies three alternative cell fates in vulval development. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):933–947. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Packman S., Loughman W. D., Fineman R. M., Zackai E., Patil S. R., Emanual B., Bartley J. A., Hanson J. W. Deletions of different segments of the long arm of chromosome 4. Am J Med Genet. 1981;8(1):73–89. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Bennett S. R., Kwitek A. E., Small K. W., Schinzel A., Alward W. L., Weber J. L., Bell G. I., Buetow K. H. Linkage of Rieger syndrome to the region of the epidermal growth factor gene on chromosome 4. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):46–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K. E., Nakamura H. Origin of the irideal striated muscle in birds. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Aug;88:1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. Differential expression of multiple fork head related genes during gastrulation and axial pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 1993 May;118(1):47–59. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. B. Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome: a theory of mechanism and distinctions from the iridocorneal endothelial syndrome. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1983;81:736–784. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathacopoulos R. A., Bateman J. B., Sparkes R. S., Hepler R. S. The Rieger syndrome and a chromosome 13 deletion. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1987 Jul-Aug;24(4):198–203. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19870701-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Blader P., Henrique D., Ingham P. W. Axial, a zebrafish gene expressed along the developing body axis, shows altered expression in cyclops mutant embryos. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1436–1446. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabbara K. F., Khouri F. P., Kaloustian VM der Reiger's syndrome with chromosomal anomaly (report of a case). Can J Ophthalmol. 1973 Jul;8(3):488–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Haines J. L., Paglinauan C., Fine A., Sporn C., Lou D. Genetic linkage of autosomal dominant juvenile glaucoma to 1q21-q31 in three affected pedigrees. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):299–303. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkowicz M. I., Keates E. U., Levy P. L. Primary mesodermal iris dysgenesis. Report of pedigrees in three generations. Ann Ophthalmol. 1971 Aug;3(8):842–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


