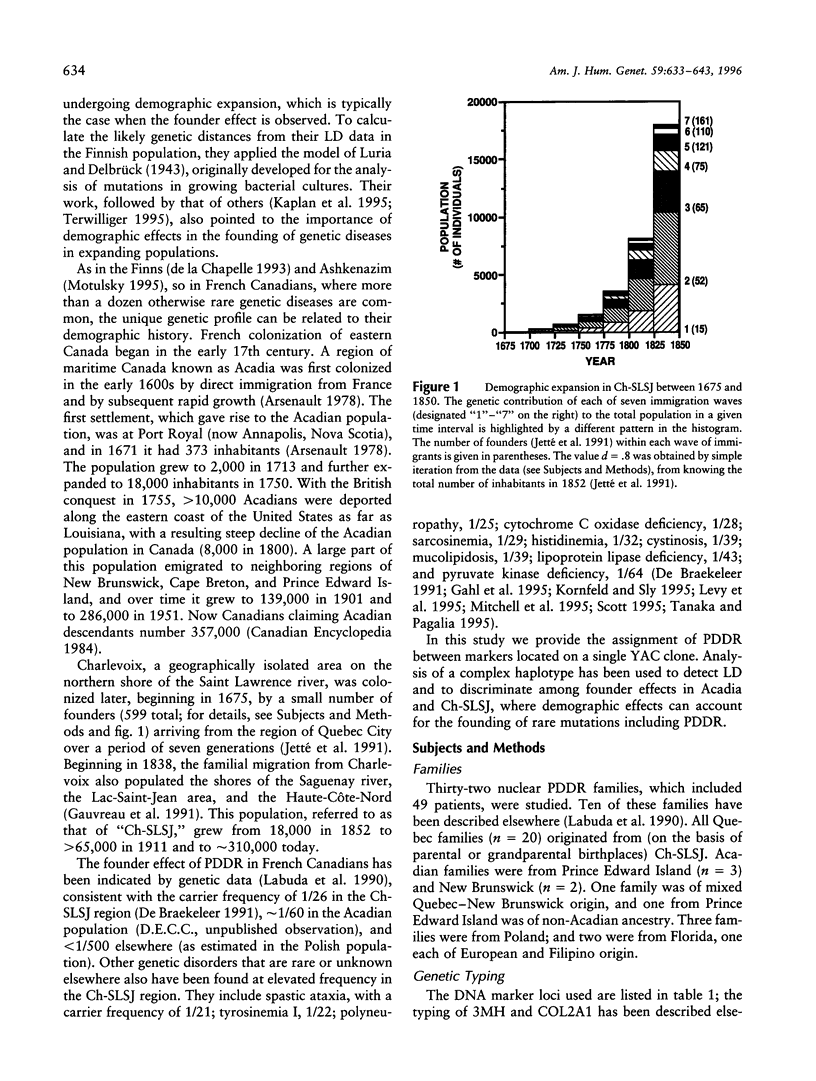
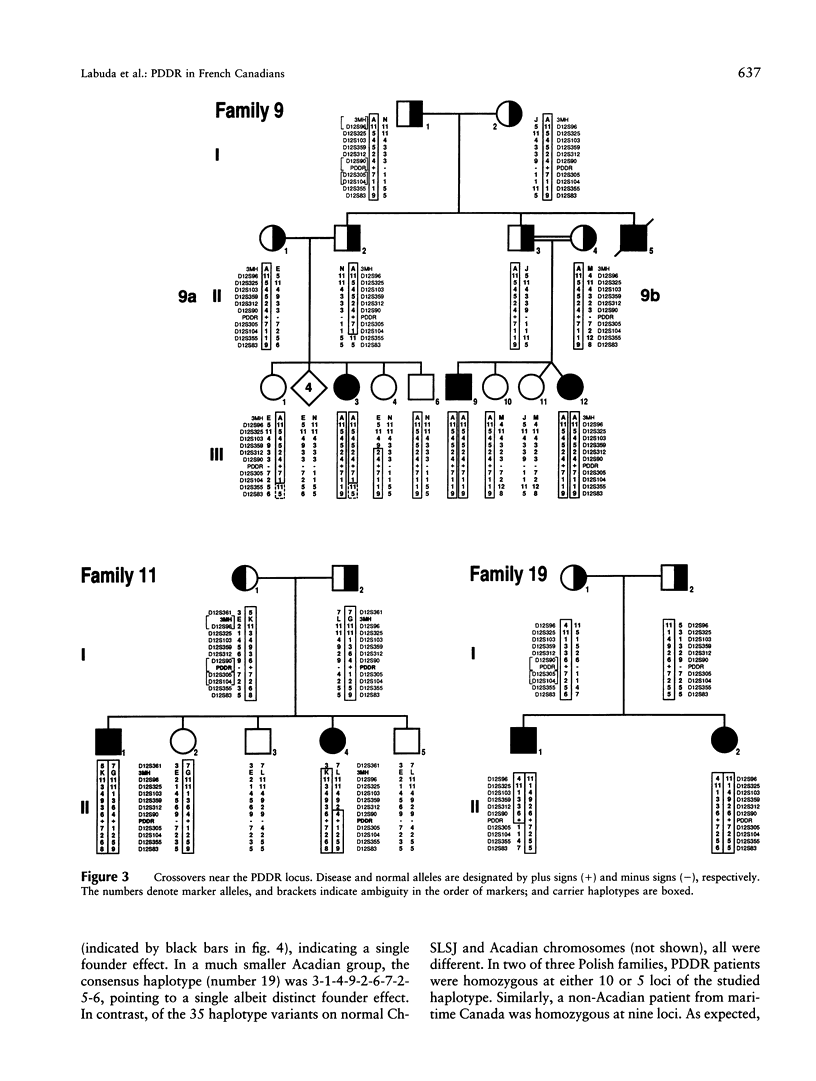
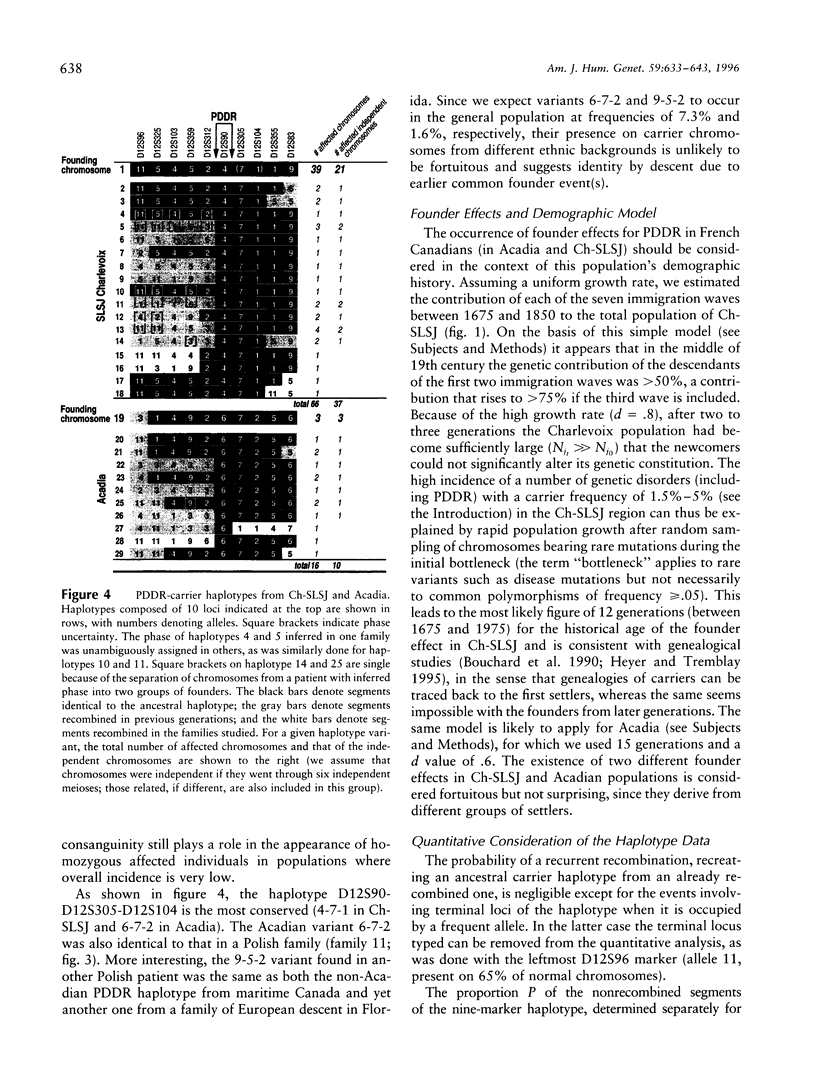
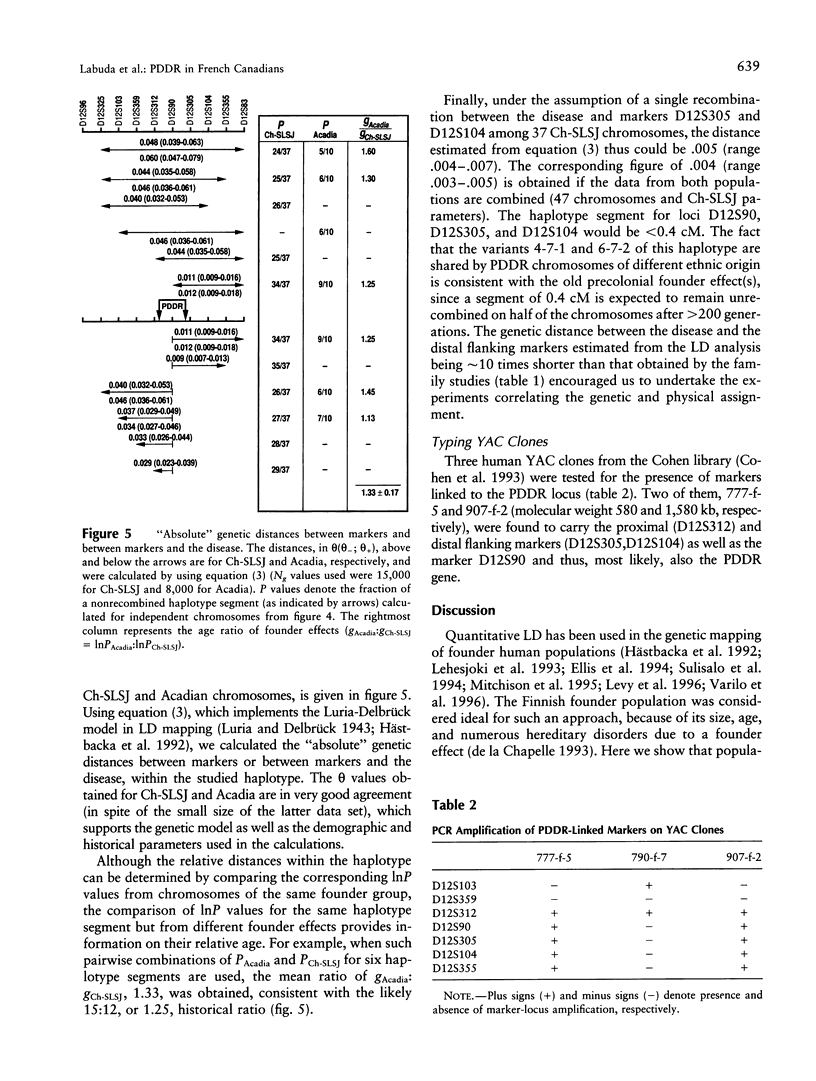
Abstract
Pseudo-vitamin D-deficiency rickets (PDDR) was mapped close to D12S90 and between proximal D12S312 and distal (D12S305, D12S104) microsatellites that were subsequently found on a single YAC clone. Analysis of a complex haplotype in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with the disease discriminated among distinct founder effects in French Canadian populations in Acadia and in Charlevoix-Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean (Ch-SLSJ), as well as an earlier one in precolonial Europe. A simple demographic model suggested the historical age of the founder effect in Ch-SLSJ to be approximately 12 generations. The corresponding LD data are consistent with this figure when they are analyzed within the framework of Luria-Delbrück model, which takes into account the population growth. Population sampling due to a limited number of first settlers and the rapid demographic expansion appear to have played a major role in the founding of PDDR in Ch-SLSJ and, presumably, other genetic disorders endemic to French Canada. Similarly, the founder effect in Ashkenazim, coinciding with their early settlement in medieval Poland and subsequent expansion eastward, could explain the origin of frequent genetic diseases in this population.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen D., Chumakov I., Weissenbach J. A first-generation physical map of the human genome. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):698–701. doi: 10.1038/366698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvin E. E., Glorieux F. H., Marie P. J., Pettifor J. M. Vitamin D dependency: replacement therapy with calcitriol? J Pediatr. 1981 Jul;99(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80952-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N. A., Roe A. M., Kozloski J., Proytcheva M., Falk C., German J. Linkage disequilibrium between the FES, D15S127, and BLM loci in Ashkenazi Jews with Bloom syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;55(3):453–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E. Mitochondrial and nuclear genetic contribution of female founders to a contemporary population in northeast Quebec. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1450–1455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E., Tremblay M. Variability of the genetic contribution of Quebec population founders associated to some deleterious genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Apr;56(4):970–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H S. The Numerical Results of Diverse Systems of Breeding, with Respect to Two Pairs of Characters, Linked or Independent, with Special Relation to the Effects of Linkage. Genetics. 1917 Mar;2(2):97–154. doi: 10.1093/genetics/2.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Likelihood methods for locating disease genes in nonequilibrium populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):18–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Dib C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Povey S., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. An index marker map of chromosome 9 provides strong evidence for positive interference. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Dec;53(6):1279–1288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda M., Fujiwara T. M., Ross M. V., Morgan K., Garcia-Heras J., Ledbetter D. H., Hughes M. R., Glorieux F. H. Two hereditary defects related to vitamin D metabolism map to the same region of human chromosome 12q13-14. J Bone Miner Res. 1992 Dec;7(12):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650071212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda M., Lemieux N., Tihy F., Prinster C., Glorieux F. H. Human 25-hydroxyvitamin D 24-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 subunit maps to a different chromosomal location than that of pseudovitamin D-deficient rickets. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Nov;8(11):1397–1406. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650081114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda M., Morgan K., Glorieux F. H. Mapping autosomal recessive vitamin D dependency type I to chromosome 12q14 by linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):28–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Norio R., Tirrito S., Sistonen P., Lander E., de la Chapelle A. Localization of the EPM1 gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy on chromosome 21: linkage disequilibrium allows high resolution mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E. N., Shen Y., Kupelian A., Kruglyak L., Aksentijevich I., Pras E., Balow J. E., Jr, Linzer B., Chen X., Shelton D. A. Linkage disequilibrium mapping places the gene causing familial Mediterranean fever close to D16S246. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;58(3):523–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison H. M., O'Rawe A. M., Taschner P. E., Sandkuijl L. A., Santavuori P., de Vos N., Breuning M. H., Mole S. E., Gardiner R. M., Järvelä I. E. Batten disease gene, CLN3: linkage disequilibrium mapping in the Finnish population, and analysis of European haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):654–662. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky A. G. Jewish diseases and origins. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):99–101. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Kramer P., Almasy L., Singer B., Fahn S., Breakefield X., Bressman S. Genetic analysis of idiopathic torsion dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews and their recent descent from a small founder population. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):152–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R B. Some Applications of Mathematics to Breeding Problems III. Genetics. 1918 Jul;3(4):375–389. doi: 10.1093/genetics/3.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre J. L., Simon-Bouy B., Mornet E., Jaume-Roig B., Balassopoulou A., Schwartz M., Taillandier A., Boué J., Boué A. Studies of RFLP closely linked to the cystic fibrosis locus throughout Europe lead to new considerations in populations genetics. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):449–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00195818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Klockars J., Mäkitie O., Francomano C. A., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P. High-resolution linkage-disequilibrium mapping of the cartilage-hair hypoplasia gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;55(5):937–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varilo T., Savukoski M., Norio R., Santavuori P., Peltonen L., Järvelä I. The age of human mutation: genealogical and linkage disequilibrium analysis of the CLN5 mutation in the Finnish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;58(3):506–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. S., Zenger R., O'Brien E., Nyman D., Eriksson A. W., Renlund M., Jorde L. B. Linkage disequilibrium patterns vary with chromosomal location: a case study from the von Willebrand factor region. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):348–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




