Abstract
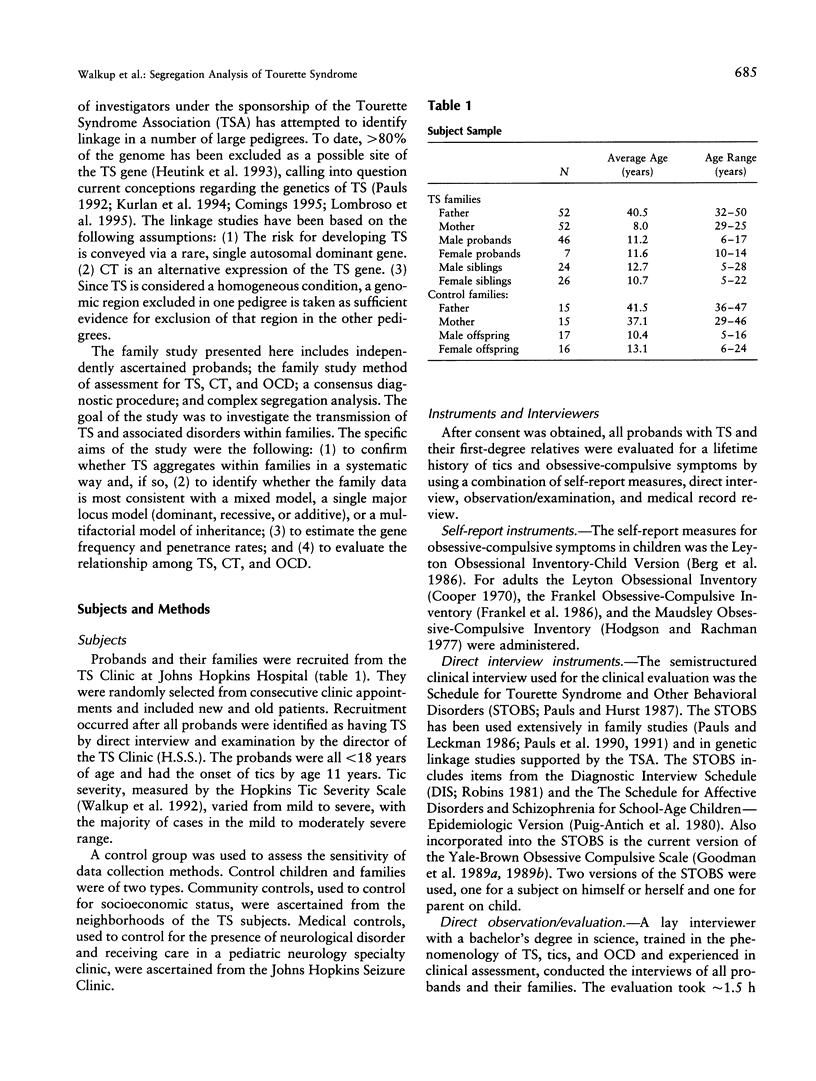
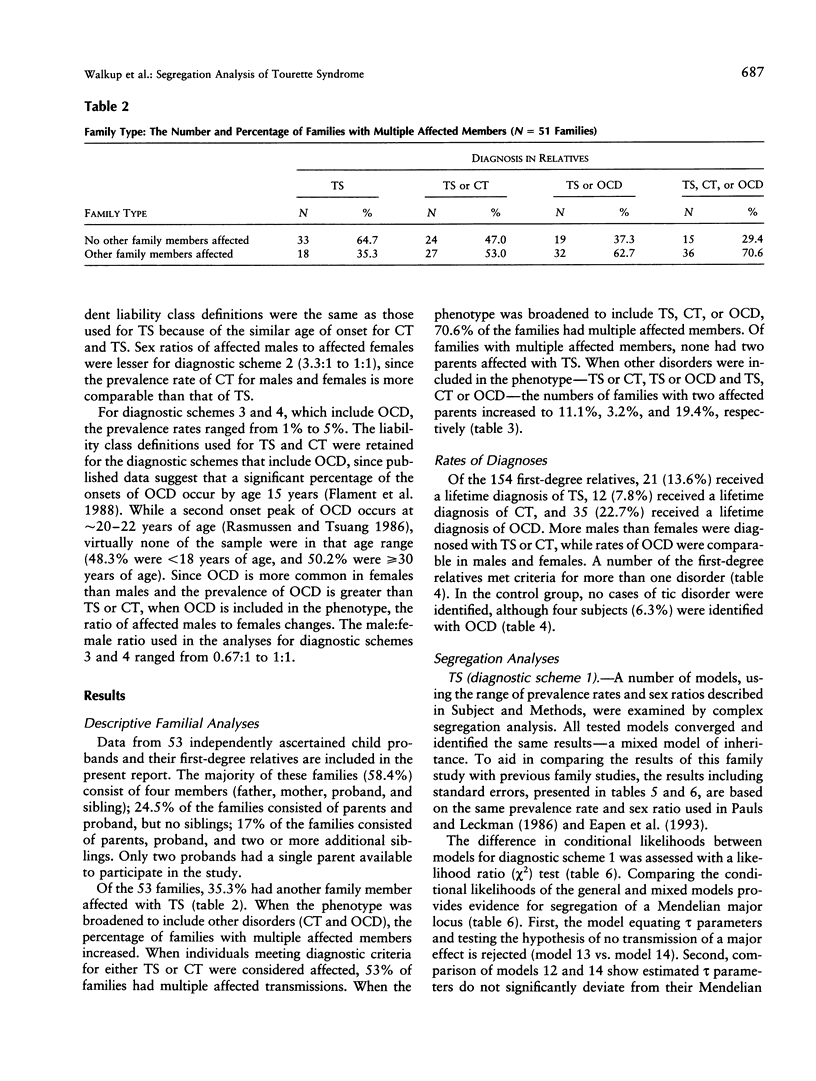
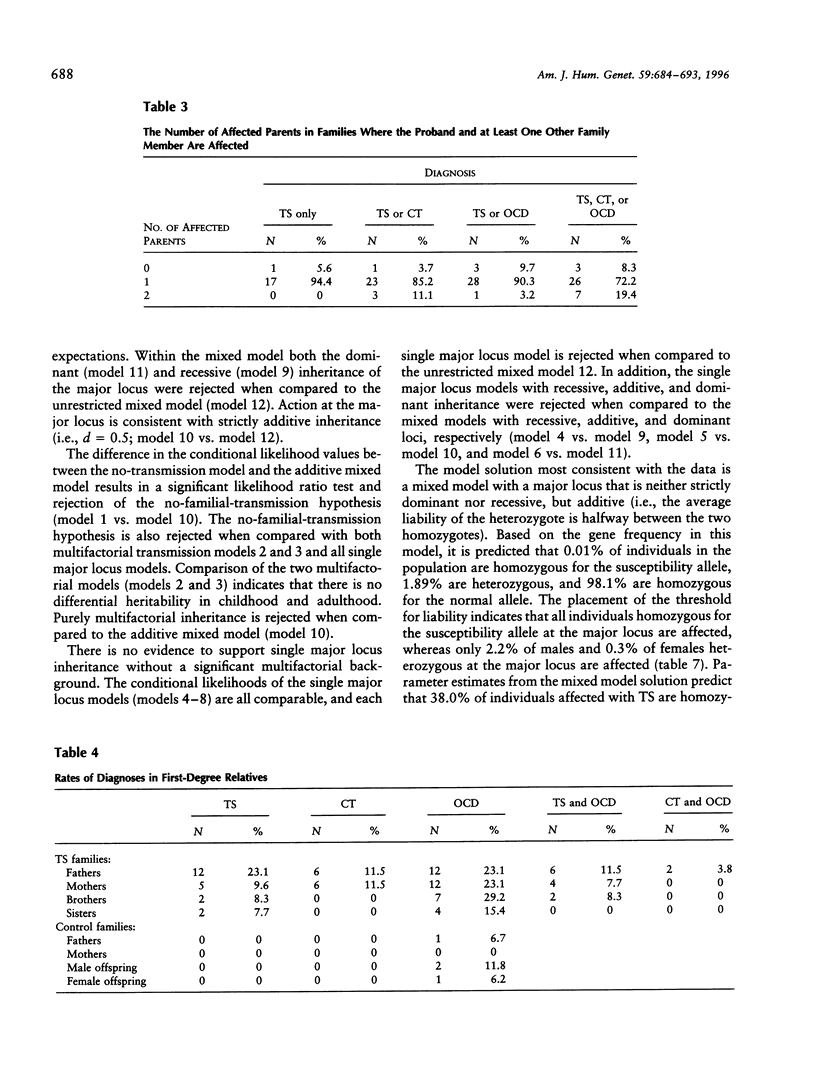
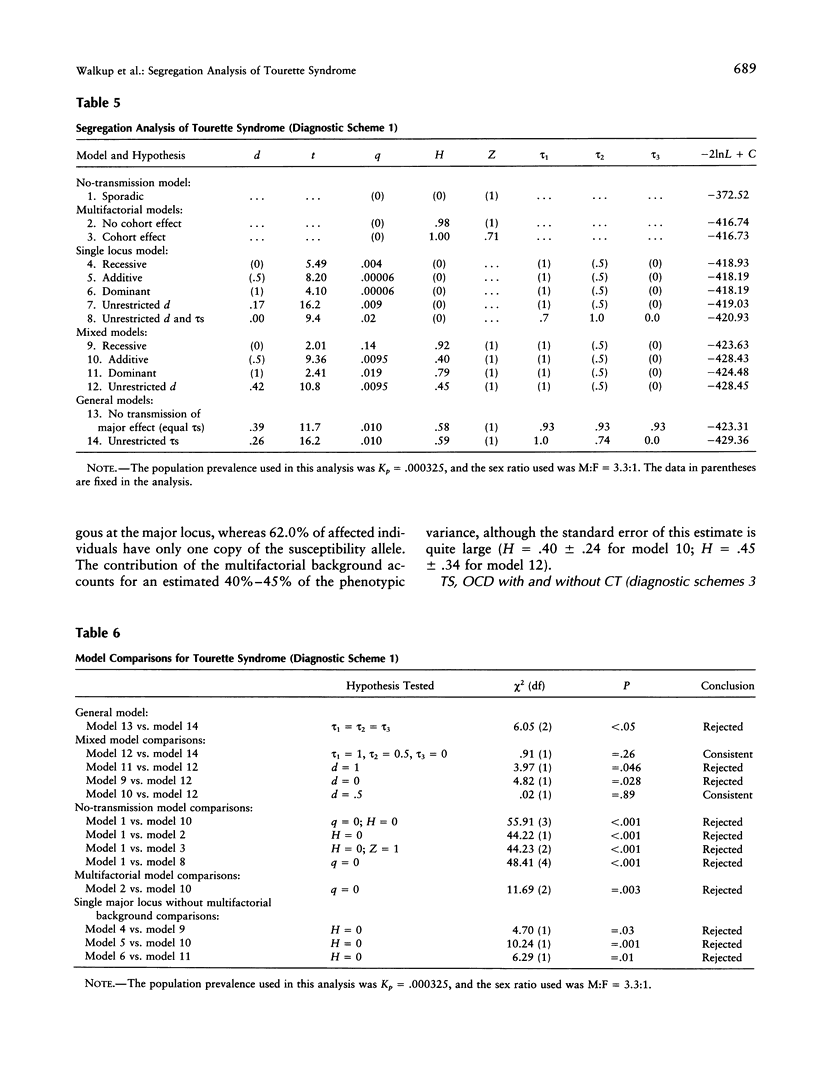
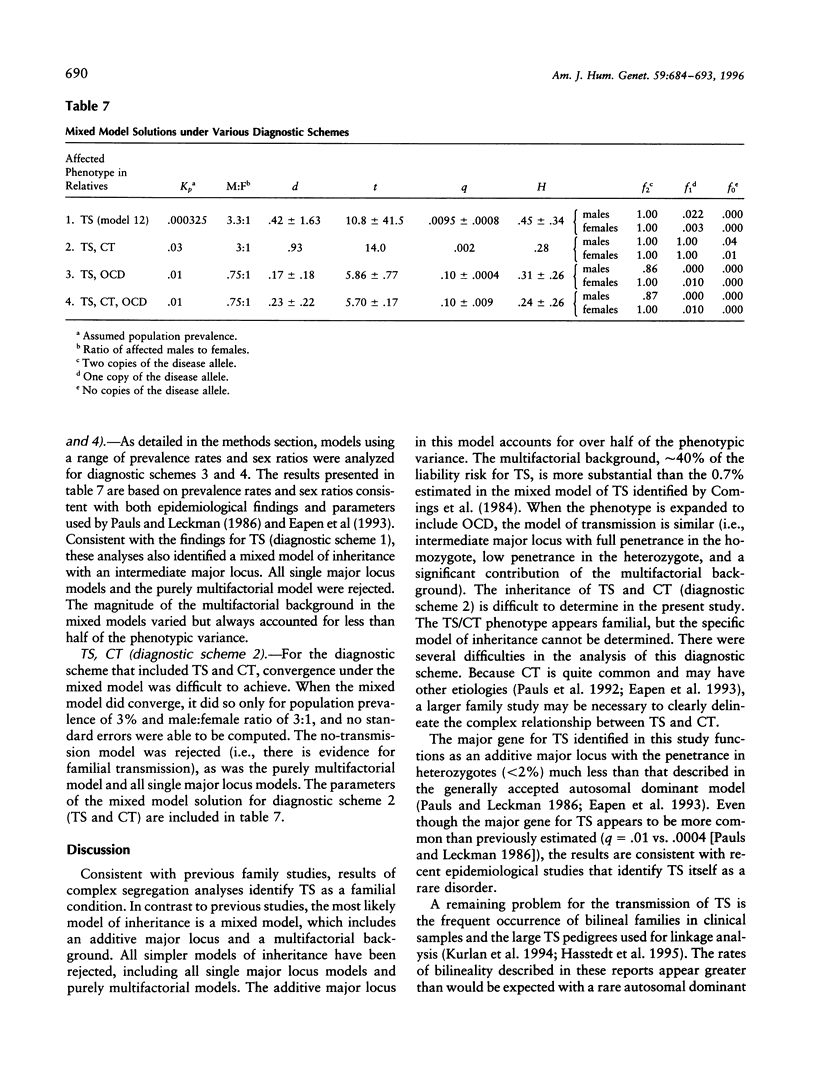
To investigate the transmission of Tourette syndrome (TS) and associated disorders within families, complex segregation analysis was performed on family study data obtained from 53 independently ascertained children and adolescents with TS and their 154 first-degree relatives. The results suggest that the susceptibility for TS is conveyed by a major locus in combination with a multifactorial background. Other models of inheritance were definitively rejected, including strictly polygenic models, all single major locus models, and mixed models with dominant and recessive major loci. The frequency of the TS susceptibility allele was estimated to be .01. The major locus accounts for over half of the phenotypic variance for TS, whereas the multifactorial background accounts for approximately 40% of phenotypic variance. Penetrance estimates suggest that all individuals homozygous for the susceptibility allele at the major locus are affected, whereas only 2.2% of males and 0.3% of females heterozygous at the major locus are affected. Of individuals affected with TS, approximately 62% are heterozygous and approximately 38% are homozygous at the major locus. While none of the families had two parents affected with TS, 19% of families had two parents affected with the broader, phenotype, which includes TS, chronic tic disorder, or obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. J., Leonard H. L., Swedo S. E. Case study: a new infection-triggered, autoimmune subtype of pediatric OCD and Tourette's syndrome. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1995 Mar;34(3):307–311. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199503000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apter A., Pauls D. L., Bleich A., Zohar A. H., Kron S., Ratzoni G., Dycian A., Kotler M., Weizman A., Gadot N. An epidemiologic study of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome in Israel. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;50(9):734–738. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820210068008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Shapiro E., Shapiro A., Rainer J. D. Genetic analysis of Tourette syndrome suggesting major gene effect. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Sep;33(5):767–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd L., Kerbeshian J., Wikenheiser M., Fisher W. A prevalence study of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome in North Dakota school-age children. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1986 Jul;25(4):552–553. doi: 10.1016/s0002-7138(10)60016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caine E. D., McBride M. C., Chiverton P., Bamford K. A., Rediess S., Shiao J. Tourette's syndrome in Monroe County school children. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):472–475. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Comings B. G., Devor E. J., Cloninger C. R. Detection of major gene for Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):586–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Tourette's syndrome: a behavioral spectrum disorder. Adv Neurol. 1995;65:293–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. The Leyton obsessional inventory. Psychol Med. 1970 Nov;1(1):48–64. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700040010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D., Robertson M. M., Gurling H. M. Autosomal dominant gene transmission in a large kindred with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Jun;160:845–849. doi: 10.1192/bjp.160.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devor E. J. Complex segregation analysis of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: further evidence for a major locus mode of transmission. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):704–709. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eapen V., Pauls D. L., Robertson M. M. Evidence for autosomal dominant transmission in Tourette's syndrome. United Kingdom cohort study. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 May;162:593–596. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament M. F., Whitaker A., Rapoport J. L., Davies M., Berg C. Z., Kalikow K., Sceery W., Shaffer D. Obsessive compulsive disorder in adolescence: an epidemiological study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1988 Nov;27(6):764–771. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198811000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel M., Cummings J. L., Robertson M. M., Trimble M. R., Hill M. A., Benson D. F. Obsessions and compulsions in Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 1986 Mar;36(3):378–382. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman W. K., Price L. H., Rasmussen S. A., Mazure C., Delgado P., Heninger G. R., Charney D. S. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. II. Validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Nov;46(11):1012–1016. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810110054008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman W. K., Price L. H., Rasmussen S. A., Mazure C., Fleischmann R. L., Hill C. L., Heninger G. R., Charney D. S. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Nov;46(11):1006–1011. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810110048007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Leppert M., Filloux F., van de Wetering B. J., McMahon W. M. Intermediate inheritance of Tourette syndrome, assuming assortative mating. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Sep;57(3):682–689. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J. Phenotypic assortative mating in segregation analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(2):109–127. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson R. J., Rachman S. Obsessional-compulsive complaints. Behav Res Ther. 1977;15(5):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde T. M., Aaronson B. A., Randolph C., Rickler K. C., Weinberger D. R. Relationship of birth weight to the phenotypic expression of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome in monozygotic twins. Neurology. 1992 Mar;42(3 Pt 1):652–658. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Pauls D. L. Genetic hypotheses for Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol. 1982;35:243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan R., Eapen V., Stern J., McDermott M. P., Robertson M. M. Bilineal transmission in Tourette's syndrome families. Neurology. 1994 Dec;44(12):2336–2342. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.12.2336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Elston R. C. A unified model for complex segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):816–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Dolnansky E. S., Hardin M. T., Clubb M., Walkup J. T., Stevenson J., Pauls D. L. Perinatal factors in the expression of Tourette's syndrome: an exploratory study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1990 Mar;29(2):220–226. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199003000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Price R. A., Walkup J. T., Ort S., Pauls D. L., Cohen D. J. Nongenetic factors in Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;44(1):100–100. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800130112025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso P. J., Scahill L. D., Chappell P. B., Pauls D. L., Cohen D. J., Leckman J. F. Tourette's syndrome: a multigenerational, neuropsychiatric disorder. Adv Neurol. 1995;65:305–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L. Issues in genetic linkage studies of Tourette syndrome. Phenotypic spectrum and genetic model parameters. Adv Neurol. 1992;58:151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Leckman J. F., Cohen D. J. Familial relationship between Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome, attention deficit disorder, learning disabilities, speech disorders, and stuttering. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;32(5):1044–1050. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199309000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Leckman J. F. The inheritance of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome and associated behaviors. Evidence for autosomal dominant transmission. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 16;315(16):993–997. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610163151604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Pakstis A. J., Kurlan R., Kidd K. K., Leckman J. F., Cohen D. J., Kidd J. R., Como P., Sparkes R. Segregation and linkage analyses of Tourette's syndrome and related disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1990 Mar;29(2):195–203. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Raymond C. L., Stevenson J. M., Leckman J. F. A family study of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):154–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. A., Leckman J. F., Pauls D. L., Cohen D. J., Kidd K. K. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome: tics and central nervous system stimulants in twins and nontwins. Neurology. 1986 Feb;36(2):232–237. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. A., Pauls D. L., Kruger S. D., Caine E. D. Family data support a dominant major gene for Tourette syndrome. Psychiatry Res. 1988 Jun;24(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen S. A., Tsuang M. T. Clinical characteristics and family history in DSM-III obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1986 Mar;143(3):317–322. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N., Helzer J. E., Croughan J., Ratcliff K. S. National Institute of Mental Health Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Its history, characteristics, and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;38(4):381–389. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780290015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer H. S., Walkup J. T. Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders. Diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991 Jan;70(1):15–32. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199101000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkup J. T., Rosenberg L. A., Brown J., Singer H. S. The validity of instruments measuring tic severity in Tourette's syndrome. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1992 May;31(3):472–477. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199205000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



