Abstract
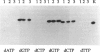
A pronounced genetic polymorphism of the interferon type I gene family has been assumed on the basis of RFLP analysis of the genomic region as well as the large number of sequences published compared to the number of loci. However, IFNA2 is the only locus that has been carefully analyzed concerning gene frequency, and only naturally occurring rare alleles have been found. We have extended the studies on a variation of expressed sequences by studying the IFNA1, IFNA2, IFNA10, IFNA13, IFNA14, and IFNA17 genes. Genomic white-blood-cell DNA from a population sample of blood donors and from a family material were screened by single-nucleotide primer extension (allele-specific primer extension) of PCR fragments. Because of sequence similarities, in some cases "nested" PCR was used, and, when applicable, restriction analysis or control sequencing was performed. All individuals carried the interferon-alpha 1 and interferon-alpha 13 variants but not the LeIF D variant. At the IFNA2 and IFNA14 loci only one sequence variant was found, while in the IFNA10 and IFNA17 groups two alleles were detected in each group. The IFNA10 and IFNA17 alleles segregated in families and showed a close fit to the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There was a significant linkage disequilibrium between IFNA10 and IFNA17 alleles. The fact that the extent of genetic polymorphism was lower than expected suggests that a majority of the previously described gene sequences represent nonpolymorphic rare mutants that may have arisen in tumor cell lines.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew C., Windass J. D. Identification of a functional allele of a human interferon-alpha gene previously characterized as a pseudogene. J Interferon Res. 1989 Aug;9(4):407–417. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Molecular analysis of the human interferon-alpha gene family. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary C. M., Donnelly R. J., Soh J., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Knockout and reconstitution of a functional human type I interferon receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18747–18749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. S., Gewert D. R., Barber K. A., Lewis A. P., Sims M. J., Davies S. L., Salom C. L., Wood J., Thomas H. C., Thursz M. Interferon (IFN)-alpha 2 genotype analysis of Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients undergoing recombinant IFN-alpha 2a therapy. J Infect Dis. 1994 Apr;169(4):875–878. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.4.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Bohlander S., Allen G. Nomenclature of the human interferon genes. J Interferon Res. 1994 Aug;14(4):221–222. doi: 10.1089/jir.1994.14.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipaola M., Smith T., Ferencz-Biro K., Liao M. J., Testa D. Interferon-alpha 2 produced by normal human leukocytes is predominantly interferon-alpha 2b. J Interferon Res. 1994 Dec;14(6):325–332. doi: 10.1089/jir.1994.14.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B., Swetly P. MOlecular cloning of human alpha and beta interferon genes from Namalwa cells. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(4):575–585. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz M. O., Pomykala H. M., Bohlander S. K., Maltepe E., Malik K., Brownstein B., Olopade O. I. Structure of the human type-I interferon gene cluster determined from a YAC clone contig. Genomics. 1994 Aug;22(3):540–552. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel S. L., Pestka S. Human interferon-alpha A, -alpha 2, and -alpha 2(Arg) genes in genomic DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12565–12569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewert D. R., Sharp N. A., Barber K. A., Cooper H., Tucker D., Lewis A. P., Thursz M., Crowe J. S. Detection of rare allelic variants of the interferon-alpha 2 gene in human genomic DNA. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995 May;15(5):403–406. doi: 10.1089/jir.1995.15.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewert D., Salom C., Barber K., Macbride S., Cooper H., Lewis A., Wood J., Crowe S. Analysis of interferon-alpha 2 sequences in human genomic DNA. J Interferon Res. 1993 Jun;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1089/jir.1993.13.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henco K., Brosius J., Fujisawa A., Fujisawa J. I., Haynes J. R., Hochstadt J., Kovacic T., Pasek M., Schamböck A., Schmid J. Structural relationship of human interferon alpha genes and pseudogenes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):227–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90401-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G. Estimation of linkage disequilibrium in randomly mating populations. Heredity (Edinb) 1974 Oct;33(2):229–239. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1974.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi K., Utsumi J., Kitagawa T., Shimizu H., Kobayashi S. Structural characterization of fibroblast human interferon-beta 1. J Interferon Res. 1988 Jun;8(3):375–384. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta K., Monahan J., Collier K. J., Pestka S. Detection of human leukocyte interferon-alpha A and -alpha 2 genes in genomic DNAs by the use of deoxyoctadecyloligonucleotide probes. J Interferon Res. 1988 Feb;8(1):51–60. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluz S., Kabát P., Gibadulinová A., Vojtassák J., Fuchsberger N., Kontsek P. Interferon alpha2b is the predominant subvariant detected in human genomic DNAs. Acta Virol. 1994 Apr;38(2):101–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M. N., Hoffmann J. W., Kasper C. K., Spitzer S. G., Groce S. L., Bajaj S. P. Single nucleotide primer extension to detect genetic diseases: experimental application to hemophilia B (factor IX) and cystic fibrosis genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1143–1147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfo S., Gribaudo G., Angeretti A., Gariglio M. Mechanisms of viral inhibition by interferons. Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Mar;65(3):415–442. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(95)98599-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Purification, bacterial expression, and biological activities of the human interferons. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1 Suppl):128s–136s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12282005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Adelman J., Dull T. J., Gross M., Goeddel D., Ullrich A. DNA sequence of two closely linked human leukocyte interferon genes. Science. 1981 Jun 5;212(4499):1159–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.6165082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Lee N., Dipaola M., Hussain M., Brissette R., Ni D., Smith T., Desai M., Ferencz-Biro K., Testa D. Distribution of interferon-alpha 2 genes in humans. J Interferon Res. 1994 Aug;14(4):183–185. doi: 10.1089/jir.1994.14.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind L., Lundström A., Hofer P. A., Holmgren G. The gene for diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma of the type found in northern Sweden is localized to chromosome 12q11-q13. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1789–1793. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Edlund T., Lindenmaier W., Ny T., Collins J., Lundgren E., von Gabain A. Novel cluster of alpha-interferon gene sequences in a placental cosmid DNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2435–2439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., von Gabain A., Edlund T., Ny T., Lundgren E. Differential expression of interferon genes in a substrain of Namalwa cells. J Interferon Res. 1985 Spring;5(2):229–238. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., McCandliss R., Gross M., Sloma A., Familletti P. C., Tabor J. M., Evinger M., Levy W. P., Pestka S. Construction and identification of bacterial plasmids containing nucleotide sequence for human leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7010–7013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Schwarzstein M., Streuli M., Panem S., Nagata S., Weissmann C. The nucleotide sequence of a cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNA. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Taira H., Hall A., Johnsrud L., Streuli M., Ecsödi J., Boll W., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Synthesis in E. coli of a polypeptide with human leukocyte interferon activity. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):316–320. doi: 10.1038/284316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson M., Feder J., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., von Gabain A. Close linkage of alpha and beta interferons and infrequent duplication of beta interferon in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4473–4476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Nagata S., Weissmann C. At least three human type alpha interferons: structure of alpha 2. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6158094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Mantei N., Schwarzstein M., Nagata S., Muramatsu M., Weissmann C. Human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are structurally related. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):547–549. doi: 10.1038/285547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Kioussis D., Weissmann C. Two non-allelic human interferon alpha genes with identical coding regions. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1809–1812. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Apperson S., May L., Stebbing N. Comparison of the antiviral activities of various cloned human interferon-alpha subtypes in mammalian cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):233–237. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]