Abstract
The primary molecular defect underlying Niemann-Pick C disease (NPC) is still unknown. A wide spectrum of clinical and biochemical phenotypes has previously been documented. Indication of genetic heterogeneity has recently been provided for one patient. In the present study, somatic cell hybridization experiments were carried out on skin fibroblast cultures from 32 unrelated NPC patients covering the range of known clinical and biochemical phenotypes. The criterion for complementation was the restoration of a normal intracellular fluorescent pattern in polykaryons stained with filipin to document cholesterol distribution. Crosses between the various cell lines revealed a major complementation group comprising 27 unrelated patients and a second minor group comprising 5 patients. Linkage analysis in one multiplex family belonging to the minor complementation group showed that the mutated gene does not map to the 18q11-12 region assigned to the major gene. Patients in the first group spanned the whole spectrum of clinical and cellular phenotypes. No consistent clinical or biochemical phenotypes was associated with the second complementation group. Three of the five group 2 patients, however, presented with a new rare phenotype associated with severe pulmonary involvement leading to death within the first year of life. No biochemical abnormality specific of either group could be demonstrated with regard to tissue lipid storage pattern, intralysosomal cholesterol storage, and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Mutations affecting at least two different genes have thus been shown to underlie NPC. The two gene products may function together or sequentially in a common metabolic pathway affecting intracellular cholesterol transport.
Full text
PDF
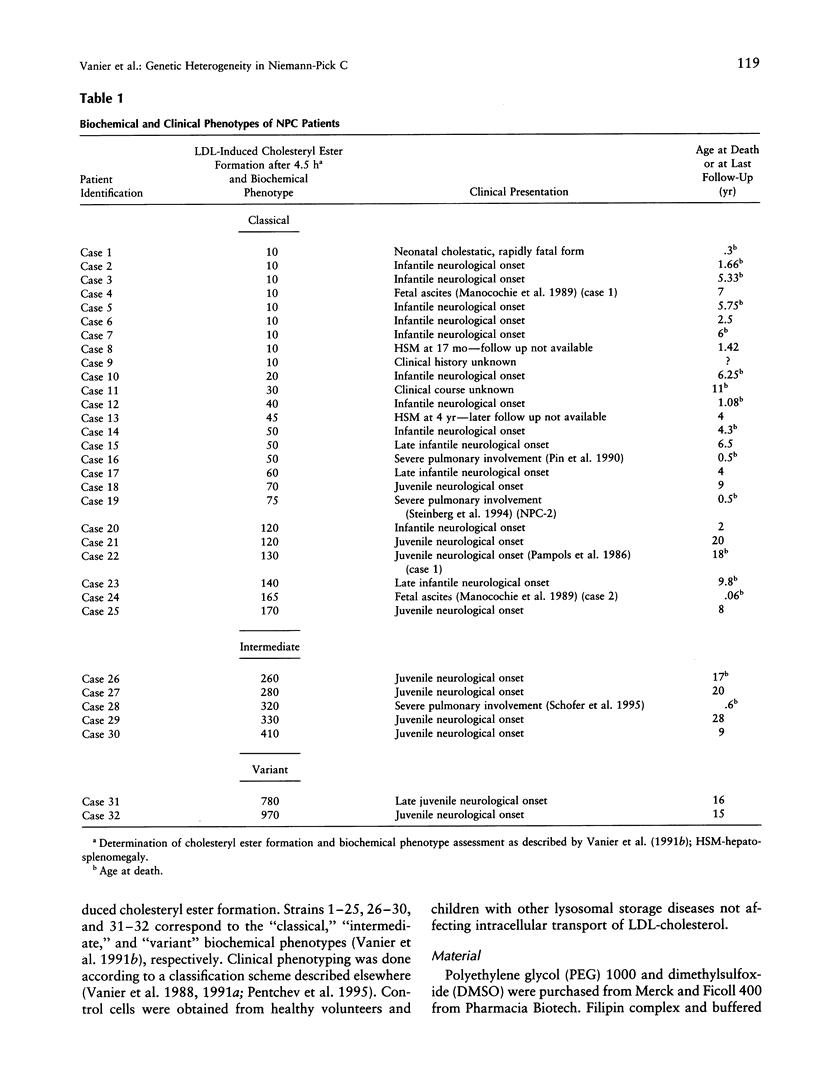

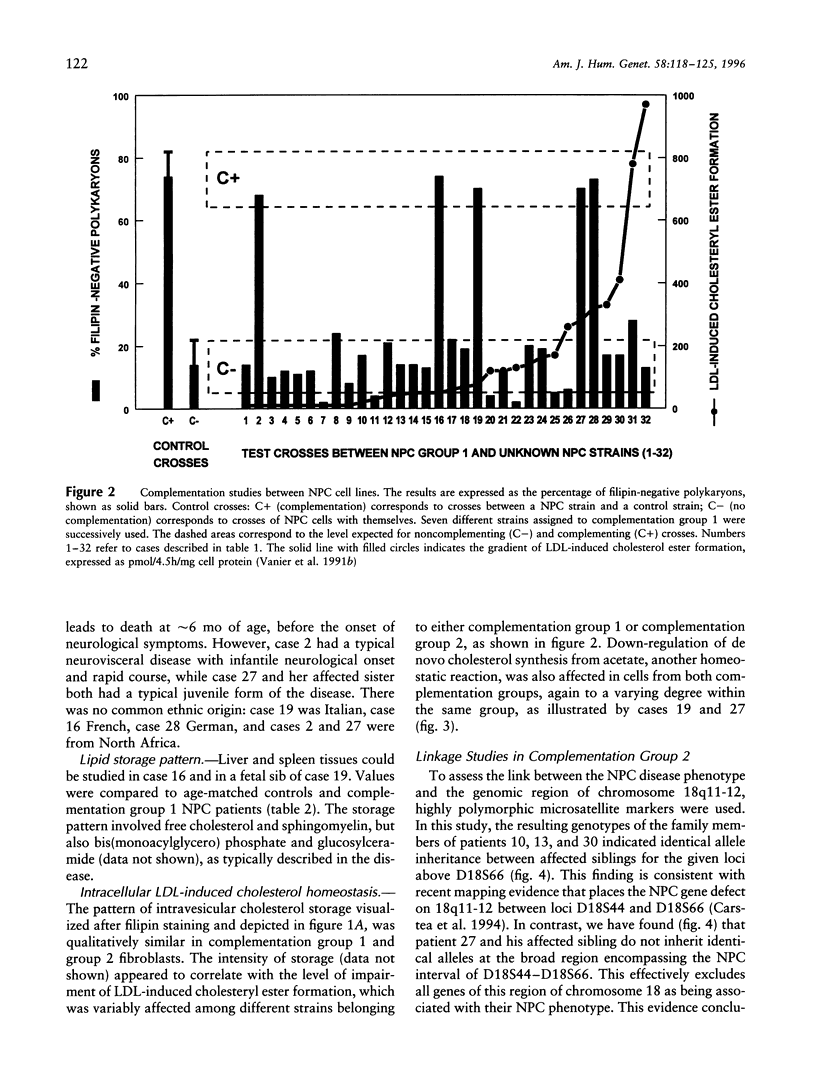


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argoff C. E., Comly M. E., Blanchette-Mackie J., Kruth H. S., Pye H. T., Goldin E., Kaneski C., Vanier M. T., Brady R. O., Pentchev P. G. Type C Niemann-Pick disease: cellular uncoupling of cholesterol homeostasis is linked to the severity of disruption in the intracellular transport of exogenously derived cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 5;1096(4):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90068-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler L. M., Shankaran R., Das I., Callahan J. W. Cholesterol esterification and Niemann-Pick disease: an approach to identifying the defect in fibroblasts. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):505–511. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brul S., Westerveld A., Strijland A., Wanders R. J., Schram A. W., Heymans H. S., Schutgens R. B., van den Bosch H., Tager J. M. Genetic heterogeneity in the cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome and other inherited disorders with a generalized impairment of peroxisomal functions. A study using complementation analysis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1710–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI113510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadigan K. M., Spillane D. M., Chang T. Y. Isolation and characterization of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in intracellular low density lipoprotein-cholesterol trafficking. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):295–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstea E. D., Polymeropoulos M. H., Parker C. C., Detera-Wadleigh S. D., O'Neill R. R., Patterson M. C., Goldin E., Xiao H., Straub R. E., Vanier M. T. Linkage of Niemann-Pick disease type C to human chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2002–2004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N. K., Daunais M. A., Liscum L. A second complementation class of cholesterol transport mutants with a variant Niemann-Pick type C phenotype. J Lipid Res. 1994 Oct;35(10):1839–1849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N. K., Reed K. L., Daunais M. A., Faust J. R., Liscum L. Isolation and characterization of Chinese hamster ovary cells defective in the intracellular metabolism of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4889–4896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie I. K., Chong S., Mieli-Vergani G., Lake B. D., Mowat A. P. Fetal ascites: an unusual presentation of Niemann-Pick disease type C. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Oct;64(10 Spec No):1391–1393. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.10_spec_no.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. V., Carey W. F. A method for enrichment of hybrid somatic cells: complementation studies in certain lysosomal enzymopathies. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1985;8(3):95–99. doi: 10.1007/BF01819286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Vanier M. T., Carstea E. D., Parker C. C., Goldin E., Roff C. F. The Niemann-Pick C lesion and its relationship to the intracellular distribution and utilization of LDL cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Feb 22;1225(3):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin I., Pradines S., Pincemaille O., Frappat P., Brambilla E., Vanier M. T., Bost M. Forme respiratoire mortelle de maladie de Niemann-Pick type C. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1990 May;47(5):373–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Glodek A., Gorski M., Adams M. D., Moreno R. F., Fitzgerald M. G., Venter J. C., Merril C. R. Chromosomal assignment of 46 brain cDNAs. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90439-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pámpols T., Pineda M., Ferreter M., Fernández E. Enfermedad de Niemann-Pick tipo C en dos hermanos. Bases bioquímicas del diagnóstico. An Esp Pediatr. 1986 Apr;24(4):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., Rousson R., Bonnet J., Pentchev P. G., Louisot P., Vanier M. T. Abnormal cholesterol metabolism in imipramine-treated fibroblast cultures. Similarities with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 2;1043(2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitsky K., Bar-Shira A., Gilad S., Rotman G., Ziv Y., Vanagaite L., Tagle D. A., Smith S., Uziel T., Sfez S. A single ataxia telangiectasia gene with a product similar to PI-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1749–1753. doi: 10.1126/science.7792600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu H. S., Rastogi S. A., Byers D. M., Guernsey D. L., Cook H. W., Palmer F. B., Spence M. W. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase activities are differentially affected in Niemann-Pick type C and type D fibroblasts. Biochem Cell Biol. 1993 Sep-Oct;71(9-10):467–474. doi: 10.1139/o93-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. J., Ward C. P., Fensom A. H. Complementation studies in Niemann-Pick disease type C indicate the existence of a second group. J Med Genet. 1994 Apr;31(4):317–320. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Speer M. C., Luo Y., Rojas K., Overhauser J., Ott J., Gilliam T. C. A microsatellite genetic linkage map of human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):48–56. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T. Biochemical studies in Niemann-Pick disease. I. Major sphingolipids of liver and spleen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 7;750(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., Rousson R., Duthel S., Harzer K., Pentchev P. G., Revol A., Louisot P. Type C Niemann-Pick disease: biochemical aspects and phenotypic heterogeneity. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(4-5):307–314. doi: 10.1159/000112178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., Rousson R., Gazzah N., Juge M. C., Pentchev P. G., Revol A., Louisot P. Type C Niemann-Pick disease: spectrum of phenotypic variation in disruption of intracellular LDL-derived cholesterol processing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 5;1096(4):328–337. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90069-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Rousson R., Garcia I., Bailloud G., Juge M. C., Revol A., Louisot P. Biochemical studies in Niemann-Pick disease. III. In vitro and in vivo assays of sphingomyelin degradation in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells for the diagnosis of the various forms of the disease. Clin Genet. 1985 Jan;27(1):20–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Wenger D. A., Comly M. E., Rousson R., Brady R. O., Pentchev P. G. Niemann-Pick disease group C: clinical variability and diagnosis based on defective cholesterol esterification. A collaborative study on 70 patients. Clin Genet. 1988 May;33(5):331–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1988.tb03460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]