Abstract
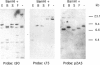
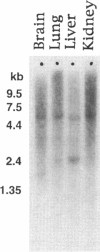
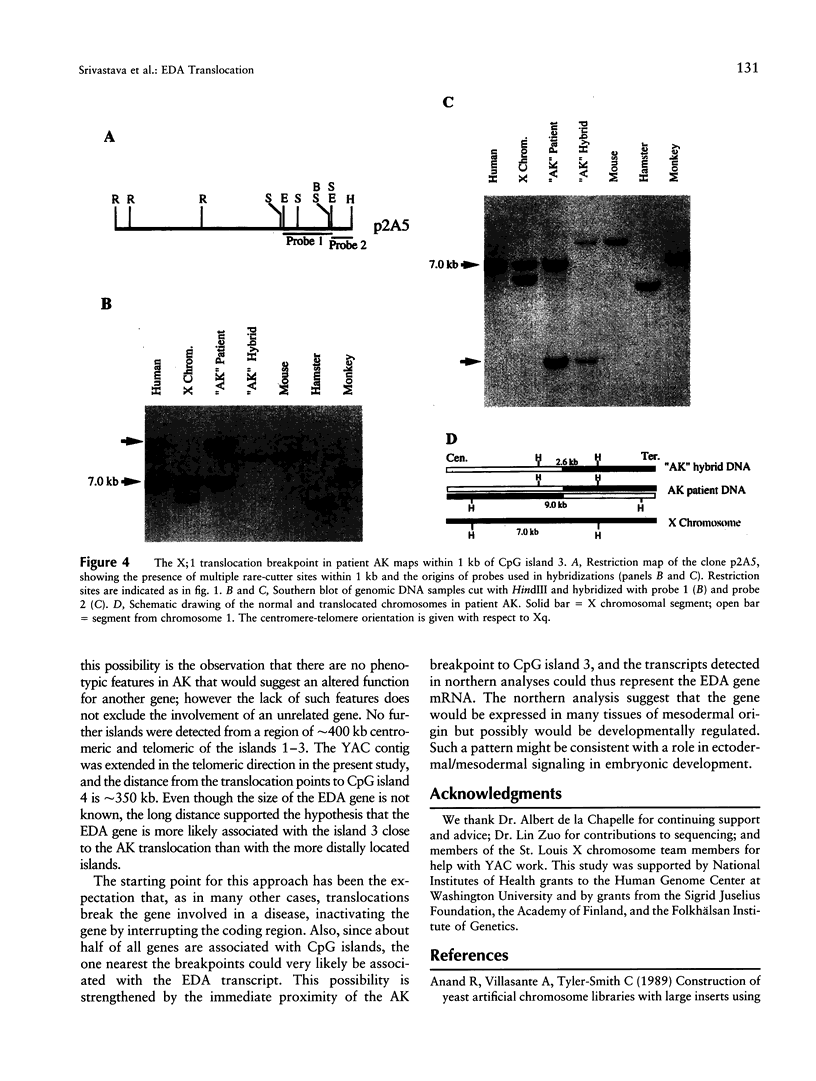
In order to identify the gene for human X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (EDA), a translocation breakpoint in a female with t(X;1)(q13.1;p36.3) and EDA (patient AK) was finely mapped. The EDA region contains five groups of rare-cutter restriction sites that define CpG islands. The two more centromeric of these islands are associated with transcripts of 3.5 kb and 1.8 kb. The third CpG island maps within <1 kb of the translocation breakpoint in patient AK, as indicated by a genomic rearrangement, and approximately 100 kb centromeric from another previously mapped translocation breakpoint (patient AnLy). Northern analysis with a probe from this CpG island detected an approximately 6-kb mRNA in several fetal tissues tested. An extended YAC contig of 1,200 kb with an average of fivefold coverage was constructed. The two most telomeric CpG islands map 350 kb telomeric of the two translocations. Taken together, the results suggest that the CpG island just proximal of the AK translocation breakpoint lies at the 5' end of a candidate gene for EDA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchard M. M., Taillon-Miller P., Nowotny P., Nowotny V. PCR buffer optimization with uniform temperature regimen to facilitate automation. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Feb;2(3):234–240. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blecher S. R. Anhidrosis and absence of sweat glands in mice hemizygous for the Tabby gene: supportive evidence for the hypothesis of homology between Tabby and human anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia (Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome). J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):720–722. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Sarfarazi M., Thomas N. S., Roberts K., Harper P. S. X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: DNA probe linkage analysis and gene localization. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):378–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00284112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Alembik Y., Arveiler B., Formiga L., Gilgenkrantz S., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: DXS159, a closely linked proximal marker. Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;80(2):177–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00702863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kere J., Grzeschik K. H., Limon J., Gremaud M., Schlessinger D., de la Chapelle A. Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia gene region cloned in yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):305–310. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kere J., Nagaraja R., Mumm S., Ciccodicola A., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Mapping human chromosomes by walking with sequence-tagged sites from end fragments of yeast artificial chromosome inserts. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kølvraa S., Kruse T. A., Jensen P. K., Linde K. H., Vestergaard S. R., Bolund L. Close linkage between X-linked ectodermal dysplasia and a cloned DNA sequence detecting a two allele restriction fragment length polymorphism in the region Xp11-q12. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):284–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00282550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. T., Murgia A., Sosnoski D. M., Olivos I. M., Nussbaum R. L. Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library for Xpter-Xq27.3: a systematic determination of cocloning rate and X-chromosome representation. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):526–533. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90444-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limon J., Filipiuk J., Nedoszytko B., Mrózek K., Castrén M., Larramendy M., Roszkiewicz J. X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and de novo t(X;1) in a female. Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;87(3):338–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00200916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermot K. D., Hultén M. Female with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and de novo (X;9) translocation. Clinical documentation of the AnLy cell line case. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):577–579. doi: 10.1007/BF00210814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermot K. D., Winter R. M., Malcolm S. Gene localisation of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (C-S-T syndrome). Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):172–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00282084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella R., Srivastava A. K. Physical linkage of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) to polymorphic markers on the X chromosome. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1095–1101. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja R., Kere J., MacMillan S., Masisi M. J., Johnson D., Molini B. J., Halley G. R., Wein K., Trusgnich M., Eble B. Characterization of four human YAC libraries for clone size, chimerism and X chromosome sequence representation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 25;22(16):3406–3411. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.16.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarialho-Kere U. K., Welgus H. G., Parks W. C. Distinct mechanisms regulate interstitial collagenase and 92-kDa gelatinase expression in human monocytic-like cells exposed to bacterial endotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17354–17361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan D. D., Blanchard M. M., Burough F. W., Nowotny V. Screening yeast artificial chromosome libraries with robot-aided automation. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1993;10(6):128–143. doi: 10.1016/1050-3862(93)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Chelly J., Zonana J., Davies K. J., Morgan S., Gault J., Rack K. A., Buckle V. J., Brockdorff N., Clarke A. Characterisation of molecular DNA rearrangements within the Xq12-q13.1 region, in three patients with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (EDA). Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1679–1685. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Little R. D., Abidi F., Porta G., Labella T., Cooper T., Della Valle G., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Human Xq24-Xq28: approaches to mapping with yeast artificial chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonana J., Clarke A., Sarfarazi M., Thomas N. S., Roberts K., Marymee K., Harper P. S. X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: localization within the region Xq11-21.1 by linkage analysis and implications for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):75–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonana J., Gault J., Davies K. J., Jones M., Browne D., Litt M., Brockdorff N., Rastan S., Clarke A., Thomas N. S. Detection of a molecular deletion at the DXS732 locus in a patient with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (EDA), with the identification of a unique junctional fragment. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;52(1):78–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]