Abstract
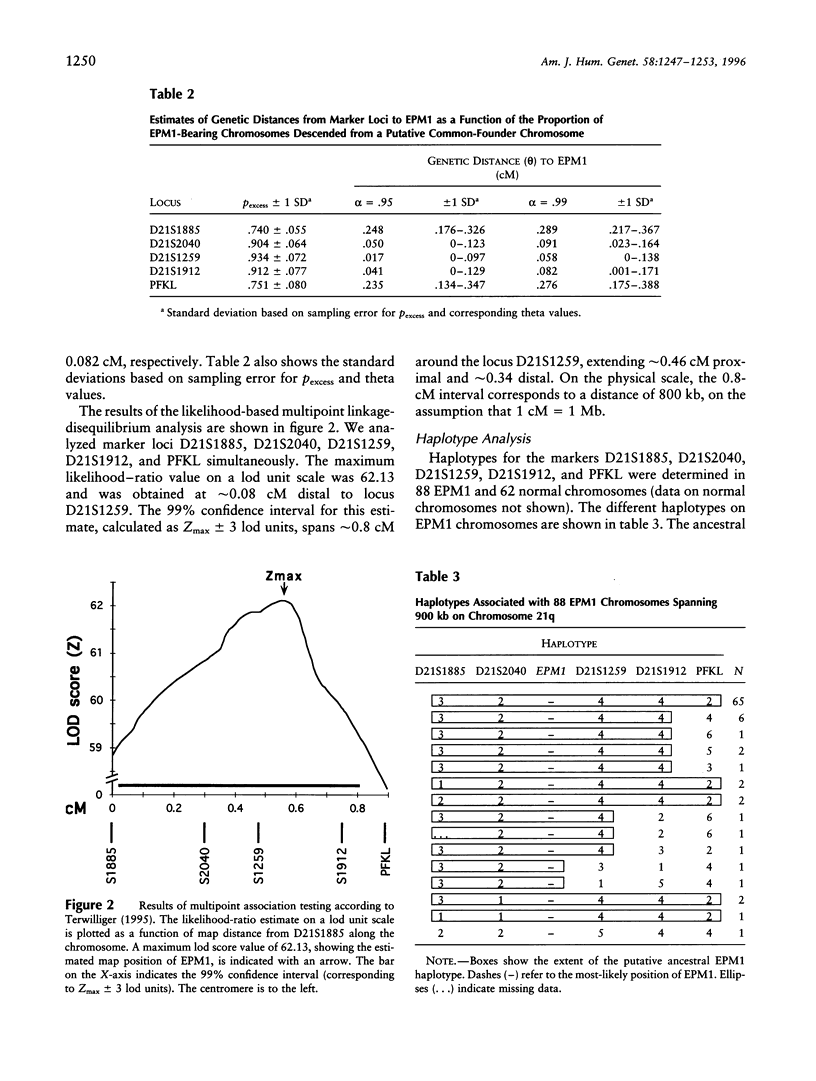
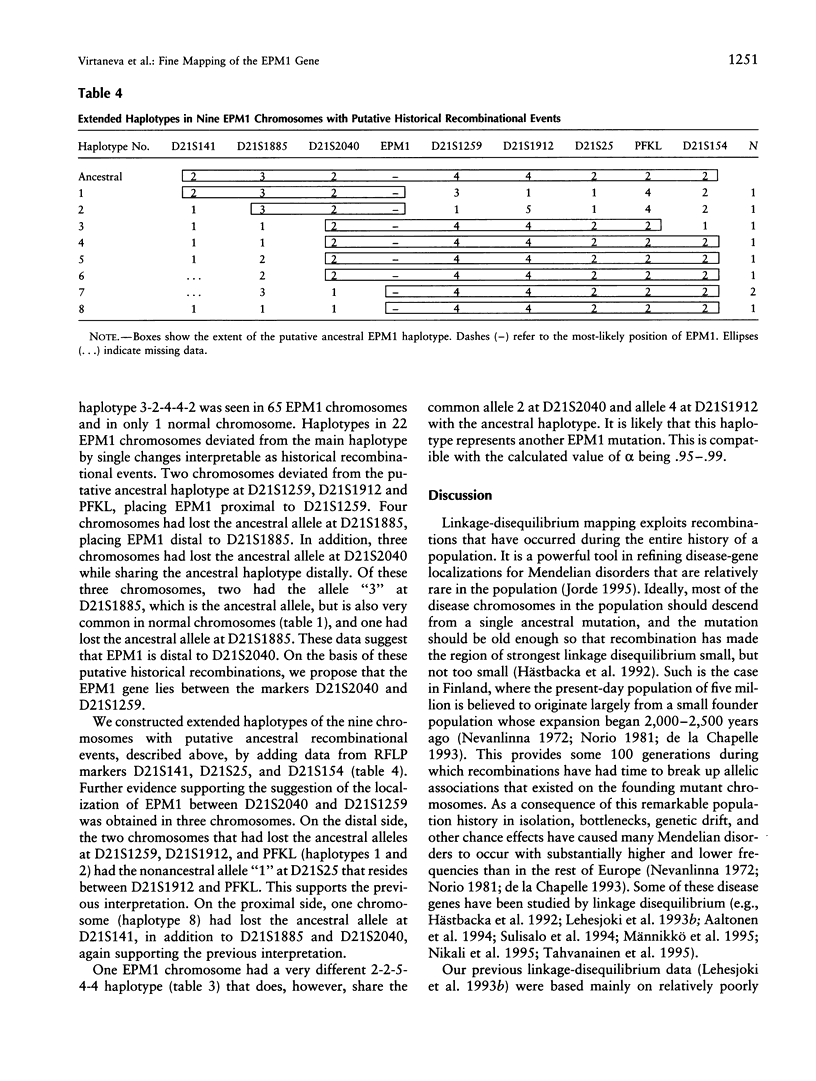
The EPM1 locus responsible for progressive myoclonus epilepsy of Unverricht-Lundborg type (MIM 254800) maps to a region in distal chromosome 21q where positional cloning has been hampered by the lack of physical and genetic mapping resolution. We here report the use of a recently constituted contig of cosmid, BAC, and P1 clones that allowed new polymorphic markers to be positioned. These were typed in 53 unrelated disease families from an isolated Finnish population in which a putative single ancestral EPM1 mutation has segregated for an estimated 100 generations. By thus exploiting historical recombinations in haplotype analysis, EPM1 could be assigned to the ~175-kb interval between the markers D21S2040 and D21S1259.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen J., Björses P., Sandkuijl L., Perheentupa J., Peltonen L. An autosomal locus causing autoimmune disease: autoimmune polyglandular disease type I assigned to chromosome 21. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):83–87. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkovic S. F., Andermann F., Carpenter S., Wolfe L. S. Progressive myoclonus epilepsies: specific causes and diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 31;315(5):296–305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607313150506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faham M., Cox D. R. A novel in vivo method to detect DNA sequence variation. Genome Res. 1995 Dec;5(5):474–482. doi: 10.1101/gr.5.5.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Ichikawa H., Ohki M., Patterson D., Cheng J. F. Localization of cDNAs to a region poorly represented in the CEPH chromosome 21 YAC contig: candidate genes for genetic diseases mapped to 21q22.3. Genomics. 1995 Nov 20;30(2):376–379. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Mahtani M. M., Clines G., Reeve-Daly M. P., Daly M., Hamilton B. A., Kusumi K., Trivedi B., Weaver A. The diastrophic dysplasia gene encodes a novel sulfate transporter: positional cloning by fine-structure linkage disequilibrium mapping. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa H., Hosoda F., Arai Y., Shimizu K., Ohira M., Ohki M. A NotI restriction map of the entire long arm of human chromosome 21. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):361–366. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B. Linkage disequilibrium as a gene-mapping tool. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):11–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Weir B. S. Are moment bounds on the recombination fraction between a marker and a disease locus too good to be true? Allelic association mapping revisited for simple genetic diseases in the Finnish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1486–1498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Donner M., Majuri H., Haltia M., Norio R. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy. A clinical and histopathological study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1974;50(3):307–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Eldridge R., Eldridge J., Wilder B. J., de la Chapelle A. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy of Unverricht-Lundborg type: a clinical and molecular genetic study of a family from the United States with four affected sibs. Neurology. 1993 Nov;43(11):2384–2386. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.11.2384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Norio R., Tirrito S., Sistonen P., Lander E., de la Chapelle A. Localization of the EPM1 gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy on chromosome 21: linkage disequilibrium allows high resolution mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Pandolfo M., Antonelli A., Kyllerman M., Wahlström J., Nergårdh A., Burmeister M., Sistonen P., Norio R. Linkage studies in progressive myoclonus epilepsy: Unverricht-Lundborg and Lafora's diseases. Neurology. 1992 Aug;42(8):1545–1550. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.8.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Sistonen P., Miao J., Hästbacka J., Norio R., de la Chapelle A. Localization of a gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy to chromosome 21q22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3696–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männikkö M., Kestailä M., Holmberg C., Norio R., Ryynänen M., Olsen A., Peltonen L., Tryggvason K. Fine mapping and haplotype analysis of the locus for congenital nephrotic syndrome on chromosome 19q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1377–1383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevanlinna H. R. The Finnish population structure. A genetic and genealogical study. Hereditas. 1972;71(2):195–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1972.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikali K., Suomalainen A., Terwilliger J., Koskinen T., Weissenbach J., Peltonen L. Random search for shared chromosomal regions in four affected individuals: the assignment of a new hereditary ataxia locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 May;56(5):1088–1095. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norio R., Koskiniemi M. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy: genetic and nosological aspects with special reference to 107 Finnish patients. Clin Genet. 1979 May;15(5):382–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human liver-type 6-phosphofructokinase (PFKL) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2517–2517. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone N. E., Fan J. B., Willour V., Pennacchio L. A., Warrington J. A., Hu A., de la Chapelle A., Lehesjoki A. E., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Construction of a 750-kb bacterial clone contig and restriction map in the region of human chromosome 21 containing the progressive myoclonus epilepsy gene. Genome Res. 1996 Mar;6(3):218–225. doi: 10.1101/gr.6.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Klockars J., Mäkitie O., Francomano C. A., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P. High-resolution linkage-disequilibrium mapping of the cartilage-hair hypoplasia gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;55(5):937–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahvanainen E., Forsius H., Damsten M., Karila E., Kolehmainen J., Weissenbach J., Sistonen P., de la Chapelle A. Linkage disequilibrium mapping of the cornea plana congenita gene CNA2. Genomics. 1995 Dec 10;30(3):409–414. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


