Abstract
Werner syndrome (WS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by premature onset of a number of age-related diseases. The gene for WS, WRN, has been mapped to the 8p 11.1-21.1 region with further localization through linkage disequilibrium mapping. Here we present the results of linkage disequilibrium and ancestral haplotype analyses of 35 markers to further refine the location of WRN. We identified an interval in this region in which 14 of 18 markers tested show significant evidence of linkage disequilibrium in at least one of the two populations tested. Analysis of extended and partial haplotypes covering 21 of the markers studied supports the existence of both obligate and probable ancestral recombinant events which localize WRN almost certainly to the interval between D8S2196 and D8S2186, and most likely to the narrower interval between D8S2168 and D8S2186. These haplotype analyses also suggest that there are multiple WRN mutations in each of the two populations under study. We also present a comparison of approaches to performing disequilibrium tests with multiallelic markers, and show that some commonly used approximations for such tests perform poorly in comparison to exact probability tests. Finally, we discuss some of the difficulties introduced by the high mutation rate at microsatellite markers which influence our ability to use ancestral haplotype analysis to localize disease genes.
Full text
PDF





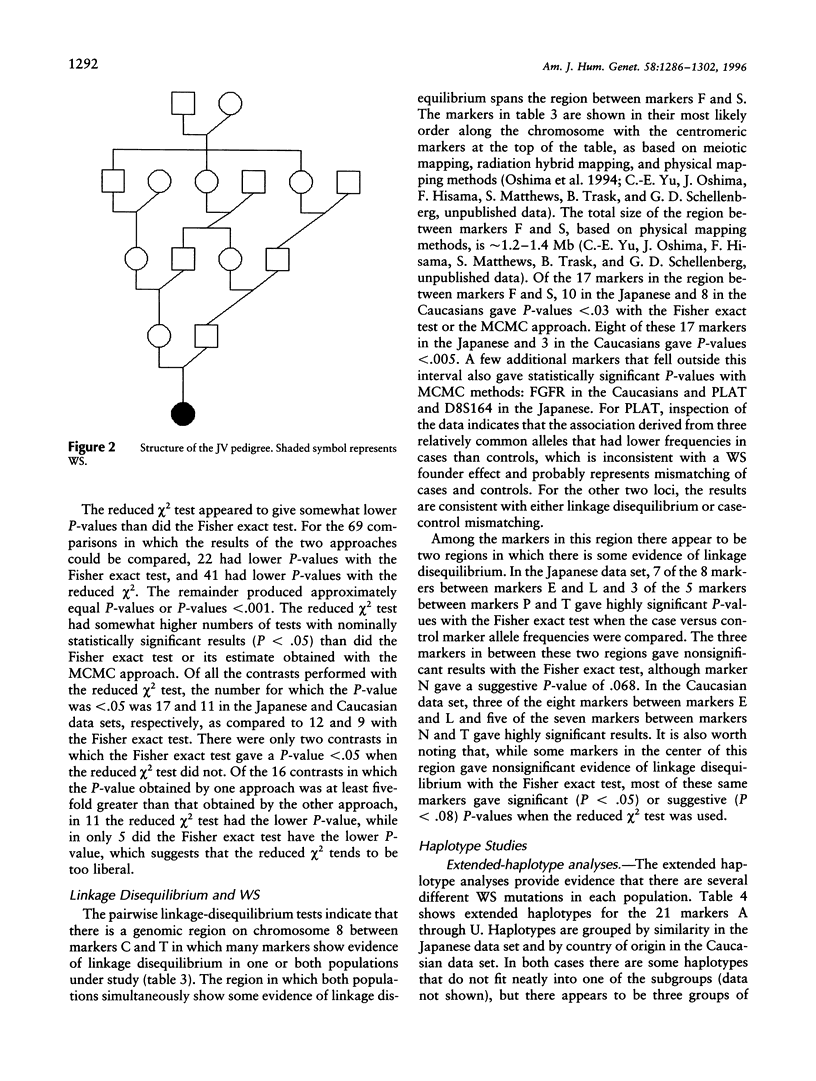

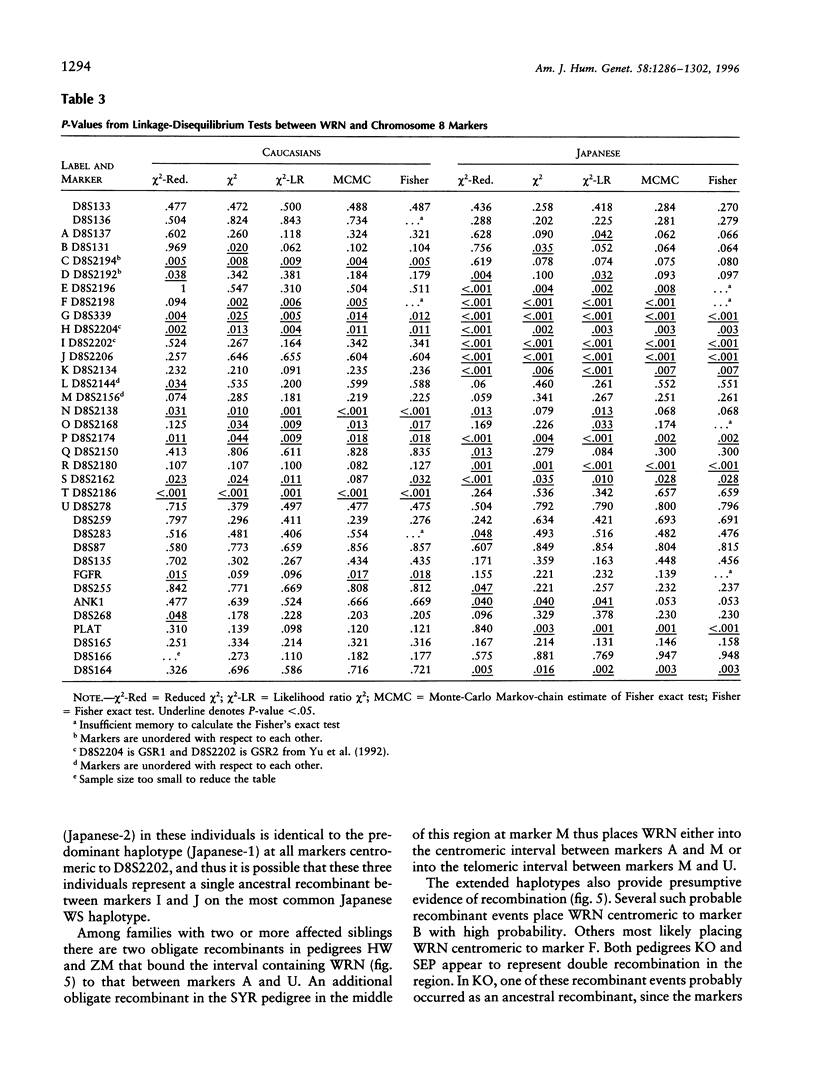








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew S., Theilmann J., Hedrick A., Mah D., Weber B., Hayden M. R. Nonrandom association between Huntington disease and two loci separated by about 3 Mb on 4p16.3. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90246-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehnke M. Limits of resolution of genetic linkage studies: implications for the positional cloning of human disease genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):379–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEPPELLINI R., SINISCALCO M., SMITH C. A. The estimation of gene frequencies in a random-mating population. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Oct;20(2):97–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N. A., Groden J., Ye T. Z., Straughen J., Lennon D. J., Ciocci S., Proytcheva M., German J. The Bloom's syndrome gene product is homologous to RecQ helicases. Cell. 1995 Nov 17;83(4):655–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N. A., Roe A. M., Kozloski J., Proytcheva M., Falk C., German J. Linkage disequilibrium between the FES, D15S127, and BLM loci in Ashkenazi Jews with Bloom syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;55(3):453–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Martin G. M., Schultz A. L., Motulsky A. G. Werner's syndrome a review of its symptomatology, natural history, pathologic features, genetics and relationship to the natural aging process. Medicine (Baltimore) 1966 May;45(3):177–221. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196605000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk C. T., Rubinstein P. Haplotype relative risks: an easy reliable way to construct a proper control sample for risk calculations. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;51(Pt 3):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb00875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Rubenstein M., Weber J., Woods K., Drayna D. Genetic linkage of Werner's syndrome to five markers on chromosome 8. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):735–738. doi: 10.1038/355735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S. W., Thompson E. A. Performing the exact test of Hardy-Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics. 1992 Jun;48(2):361–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heale S. M., Petes T. D. The stabilization of repetitive tracts of DNA by variant repeats requires a functional DNA mismatch repair system. Cell. 1995 Nov 17;83(4):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick P. W. Gametic disequilibrium measures: proceed with caution. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):331–341. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández J. L., Weir B. S. A disequilibrium coefficient approach to Hardy-Weinberg testing. Biometrics. 1989 Mar;45(1):53–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Maximum-likelihood estimation of gene location by linkage disequilibrium. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):705–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. R. The sampling distribution of linkage disequilibrium under an infinite allele model without selection. Genetics. 1985 Mar;109(3):611–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B., Watkins W. S., Carlson M., Groden J., Albertsen H., Thliveris A., Leppert M. Linkage disequilibrium predicts physical distance in the adenomatous polyposis coli region. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):884–898. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Likelihood methods for locating disease genes in nonequilibrium populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):18–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara K., Nakura J., Ye L., Mitsuda N., Kamino K., Zhao Y., Fujioka Y., Miki T., Ogihara T. Carrier detection of Werner's syndrome using a microsatellite that exhibits linkage disequilibrium with the Werner's syndrome locus. Jpn J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;39(4):403–409. doi: 10.1007/BF01892385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G., Gutman G. A. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):203–221. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewontin R. C. On measures of gametic disequilibrium. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):849–852. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. M. Genetic syndromes in man with potential relevance to the pathobiology of aging. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978;14(1):5–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. M., Sprague C. A., Epstein C. J. Replicative life-span of cultivated human cells. Effects of donor's age, tissue, and genotype. Lab Invest. 1970 Jul;23(1):86–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakura J., Miki T., Nagano K., Kihara K., Ye L., Kamino K., Fujiwara Y., Yoshida S., Murano S., Fukuchi K. Close linkage of the gene for Werner's syndrome to ANK1 and D8S87 on the short arm of chromosome 8. Gerontology. 1993;39 (Suppl 1):11–15. doi: 10.1159/000213560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakura J., Wijsman E. M., Miki T., Kamino K., Yu C. E., Oshima J., Fukuchi K., Weber J. L., Piussan C., Melaragno M. I. Homozygosity mapping of the Werner syndrome locus (WRN). Genomics. 1994 Oct;23(3):600–608. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. M., Wijsman E. M. Design and sample-size considerations in the detection of linkage disequilibrium with a disease locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;55(3):574–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima J., Yu C. E., Boehnke M., Weber J. L., Edelhoff S., Wagner M. J., Wells D. E., Wood S., Disteche C. M., Martin G. M. Integrated mapping analysis of the Werner syndrome region of chromosome 8. Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):100–113. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitsky K., Bar-Shira A., Gilad S., Rotman G., Ziv Y., Vanagaite L., Tagle D. A., Smith S., Uziel T., Sfez S. A single ataxia telangiectasia gene with a product similar to PI-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1749–1753. doi: 10.1126/science.7792600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Martin G. M., Wijsman E. M., Nakura J., Miki T., Ogihara T. Homozygosity mapping and Werner's syndrome. Lancet. 1992 Apr 18;339(8799):1002–1002. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91590-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham P. C., Curtis D. Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;59(Pt 1):97–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1995.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirugo G., Cocozza S., Brice A., Cavalcanti F., De Michele G., Dones I., Filla A., Koenig M., Lorenzetti D., Monticelli A. Linkage disequilibrium analysis of Friedreich's ataxia in 140 Caucasian families: positioning of the disease locus and evaluation of allelic heterogeneity. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(2):133–143. doi: 10.1159/000472400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W., Rubenstein M., Goto M., Drayna D. A genetic analysis of the Werner syndrome region on human chromosome 8p. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):685–690. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomfohrde J., Wood S., Schertzer M., Wagner M. J., Wells D. E., Parrish J., Sadler L. A., Blanton S. H., Daiger S. P., Wang Z. Human chromosome 8 linkage map based on short tandem repeat polymorphisms: effect of genotyping errors. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhrhammer N., Lange E., Porras O., Naeim A., Chen X., Sheikhavandi S., Chiplunkar S., Yang L., Dandekar S., Liang T. Sublocalization of an ataxia-telangiectasia gene distal to D11S384 by ancestral haplotyping in Costa Rican families. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;57(1):103–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Wong C. Mutation of human short tandem repeats. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1123–1128. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S., Cockerham C. C. Testing Hypotheses about Linkage Disequilibrium with Multiple Alleles. Genetics. 1978 Mar;88(3):633–642. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S. Inferences about linkage disequilibrium. Biometrics. 1979 Mar;35(1):235–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye L., Nakura J., Mitsuda N., Fujioka Y., Kamino K., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Miki T., Ogihara T. Genetic association between chromosome 8 microsatellite (MS8-134) and Werner syndrome (WRN): chromosome microdissection and homozygosity mapping. Genomics. 1995 Aug 10;28(3):566–569. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Oshima J., Goddard K. A., Miki T., Nakura J., Ogihara T., Poot M., Hoehn H., Fraccaro M., Piussan C. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype studies of chromosome 8p 11.1-21.1 markers and Werner syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):356–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn L. M., Kwiatkowski D. J. A 37-marker PCR-based genetic linkage map of human chromosome 9: observations on mutations and positive interference. Genomics. 1995 Jul 20;28(2):140–146. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouros E., Golding G. B., MacKay T. F. The effect of combining alleles into electrophoretic classes on detecting linkage disequilibrium. Genetics. 1977 Mar;85(3):543–550. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



