Abstract
Abnormal CAG expansions in the IT-15 gene are associated with Huntington disease (HD). In the diagnostic setting it is necessary to define the limits of the CAG size ranges on normal and HD-associated chromosomes. Most large analyses that defined the limits of the normal and pathological size ranges employed PCR assays, which included the CAG repeats and a CCG repeat tract that was thought to be invariant. Many of these experiments found an overlap between the normal and disease size ranges. Subsequent findings that the CCG repeats vary by 8 trinucleotide lengths suggested that the limits of the normal and disease size ranges should be reevaluated with assays that exclude the CCG polymorphism. Since patients with between 30 and 40 repeats are rare, a consortium was assembled to collect such individuals.
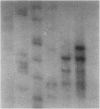
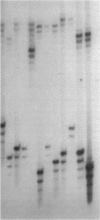
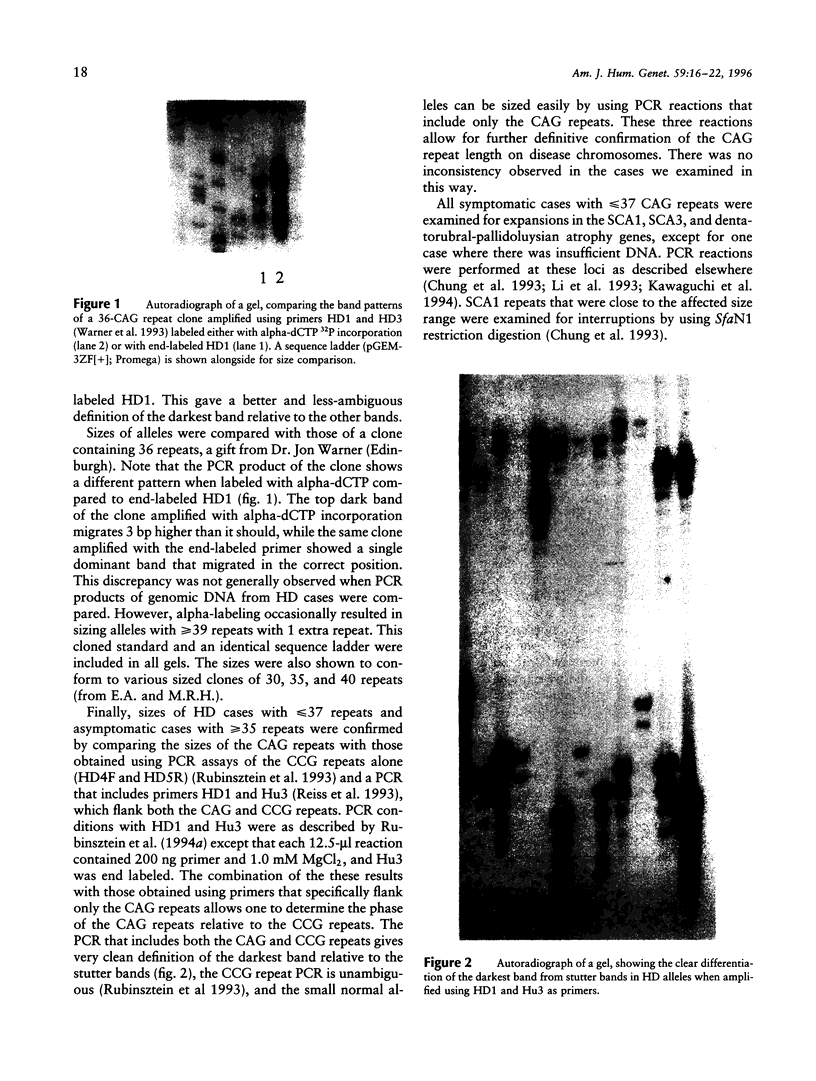
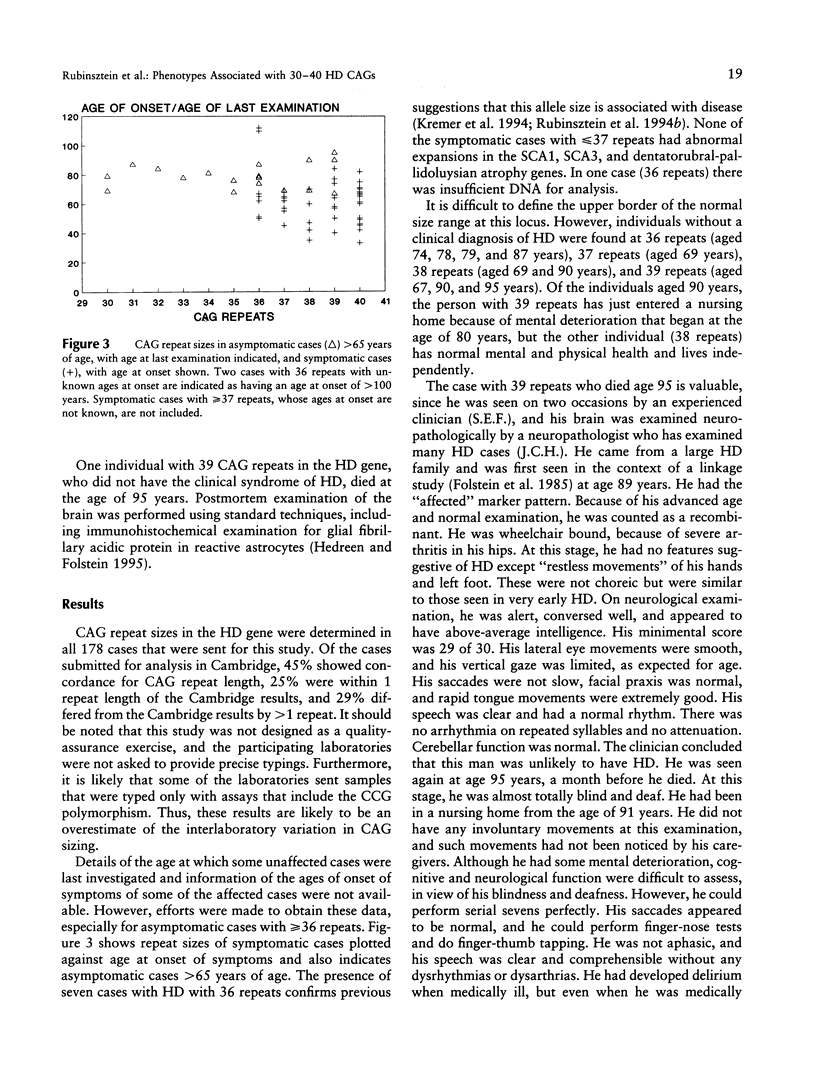
All 178 samples were reanalyzed in Cambridge by using assays specific for the CAG repeats. We have optimized methods for reliable sizing of CAG repeats and show cases that demonstrate the dangers of using PCR assays that include both the CAG and CCG polymorphisms. Seven HD patients had 36 repeats, which confirms that this allele is associated with disease. Individuals without apparent symptoms or signs of HD were found at 36 repeats (aged 74, 78, 79, and 87 years), 37 repeats (aged 69 years), 38 repeats (aged 69 and 90 years), and 39 repeats (aged 67, 90, and 95 years). The detailed case histories of an exceptional case from this series will be presented: a 95-year-old man with 39 repeats who did not have classical features of HD. The apparently healthy survival into old age of some individuals with 36–39 repeats suggests that the HD mutation may not always be fully penetrant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew S. E., Goldberg Y. P., Kremer B., Telenius H., Theilmann J., Adam S., Starr E., Squitieri F., Lin B., Kalchman M. A. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):398–403. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew S. E., Goldberg Y. P., Theilmann J., Zeisler J., Hayden M. R. A CCG repeat polymorphism adjacent to the CAG repeat in the Huntington disease gene: implications for diagnostic accuracy and predictive testing. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):65–67. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron L. H., Warner J. P., Porteous M., Holloway S., Simpson S., Davidson R., Brock D. J. A study of the Huntington's disease associated trinucleotide repeat in the Scottish population. J Med Genet. 1993 Dec;30(12):1003–1007. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.12.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton J. W., Uitti R. J., Ahlskog J. E., Robinson R. G., Kremer B., Hayden M. R. Hereditary late-onset chorea without significant dementia: genetic evidence for substantial phenotypic variation in Huntington's disease. Neurology. 1995 Mar;45(3 Pt 1):443–447. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burright E. N., Clark H. B., Servadio A., Matilla T., Feddersen R. M., Yunis W. S., Duvick L. A., Zoghbi H. Y., Orr H. T. SCA1 transgenic mice: a model for neurodegeneration caused by an expanded CAG trinucleotide repeat. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung M. Y., Ranum L. P., Duvick L. A., Servadio A., Zoghbi H. Y., Orr H. T. Evidence for a mechanism predisposing to intergenerational CAG repeat instability in spinocerebellar ataxia type I. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):254–258. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyao M., Ambrose C., Myers R., Novelletto A., Persichetti F., Frontali M., Folstein S., Ross C., Franz M., Abbott M. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):387–392. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein S. E., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Meyers D. A., Chase G. A., Abbott M. H., Franz M. L., Waber P. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Conneally P. M., Hobbs W. Huntington's disease: two families with differing clinical features show linkage to the G8 probe. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):776–779. doi: 10.1126/science.2992086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg Y. P., McMurray C. T., Zeisler J., Almqvist E., Sillence D., Richards F., Gacy A. M., Buchanan J., Telenius H., Hayden M. R. Increased instability of intermediate alleles in families with sporadic Huntington disease compared to similar sized intermediate alleles in the general population. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Oct;4(10):1911–1918. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.10.1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedreen J. C., Folstein S. E. Early loss of neostriatal striosome neurons in Huntington's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995 Jan;54(1):105–120. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199501000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Okamoto T., Taniwaki M., Aizawa M., Inoue M., Katayama S., Kawakami H., Nakamura S., Nishimura M., Akiguchi I. CAG expansions in a novel gene for Machado-Joseph disease at chromosome 14q32.1. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):221–228. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer B., Almqvist E., Theilmann J., Spence N., Telenius H., Goldberg Y. P., Hayden M. R. Sex-dependent mechanisms for expansions and contractions of the CAG repeat on affected Huntington disease chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):343–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer B., Goldberg P., Andrew S. E., Theilmann J., Telenius H., Zeisler J., Squitieri F., Lin B., Bassett A., Almqvist E. A worldwide study of the Huntington's disease mutation. The sensitivity and specificity of measuring CAG repeats. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 19;330(20):1401–1406. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405193302001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Cuppens H., Dierick H., Van Zandt K., Dom R., Fryns J. P., Evers-Kiebooms G., Decruyenaere M., Demyttenaere K., Marynen P. Limited expansion of the (CAG)n repeat of the Huntington gene: a premutation (?). Eur J Hum Genet. 1994;2(1):44–50. doi: 10.1159/000472340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. H., McInnis M. G., Margolis R. L., Antonarakis S. E., Ross C. A. Novel triplet repeat containing genes in human brain: cloning, expression, and length polymorphisms. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):572–579. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan F., Janas J., Popovich B. W. A novel CAG repeat configuration in the SCA1 gene: implications for the molecular diagnostics of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2411–2413. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riess O., Noerremoelle A., Soerensen S. A., Epplen J. T. Improved PCR conditions for the stretch of (CAG)n repeats causing Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):637–637. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A. When more is less: pathogenesis of glutamine repeat neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron. 1995 Sep;15(3):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Amos W., Leggo J., Goodburn S., Ramesar R. S., Old J., Bontrop R., McMahon R., Barton D. E., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Mutational bias provides a model for the evolution of Huntington's disease and predicts a general increase in disease prevalence. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):525–530. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Barton D. E., Davison B. C., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Analysis of the huntingtin gene reveals a trinucleotide-length polymorphism in the region of the gene that contains two CCG-rich stretches and a correlation between decreased age of onset of Huntington's disease and CAG repeat number. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1713–1715. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Leggo J., Goodburn S., Crow T. J., Lofthouse R., DeLisi L. E., Barton D. E., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Study of the Huntington's disease (HD) gene CAG repeats in schizophrenic patients shows overlap of the normal and HD affected ranges but absence of correlation with schizophrenia. J Med Genet. 1994 Sep;31(9):690–693. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.9.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., MacMillan J. C., Cheadle J. P., Fenton I., Lazarou L. P., Davies P., MacDonald M. E., Gusella J. F., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J. Relationship between trinucleotide repeat expansion and phenotypic variation in Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):393–397. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonsattel J. P., Myers R. H., Stevens T. J., Ferrante R. J., Bird E. D., Richardson E. P., Jr Neuropathological classification of Huntington's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985 Nov;44(6):559–577. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198511000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. P., Barron L. H., Brock D. J. A new polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the trinucleotide repeat that is unstable and expanded on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Mol Cell Probes. 1993 Jun;7(3):235–239. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1993.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]