Full text
PDF
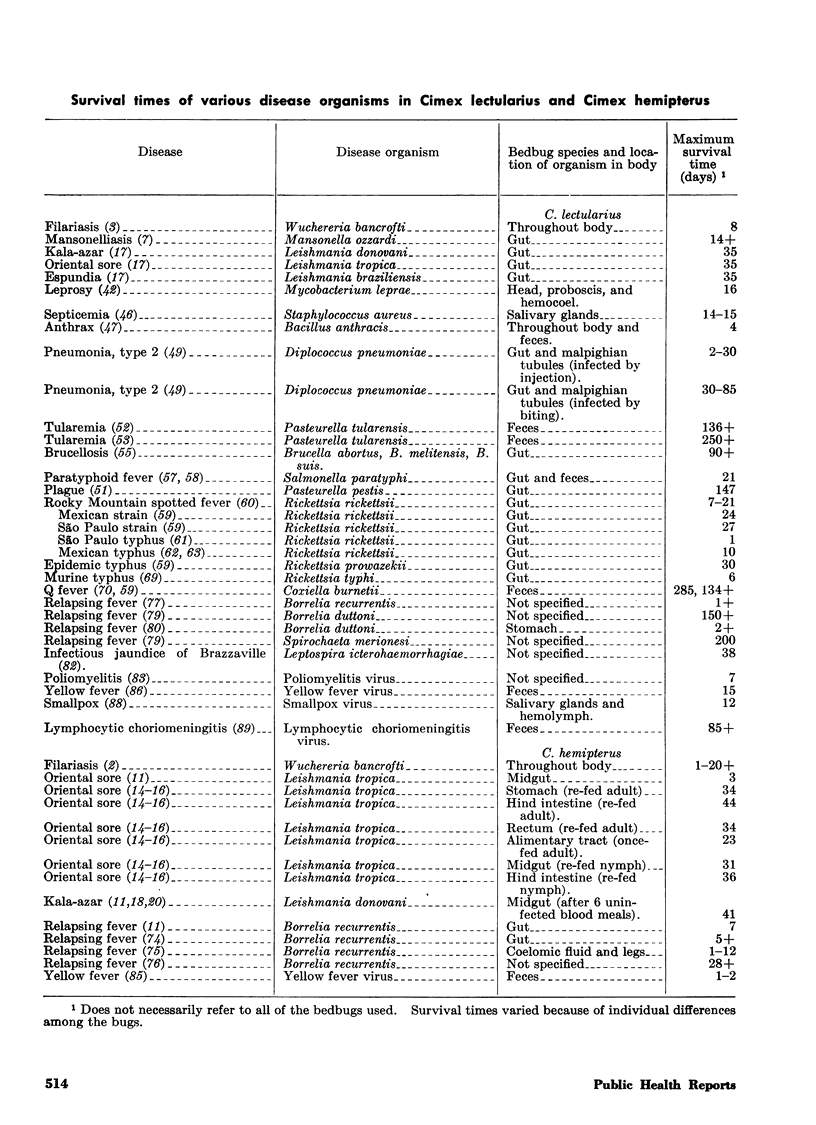










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- VENKATACHALAM P. S., BELAVADY B. Loss of haemoglobin iron due to excessive biting by bed bugs. A possible aetiological factor in the iron deficiency anaemia of infants and children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1962 May;56:218–221. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(62)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEYER F. Künstliche Ubertragung von Rickettsia rickettsi (Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever) auf Insekten, insbesondere auf Kleiderläuse. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1952 Sep;135(3-4):280–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHARTON R. H., OMAR A. H. Failure of Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi to develop in the tropical bedbug Cimex hemipterus. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1962 Jun;56:188–190. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1962.11686106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


