Abstract
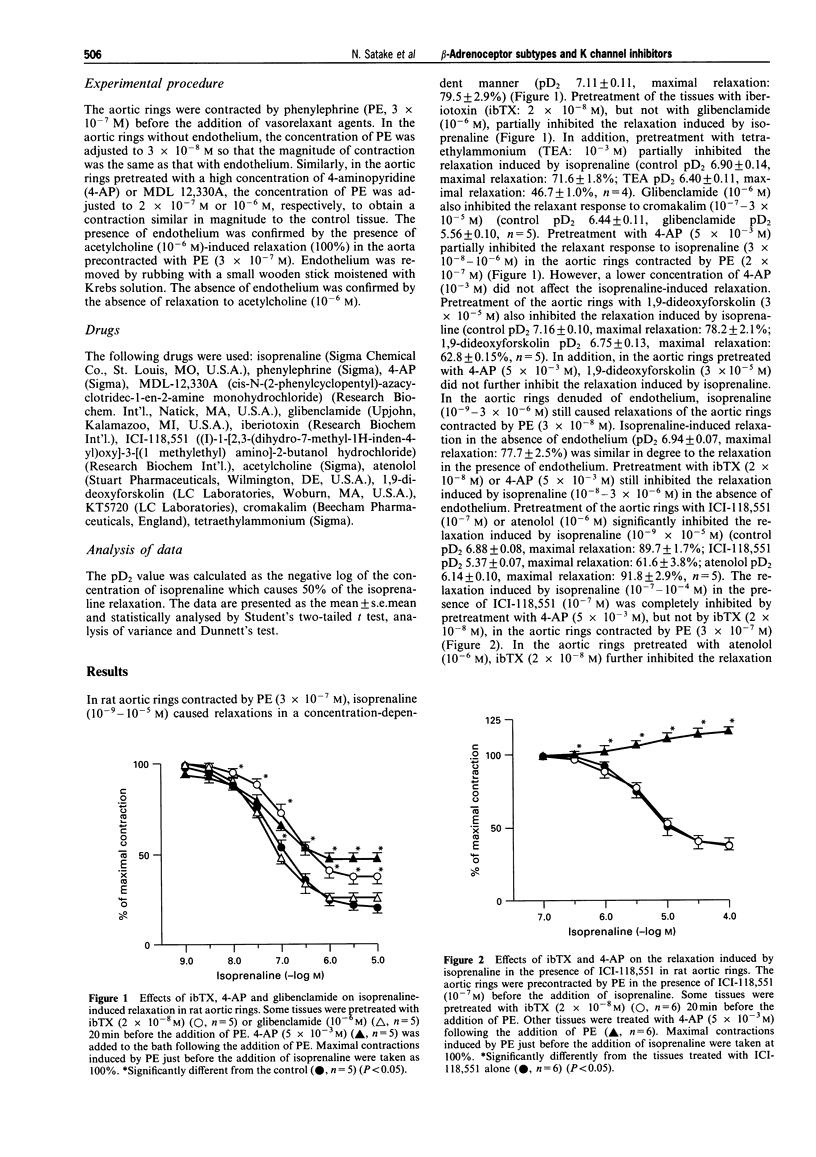
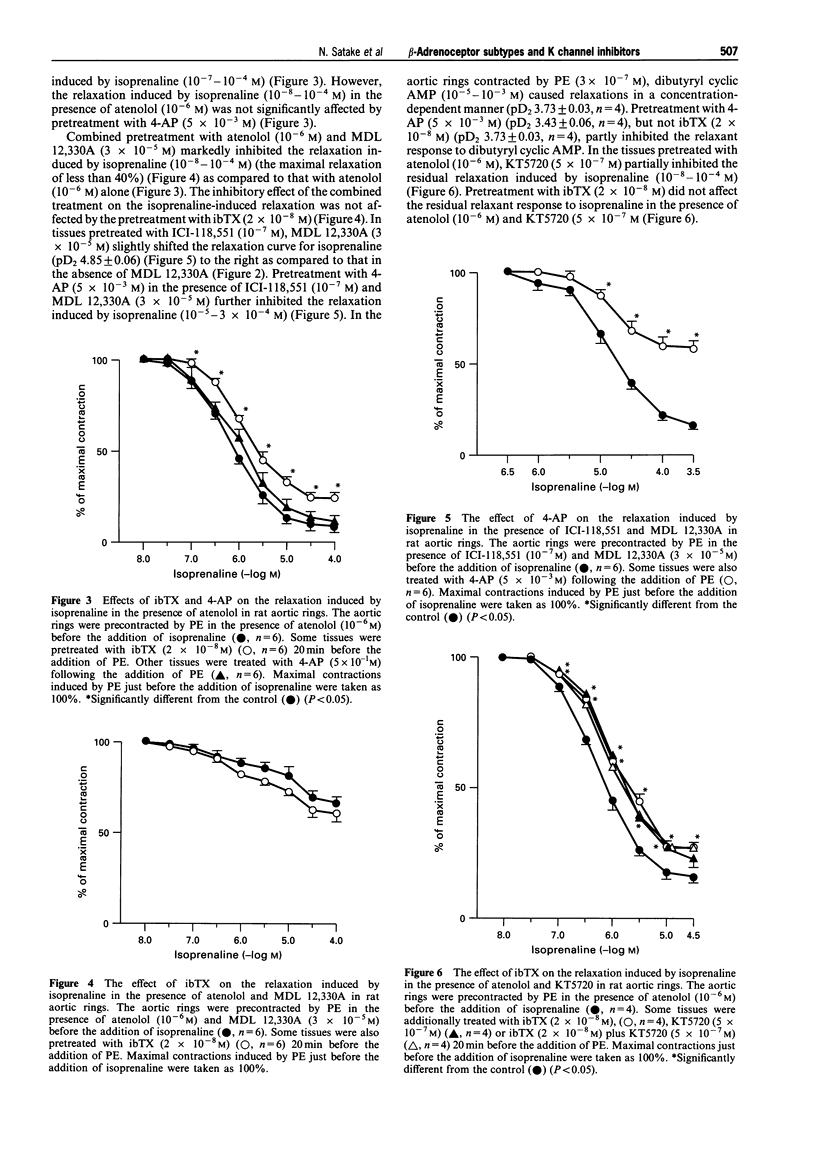
1. In rat aortic rings contracted by phenylephrine, the relaxation induced by isoprenaline was partly inhibited by iberiotoxin, (ibTX), tetraethylammonium, 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and 1,9-dideoxyforskolin, but not by glibenclamide. 2. In the presence of 4-AP, 1,9-dideoxyforskolin failed to inhibit further the relaxant response to isoprenaline. Cromakalim-induced relaxation was inhibited by glibenclamide. 3. In the absence of endothelium, ibTX and 4-AP still inhibited the relaxant response to isoprenaline. 4. The inhibitory effect of ibTX on the relaxant response to isoprenaline was eliminated by pretreatment with ICI-118,551, a beta 2-adrenoceptor antagonist, but not by atenolol, a beta 1-adrenoceptor antagonist. 5. The inhibitory effect of 4-AP on the relaxation induced by isoprenaline was abolished by atenolol, but not by ICI-118,551. 6. The inhibitory effect of ibTX on the isoprenaline-induced relaxation in the presence of atenolol was completely abolished by MDL 12,330A, an adenylate cyclase inhibitor. Further, the inhibitory effect of 4-AP on the isoprenaline-induced relaxation in the presence of ICI-118,551 was markedly reduced by MDL 12,330A. 7. The relaxation induced by dibutyryl cyclic AMP was partly inhibited by 4-AP but not by ibTX. However, in the presence of KT5720, an inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, ibTX failed to inhibit further the relaxation induced by isoprenaline. 8. These results suggest that, in rat aortic rings, KCa channels are involved in the relaxation induced by isoprenaline. In addition, KCa channels are mainly activated by beta 2-adrenoceptors through cyclic AMP-dependent pathways. Further, the inhibition of isoprenaline-relaxation by 4-AP may be related to the activation of beta 1-adrenoceptors and cyclic AMP formation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. Two components of potassium current activated by depolarization of single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:293–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilski A. J., Halliday S. E., Fitzgerald J. D., Wale J. L. The pharmacology of a beta 2-selective adrenoceptor antagonist (ICI 118,551). J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 May-Jun;5(3):430–437. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198305000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet P., Rusch N. J., Harder D. R. Characterization of an outward K+ current in freshly dispersed cerebral arterial muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Apr;418(3):292–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00370529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. P., Tomasic M., Kotlikoff M. I. Delayed rectifier potassium channels in canine and porcine airway smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:329–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl A., Kenyon J. L., Uemura D., Fusetani N., Sanders K. M. Regulation of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels by protein kinase A and phosphatase inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C387–C392. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S. Beta1 and beta2 receptor mechanisms in rat jugular veins: differences between norepinephrine and isoproterenol-induced relaxation. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):1997–2006. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. The pharmacology of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:597–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvez A., Gimenez-Gallego G., Reuben J. P., Roy-Contancin L., Feigenbaum P., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification and characterization of a unique, potent, peptidyl probe for the high conductance calcium-activated potassium channel from venom of the scorpion Buthus tamulus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11083–11090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelband C. H., Hume J. R. Ionic currents in single smooth muscle cells of the canine renal artery. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):745–758. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicelli J. F., Boissier J. R., Dumas Y., Advenier C. Effets comparés de quelques inhibiteurs beta-adrénergiques sur la résistance pulmonaire chez le Cobaye. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1973;167(2):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J., Poston L. Beta-adrenoceptor agonist mediated relaxation of rat isolated resistance arteries: a role for the endothelium and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):631–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12853.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. W., Marshall I. Novel signal transduction pathway mediating endothelium-dependent beta-adrenoceptor vasorelaxation in rat thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):684–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. S., Brunton L. L. Functional compartments in cyclic nucleotide action. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu T., Kume H., Kotlikoff M. I., Takagi K. Role of calcium-activated potassium channels in the relaxation of tracheal smooth muscles by forskolin. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994 May;21(5):367–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1994.tb02529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré E., Lazdunski M. Hormone-regulated K+ channels in follicle-enclosed oocytes are activated by vasorelaxing K+ channel openers and blocked by antidiabetic sulfonylureas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5438–5442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré E., Lazdunski M. Single-channel properties and regulation of pinacidil/glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in follicular cells from Xenopus oocyte. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jul;424(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00374601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Garber S. S., Aldrich R. W. Effect of forskolin on voltage-gated K+ channels is independent of adenylate cyclase activation. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.2454506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt N. H., Evans T. RMI 12330A, an inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and adenylate cyclase in kidney preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Pre- and post-junctional actions of procaterol, a beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulant, on dog tracheal tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Charette L., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J. Selective inhibition of relaxation of guinea-pig trachea by charybdotoxin, a potent Ca(++)-activated K+ channel inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):697–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Miyata N., Kasuya Y. Involvement of endothelial cells in relaxation and contraction responses of the aorta to isoproterenol in naive and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Su C. Role of endothelium in dilator responses of spontaneously hypertensive rat arteries. Hypertension. 1983 Nov-Dec;5(6):881–886. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.6.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume H., Graziano M. P., Kotlikoff M. I. Stimulatory and inhibitory regulation of calcium-activated potassium channels by guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11051–11055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume H., Hall I. P., Washabau R. J., Takagi K., Kotlikoff M. I. Beta-adrenergic agonists regulate KCa channels in airway smooth muscle by cAMP-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):371–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI116969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume H., Takai A., Tokuno H., Tomita T. Regulation of Ca2+-dependent K+-channel activity in tracheal myocytes by phosphorylation. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):152–154. doi: 10.1038/341152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippe C., Ardizzone C. Actions of vasopressin and isoprenaline on the ionic transport across the isolated frog skin in the presence and the absence of adenyl cyclase inhibitors MDL12330A and SQ22536. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1991;99(1-2):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(91)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B. Classification and quantitation of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 May 15;29(10):1317–1323. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Yacoub M. H., Barnes P. J. Role of potassium channels in bronchodilator responses in human airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):132–136. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Rees D. D., Schulz R., Palmer R. M. Development and mechanism of a specific supersensitivity to nitrovasodilators after inhibition of vascular nitric oxide synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2166–2170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. A., Berry J. L., Cook S. J., Foster R. W., Green K. A., Small R. C. Guinea-pig isolated trachealis: the effects of charybdotoxin on mechanical activity, membrane potential changes and the activity of plasmalemmal K(+)-channels. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1814–1818. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima M., Vanhoutte P. M. Isoproterenol causes hyperpolarization through opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle of the canine saphenous vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Huang Y., Brayden J. E., Hescheler J., Standen N. B. Arterial dilations in response to calcitonin gene-related peptide involve activation of K+ channels. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):770–773. doi: 10.1038/344770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptor-mediated responses in preparations of pulmonary artery and aorta from young and aged rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):733–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Features of 4-aminopyridine sensitive outward current observed in single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit pulmonary artery. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):561–568. doi: 10.1007/BF00584654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfründer D., Kreye V. A. Tedisamil inhibits the delayed rectifier K+ current in single smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1992 May;421(1):22–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00374728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. In vitro and in vivo comparison of two K+ channel openers, diazoxide and cromakalim, and their inhibition by glibenclamide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U. Do the K+ channel openers relax smooth muscle by opening K+ channels? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Sep;14(9):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle J. M., Bonev A. D., Brayden J. E., Nelson M. T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide activated ATP-sensitive K+ currents in rabbit arterial smooth muscle via protein kinase A. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):9–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. The calcium messenger system (1). N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 24;314(17):1094–1101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604243141707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. E., Nelson M. T. Aminopyridine inhibition and voltage dependence of K+ currents in smooth muscle cells from cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol. 1994 Dec;267(6 Pt 1):C1589–C1597. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.6.C1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Charlton M. P. Presynaptic calcium signals and transmitter release are modulated by calcium-activated potassium channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Jan;12(1):297–305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-01-00297.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-removal decreases relaxations of canine coronary arteries caused by beta-adrenergic agonists and adenosine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):139–144. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Akaike N., Kanaide H., Nakamura M. Cyclic AMP modulates Ca-activated K channel in cultured smooth muscle cells of rat aortas. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H754–H759. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Akaike N., Tomoike H., Kanaide H., Nakamura M. Ca-activated K channel in cultured smooth muscle cells of rat aortic media. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):H410–H418. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.3.H410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker R. L., Worrell R. T. Ca2(+)-sensitive K+ channel in aortic smooth muscle of rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Mar;196(3):325–332. doi: 10.3181/00379727-196-43196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton D., Miura M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Calcium-activated potassium channels mediate prejunctional inhibition of peripheral sensory nerves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1325–1329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokudome T., Taira N. Characterization of beta-adrenoceptors in the dog saphenous vein. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;31(5):731–736. doi: 10.1254/jjp.31.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Wang W., Giebisch G., Welling P. A. ATP is a coupling modulator of parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity in the renal proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6418–6422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk K. A., Matsuda J. J., Shibata E. F. A voltage-dependent potassium current in rabbit coronary artery smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:751–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Schwab A., Giebisch G. Regulation of small-conductance K+ channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):F494–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.3.F494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., White S., Geibel J., Giebisch G. A potassium channel in the apical membrane of rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F244–F253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Oda M., Ikemoto Y. Kinetics of the Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel in rat hippocampal neurons. Jpn J Physiol. 1991;41(2):297–315. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.41.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


