Abstract
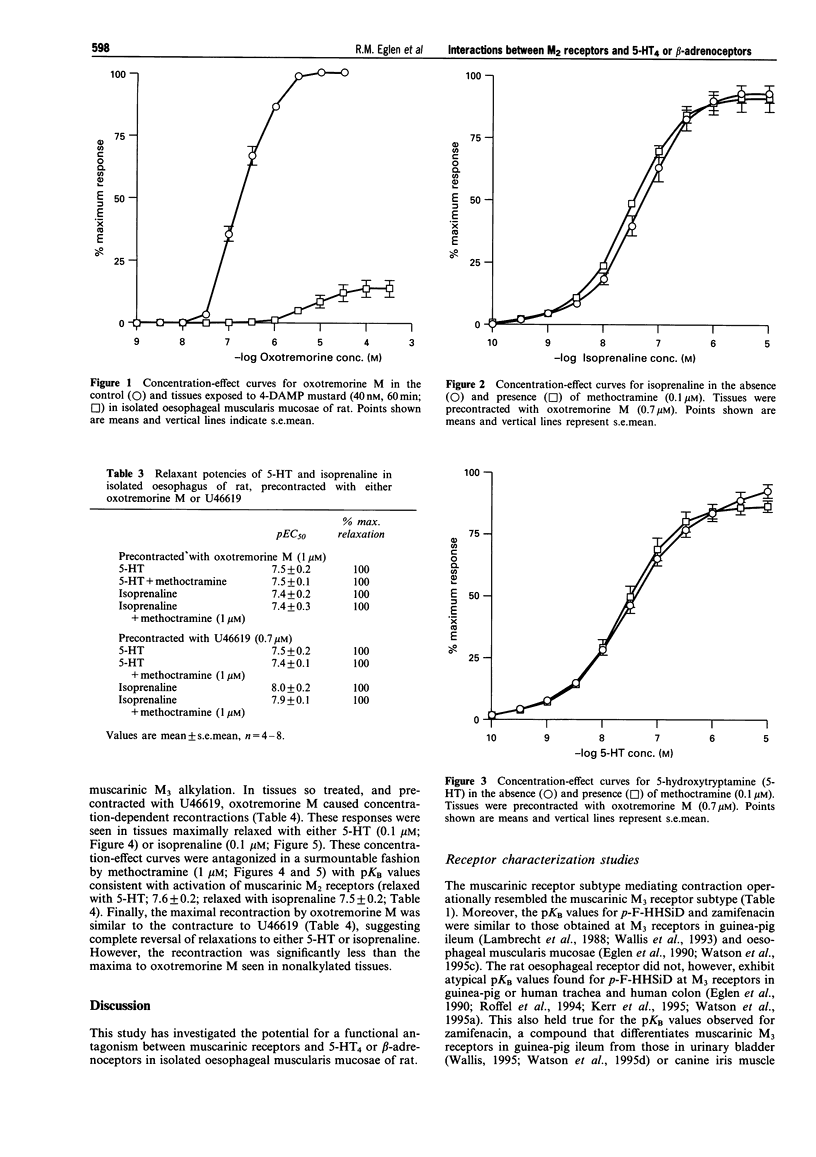
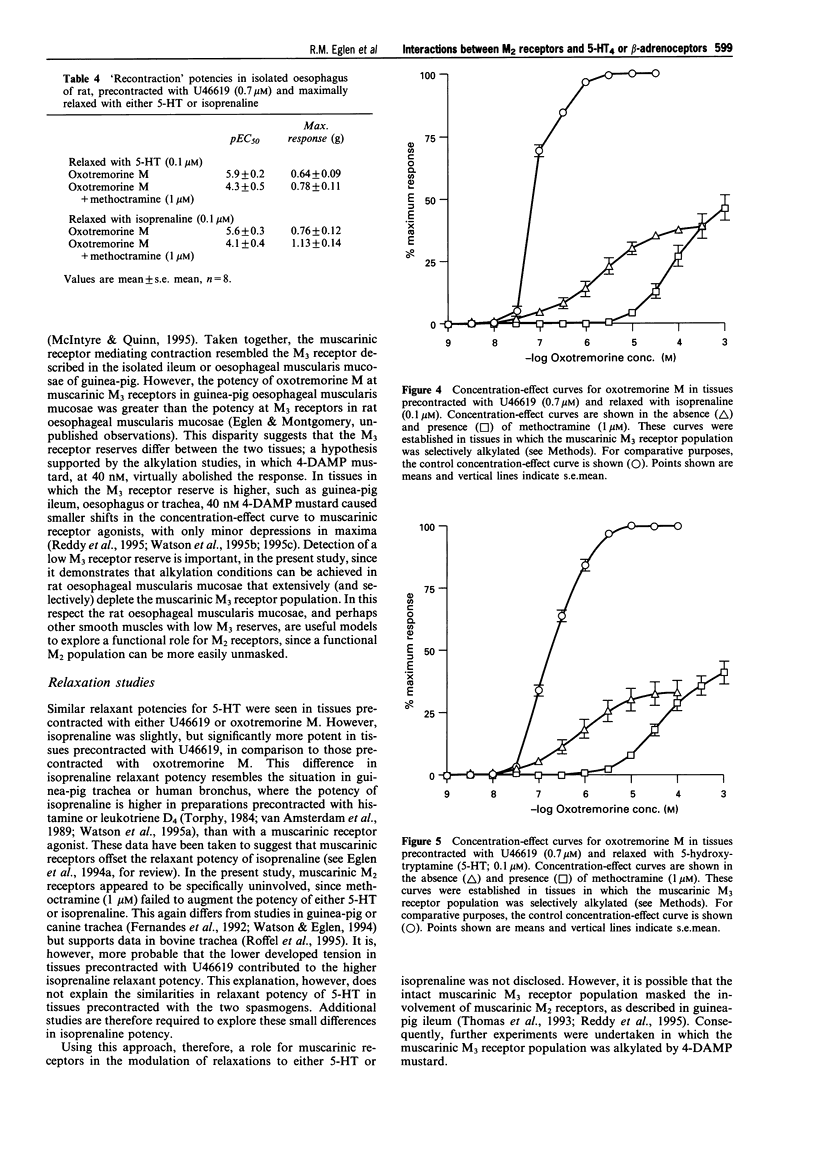
1. Relaxations of isolated oesophageal muscularis mucosae of rat are mediated by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), acting at 5-HT4 receptors, and isoprenaline, principally acting via beta 3-adrenoceptors. The aim of this study was to investigate the hypothesis that muscarinic M2 receptors, also present in this tissue, functionally oppose 5-HT and beta-adrenoceptor-relaxant effects in this preparation. 2. Contractions of rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae were induced, in a concentration-dependent manner, by the muscarinic receptor agonist, oxotremorine M (pEC50 = 6.7 +/- 0.1). The contractile responses to oxotremorine M were surmountably antagonized by the following compounds, (pKB values in parentheses): atropine (9.1 +/- 0.2), 4-DAMP (4-diphenylacetoxy-N-methyl piperidine methiodide, 8.7 +/- 0.1), p-F-HHSiD (para-fluoro-hexa-hydro-siladifenidol, 7.5 +/- 0.1), zamifenacin (8.6 +/- 0.3), himbacine (7.2 +/- 0.2), pirenzepine (6.8 +/- 0.3) and methoctramine (6.2 +/- 0.2). These data are consistent with a role for muscarinic M3 receptors mediating contractions to oxotremorine M. The contractile response was associated with a low receptor reserve, since the responses were shifted to the right and virtually abolished by the alkylating agent, 4-DAMP mustard (4-diphenylacetoxy-N-(2-chloroethyl) piperidine, 40 nM; 60 min equilibration). 3. In tissues precontracted with U46619 (0.7 microM; approx. EC90), isoprenaline (pEC50 = 8.0 +/- 0.1) and 5-HT (pEC50 = 7.5 +/- 0.2) induced concentration-dependent relaxations. The isoprenaline potency was slightly, but significantly, different in tissues precontracted with oxotremorine M (isoprenaline, pEC50 = 7.4 +/- 0.2). In contrast, the potency of 5-HT (pEC50 = 7.5 +/- 0.2), in tissues that were precontracted with 1 microM (EC90) oxotremorine M, was identical. When these experiments were repeated in the presence of the muscarinic M2 receptor antagonist, methoctramine (1 microM), there was no effect on the relaxant potencies to either 5-HT or isoprenaline. Collectively, these data suggest that muscarinic M2 receptors do not, under these conditions, modulate relaxant potencies to either 5-HT or isoprenaline. 4. In a second protocol, tissues were pre-contracted with U46619 (0.7 microM) and relaxed with either 5-HT (0.1 microM) or isoprenaline (0.1 microM). In these tissues (in which the muscarinic M3 receptor population was extensively depleted by alkylation), oxotremorine M caused concentration-dependent re-contractions (i.e. reversal of relaxations). In tissues relaxed with 5-HT, the potency of oxtremorine M was 5.9 +/- 0.2, while in tissues relaxed with isoprenaline, the potency (pEC50) = 5.6 +/- 0.3. These re-contractions were antagonized, in a surmountable fashion, by methoctramine (1 microM; pKB = 7.6 +/- 0.1). Similar observations were seen when relaxations were induced by isoprenaline (1 microM; pKB = 7.5 +/- 0.2). Under these conditions, therefore, the pKB values are consistent with activation of muscarinic M2 receptors, and inconsistent with activation of M3 receptors. 5. It is concluded that in isolated oesophageal muscularis mucosae of rat, muscarinic M3 receptors mediate direct contractions and are associated with a low receptor reserve. When this population is depleted, and the tissues relaxed via activation of receptors that augment adenylyl cyclase activity, a functional role for muscarinic M2 receptors is revealed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow R. B., Shepherd M. K., Veale M. A. Some differential effects of 4-diphenylacetoxy-N-(2-chloroethyl)-piperidine hydrochloride on guinea-pig atria and ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;42(6):412–418. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb06581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G. S., Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00169544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. The interaction of cyclic nucleotides and calcium in the control of cellular activity. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:1–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieger D., Triggle C. Pharmacological properties of mechanical responses of the rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae to vagal and field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):93–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Cornett C. M., Whiting R. L. Interaction of p-F-HHSiD (p-Fluoro-hexahydrosila-difenidol) at muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig trachea. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;342(4):394–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00169455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Reddy H., Watson N., Challiss R. A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in smooth muscle. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Apr;15(4):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Reddy H., Watson N. Selective inactivation of muscarinic receptor subtypes. Int J Biochem. 1994 Dec;26(12):1357–1368. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(94)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Thomas E. A. Functional role of M2 muscarinic receptors in the guinea pig ileum. Life Sci. 1995;56(11-12):965–971. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00035-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes L. B., Fryer A. D., Hirshman C. A. M2 muscarinic receptors inhibit isoproterenol-induced relaxation of canine airway smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Baxter G. S., Eglen R. M., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates cyclic AMP formation in the tunica muscularis mucosae of the rat oesophagus via 5-HT4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 28;211(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikawa Y., Shimo Y. Cholinergic and adrenergic innervations of the muscularis mucosae in guinea-pig esophagus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Apr;238(2):220–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr P. M., Hillier K., Wallis R. M., Garland C. J. Characterization of muscarinic receptors mediating contractions of circular and longitudinal muscle of human isolated colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;115(8):1518–1524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht G., Feifel R., Forth B., Strohmann C., Tacke R., Mutschler E. p-fluoro-hexahydro-sila-difenidol: the first M2 beta-selective muscarinic antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 26;152(1-2):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90856-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Michelson S., Villarubia C., Perkins L. A., Eglen R. M. Analysis of concentration-response relationships by seemingly unrelated nonlinear regression (SUNR) technique. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1992 Dec;28(4):209–216. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(92)90006-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy H., Watson N., Ford A. P., Eglen R. M. Characterization of the interaction between muscarinic M2 receptors and beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roffel A. F., Hamstra J. J., Elzinga C. R., Zaagsma J. Selectivity profile of some recent muscarinic antagonists in bovine and guinea-pig trachea and heart. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1994 Jul-Aug;328(1):82–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roffel A. F., Meurs H., Elzinga C. R., Zaagsma J. No evidence for a role of muscarinic M2 receptors in functional antagonism in bovine trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;115(4):665–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Baker S. A., Ehlert F. J. Functional role for the M2 muscarinic receptor in smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Ehlert F. J. Involvement of the M2 muscarinic receptor in contractions of the guinea pig trachea, guinea pig esophagus, and rat fundus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1996 Mar 22;51(6):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)02396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Ehlert F. J. Pertussis toxin blocks M2 muscarinic receptor-mediated effects on contraction and cyclic AMP in the guinea pig ileum, but not M3-mediated contractions and phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Nov;271(2):1042–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Hsu H. H., Griffin M. T., Hunter A. L., Luong T., Ehlert F. J. Conversion of N-(2-chloroethyl)-4-piperidinyl diphenylacetate (4-DAMP mustard) to an aziridinium ion and its interaction with muscarinic receptors in various tissues. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):718–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J. Differential relaxant effects of isoproterenol on methacholine- versus leukotriene D4-induced contraction in the guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 20;102(3-4):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Amsterdam R. G., Meurs H., Brouwer F., Postema J. B., Timmermans A., Zaagsma J. Role of phosphoinositide metabolism in functional antagonism of airway smooth muscle contraction by beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. M. Pre-clinical and clinical pharmacology of selective muscarinic M3 receptor antagonists. Life Sci. 1995;56(11-12):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00021-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Eglen R. M. Effects of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptor stimulation and antagonism on responses to isoprenaline of guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):179–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Magnussen H., Rabe K. F. Antagonism of beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxations of human bronchial smooth muscle by carbachol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar 14;275(3):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00048-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Reddy H., Eglen R. M. Characterization of muscarinic receptor and beta-adrenoceptor interactions in guinea-pig oesophageal muscularis mucosae. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Dec 29;294(2-3):779–785. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00656-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Reddy H., Eglen R. M. Role of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptors in guinea-pig trachea: effects of receptor alkylation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 May 24;278(3):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00121-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Reddy H., Stefanich E., Eglen R. M. Characterization of the interaction of zamifenacin at muscarinic receptors in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Oct 16;285(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00394-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer R. E., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. Noradrenaline-induced relaxation of rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae: mediation solely by innervated beta 3-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;116(3):1945–1947. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


