Abstract
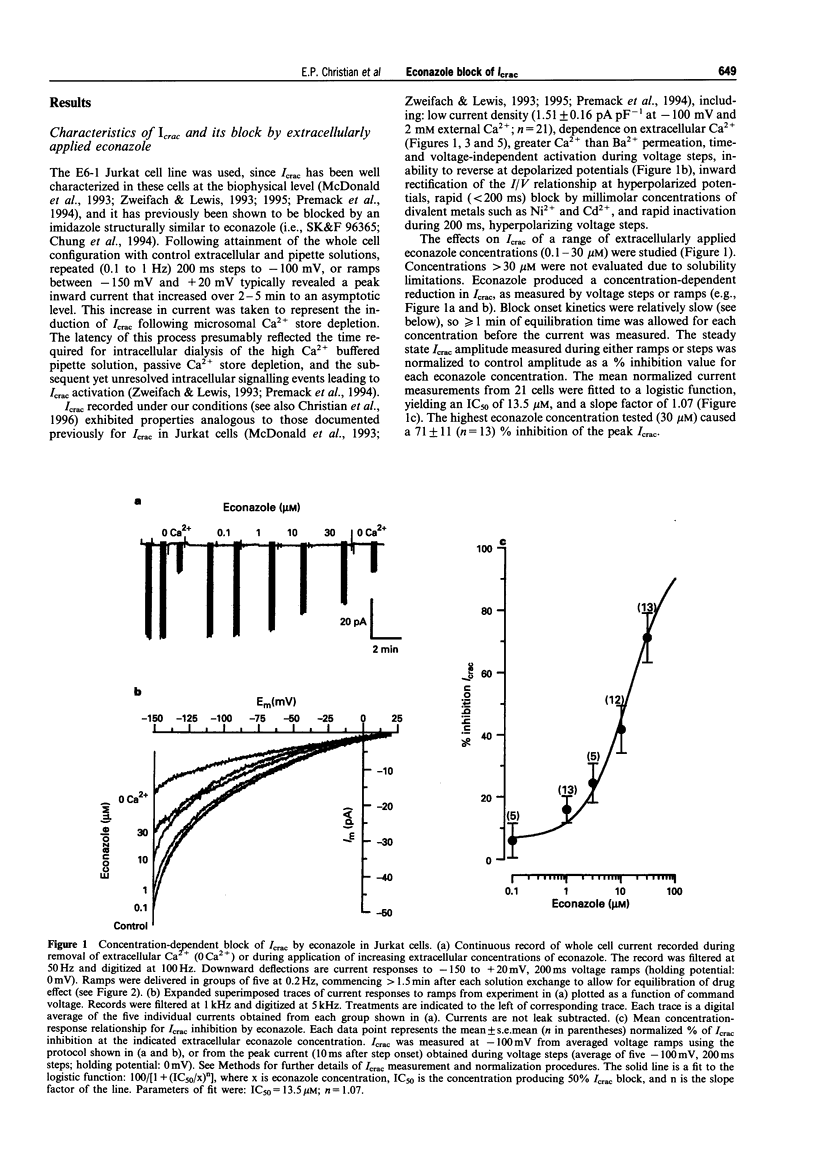
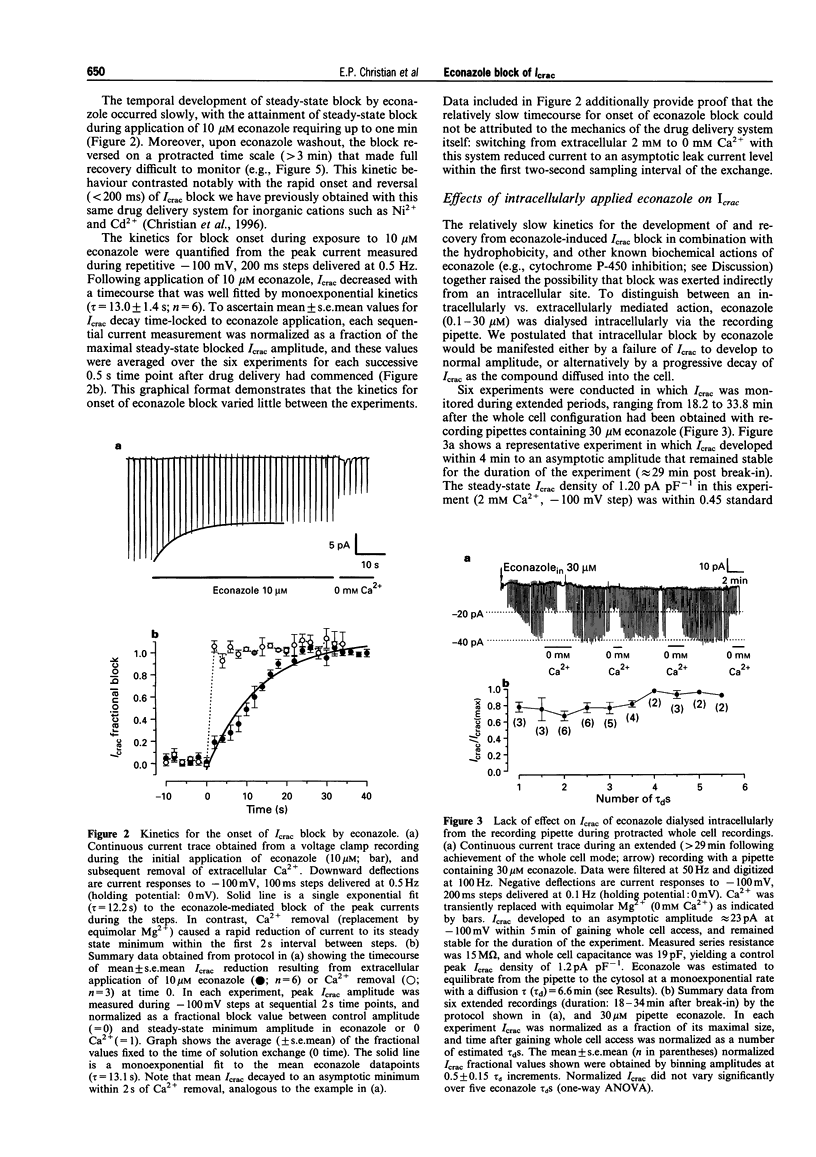
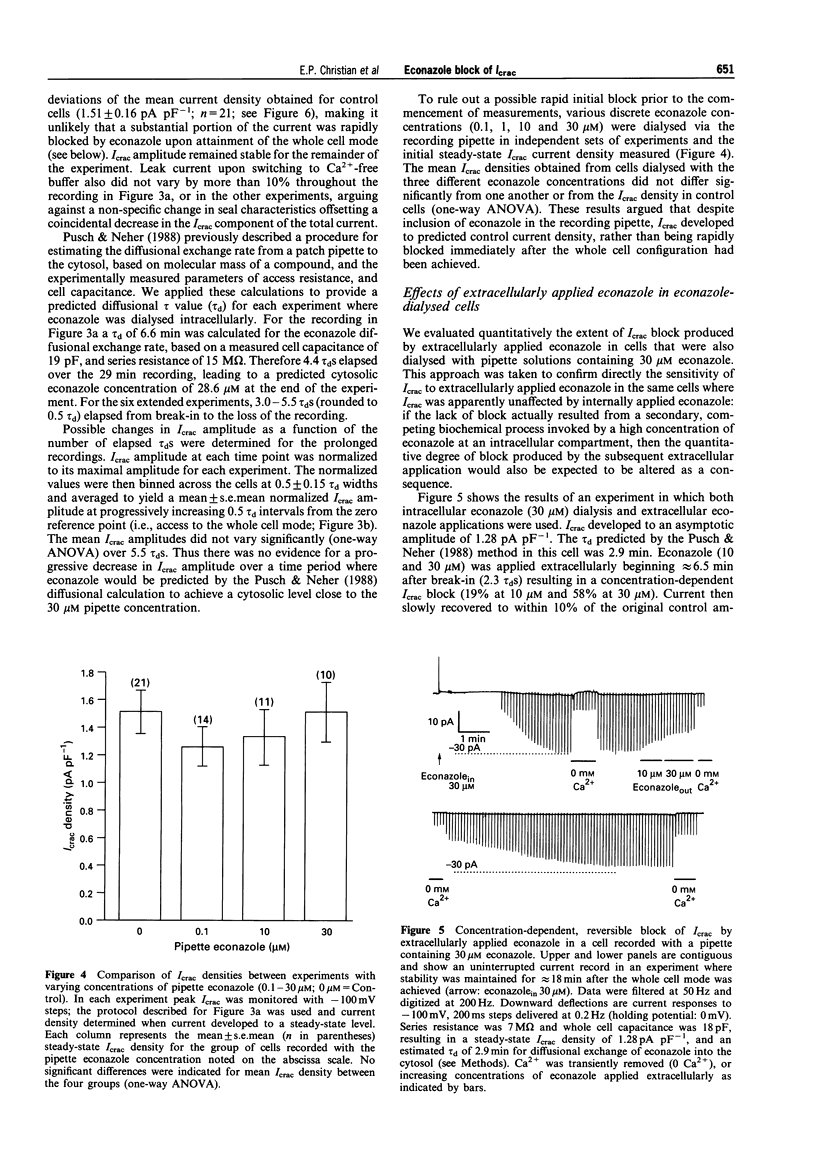
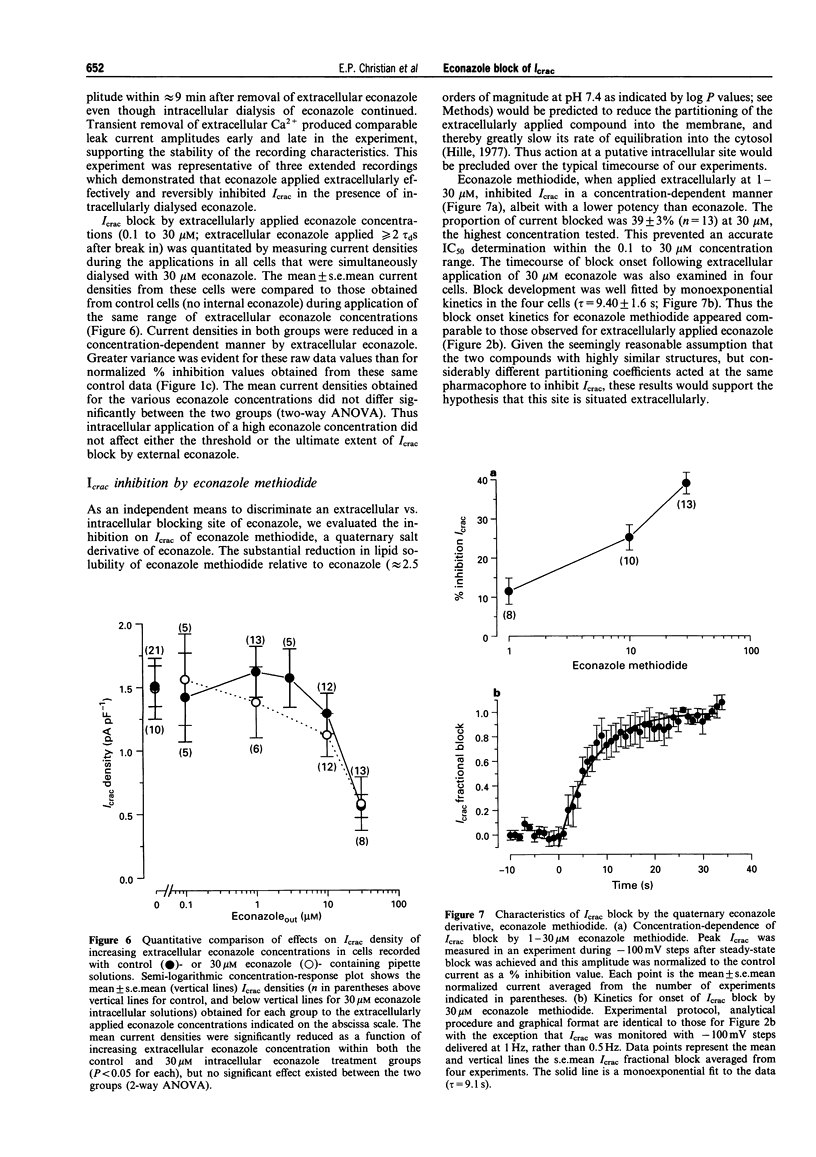
1. Standard whole cell patch clamp recording techniques were used to study the pharmacological characteristics and site of econazole-mediated inhibition of calcium release-activated calcium current (Icrac) in the human leukaemic T cell line, Jurkat. 2. Extracellularly applied econazole blocked Icrac in a concentration-dependent manner (IC50 approximately 14 microM). Block developed over a relatively slow timecourse of 30-60 s (10 microM), and only partially reversed over minutes. 3. Econazole dialysed from the pipette into the cytosol at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 30 microM did not reduce Icrac, or quantitatively affect Icrac block by extracellularly applied econazole. 4. A less lipophilic quaternary iodide derivative of econazole was synthesized to retard absorption through the cell membrane. When applied extracellularly, this compound blocked Icrac in a concentration-dependent manner with onset kinetics comparable to econazole. 5. Results with intracellularly dialysed econazole and the quaternary econazole derivative provide convergent evidence that econazole blocks Icrac via an extracellular interaction. 6. The inability of intracellularly applied econazole to inhibit Icrac argues against the notion that econazole inhibits capacitative Ca2+ entry pathways secondary to its known inhibitory effects on cytochrome P-450.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. T., Alvarez J., Montero M., Sanchez A., García-Sancho J. Agonist-induced Ca2+ influx into human platelets is secondary to the emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):783–789. doi: 10.1042/bj2800783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J., Montero M., Garcia-Sancho J. Cytochrome P450 may regulate plasma membrane Ca2+ permeability according to the filling state of the intracellular Ca2+ stores. FASEB J. 1992 Jan 6;6(2):786–792. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.2.1537469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J., Montero M., García-Sancho J. Cytochrome P-450 may link intracellular Ca2+ stores with plasma membrane Ca2+ influx. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):193–197. doi: 10.1042/bj2740193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard S. A., Lodola A., Tarbit M. H. A comparative study of 1-substituted imidazole and 1,2,4-triazole antifungal compounds as inhibitors of testosterone hydroxylations catalysed by mouse hepatic microsomal cytochromes P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 15;37(24):4643–4651. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. H., Lynch J. W. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch-clamp analysis. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(2):101–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01870526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Striessnig J. Receptor sites for Ca2+ channel antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90079-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian E. P., Spence K. T., Togo J. A., Dargis P. G., Patel J. Calcium-dependent enhancement of depletion-activated calcium current in Jurkat T lymphocytes. J Membr Biol. 1996 Mar;150(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/s002329900030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. C., McDonald T. V., Gardner P. Inhibition by SK&F 96365 of Ca2+ current, IL-2 production and activation in T lymphocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):861–868. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzius D., Hoth M., Penner R. Non-specific effects of calcium entry antagonists in mast cells. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(5-6):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00374562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The pH-dependent rate of action of local anesthetics on the node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):475–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Calcium release-activated calcium current in rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:359–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Faurot G. F., Kopanitsa M. V., Swinney D. C. Pharmacology of a Ca(2+)-influx pathway activated by emptying the intracellular Ca2+ stores in HL-60 cells: evidence that a cytochrome P-450 is not involved. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 15;302(Pt 1):187–190. doi: 10.1042/bj3020187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Mitogen-induced oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ and transmembrane Ca2+ current in human leukemic T cells. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):99–112. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Mayer B., Hymel L. J. Inhibition of Ca2+ transport pathways in thymic lymphocytes by econazole, miconazole, and SKF 96365. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C654–C662. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. V., Premack B. A., Gardner P. Flash photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates plasma membrane calcium current in human T cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3889–3896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Armstrong W. P., Benham C. D., Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Jaxa-Chamiec A., Leigh B. K., McCarthy S. A., Moores K. E., Rink T. J. SK&F 96365, a novel inhibitor of receptor-mediated calcium entry. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2710515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montero M., Alvarez J., Garcia-Sancho J. Agonist-induced Ca2+ influx in human neutrophils is secondary to the emptying of intracellular calcium stores. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):73–79. doi: 10.1042/bj2770073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M., Zaluzny L. Comparative effects of antithrombitic and antimycotic N-substituted imidazoles on rat hepatic microsomal steroid and xenobiotic hydroxylases in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 1;37(3):415–420. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premack B. A., McDonald T. V., Gardner P. Activation of Ca2+ current in Jurkat T cells following the depletion of Ca2+ stores by microsomal Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitors. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5226–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Capacitative calcium entry revisited. Cell Calcium. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(10):611–624. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90016-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues A. D., Gibson G. G., Ioannides C., Parke D. V. Interactions of imidazole antifungal agents with purified cytochrome P-450 proteins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;36(24):4277–4281. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant P., Clarkson W. D., Sage S. O., Heemskerk J. W. Calcium influx evoked by Ca2+ store depletion in human platelets is more susceptible to cytochrome P-450 inhibitors than receptor-mediated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1992 Oct;13(9):553–564. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90035-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vostal J. G., Fratantoni J. C. Econazole inhibits thapsigargin-induced platelet calcium influx by mechanisms other than cytochrome P-450 inhibition. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):525–529. doi: 10.1042/bj2950525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweifach A., Lewis R. S. Mitogen-regulated Ca2+ current of T lymphocytes is activated by depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6295–6299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweifach A., Lewis R. S. Rapid inactivation of depletion-activated calcium current (ICRAC) due to local calcium feedback. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Feb;105(2):209–226. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


