Abstract
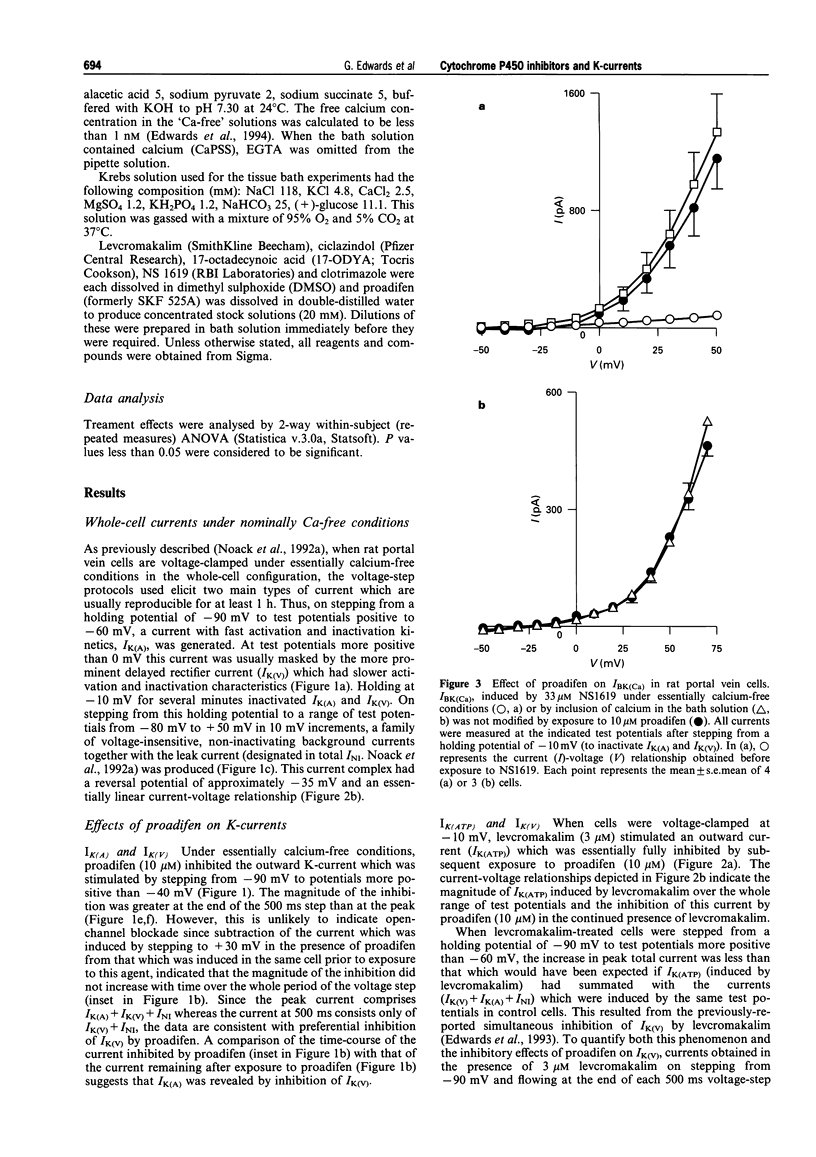
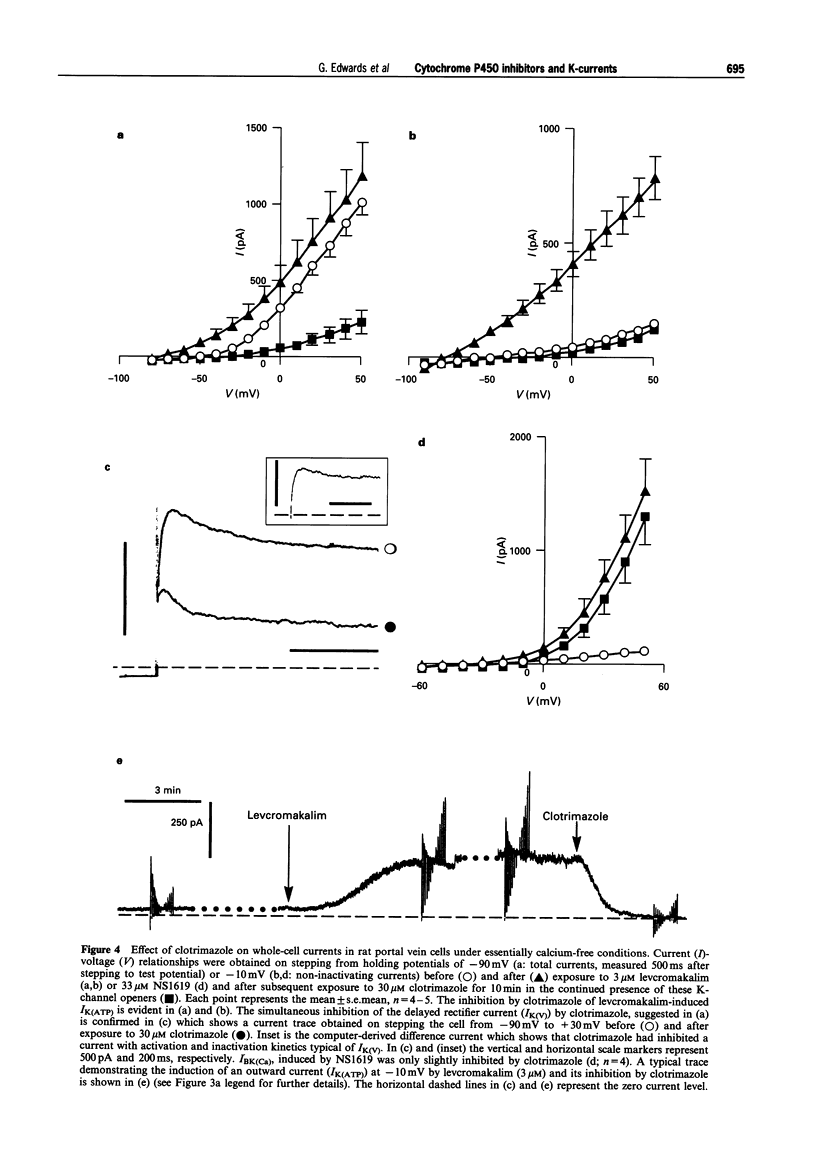
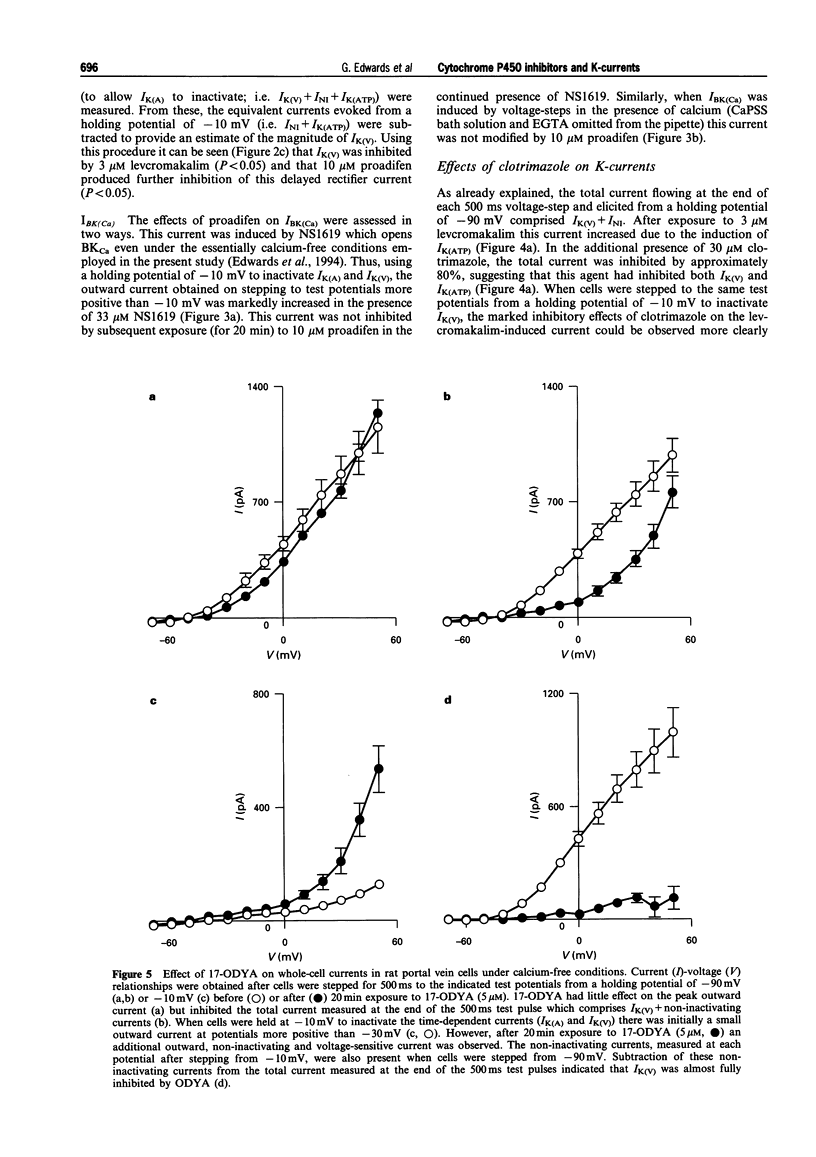
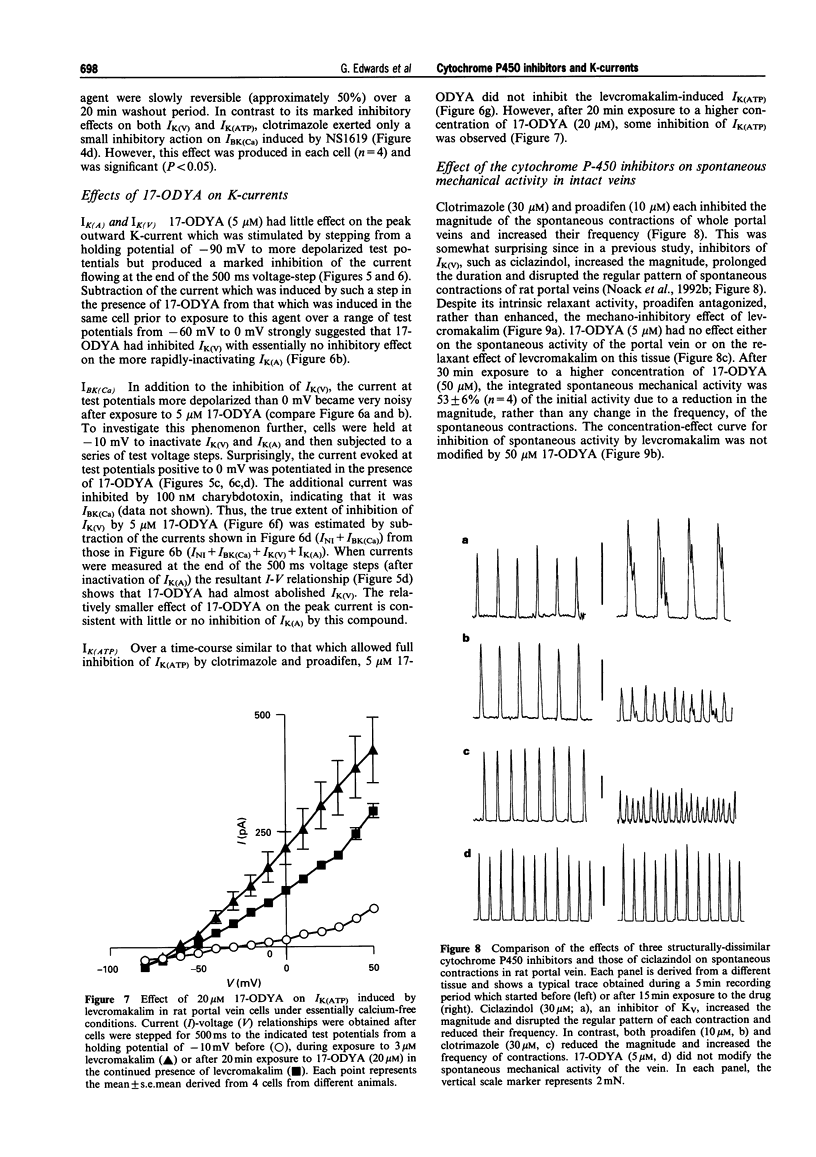
1. The effects of the cytochrome P450 inhibitors, proadifen, clotrimazole and 17-octadecynoic acid (17-ODYA) on K-currents in freshly-isolated single cells derived from rat portal vein and on mechanical activity in whole veins were studied. 2. When cells were stepped from -90 mV to a series of test potentials (from -80 to +50 mV), a delayed rectifier current (IK(V)) and an A-type current (IK(A)) could be identified. Proadifen (10 microM), clotrimazole (30 microM) and 17-ODYA (5 microM) each inhibited IK(V) but had little effect on IK(A). 3. When cells were held at -10 mV to inactivate the time-dependent K-currents, IK(V) and IK(A), levcromakalim (3 microM) induced a time-independent outward K-current (IK(ATP)) which was totally inhibited by clotrimazole (30 microM) and almost fully inhibited by proadifen (10 microM). 17-ODYA (5 microM) had no effect on IK(ATP) and exerted only a minor inhibitory action on this current at 20 microM. 4. 17-ODYA (5 microM) potentiated current flow through the large conductance, Ca-sensitive K-channel (BKCa). In contrast, proadifen (10 microM) had no effect on IBK(Ca) whereas clotrimazole (30 microM) exerted a small but significant inhibitory action. 5. Proadifen (10 microM) and clotrimazole (30 microM) each inhibited the magnitude but increased the frequency of spontaneous contractions in whole portal veins. 17-ODYA (5 microM) had no effect on spontaneous contractions but these were inhibited when the concentration of 17-ODYA was increased to 50 microM. 6. The spasmolytic effect of levcromakalim on spontaneous contractions was antagonized by proadifen (10-30 microM) in a concentration-dependent manner but 17-ODYA (up to 50 microM) was without effect. 7. These results in portal vein show that cytochrome P450 inhibitors exert profound effects on a variety of K-channel subtypes. This suggests that enzymes dependent on this cofactor may be important regulators of K-channel activity in smooth muscle. The relevance of these findings for the identification of the pathway involved in the synthesis of the endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez J., Montero M., Garcia-Sancho J. High affinity inhibition of Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels by cytochrome P-450 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11789–11793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauersachs J., Hecker M., Busse R. Display of the characteristics of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor by a cytochrome P450-derived arachidonic acid metabolite in the coronary microcirculation. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1548–1553. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. Properties of the cromakalim-induced potassium conductance in smooth muscle cells isolated from the rabbit portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):851–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Gebremedhin D., Pratt P. F., Harder D. R. Identification of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 1996 Mar;78(3):415–423. doi: 10.1161/01.res.78.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization. Beyond nitric oxide and cyclic GMP. Circulation. 1995 Dec 1;92(11):3337–3349. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.11.3337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Lueders J., Padgett W. L., Shin Y., Gusovsky F. Maitotoxin-elicited calcium influx in cultured cells. Effect of calcium-channel blockers. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Oct 12;50(8):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Ibbotson T., Weston A. H. Levcromakalim may induce a voltage-independent K-current in rat portal veins by modifying the gating properties of the delayed rectifier. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1037–1048. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Niederste-Hollenberg A., Schneider J., Noack T., Weston A. H. Ion channel modulation by NS 1619, the putative BKCa channel opener, in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1538–1547. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C. J., McPherson G. A. Evidence that nitric oxide does not mediate the hyperpolarization and relaxation to acetylcholine in the rat small mesenteric artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C. J., Plane F., Kemp B. K., Cocks T. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization: a role in the control of vascular tone. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Jan;16(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)88969-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Campbell W. B., Roman R. J. Role of cytochrome P-450 enzymes and metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of vascular tone. J Vasc Res. 1995 Mar-Apr;32(2):79–92. doi: 10.1159/000159080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Gebremedhin D., Narayanan J., Jefcoat C., Falck J. R., Campbell W. B., Roman R. Formation and action of a P-450 4A metabolite of arachidonic acid in cat cerebral microvessels. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):H2098–H2107. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.5.H2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Bara A. T., Bauersachs J., Busse R. Characterization of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor as a cytochrome P450-derived arachidonic acid metabolite in mammals. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 1;481(Pt 2):407–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Kim H. S. Activation of K+ channel in vascular smooth muscles by cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 12;230(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90805-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbotson T., Edwards G., Weston A. H. Antagonism of levcromakalim by imidazoline- and guanidine-derivatives in rat portal vein: involvement of the delayed rectifier. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1556–1564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacqz-Aigrain E., Gueguen M., Zanger U. M., Robieux I., Alvarez F. Cytochrome P450IID subfamily in non-human primates. Catalytical and immunological characterization. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöckner U., Isenberg G. Action potentials and net membrane currents of isolated smooth muscle cells (urinary bladder of the guinea-pig). Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):329–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00595685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischke V., Busse R., Hecker M. Selective inhibition by barbiturates of the synthesis of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in the rabbit carotid artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(6):969–974. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noack T., Deitmer P., Edwards G., Weston A. H. Characterization of potassium currents modulated by BRL 38227 in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):717–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noack T., Edwards G., Deitmer P., Greengrass P., Morita T., Andersson P. O., Criddle D., Wyllie M. G., Weston A. H. The involvement of potassium channels in the action of ciclazindol in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubart M., Pressler M. L., Pride H. P., Zipes D. P. Electrophysiological mechanisms in a canine model of erythromycin-associated long QT syndrome. Circulation. 1993 Oct;88(4 Pt 1):1832–1844. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.4.1832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuta H., Yoneda I. Inhibition by SKF 525A and quinacrine of endogenous glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in follicle-enclosed Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 24;252(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90583-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. G., Weston A. H. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor: a new endogenous inhibitor from the vascular endothelium. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos C., Fonteriz R., López M. G., García A. G., García-Sancho J. Inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ entry into GH3 and chromaffin cells by imidazole antimycotics and other cytochrome P450 blockers. FASEB J. 1992 Jun;6(9):2742–2747. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.9.1319362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou A. P., Imig J. D., Kaldunski M., Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Sui Z., Roman R. J. Inhibition of renal vascular 20-HETE production impairs autoregulation of renal blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 2):F275–F282. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.2.F275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt P. M., Edwards G., Weston A. H., Davis S. C., Högestätt E. D. Effects of cytochrome P450 inhibitors on EDHF-mediated relaxation in the rat hepatic artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(5):1147–1152. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt P. M., Högestätt E. D. Role of potassium channels in endothelium-dependent relaxation resistant to nitroarginine in the rat hepatic artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;117(7):1600–1606. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


