Abstract
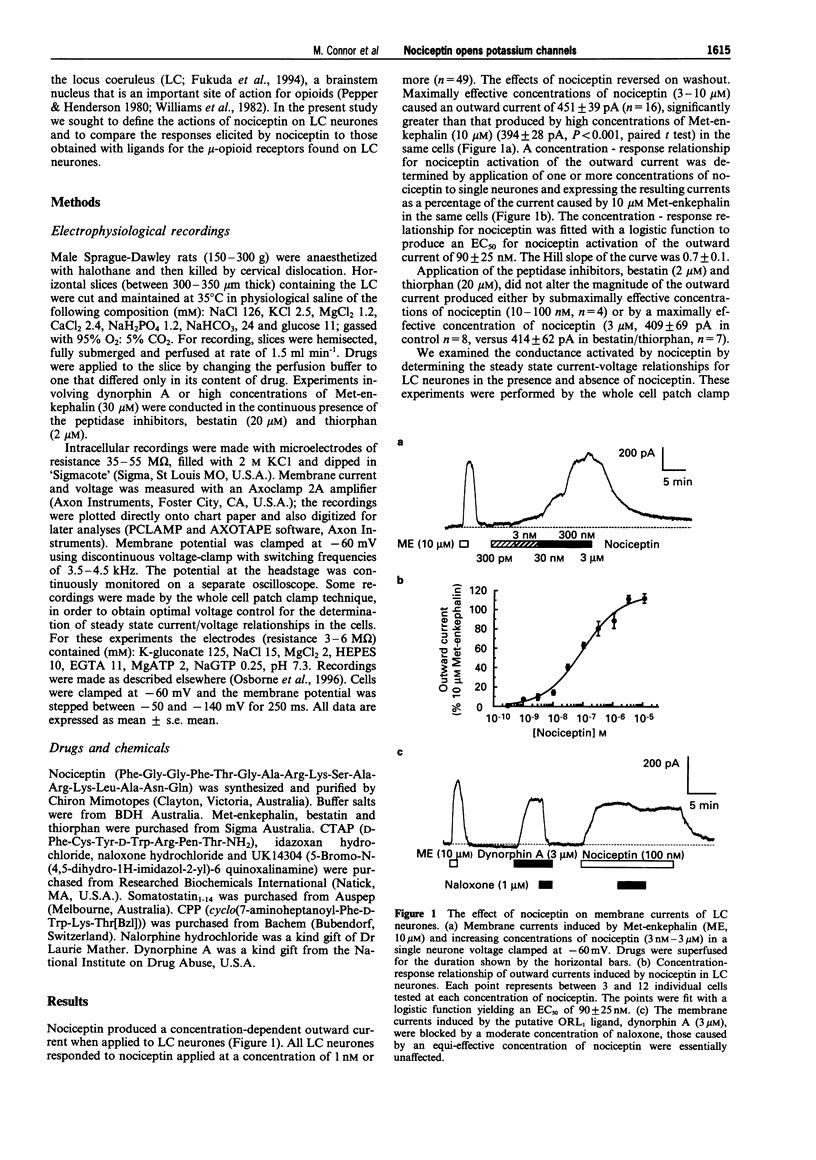
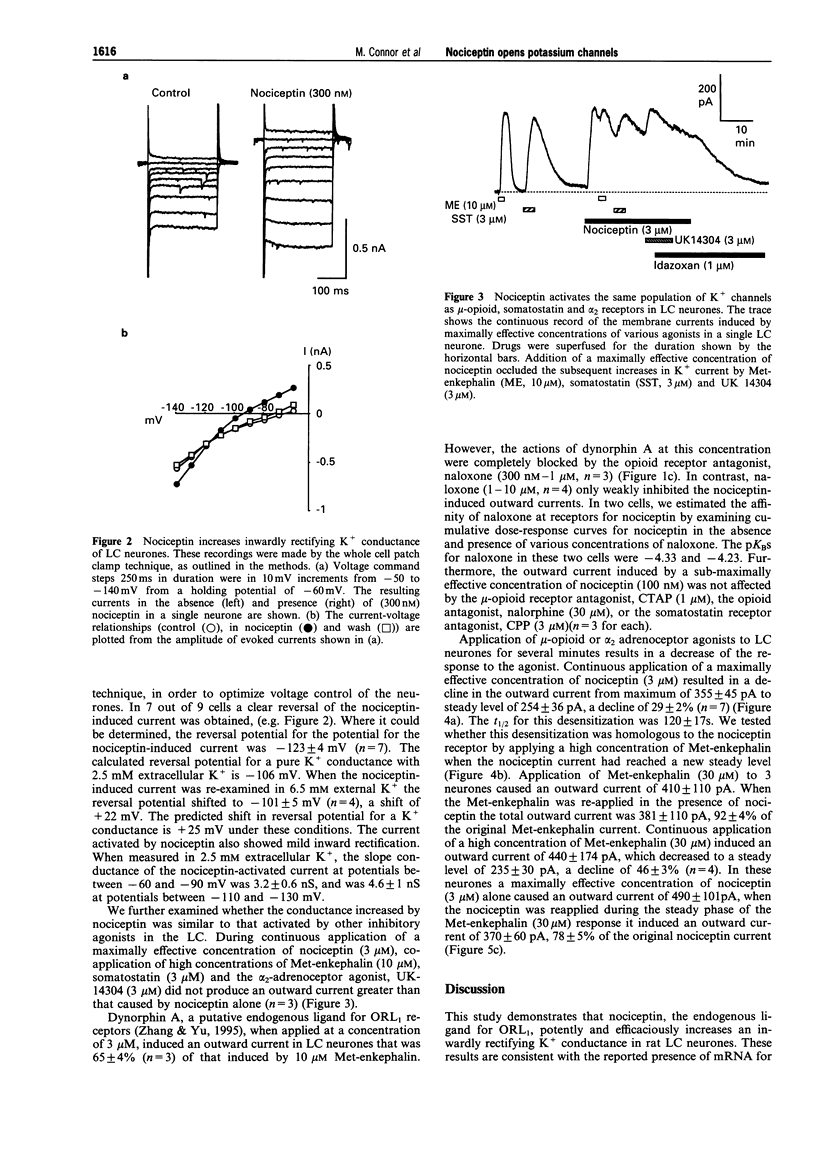
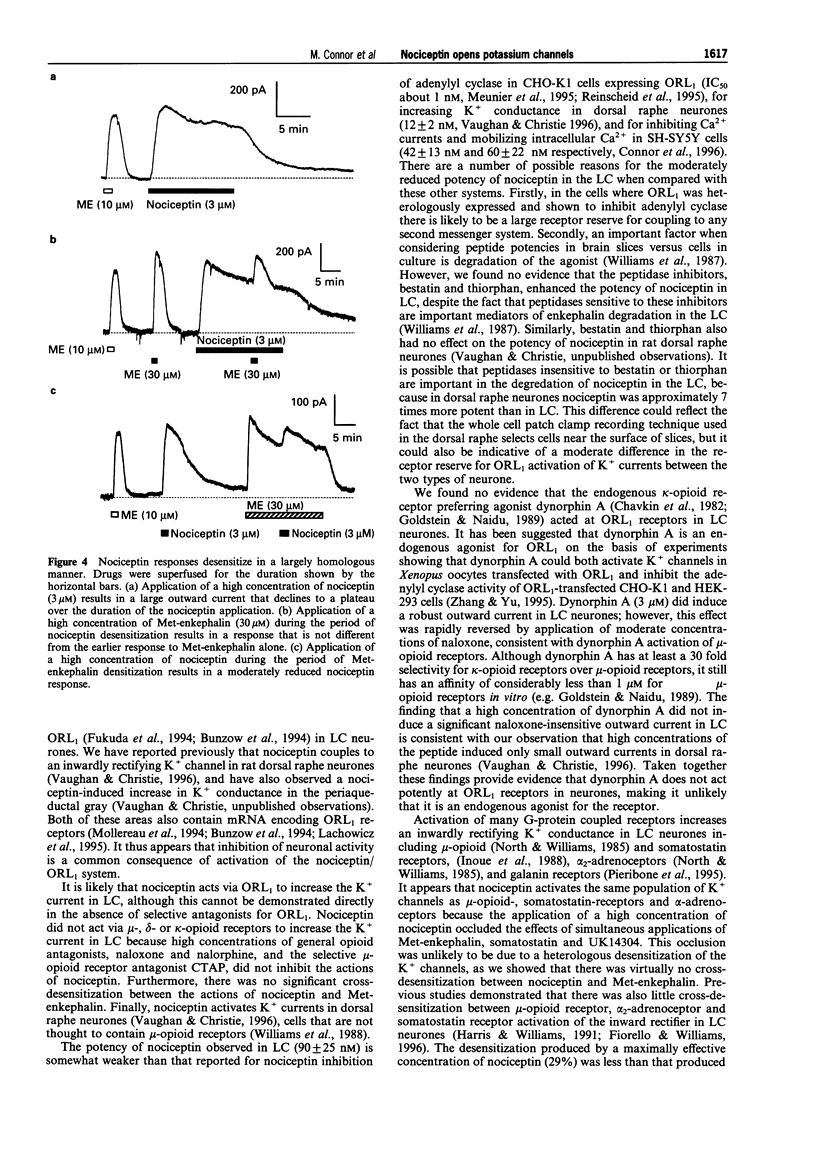
1. In this study we have examined the effects of nociceptin, an endogenous ligand for the opioid-like receptor ORL1 on the membrane properties of rat locus coeruleus (LC) neurones in vitro, using intracellular and whole cell patch clamp recording. 2. When locus coeruleus neurones were voltage clamped to -60 mV, application to nociceptin caused an outward current in all cells examined (n = 49), with an EC50 of 90 nM. Neither the potency nor the maximal effect of nociceptin was altered in the presence of the peptidase inhibitors, bestatin (20 microM) or thiorphan (2 microM). 3. The outward currents caused by nociceptin in 2.5 mM extracellular K+ reversed polarity at -123 mV, more negative than the predicted K+ reversal potential of -105 mV. Increasing extracellular K+ to 6.5 mM resulted in a shift of the reversal potential of +25 mV, a shift consistent with a K+ conductance. The conductance activated by nociceptin showed mild inward rectification. 4. Application of a high concentration of nociceptin (3 microM) occluded the current produced by simultaneous application of high concentrations of Met-enkephalin (10 microM), (3 microM) somatostatin and UK 14304 (3 microM), indicating that nociceptin activated the same conductance as mu-opioid and somatostatin receptors and alpha 2-adrenoceptors. 5. The actions of nociceptin were weakly antagonized by the opioid antagonist, naloxone, with pKb's estimated from 2 cells of -4.23 and -4.33. The mu-opioid antagonist, CTAP (D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Arg-Pen-Thr-NH2, 1 microM), the opioid antagonist, nalorphine (30 microM) or the somatostatin antagonist, CPP (cyclo(7-aminoheptanoyl-Phe-D-Trp-Lys-Thr[Bz1]) 3 microM) did not affect the nociceptin-induced current. 6. Dynorphin A (microM), another putative endogenous ligand for ORL1, caused a robust outward current in locus coeruleus neurones that was, however, completely antagonized by moderate concentrations of naloxone (300 nM-1 microM). 7. Continuous application of nociceptin (3 microM) resulted in a decrease of the outward current to a steady level of 70% of the maximum response with a t1/2 of 120s. Desensitization was largely homologous because simultaneous application of Met-enkephalin (30 microM) during the desensitized period of the nociceptin response resulted in an outward current that was 92% of control responses to Met-enkephalin in the same cells. Conversely, continuous application of Met-enkephalin (30 microM) resulted in a decrease of Met-enkephalin current to a steady level that was 54% of the initial current. During this desensitized period application of nociceptin (3 microM) resulted in a current that was 78% of the control responses to nociceptin in the same cells. 8. Thus nociceptin potently activates an inwardly rectifying K+ conductance in locus coeruleus neurones, with a pharmacological profile consistent with activation of the ORL1 receptor. Dynorphin A does not appear to be a ligand for ORL1 in rat locus coeruleus neurones.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunzow J. R., Saez C., Mortrud M., Bouvier C., Williams J. T., Low M., Grandy D. K. Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of a putative member of the rat opioid receptor gene family that is not a mu, delta or kappa opioid receptor type. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 27;347(2-3):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00561-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Specific receptor for the opioid peptide dynorphin: structure--activity relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor M., Yeo A., Henderson G. The effect of nociceptin on Ca2+ channel current and intracellular Ca2+ in the SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 May;118(2):205–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo C. D., Williams J. T. Opioid desensitization: interactions with G-protein-coupled receptors in the locus coeruleus. J Neurosci. 1996 Feb 15;16(4):1479–1485. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-04-01479.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K., Nishi M., Takeshima H., Iwabe N., Miyata T., Houtani T., Sugimoto T. cDNA cloning and regional distribution of a novel member of the opioid receptor family. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80603-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Naidu A. Multiple opioid receptors: ligand selectivity profiles and binding site signatures. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;36(2):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. C., Williams J. T. Transient homologous mu-opioid receptor desensitization in rat locus coeruleus neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2574–2581. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Somatostatin induces an inward rectification in rat locus coeruleus neurones through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:177–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachowicz J. E., Shen Y., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning of a novel G protein-coupled receptor related to the opiate receptor family. J Neurochem. 1995 Jan;64(1):34–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64010034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Mollereau C., Toll L., Suaudeau C., Moisand C., Alvinerie P., Butour J. L., Guillemot J. C., Ferrara P., Monsarrat B. Isolation and structure of the endogenous agonist of opioid receptor-like ORL1 receptor. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):532–535. doi: 10.1038/377532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollereau C., Parmentier M., Mailleux P., Butour J. L., Moisand C., Chalon P., Caput D., Vassart G., Meunier J. C. ORL1, a novel member of the opioid receptor family. Cloning, functional expression and localization. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 14;341(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. On the potassium conductance increased by opioids in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne P. B., Vaughan C. W., Wilson H. I., Christie M. J. Opioid inhibition of rat periaqueductal grey neurones with identified projections to rostral ventromedial medulla in vitro. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 15;490(Pt 2):383–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper C. M., Henderson G. Opiates and opioid peptides hyperpolarize locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):394–395. doi: 10.1126/science.7384811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieribone V. A., Xu Z. Q., Zhang X., Grillner S., Bartfai T., Hökfelt T. Galanin induces a hyperpolarization of norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in the brainstem slice. Neuroscience. 1995 Feb;64(4):861–874. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00450-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinscheid R. K., Nothacker H. P., Bourson A., Ardati A., Henningsen R. A., Bunzow J. R., Grandy D. K., Langen H., Monsma F. J., Jr, Civelli O. Orphanin FQ: a neuropeptide that activates an opioidlike G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1995 Nov 3;270(5237):792–794. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5237.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan C. W., Christie M. J. Increase by the ORL1 receptor (opioid receptor-like1) ligand, nociceptin, of inwardly rectifying K conductance in dorsal raphe nucleus neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;117(8):1609–1611. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Johnson P. S., Imai Y., Persico A. M., Ozenberger B. A., Eppler C. M., Uhl G. R. cDNA cloning of an orphan opiate receptor gene family member and its splice variant. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jul 4;348(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00557-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Christie M. J., North R. A., Roques B. P. Potentiation of enkephalin action by peptidase inhibitors in rat locus ceruleus in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Colmers W. F., Pan Z. Z. Voltage- and ligand-activated inwardly rectifying currents in dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3499–3506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Yu L. Identification of dynorphins as endogenous ligands for an opioid receptor-like orphan receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 29;270(39):22772–22776. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.39.22772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


