Abstract
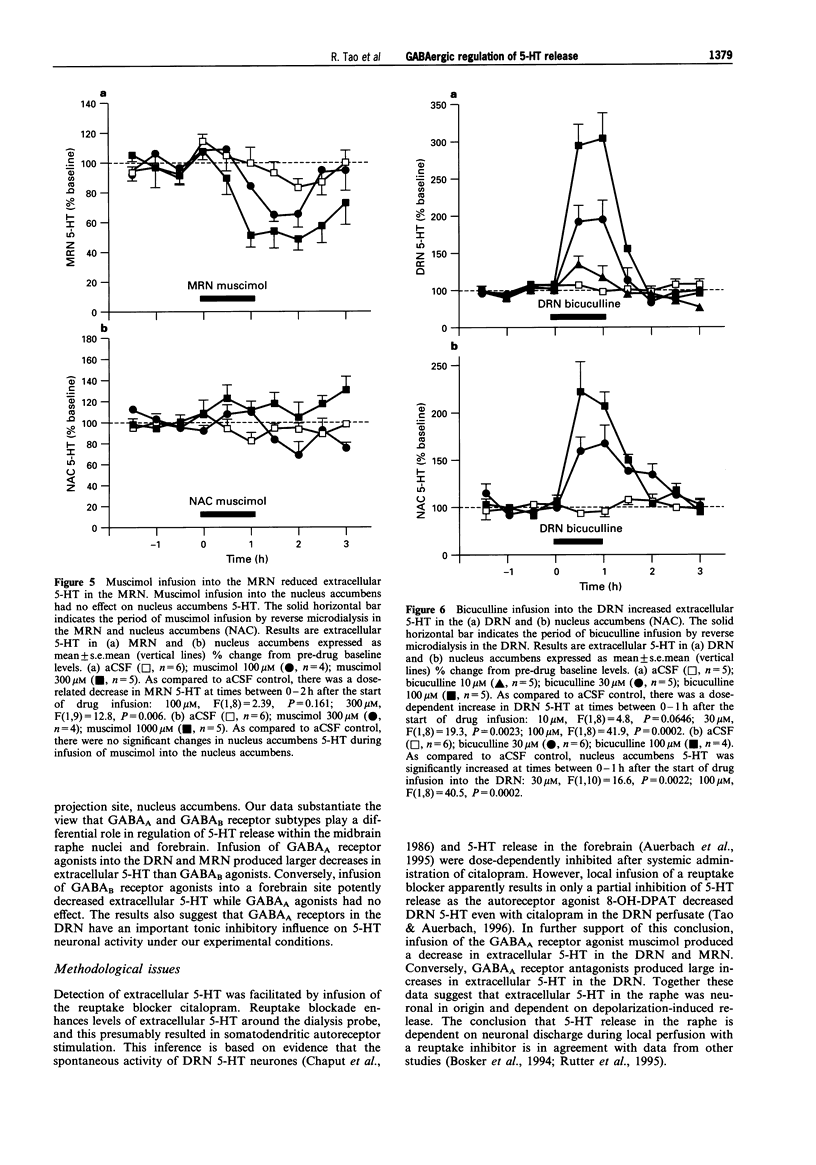
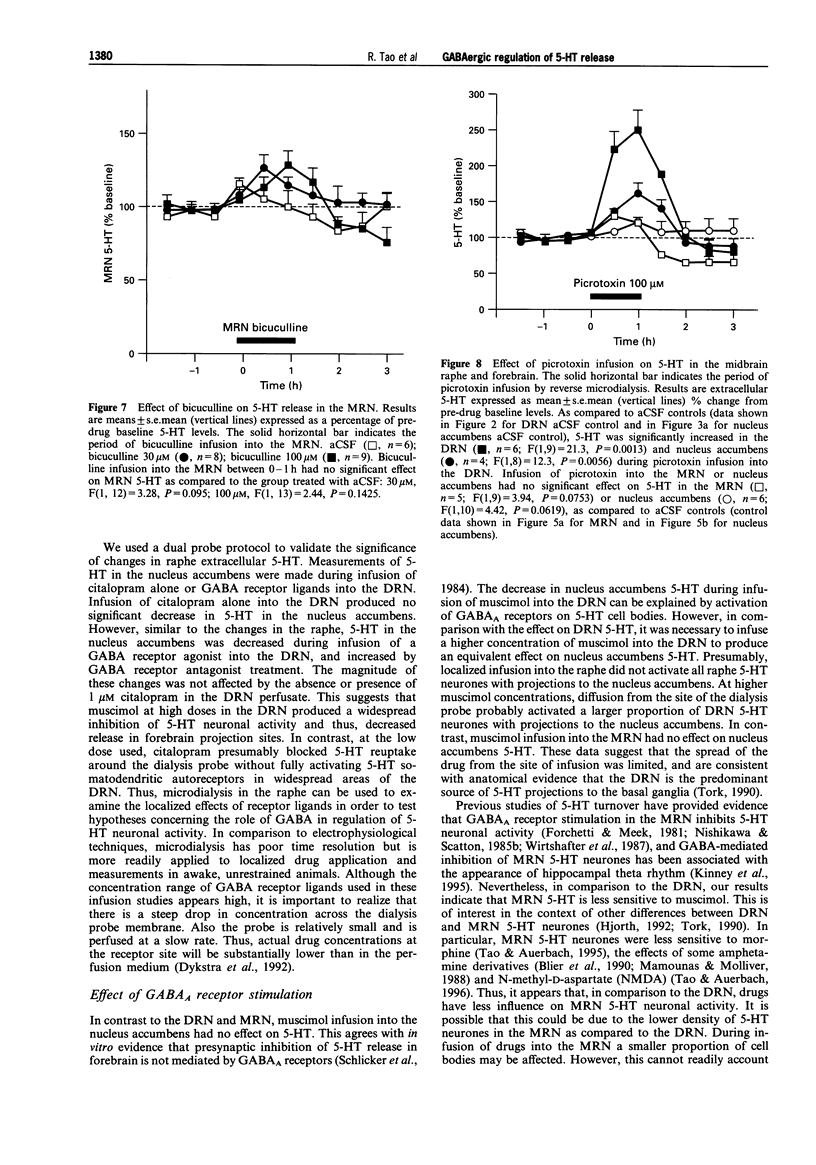
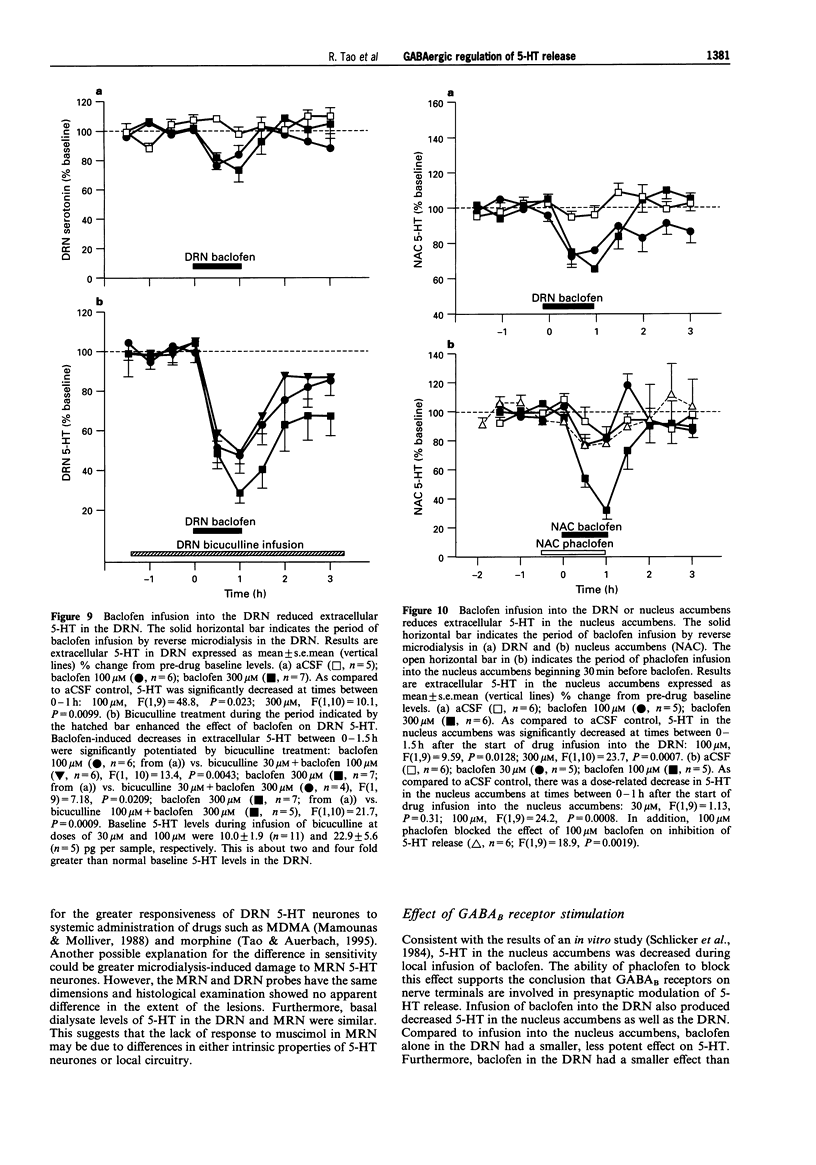
1. Extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) was determined in dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), median raphe nucleus (MRN) and nucleus accumbens by use of microdialysis in unanaesthetized rats. 2. Infusion of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)A receptor agonist muscimol into DRN and MRN resulted in decreased 5-HT in DRN and MRN, respectively. Muscimol infusion into nucleus accumbens had no effect on 5-HT. 3. Infusion of the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline into DRN resulted in increased DRN and nucleus accumbens 5-HT. Bicuculline infusion into MRN had no effect on 5-HT. This suggests that endogenous GABA had a tonic, GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory effect on 5-HT in DRN, but not in MRN. 4. Infusion of the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen into DRN produced a decrease in DRN 5-HT. Baclofen infusion into nucleus accumbens resulted in decreased nucleus accumbens 5-HT. This suggests that GABAB receptors are present in the area of cell bodies and terminals of 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neurones. 5. Infusion of the GABAB receptor antagonists phaclofen and 2-hydroxysaclofen had no effect on midbrain raphe and forebrain 5-HT. This suggests that GABAB receptors did not contribute to tonic inhibition of 5-HT release. 6. In conclusion, 5-HT release is physiologically regulated by distinct subtypes of GABA receptors in presynaptic and postsynaptic sites.
Full text
PDF
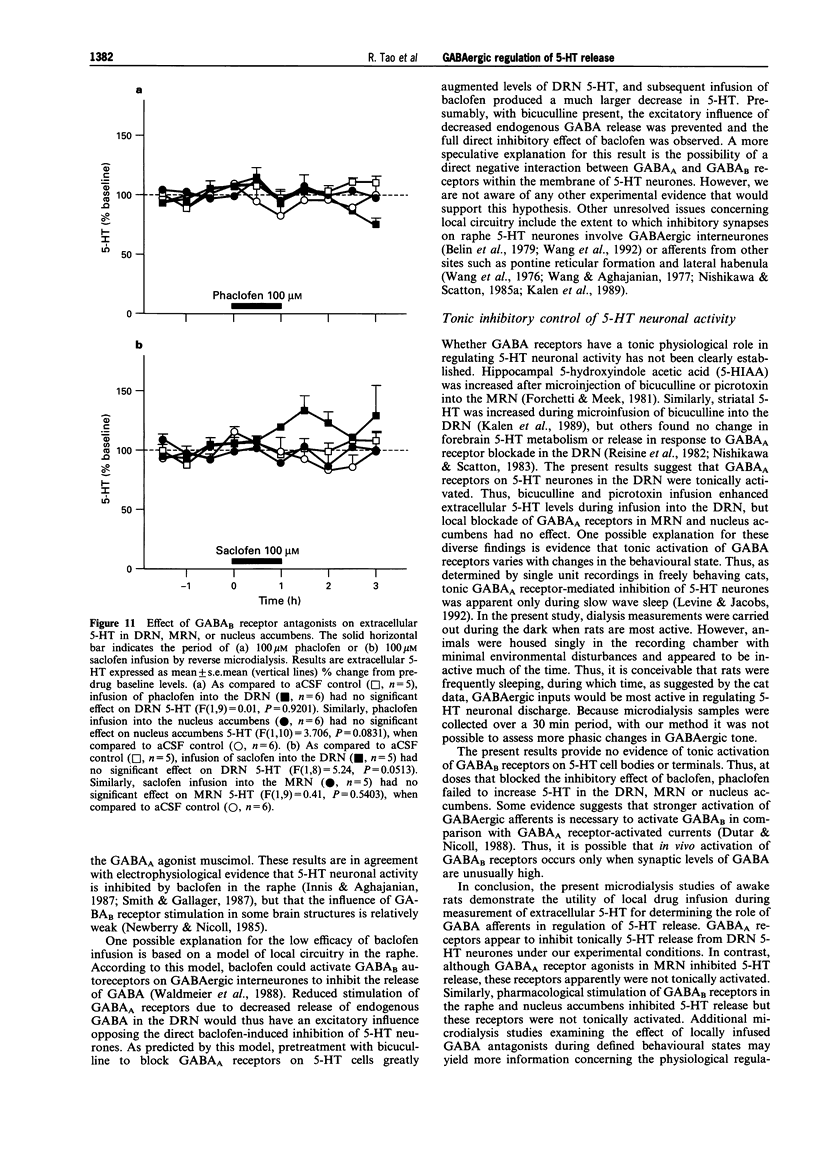


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach S. B., Lundberg J. F., Hjorth S. Differential inhibition of serotonin release by 5-HT and NA reuptake blockers after systemic administration. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Jan;34(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00137-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach S. B., Minzenberg M. J., Wilkinson L. O. Extracellular serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in hypothalamus of the unanesthetized rat measured by in vivo dialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: dialysate serotonin reflects neuronal release. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 16;499(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin M. F., Aguera M., Tappaz M., McRae-Degueurce A., Bobillier P., Pujol J. F. GABA-accumulating neurons in the nucleus raphe dorsalis and periaqueductal gray in the rat: a biochemical and radioautographic study. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 13;170(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blier P., Serrano A., Scatton B. Differential responsiveness of the rat dorsal and median raphe 5-HT systems to 5-HT1 receptor agonists and p-chloroamphetamine. Synapse. 1990;5(2):120–133. doi: 10.1002/syn.890050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosker F., Klompmakers A., Westenberg H. Extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in median raphe nucleus of the conscious rat is decreased by nanomolar concentrations of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin and is sensitive to tetrodotoxin. J Neurochem. 1994 Dec;63(6):2165–2171. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63062165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaput Y., de Montigny C., Blier P. Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;333(4):342–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00500007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra K. H., Hsiao J. K., Morrison P. F., Bungay P. M., Mefford I. N., Scully M. M., Dedrick R. L. Quantitative examination of tissue concentration profiles associated with microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1992 Mar;58(3):931–940. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchetti C. M., Meek J. L. Evidence for a tonic GABAergic control of serotonin neurons in the median raphe nucleus. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallager D. W., Aghajanian G. K. Effect of antipsychotic drugs on the firing of dorsal raphe cells. II. Reversal by picrotoxin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;39(2):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héry F., Ternaux J. P. Regulation of release processes in central serotoninergic neurons. J Physiol (Paris) 1981;77(2-3):287–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Aghajanian G. K. Pertussis toxin blocks 5-HT1A and GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 10;143(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. L., Fornal C. A. Activity of brain serotonergic neurons in the behaving animal. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):563–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalén P., Strecker R. E., Rosengren E., Björklund A. Endogenous release of neuronal serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the caudate-putamen of the rat as revealed by intracerebral dialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1422–1435. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalén P., Strecker R. E., Rosengren E., Björklund A. Regulation of striatal serotonin release by the lateral habenula-dorsal raphe pathway in the rat as demonstrated by in vivo microdialysis: role of excitatory amino acids and GABA. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):187–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90901-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney G. G., Kocsis B., Vertes R. P. Injections of muscimol into the median raphe nucleus produce hippocampal theta rhythm in the urethane anesthetized rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995 Aug;120(3):244–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02311170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. S., Jacobs B. L. Neurochemical afferents controlling the activity of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus: microiontophoretic studies in the awake cat. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4037–4044. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04037.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamounas L. A., Molliver M. E. Evidence for dual serotonergic projections to neocortex: axons from the dorsal and median raphe nuclei are differentially vulnerable to the neurotoxin p-chloroamphetamine (PCA). Exp Neurol. 1988 Oct;102(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers D. A. The GABAA receptor: new insights from single-channel recording. Synapse. 1987;1(1):96–101. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Scatton B. Evidence for a GABAergic inhibitory influence on serotonergic neurons originating from the dorsal raphe. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 21;279(1-2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Scatton B. Inhibitory influence of GABA on central serotonergic transmission. Involvement of the habenulo-raphé pathways in the GABAergic inhibition of ascending cerebral serotonergic neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 1;331(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90717-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Scatton B. Inhibitory influence of GABA on central serotonergic transmission. Raphé nuclei as the neuroanatomical site of the GABAergic inhibition of cerebral serotonergic neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 1;331(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90718-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T. D., Soubrié P., Artaud F., Glowinski J. Involvement of lateral habenula-dorsal raphe neurons in the differential regulation of striatal and nigral serotonergic transmission cats. J Neurosci. 1982 Aug;2(8):1062–1071. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-08-01062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romandini S., Samanin R. Muscimol injections in the nucleus raphé dorsalis block the antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats: apparent lack of 5-hydroxytryptamine involvement in muscimol's effect. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;81(1):25–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. J., Gundlah C., Auerbach S. B. Systemic uptake inhibition decreases serotonin release via somatodendritic autoreceptor activation. Synapse. 1995 Jul;20(3):225–233. doi: 10.1002/syn.890200306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Classen K., Göthert M. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(2):99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00517304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Clark D., Grahame-Smith D. G. In vivo measurement of extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in hippocampus of the anaesthetized rat using microdialysis: changes in relation to 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neuronal activity. J Neurochem. 1989 Jul;53(1):234–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Hjorth S., Grahame-Smith D. G. Pharmacological characterization of 8-OH-DPAT-induced inhibition of rat hippocampal 5-HT release in vivo as measured by microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):989–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Gallager D. GABA, benzodiazepine and serotonergic receptor development in the dorsal raphe nucleus: electrophysiological studies. Brain Res. 1987 Oct;432(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao R., Auerbach S. B. Anesthetics block morphine-induced increases in serotonin release in rat CNS. Synapse. 1994 Dec;18(4):307–314. doi: 10.1002/syn.890180406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao R., Auerbach S. B. Differential effect of NMDA on extracellular serotonin in rat midbrain raphe and forebrain sites. J Neurochem. 1996 Mar;66(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66031067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao R., Auerbach S. B. Involvement of the dorsal raphe but not median raphe nucleus in morphine-induced increases in serotonin release in the rat forebrain. Neuroscience. 1995 Sep;68(2):553–561. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00154-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao R., Hjorth S. Differences in the in vitro and in vivo 5-hydroxytryptamine extraction performance among three common microdialysis membranes. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1778–1785. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törk I. Anatomy of the serotonergic system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:9–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Wicki P., Feldtrauer J. J., Baumann P. A. Potential involvement of a baclofen-sensitive autoreceptor in the modulation of the release of endogenous GABA from rat brain slices in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;337(3):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00168841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. P., Ochiai H., Nakai Y. GABAergic innervation of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat studied by electron microscopy double immunostaining. Brain Res Bull. 1992 Dec;29(6):943–948. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(92)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Aghajanian G. K. Physiological evidence for habenula as major link between forebrain and midbrain raphe. Science. 1977 Jul 1;197(4298):89–91. doi: 10.1126/science.194312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Gallager D. W., Aghajanian G. K. Stimulation of pontine reticular formation suppresses firing of serotonergic neuronses in the dorsal raphe. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):365–368. doi: 10.1038/264365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. O., Auerbach S. B., Jacobs B. L. Extracellular serotonin levels change with behavioral state but not with pyrogen-induced hyperthermia. J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2732–2741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02732.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtshafter D., Klitenick M. A., Asin K. E. Is dopamine involved in the hyperactivity produced by injections of muscimol into the median raphe nucleus? Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Jul;30(3):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]