Abstract
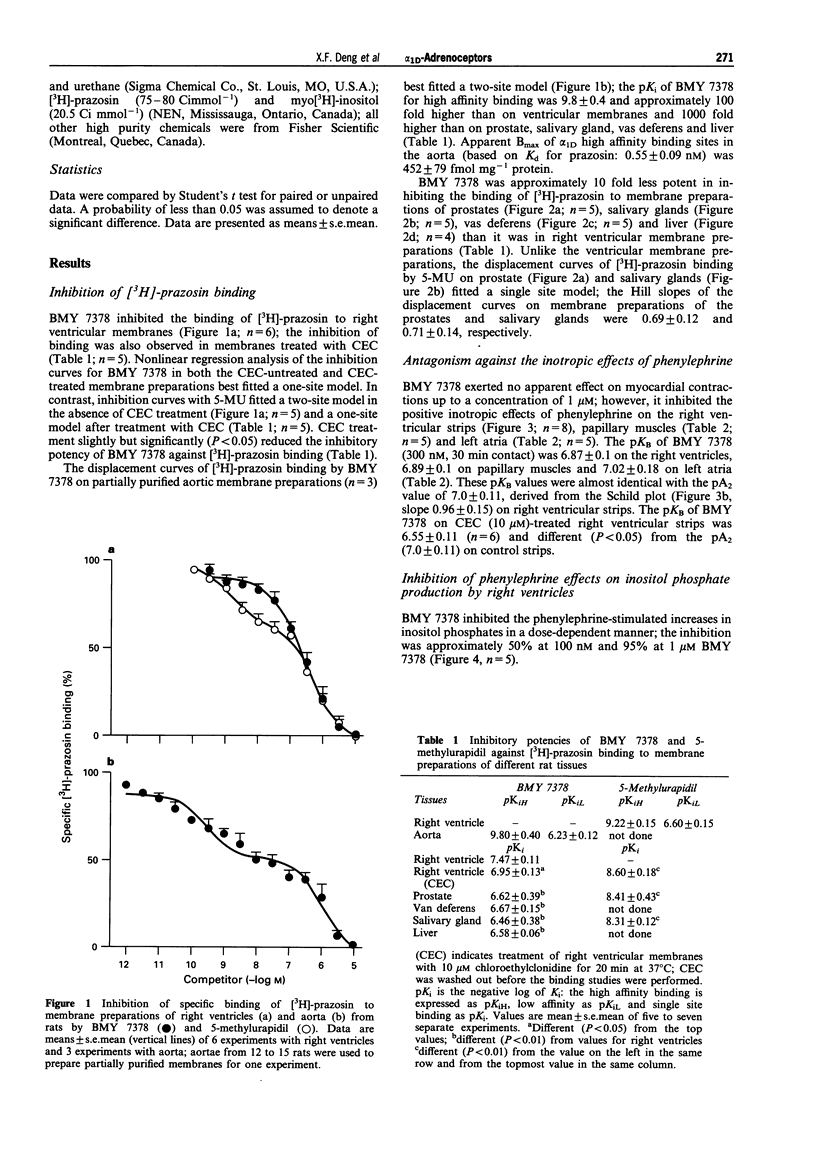
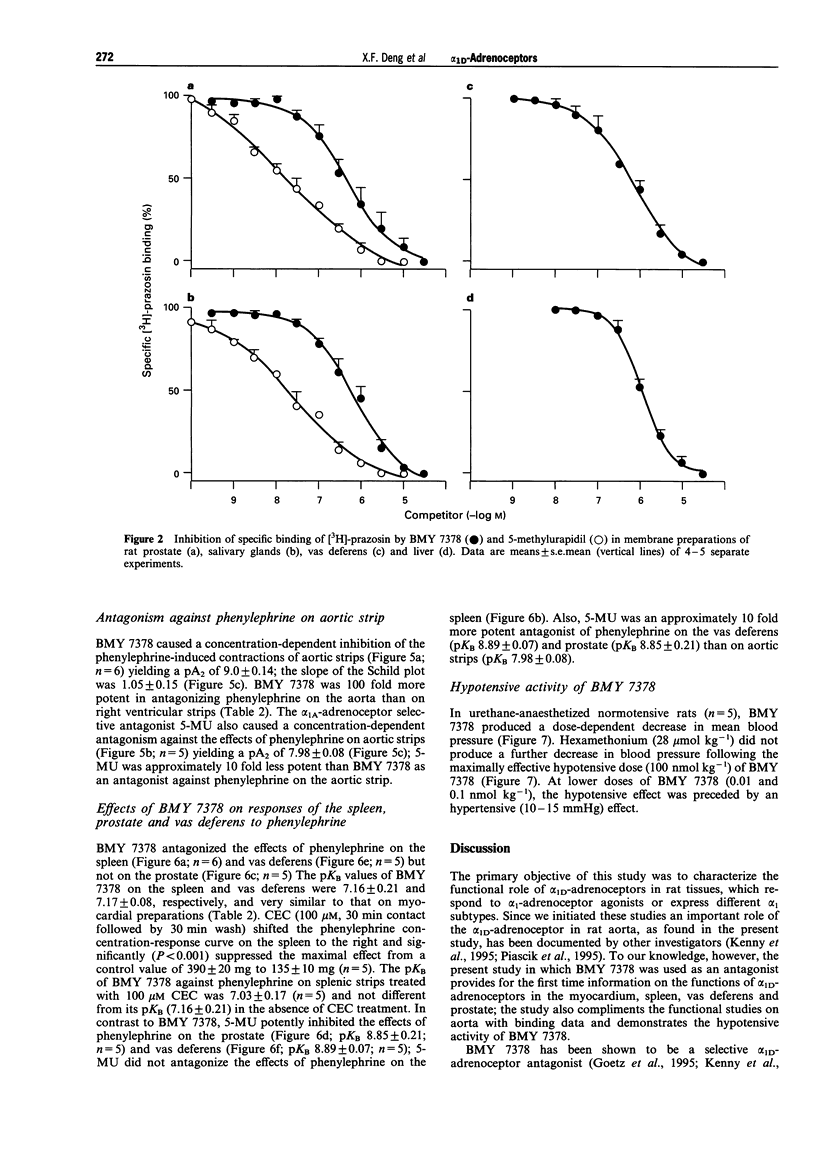
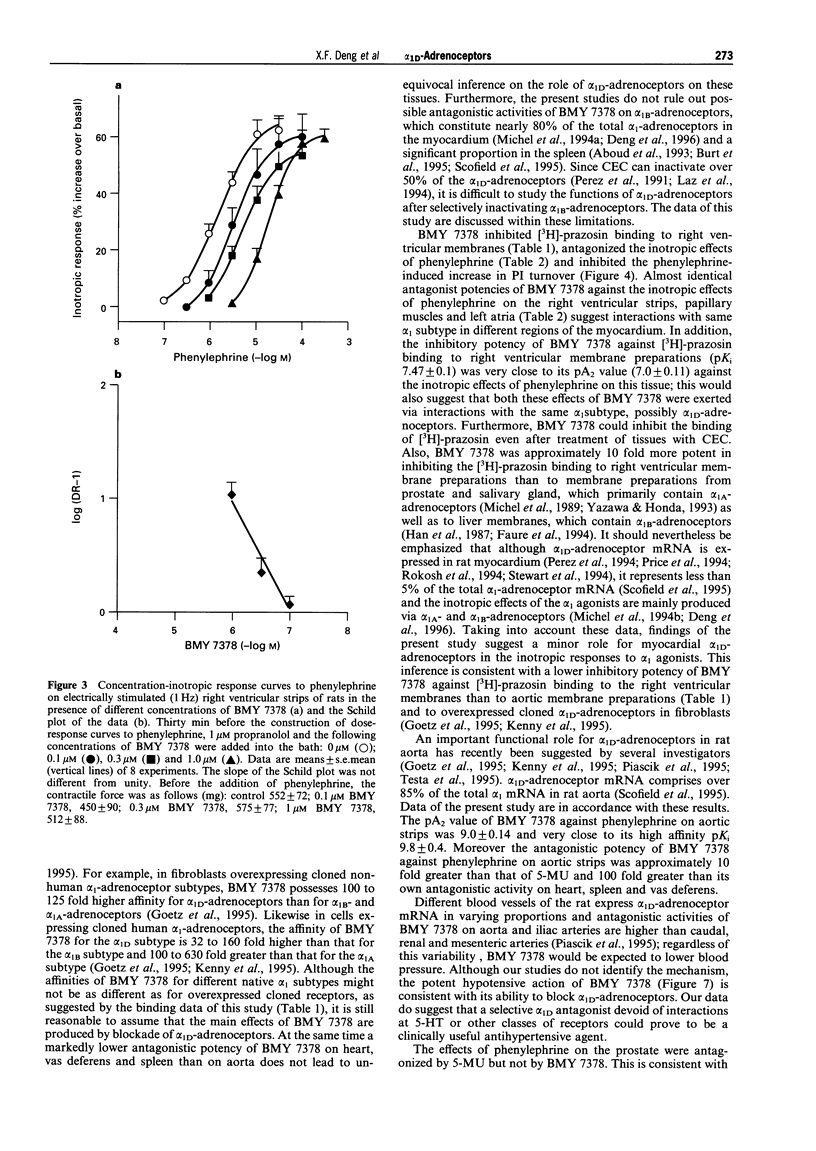
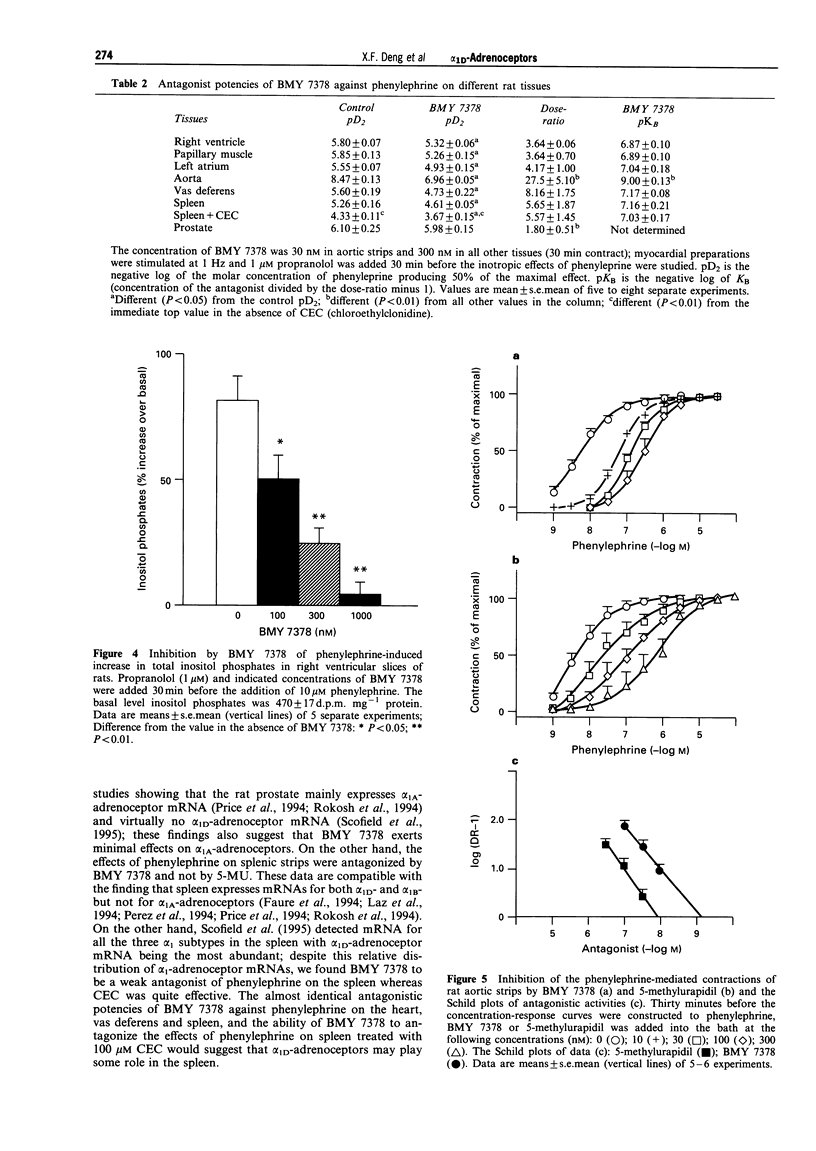
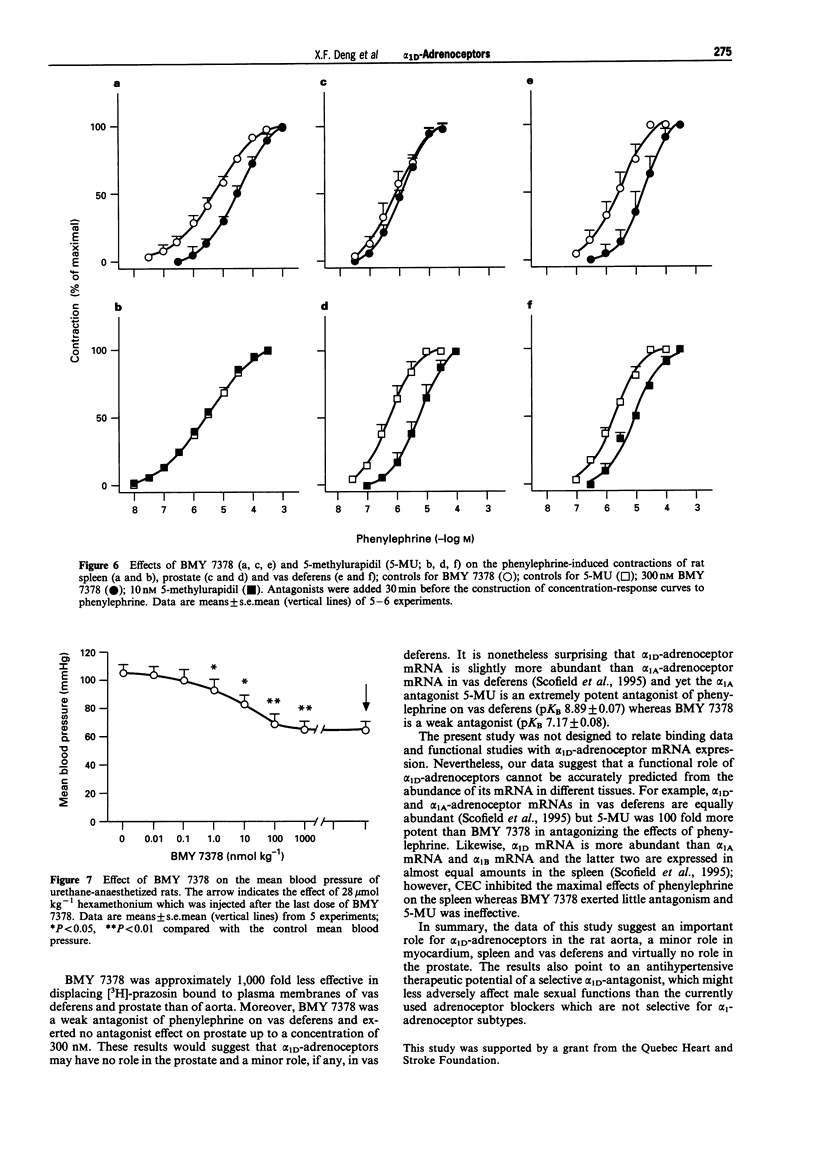
1. This study was done to characterize the functional role of alpha 1D-adrenoceptors in rat myocardium, aorta, spleen, vas deferens and prostate by use of the selective antagonist BMY 7378. 2. BMY 7378 inhibited [3H]-prazosin binding to aortic membranes with a potency (pKi 9.8 +/- 0.40) approximately 100 fold higher than in right ventricular membranes (pKi 7.47 +/- 0.11) and approximately 1,000 fold higher than that in plasma membranes of the prostate (pKi 6.62 +/- 0.39), vas deferens (pKi 6.67 +/- 0.15), salivary gland (pKi 6.46 +/- 0.38) and liver (6.58 +/- 0.06). 3. BMY 7378 antagonized the positive inotropic effects of phenylephrine (in the presence of 1 microM propranolol) on right ventricles (pA2 7.0 +/- 0.11), left atria (pKB 7.04 +/- 0.18) and papillary muscles (pKB 6.9 +/- 0.1) and inhibited phenylephrine-induced increase in inositol phosphates. 4. BMY 7378 was approximately 100 fold more potent as an antagonist of phenylephrine on aortic strips (pA2 9.0 +/- 0.13) than on vas deferens (pKB 7.17 +/- 0.08) and spleen (pKB 7.16 +/- 0.21); it was ineffective on the prostate. 5. Chloroethylclonidine suppressed the maximal effects of phenylephrine on spleen; 5-methylurapidil antagonized the effects of phenylephrine on aortic strips (pA2 7.98 +/- 0.08), vas deferens (pKB 8.89 +/- 0.07) and prostate (pKB 8.85 +/- 0.21). 6. BMY 7378 caused a dose (0.1-100 nmol kg-1)-dependent decrease in mean blood pressure of urethane-anaesthetized rats and its hypotensive efficacy was equal to that of hexamethonium. 7. The data suggest that alpha 1D-adrenoceptors play a significant role in rat aorta, a minor role in the heart, vas deferens and spleen and virtually no role in the prostate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besse J. C., Furchgott R. F. Dissociation constants and relative efficacies of agonists acting on alpha adrenergic receptors in rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Apr;197(1):66–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt R. P., Chapple C. R., Marshall I. Evidence for a functional alpha 1A- (alpha 1C-) adrenoceptor mediating contraction of the rat epididymal vas deferens and an alpha 1B-adrenoceptor mediating contraction of the rat spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;115(3):467–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. F., Chemtob S., Almazan G., Varma D. R. Ontogenic differences in the functions of myocardial alpha1 adrenoceptor subtypes in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Mar;276(3):1155–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Arbilla S., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Bylund D. B., Clarke D. E., Eikenburg D. C., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Ruffolo R. R., Jr International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesh G., Deth R. C. Different affinity states of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors defined by agonists and antagonists in bovine aorta plasma membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):430–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Chalmers D. H., Philpott P. C., Naylor A. M. Characterization of an alpha 1D-adrenoceptor mediating the contractile response of rat aorta to noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(6):981–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laz T. M., Forray C., Smith K. E., Bard J. A., Vaysse P. J., Branchek T. A., Weinshank R. L. The rat homologue of the bovine alpha 1c-adrenergic receptor shows the pharmacological properties of the classical alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):414–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Identification of a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the alpha 1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):883–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Hanft G., Gross G. Functional studies on alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating inotropic effects in rat right ventricle. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Hanft G., Gross G. Radioligand binding studies of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Malik N., Gaivin R., Graham R. M. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of the rat homolog of the bovine alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor provide evidence for its classification as the alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Guarino R. D., Smith M. S., Soltis E. E., Saussy D. L., Jr, Perez D. M. The specific contribution of the novel alpha-1D adrenoceptor to the contraction of vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Dec;275(3):1583–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Chari R. S., Berkowitz D. E., Meyers W. C., Schwinn D. A. Expression of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype mRNA in rat tissues and human SK-N-MC neuronal cells: implications for alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype classification. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;46(2):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofield M. A., Liu F., Abel P. W., Jeffries W. B. Quantification of steady state expression of mRNA for alpha-1 adrenergic receptor subtypes using reverse transcription and a competitive polymerase chain reaction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Nov;275(2):1035–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Karns L. R., Chang K. C., Long C. S., Kariya K., Simpson P. C. Cloning of the rat alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor from cardiac myocytes. alpha 1C, alpha 1B, and alpha 1D mRNAs are present in cardiac myocytes but not in cardiac fibroblasts. Circ Res. 1994 Oct;75(4):796–802. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.4.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzic A., Pucéat M., Vassort G., Vogel S. M. Cardiac alpha 1-adrenoceptors: an overview. Pharmacol Rev. 1993 Jun;45(2):147–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa R., Destefani C., Guarneri L., Poggesi E., Simonazzi I., Taddei C., Leonardi A. The alpha 1d-adrenoceptor subtype is involved in the noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat aorta. Life Sci. 1995;57(13):PL159–PL163. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)02079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. B., Harden T. K., Molinoff P. B. beta-adrenergic receptors in rat liver: effects of adrenalectomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1343–1347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa H., Honda K. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype in the rat prostate is preferentially the alpha 1A type. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;62(3):297–304. doi: 10.1254/jjp.62.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocca F. D., Hyslop D. K., Smith D. W., Maayani S. BMY 7378, a buspirone analog with high affinity, selectivity and low intrinsic activity at the 5-HT1A receptor in rat and guinea pig hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 4;137(2-3):293–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


