Abstract
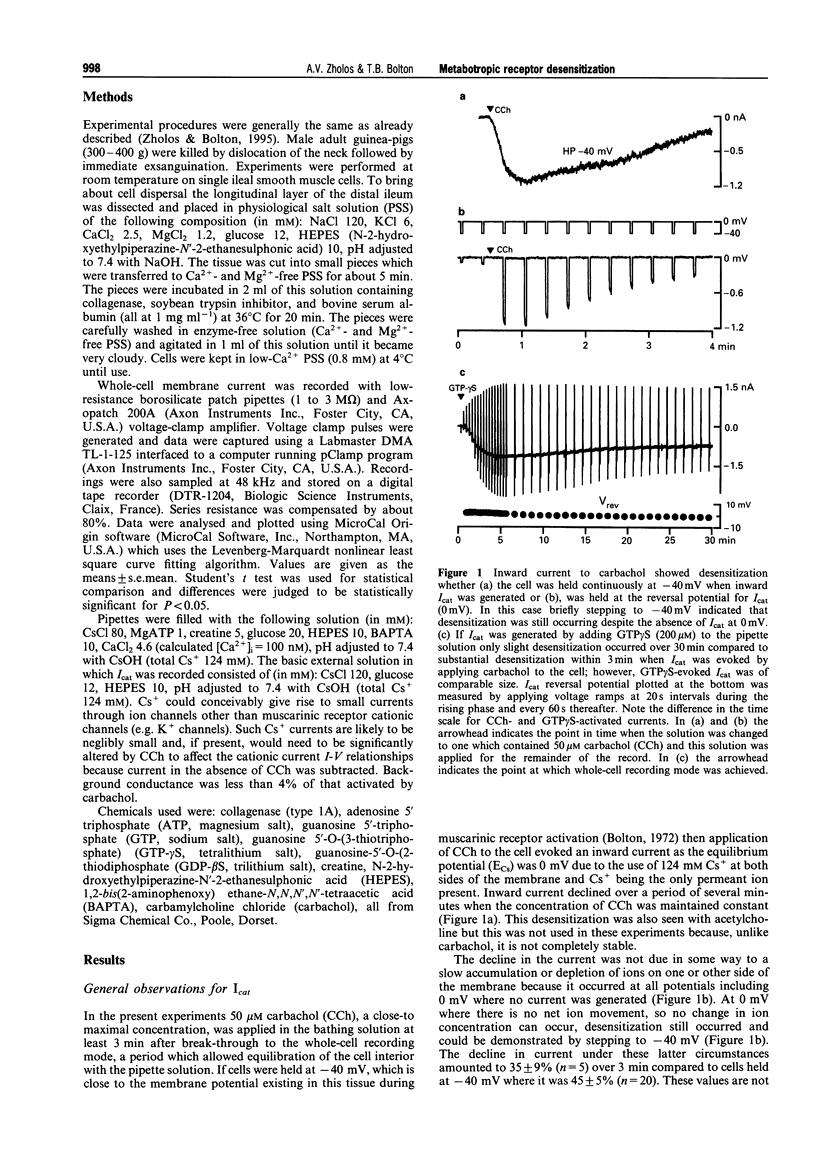
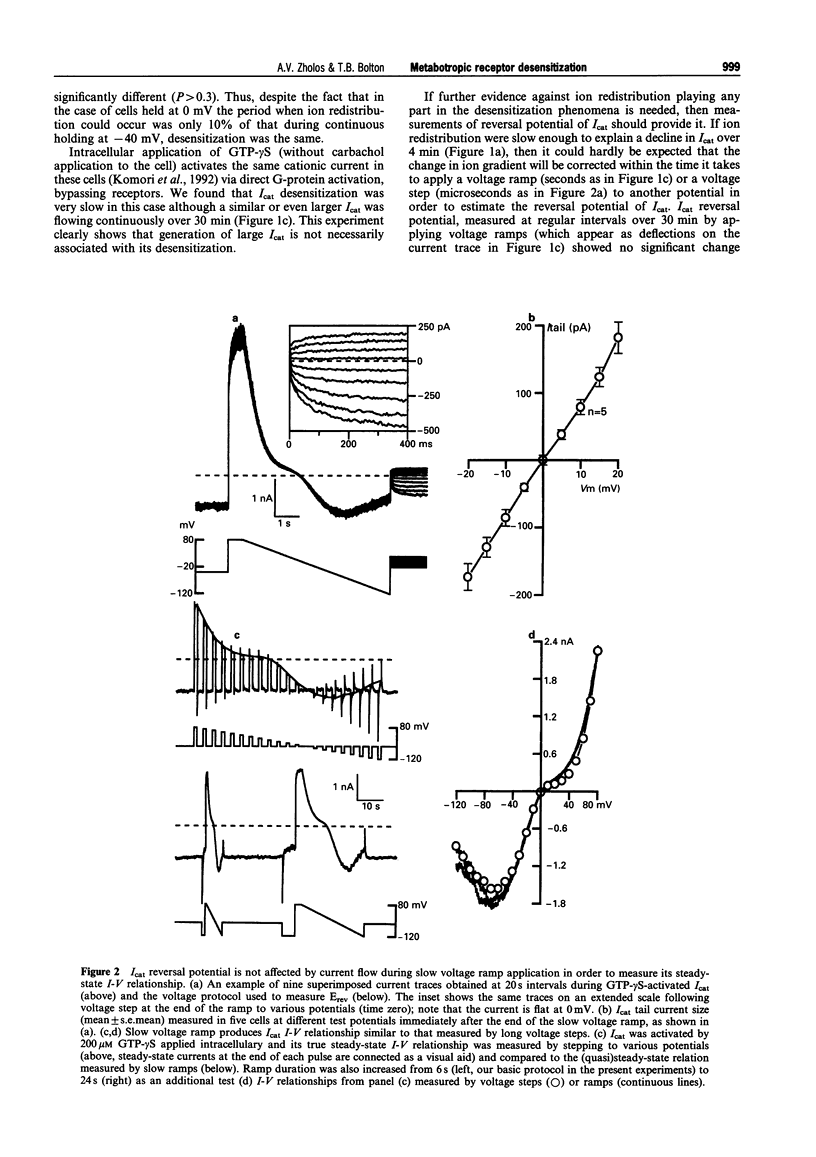
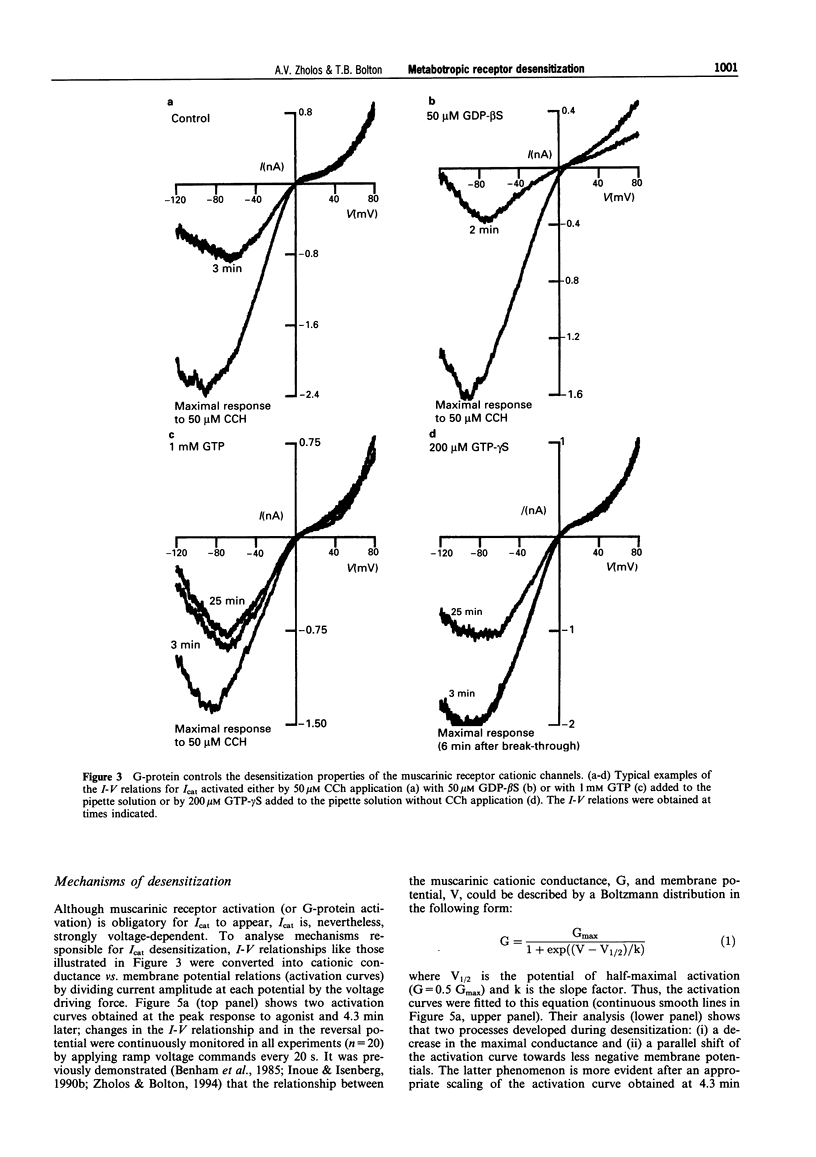
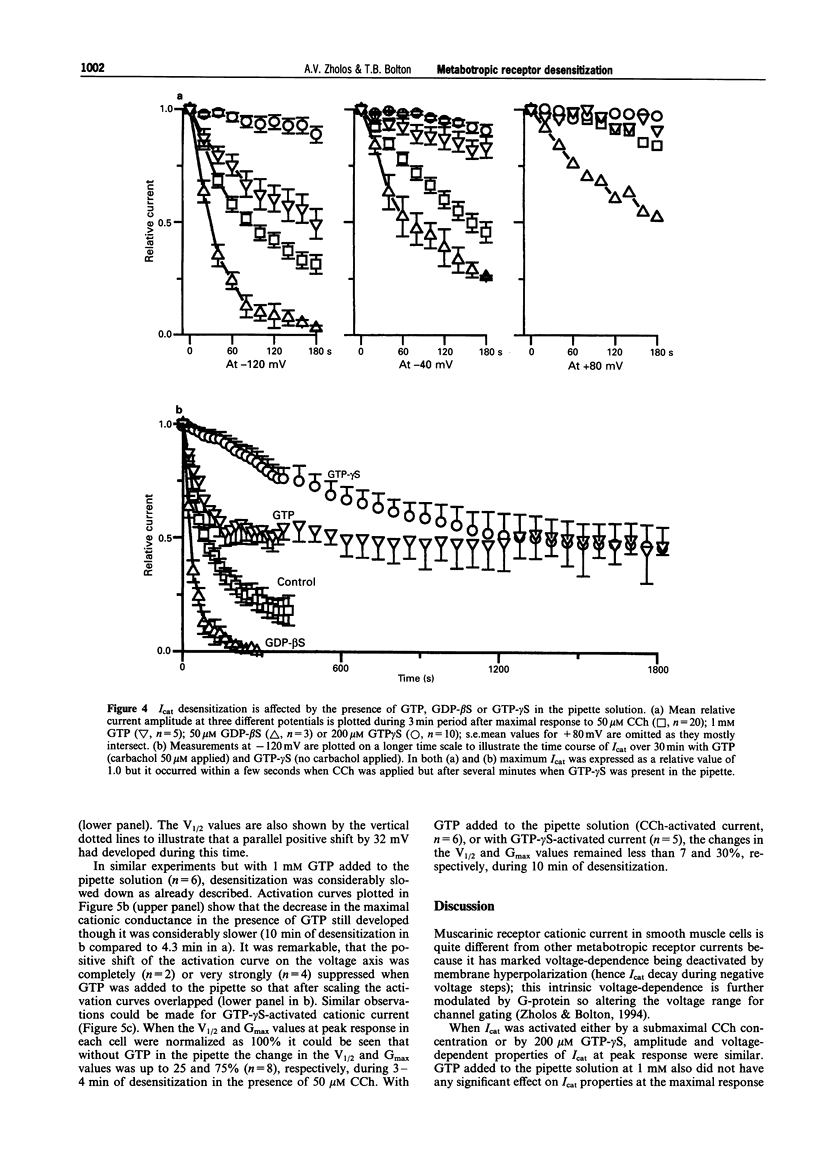
1. Cationic current (Icat) was evoked in single isolated smooth muscle cells either by activating muscarinic receptors with the stable muscarinic agonist, carbachol (CCh), or by dialysing cells with GTP-gamma S. It was studied using patch-clamp recording techniques in cells obtained by enzymatic digestion from the longitudinal muscle layer of the guinea-pig small intestine. 2. Icat appears only when muscarinic receptors or G-proteins are activated, but it is strongly voltage-dependent. Its activation could be described by the Boltzmann equation. During desensitization of Icat evoked by 50 microM CCh, the slope factor, k, remained constant whereas the maximal conductance, Gmax, slowly decreased and the potential of half-maximal activation, V1/2, shifted positively by 32 mV during 4 min. 3. At peak response either to extracellular application of CCh (GTP-free, or 1 mM GTP-containing, pipette solution) or to intracellular application of GTP-gamma S (no CCh), the size and voltage-dependent properties of Icat were similar. However, Icat desensitization was slower in the presence of GTP (CCh applied) in the pipette solution and much slower with GTP-gamma S in the pipette (no CCh) compared to GTP-free pipette solution (CCh applied); the decrease in Gmax with time was much delayed and the positive shift of the activation curve was inhibited. GDP-beta S added to the pipette solution at 2 mM abolished Icat in response to applied CCh; 50 microM did not prevent Icat generation but significantly accelerated desensitization. 4. It was concluded that the rate of desensitization of the carbachol-evoked cationic current was due to a decline in the concentration of activated G-protein in the cell, which reduced the maximum number of channels which could be opened and shifted their activation range to less negative potentials.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. The depolarizing action of acetylcholine or carbachol in intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):647–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. The role of electrogenic sodium pumping in the response of smooth muscle to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):713–731. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase cycle. Multiple sites of regulation by beta-adrenergic receptor and Mg2+ studied in reconstituted receptor-Gs vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1656–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Mechanism of muscarinic receptor-induced K+ channel activation as revealed by hydrolysis-resistant GTP analogues. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Apr;91(4):469–493. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.4.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Adham N., Whiting R. L. Acute desensitization of muscarinic receptors in the isolated guinea-pig ileal longitudinal muscle. J Auton Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;12(3):137–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1992.tb00371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The effect of GTP and Mg2+ on the GTPase activity and the fluorescent properties of Go. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):757–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Droogmans G., Casteels R. Carbachol-induced nonspecific desensitization in guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;343(6):580–587. doi: 10.1007/BF00184288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im M. J., Riek R. P., Graham R. M. A novel guanine nucleotide-binding protein coupled to the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. II. Purification, characterization, and reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18952–18960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Acetylcholine activates nonselective cation channels in guinea pig ileum through a G protein. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1173–C1178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Acetylcholine activates single sodium channels in smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00581898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner P. D. Studies on the loss of acetylcholine sensitivity in ileal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Sep;186(3):552–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Takewaki T., Ohashi H. GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. Short-term desensitization of muscarinic K+ channel current in isolated atrial myocytes and possible role of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Oct;410(3):227–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00580270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane receptor desensitization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90139-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahama P. A., Linderman J. J. A Monte Carlo study of the dynamics of G-protein activation. Biophys J. 1994 Sep;67(3):1345–1357. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80606-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubagwa K., Gilbert J. C., Pappano A. J. Differential time course for desensitization to muscarinic effects on K+ and Ca2+ channels. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(5-6):542–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00374576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldershaw K. A., Richardson A., Taylor C. W. Prolonged exposure to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate does not cause intrinsic desensitization of the intracellular Ca(2+)-mobilizing receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16312–16316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., ROTHSCHILD A. M. THE CHANGES IN RESPONSE AND IN IONIC CONTENT OF SMOOTH MUSCLE PRODUCED BY ACETYLCHOLINE ACTON AND BY CALCIUM DEFICIENCY. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Apr;24:437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen W. J., Neubig R. R. Rapid kinetics of alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a distal rate-limiting step. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8778–8786. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tota M. R., Kahler K. R., Schimerlik M. I. Reconstitution of the purified porcine atrial muscarinic acetylcholine receptor with purified porcine atrial inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8175–8182. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zang W. J., Yu X. J., Honjo H., Kirby M. S., Boyett M. R. On the role of G protein activation and phosphorylation in desensitization to acetylcholine in guinea-pig atrial cells. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:649–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Bolton T. B. Effects of divalent cations on muscarinic receptor cationic current in smooth muscle from guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1995 Jul 1;486(Pt 1):67–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Bolton T. B. G-protein control of voltage dependence as well as gating of muscarinic metabotropic channels in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 15;478(Pt 2):195–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Komori S., Ohashi H., Bolton T. B. Ca2+ inhibition of inositol trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in single smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 15;481(Pt 1):97–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



