Abstract
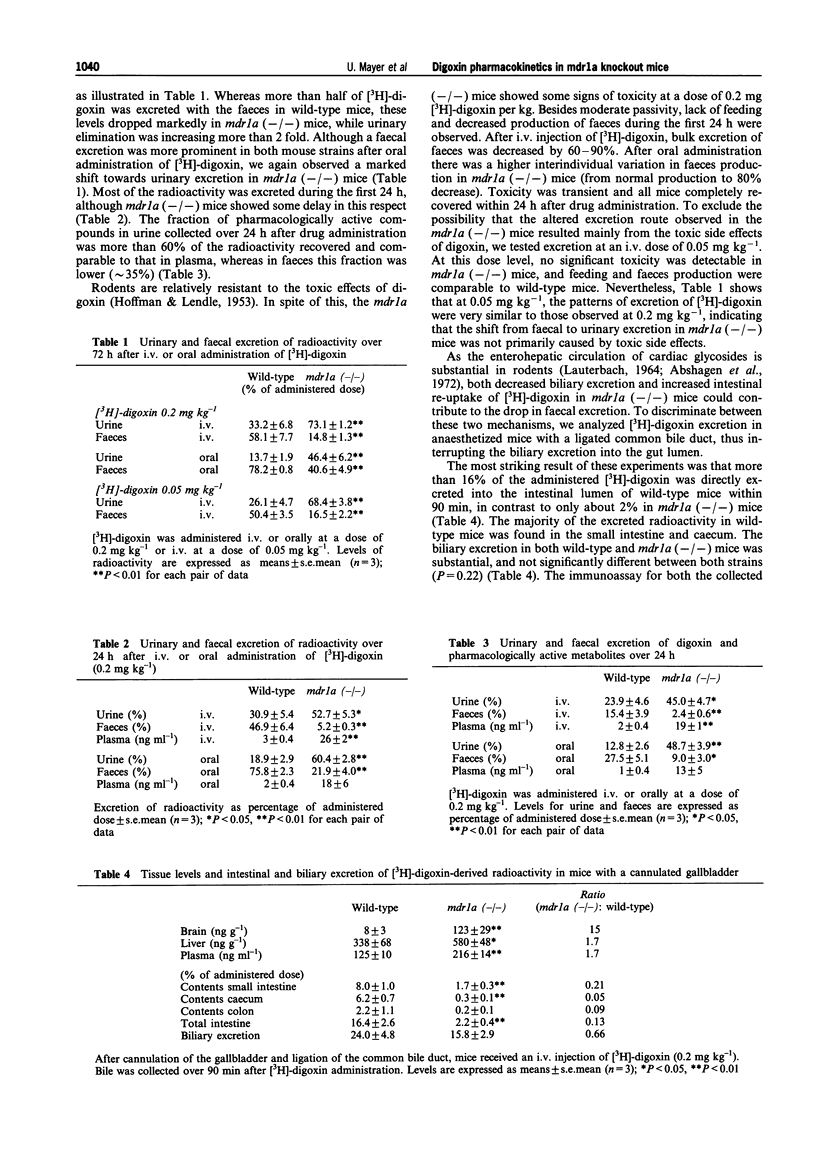
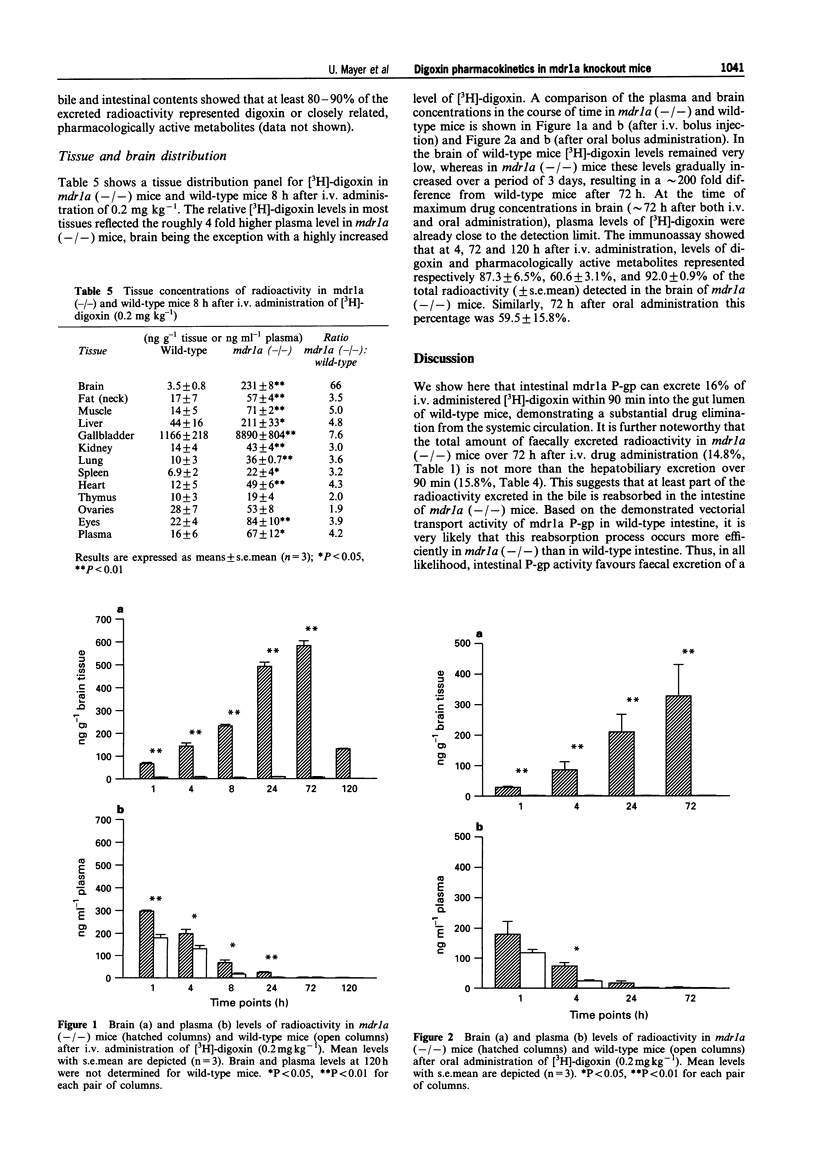
1. We have used mice with a disrupted mdr 1a P-glycoprotein gene (mdr 1a (-/-) mice) to study the role of P-glycoprotein in the pharmacokinetics of digoxin, a model P-glycoprotein substrate. 2. [3H]-digoxin at a dose of 0.2 mg kg-1 was administered as a single i.v. or oral bolus injection. We focussed on intestinal mucosa and brain endothelial cells, two major pharmacological barriers, as the mdr 1a P-glycoprotein is the only P-glycoprotein normally present in these tissues. 3. Predominant faecal excretion of [3H]-digoxin in wild-type mice shifted towards predominantly urinary excretion in mdr 1a (-/-) mice. 4. After interruption of the biliary excretion into the intestine, we found a substantial excretion of [3H]-digoxin via the gut mucosa in wild-type mice (16% of administered dose over 90 min). This was only 2% in mdr 1a (-/-) mice. Biliary excretion of [3H]-digoxin was not dramatically decreased (24% in wild-type mice versus 16% in mdr 1a (-/-) mice). 5. After a single bolus injection, brain levels of [3H]-digoxin in wild-type mice remained very low, whereas in mdr 1a (-/-) mice these levels continuously increased over a period of 3 days, resulting in a approximately 200 fold higher concentration than in wild-type mice. 6. These data demonstrate the in vivo contribution of intestinal P-glycoprotein to direct elimination of [3H]-digoxin from the systemic circulation and to the pattern of [3H]-digoxin disposition, and they underline the importance of P-glycoprotein for the blood-brain barrier.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abshagen U., von Bergmann K., Rietbrock N. Evaluation of the enterohepatic circulation after 3 H-digoxin administration in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;275(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00505063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini N., Scotlandi K., Barbanti-Bròdano G., Manara M. C., Maurici D., Bacci G., Bertoni F., Picci P., Sottili S., Campanacci M. Expression of P-glycoprotein in high-grade osteosarcomas in relation to clinical outcome. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 23;333(21):1380–1385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511233332103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy W. T., Dalton W. S., Dorr R. T. The clinical relevance of multidrug resistance. Cancer Invest. 1990;8(5):547–562. doi: 10.3109/07357909009012080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourhis J., Bénard J., Hartmann O., Boccon-Gibod L., Lemerle J., Riou G. Correlation of MDR1 gene expression with chemotherapy in neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Sep 20;81(18):1401–1405. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.18.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., O'Brien J. P., Casals D., Rittman-Grauer L., Biedler J. L., Melamed M. R., Bertino J. R. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):695–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton W. S., Crowley J. J., Salmon S. S., Grogan T. M., Laufman L. R., Weiss G. R., Bonnet J. D. A phase III randomized study of oral verapamil as a chemosensitizer to reverse drug resistance in patients with refractory myeloma. A Southwest Oncology Group study. Cancer. 1995 Feb 1;75(3):815–820. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950201)75:3<815::aid-cncr2820750311>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lannoy I. A., Koren G., Klein J., Charuk J., Silverman M. Cyclosporin and quinidine inhibition of renal digoxin excretion: evidence for luminal secretion of digoxin. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):F613–F622. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.4.F613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flasch H., Heinz N. Konzentration von Herzglykosiden im Myokard und im Gehirn. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(6):1213–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. M., Hait W. N. Pharmacology of drugs that alter multidrug resistance in cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Sep;42(3):155–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN G., LENDLE L. Nachweis extrakardialer Digitaliswirkungen an der Ratte. II. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953 Jan 5;217(2):184–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager W. D., Fenster P., Mayersohn M., Perrier D., Graves P., Marcus F. I., Goldman S. Digoxin-quinidine interaction Pharmacokinetic evaluation. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 31;300(22):1238–1241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905313002202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori R., Okamura N., Aiba T., Tanigawara Y. Role of P-glycoprotein in renal tubular secretion of digoxin in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1620–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Woodland C., Harper P. A., Koren G. The mechanism of the verapamil-digoxin interaction in renal tubular cells (LLC-PK1). Life Sci. 1993;53(24):PL399–PL403. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90495-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):152–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. S., Wiernik P. H. Neurotoxicity of antineoplastic drugs. Semin Oncol. 1982 Mar;9(1):103–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann J., Rietbrock N., Schnieders B. Tissue distribution and elimination of digoxin and methyldigoxin after single and multiple doses in dogs. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):219–234. doi: 10.1097/00005344-197903000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUTERBACH F. ENTERALE RESORPTION, BILIAERE AUSSCHEIDUNG UND ENTERO-HEPATISCHER KREISLAUF VON HERZGLYKOSIDEN BEI DER RATTE. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 Jun 11;247:391–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauterbach F. Die enterale Sekretion kardiotoner Steroide--Untersuchungen zum Mechanismus des Resorptionsvorganges. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1969;264(3):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS F. I., KAPADIA G. J., KAPADIA G. G. THE METABOLISM OF DIGOXIN IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Aug;145:203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marie J. P., Zittoun R., Sikic B. I. Multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene expression in adult acute leukemias: correlations with treatment outcome and in vitro drug sensitivity. Blood. 1991 Aug 1;78(3):586–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Glasberg M., Frenkel E., Barnett P. Neurotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents after blood-brain barrier modification: neuropathological studies. Ann Neurol. 1983 Sep;14(3):316–324. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Hirai M., Tanigawara Y., Tanaka K., Yasuhara M., Ueda K., Komano T., Hori R. Digoxin-cyclosporin A interaction: modulation of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein in the kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinedo H. M., Giaccone G. P-glycoprotein--a marker of cancer-cell behavior. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 23;333(21):1417–1419. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511233332111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietbrock N., Abshagen U., von Bergmann K., Kewitz H. Pharmacokinetics of digoxin and its 4'''-acetyl- and methylderivates in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(2):171–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00501851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Smit J. J., van Tellingen O., Beijnen J. H., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., van der Valk M. A., Robanus-Maandag E. C., te Riele H. P. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Borst P. Absence of the mdr1a P-Glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone, digoxin, and cyclosporin A. J Clin Invest. 1995 Oct;96(4):1698–1705. doi: 10.1172/JCI118214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Margolies M. N., Smith T. W. Renal and gastrointestinal excretion of ouabain in dog and man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Mar;188(3):615–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegers H. P. Chemotherapy for brain metastases: recent developments and clinical considerations. Cancer Treat Rev. 1990 Mar;17(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0305-7372(90)90076-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikic B. I., Fisher G. A., Lum B. L., Brophy N. A., Yahanda A. M., Adler K. M., Halsey J. Clinical reversal of multidrug resistance. Cancer Treat Res. 1994;73:149–165. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2632-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiness E. Renal tubular secretion of digoxin. Circulation. 1974 Jul;50(1):103–107. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.50.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su S. F., Huang J. D. Inhibition of the intestinal digoxin absorption and exsorption by quinidine. Drug Metab Dispos. 1996 Feb;24(2):142–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawara Y., Okamura N., Hirai M., Yasuhara M., Ueda K., Kioka N., Komano T., Hori R. Transport of digoxin by human P-glycoprotein expressed in a porcine kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Nov;263(2):840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaut F., Tsuruo T., Hamada H., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7735–7738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruo T., Iida H., Tsukagoshi S., Sakurai Y. Overcoming of vincristine resistance in P388 leukemia in vivo and in vitro through enhanced cytotoxicity of vincristine and vinblastine by verapamil. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1967–1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twentyman P. R., Bleehen N. M. Resistance modification by PSC-833, a novel non-immunosuppressive cyclosporin [corrected]. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(12):1639–1642. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90435-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. H., Bates S. E., Fojo A., Bryant G., Zhan Z., Regis J., Wittes R. E., Jaffe E. S., Steinberg S. M., Herdt J. Controlled trial of dexverapamil, a modulator of multidrug resistance, in lymphomas refractory to EPOCH chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995 Aug;13(8):1995–2004. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.8.1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart G. C., Bissett D., Paul J., Jodrell D., Harnett A., Habeshaw T., Kerr D. J., Macham M. A., Soukop M., Leonard R. C. Quinidine as a resistance modulator of epirubicin in advanced breast cancer: mature results of a placebo-controlled randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Sep;12(9):1771–1777. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.9.1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen A. R., Sikic B. I. Multidrug resistance in lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Nov;12(11):2453–2459. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.11.2453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lannoy I. A., Silverman M. The MDR1 gene product, P-glycoprotein, mediates the transport of the cardiac glycoside, digoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91593-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asperen J., Schinkel A. H., Beijnen J. H., Nooijen W. J., Borst P., van Tellingen O. Altered pharmacokinetics of vinblastine in Mdr1a P-glycoprotein-deficient Mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Jul 17;88(14):994–999. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.14.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bergmann K., Abshagen U., Rietbrock N. Quantitative analysis of digoxin, 4'''-acetyldigoxin and 4'''-methyldigoxin and their metabolites in bile and urine of rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;273(1):154–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00508087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


