Abstract
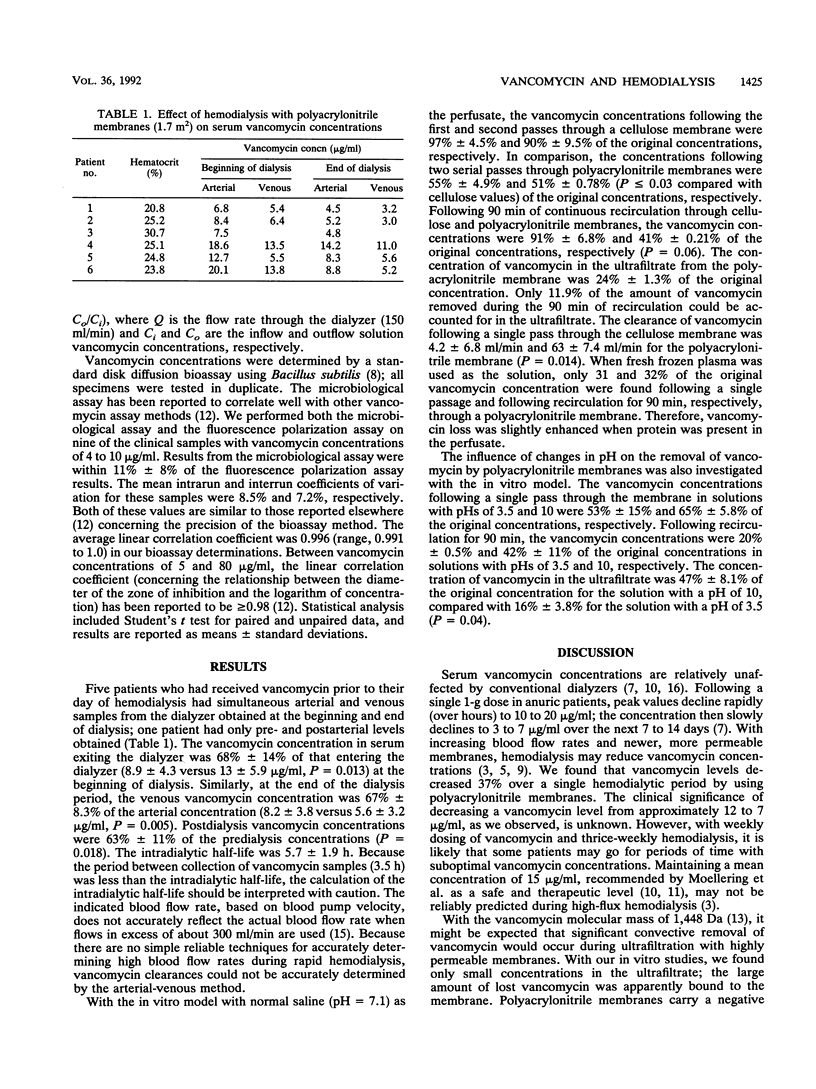
Levels of vancomycin in serum are traditionally believed to be unaffected by hemodialysis. By both in vivo and in vitro techniques, the effects of a newer, more permeable dialyzer membrane on vancomycin concentrations were investigated. Six patients who were receiving vancomycin and undergoing maintenance hemodialysis with polyacrylonitrile dialyzer membranes had postdialysis levels in serum that were 63% of predialysis levels; the intradialytic half-life was 5.7 h. Vancomycin concentrations in serum exiting the dialyzer were 68% of those simultaneously entering the dialyzer at the beginning of dialysis. When polyacrylonitrile and conventional cellulose membranes were perfused in vitro with a recirculating solution of vancomycin, vancomycin concentrations fell to 39 and 91%, respectively, of the original concentration. The vancomycin concentration in the ultrafiltrate collected from the polyacrylonitrile membranes was only 23% of the original perfusate concentration. A significant decrease in the serum vancomycin concentration may occur during hemodialysis with newer high-flux dialyzer membranes. It appears that vancomycin binds to polyacrylonitrile membranes; this binding does not require the presence of protein and is affected by the pH of the perfusate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barg N. L., Supena R. B., Fekety R. Persistent staphylococcal bacteremia in an intravenous drug abuser. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):209–211. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brusch J., Bergeron M. G., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. 3. Intermittent vs. continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):73–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Mauro L. S. Vancomycin dosing chart for use in patients with renal impairment. Am J Kidney Dis. 1988 Jan;11(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(88)80168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha B. A., Quintiliani R., Deglin J. M., Izard M. W., Nightingale C. H. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in anuria. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3 Suppl:S269–S272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanese D. M., Alfrey P. S., Molitoris B. A. Markedly increased clearance of vancomycin during hemodialysis using polysulfone dialyzers. Kidney Int. 1989 Jun;35(6):1409–1412. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Krogstad D. J., Greenblatt D. J. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in normal subjects and in patients with reduced renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3 Suppl:S230–S235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Krogstad D. J., Greenblatt D. J. Vancomycin therapy in patients with impaired renal function: a nomogram for dosage. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Mar;94(3):343–346. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Krogstad D. J., Granich G. G., Murray P. R. Laboratory evaluation of five assay methods for vancomycin: bioassay, high-pressure liquid chromatography, fluorescence polarization immunoassay, radioimmunoassay, and fluorescence immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.311-316.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. R. Structural features of vancomycin. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3 Suppl:S205–S209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf K. W., Rieger J., Doht B., Ansorg R., Scheler F. Drug elimination by hemofiltration. J Dial. 1977;1(7):677–678. doi: 10.3109/08860227709037663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. F., Schniepp B. J., Kurtz S. B., McCarthy J. T. Inaccurate blood flow rate during rapid hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991 Jan;17(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. C., Lee H. S., Ti T. Y., Lee E. J. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous vancomycin in patients with end-stage renal failure. Ther Drug Monit. 1990 Jan;12(1):29–34. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199001000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


