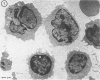
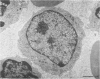
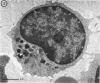
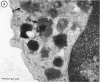
Abstract
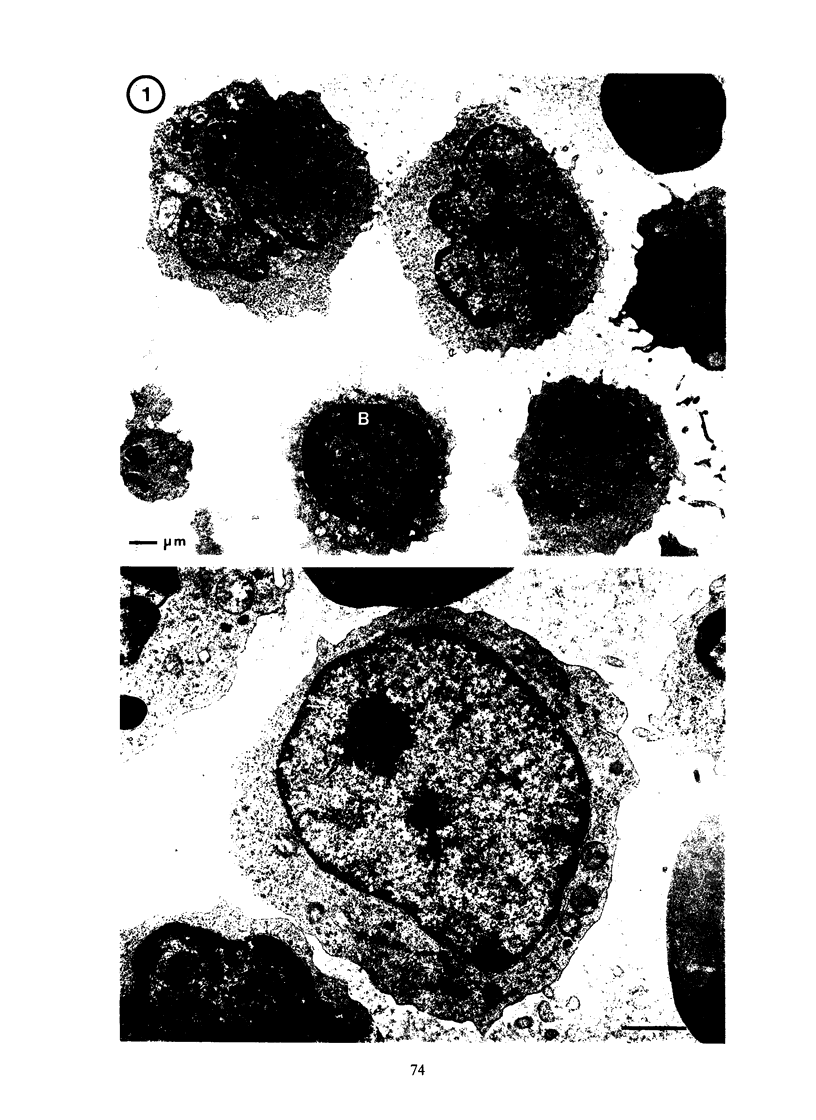
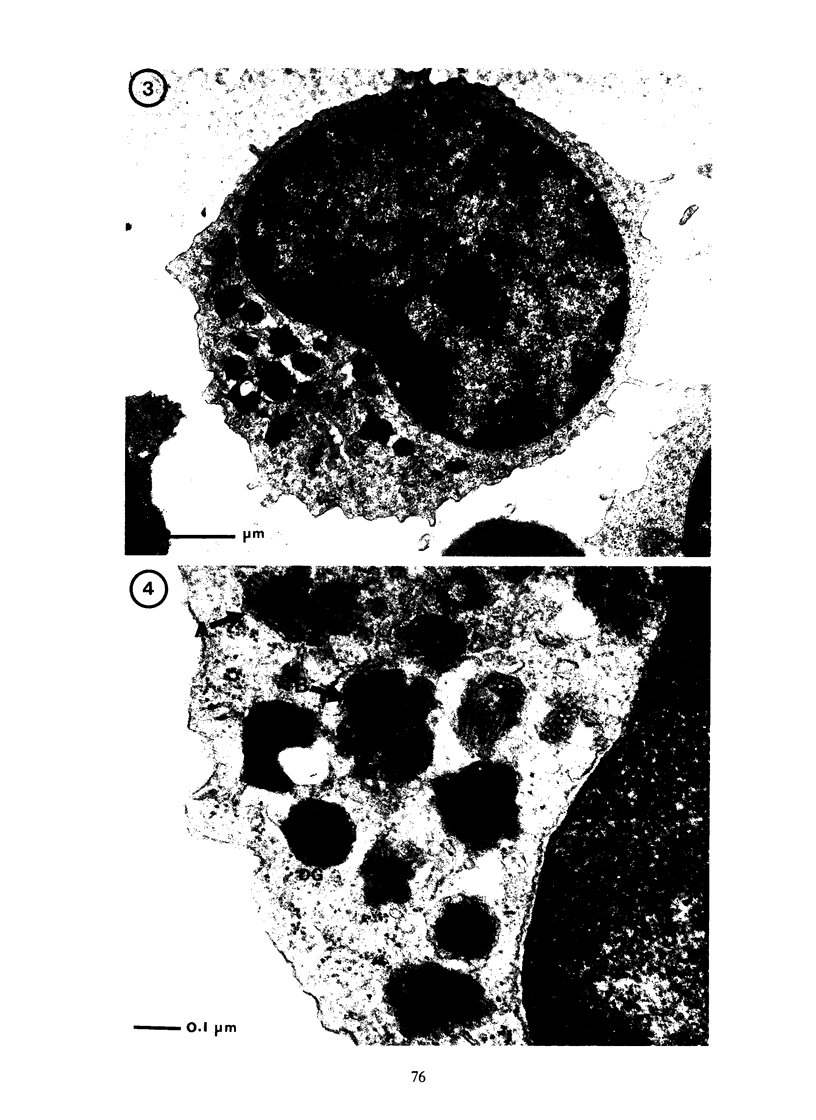
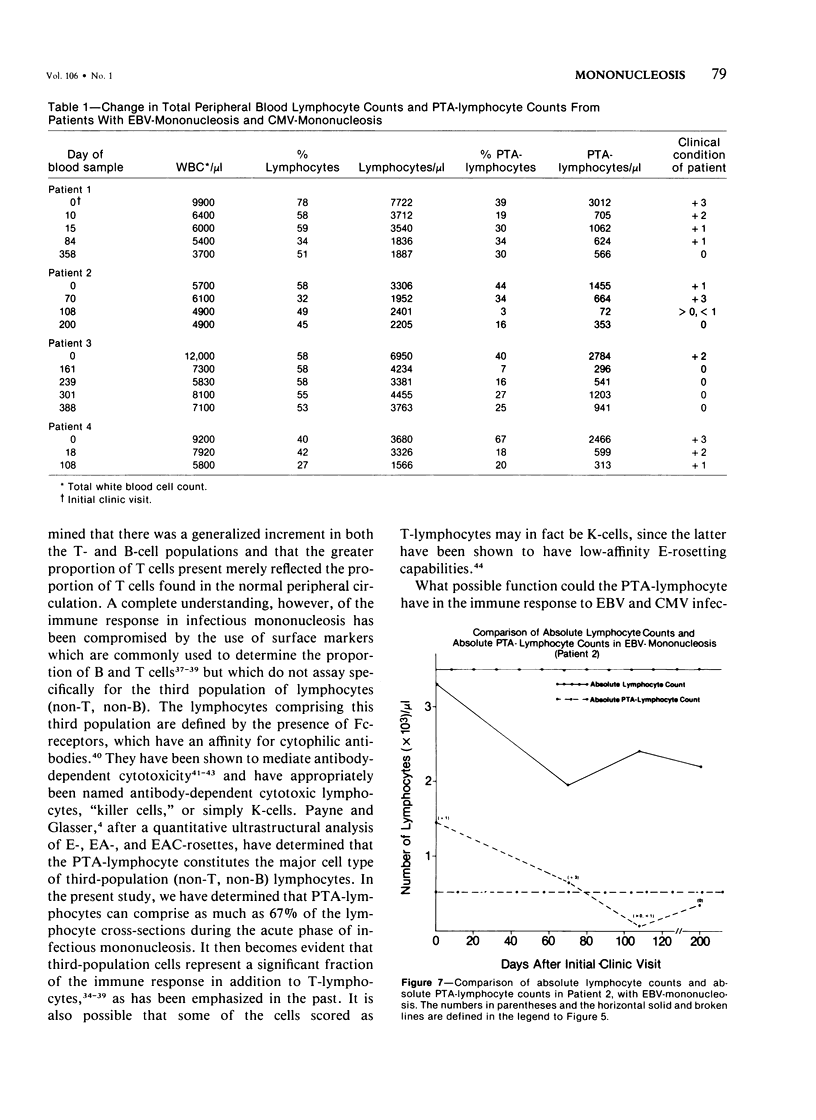
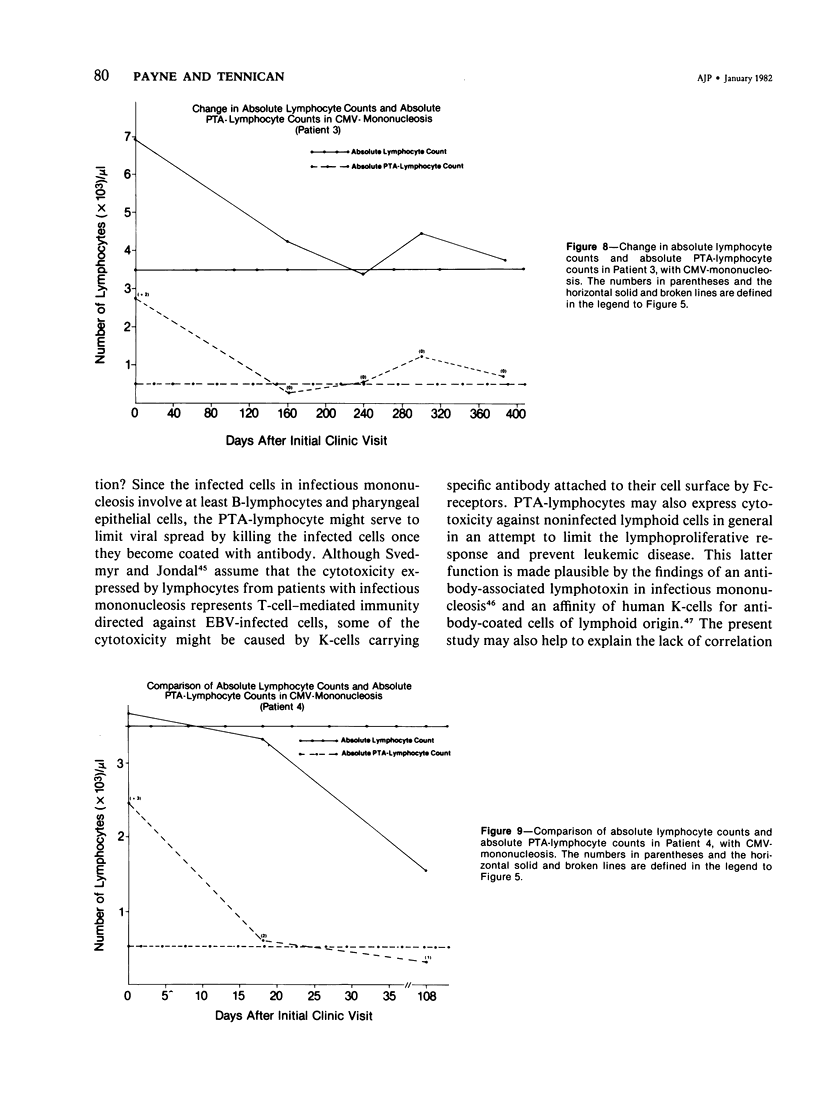
In the normal peripheral circulation there exists a subpopulation of lymphocytes that is ultrastructurally distinct. This lymphocyte is identified with the electron microscope by the presence of cytoplasmic microtubulelike inclusions called parallel tubular arrays (PTAs) and contains Fc-receptors for cytophilic antibody. In this study, lymphocytes containing PTAs (PTA-lymphocytes) were quantitated from serial peripheral blood specimens obtained from two patients with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) mononucleosis and two patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) mononucleosis. These data were then correlated with the clinical state of the patient. It was determined that both the percentage and absolute number of PTA-lymphocytes were highest during the acute phase of the illness. In follow-up specimens, three of the four patients' absolute lymphocyte count fell to within normal limits before the absolute PTA-lymphocyte count. In one patient, the absolute PTA-lymphocyte count was significantly elevated 13 months after the initial clinic visit. Although the PTA-lymphocyte count was highest during the acute phase of the illness, there was no consistent correlation with the clinical state of the patient during follow-up. The estimation of absolute PTA-lymphocyte counts was determined to be valid after a morphometric analysis of the cellular areas occupied by PTAs during the acute and convalescent phases of the disease revealed no statistical differences. Electron microscopy was also performed on the peripheral blood of a patient with syphilis. Although a hematologic workup of this patient during the acute phase of his illness revealed a large number of atypical lymphocytes, electron-microscopic examination of the same specimen revealed both a normal number and a normal percentage of PTA-lymphocytes. The immunologic role of this ultrastructurally distinct third population (non-T, non-B) of lymphocytes, or "killer cells," in the course of infectious mononucleosis is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G. Blood lymphoblasts in infectious mononucleosis express the surface glycoprotein pattern of killer T cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 May;10(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appay M. D., Bariety J., Bretton R. Characterization by immunoperoxidase of the lymphocytes with bundle-shaped tubular (BST) inclusions in human normal peripheral blood. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E., Best J. M., Waller D. K. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM in infectious mononucleosis, Burkitt lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 1972 Jun 3;1(7762):1205–1208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90925-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., DeLor C. J., Clausen K. P., Hurtubise P., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):363–367. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariety J., Amor B., Kahan A., Balafrej J. L., Delbarre F. Ultrastructural anomalies in mononuclear cells of peripheral blood in S.L.E.: Presence of virus-like inclusions. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1971 Aug-Sep;16(7):715–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher R. W., Czarnetzki B. M., Campbell P. B. Ultrastructure of inclusions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1975 Mar;78(3):461–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier A. M., Chess L., Schlossman S. F. Human antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Isolation and identification of a subpopulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes which kill antibody-coated autologous target cells. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1580–1586. doi: 10.1172/JCI108240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunning R. D., Parkin J. Ultrastructural studies of parallel tubular arrays in human lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):59–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C. Lymphoid cells as effectors of immunologic cytolysis. Hosp Pract. 1977 Nov;12(11):57–68. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1977.11707225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. H., Hirshaut Y., Stevens D., Hull E. W., Davis J. H., Carbone P. P. Infectious mononucleosis followed by Burkitt's tumor. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):591–593. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryll A., Cazalis P., Ryckewaert A. Lymphocyte tubular structures in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Sep;30(9):822–826. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.9.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg R. N., Eberle B. J., Williams R. C., Jr T- and B-cells in peripheral blood during infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):104–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Cadoni A., Franzi A. T., Ghigliotti C., Leprini A., Zicca A., Grossi C. E. Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Similarities between the cells of the third population and TG lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):562–570. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser L., Payne C., Corrigan J. J., Jr The in vivo development of plasma cells: a morphologic study of human cerebrospinal fluid. Neurology. 1977 May;27(5):448–459. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.5.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. R., Sylvester R. A., Talal N., Tuffanelli D. L. Virus-like structures in lymphocytes of patients with systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Sep;79(3):396–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-3-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Schaff Z. Significance of tubuloreticular inclusions in the pathobiology of human diseases. Pathobiol Annu. 1976;6:221–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
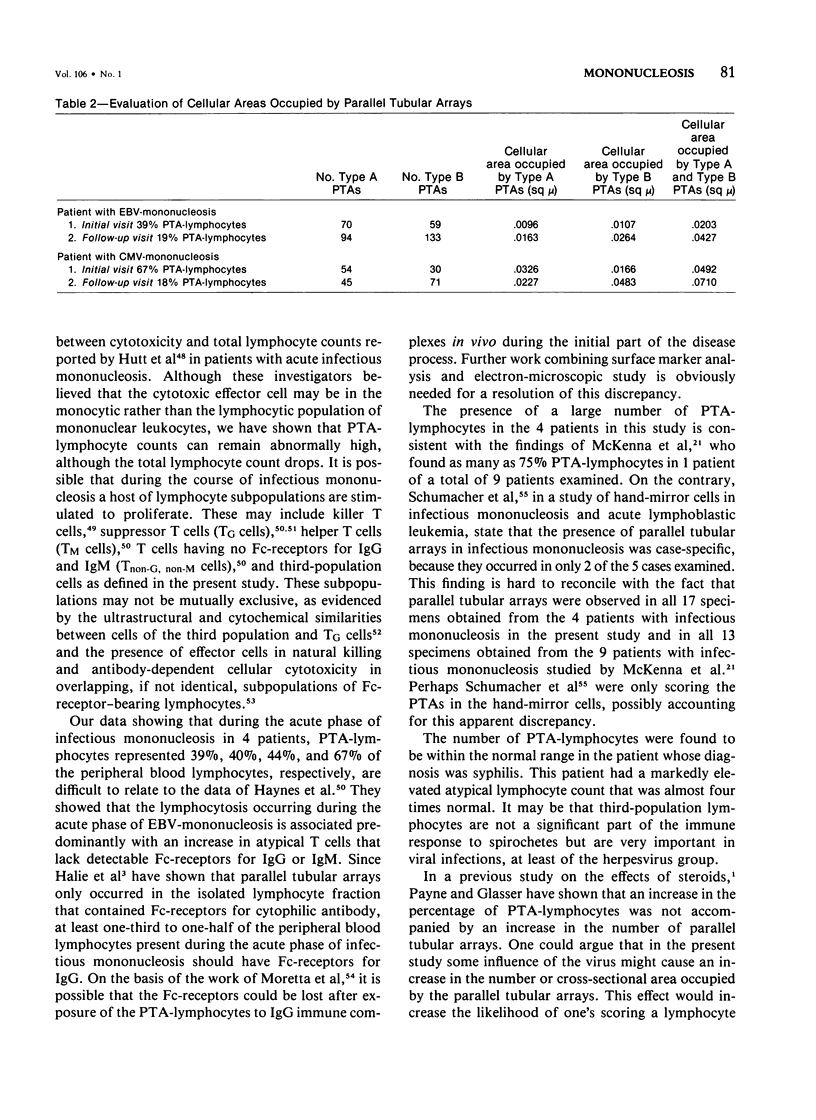
- Halie M. R., Splett-Romascano M., Molenaar I., Nieweg H. O. Parallel tubular structures in lymphocytes. I. Occurrence in patients with Hodgkin's Disease. Acta Haematol. 1975;54(1):18–26. doi: 10.1159/000208046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Schooley R. T., Grouse J. E., Payling-Wright C. R., Dolin R., Fauci A. S. Characterization of thymus-derived lymphocyte subsets in acute Epstein-Barr virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):699–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland H. C. Atypical lymphocytes. Morphologic features. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Aug;49(8):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig T., Jeremic M., Stavem P. A new type of inclusion bodies in lymphocytes. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(2):81–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb01723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. W., Lattos D. B., Nelson D. B., Reeb K., Hong R. Antibody-associated lymphotoxin in acute infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1033–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI107268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn D., Andreewa P., Rodt H., Thiel E., Eulitz M. Demonstration of the Fc-receptor of blood cells by soluble peroxidase-anti-peroxidase (PAP) complexes. Blut. 1978 May 18;36(5):263–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01880677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn D. Neue Organelle im peripheren Lymphozyten? Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1968 Nov 1;93(44):2099–2100. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1110887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt L. M., Huang Y. T., Dascomb H. E., Pagano J. S. Enhanced destruction of lymphoid cell lines by peripheral blood leukocytes taken from patients with acute infectious mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura M., Block S. R., Mellors R. C. Electron microscopic study of distinctive structures in peripheral blood lymphocytes obtained from twins with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):561–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna R. W., Parkin J., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Kersey J. H., Brunning R. D. Ultrastructural, cytochemical, and membrane surface marker characteristics of the atypical lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):505–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna R. W., Parkin J., Kersey J. H., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Peterson L., Brunning R. D. Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder with unusual clinical, morphologic, ultrastructural and membrane surface marker characteristics. Am J Med. 1977 Apr;62(4):588–596. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Romanzi C. A. Loss of Fc receptors for IgG from human T lymphocytes exposed to IgG immune complexes. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):618–620. doi: 10.1038/272618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noonan S. M., Weiss L., Riddle J. M. Ultrastructural observations of cytoplasmic inclusions in Tay-Sachs lymphocytes. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Nov;100(11):595–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Sheldon P. J., Holborow E. J. T- and B-cell subpopulations in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. B-cell characteristics of human peripheral and cord blood lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. Selective transformation of B lymphocytes by E.B. virus. Lancet. 1973 Jul 14;2(7820):93–94. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Perlin E. Atypical lymphocytes in acute infectious mononucleosis. Identification by multiple T and B lymphocyte markers. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1145–1148. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Glasser L. Evaluation of surface markers on normal human lymphocytes containing parallel tubular arrays: a quantitative ultrastructural study. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):567–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Glasser L. The effect of steroids on peripheral blood lymphocytes containing parallel tubular arrays. Am J Pathol. 1978 Sep;92(3):611–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Jones J. F., Sieber O. F., Jr, Fulginiti V. A. Parallel tubular arrays in severe combined immunodeficiency disease: an ultrastructural study of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):55–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Nagle R. B. Complement receptors on normal human lymphocytes containing parallel tubular arrays. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jun;99(3):645–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. E., Brown N., Andiman W., Halliday K., Francke U., Robert M. F., Andersson-Anvret M., Horstmann D., Miller G. Diffuse polyclonal B-cell lymphoma during primary infection with Epstein-Barr virus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1293–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Thomas W. J., Creegan W. J., Pitts L. L. Infectious mononucleosis and acute lymphoblastic leukemia--hand mirror cells: a qualitative and quantitative ultrastructural study. Am J Hematol. 1980;9(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830090108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwendemann G. Lymphocyte inclusions in the juvenile type of generalized ceroid-lipofuscinosis. An electron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1976 Dec 21;36(4):327–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00699638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon P. J., Hemsted E. H., Papamichail M., Holborow E. J. Thymic origin of atypical lymphoid cells in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 May 26;1(7813):1153–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiftan T. A., Mendelsohn J. The circulating "atypical" lymphocyte. Hum Pathol. 1978 Jan;9(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Dechairo D., Miller G. Malignant lymphoma in cottontop marmosets after inoculation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2487–2491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. T., Bausher J. C. Epstein-Barr virus infection in relation to infectious mononucleosis and Burkitt's lymphoma. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:39–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stekhoven J. H., van Haelst U. J. Ultrastructural study of so-called curvilinear bodies and fingerprint structures in lymphocytes in late-infantile amaurotic idiocy. Acta Neuropathol. 1976 Aug 16;35(4):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Byron K. S., Brewster F. E., Purtilo D. T. Deficient natural killer cell activity in x-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):543–545. doi: 10.1126/science.6158759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Jondal M. Cytotoxic effector cells specific for B Cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus are present in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Magrath I., Koski I., Dooley N., Blaese M. Activation of suppressor T cells during Epstein-Barr-virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 22;301(21):1133–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911223012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virolainen M., Andersson L. C., Lalla M., von Essen R. T-lymphocyte proliferation in mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Nov;2(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Boozer R. B., Herberman R. B. Low affinity E-rosette formation by the human K cell. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):90–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Giant organelles containing tubules in Chediak-Higashi lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1972 Nov;69(2):225–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Froland S. S., Michaelsen T. E. Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity mediated by human Fc-receptor-bearing cells lacking markers for B- and T-lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(1):139–154. doi: 10.1159/000231208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzleben C. L. Lymphocyte inclusions in late-onset amaurotic idiocy. Value as a diagnostic test and genetic marker. Neurology. 1972 Oct;22(10):1075–1078. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.10.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yata J., Desgranges C., de Thé G., Tachibana T. Lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Properties of atypical cells and origin on the lymphoblastoid lines. Biomedicine. 1973 Nov 20;19(11):479–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The ultrastructure of lymphocytes. Semin Hematol. 1969 Jan;6(1):4–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]