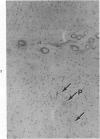
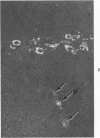
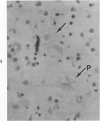
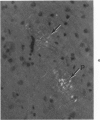
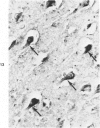
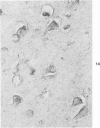
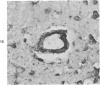
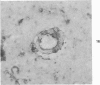
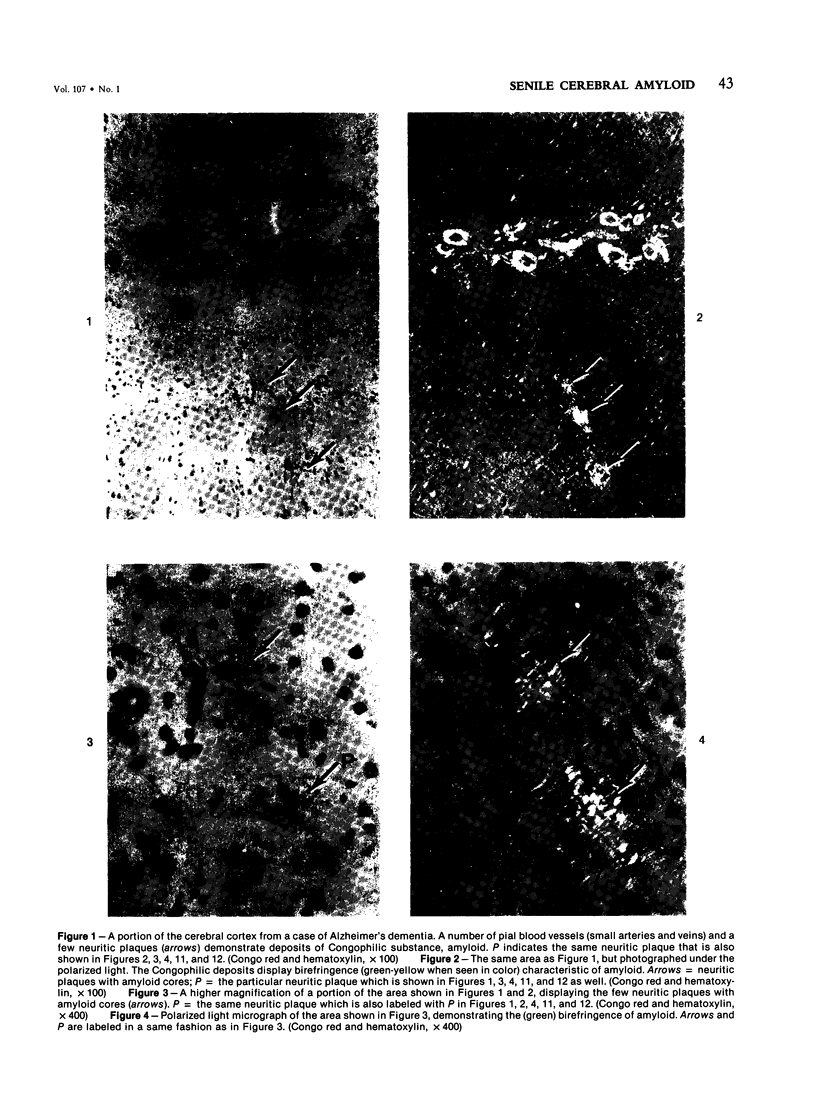
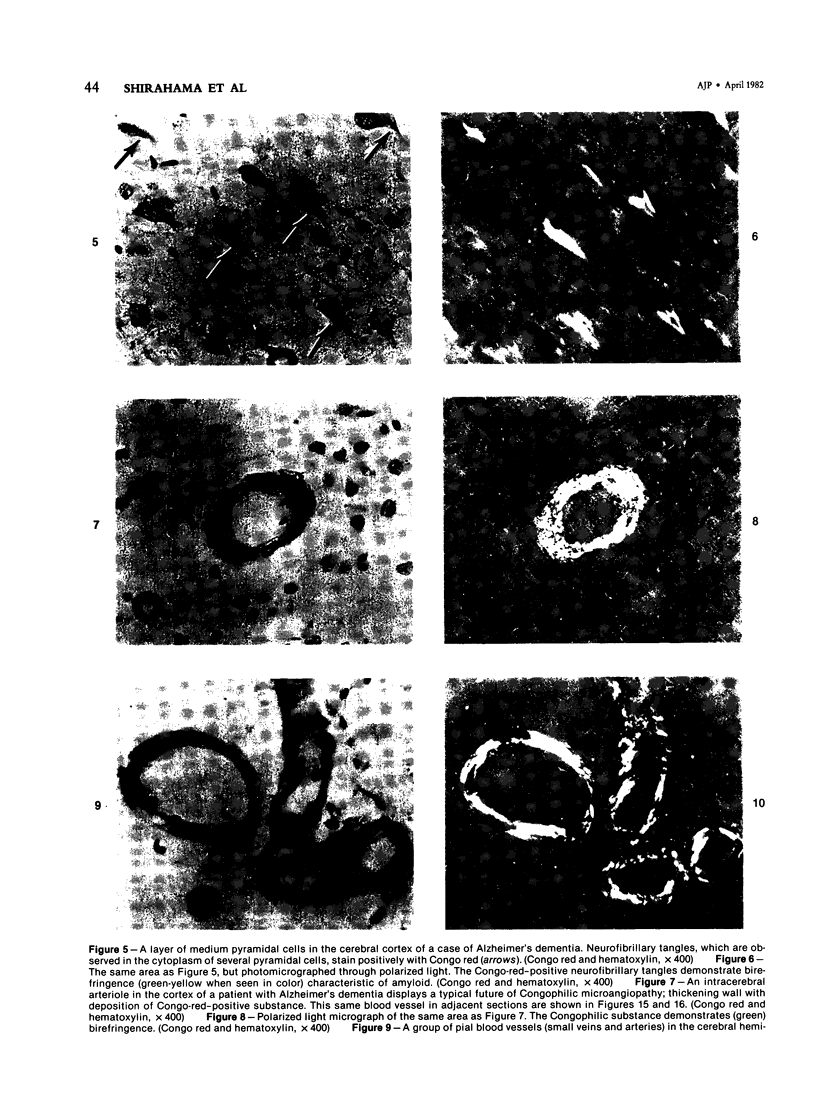
Abstract
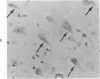
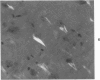
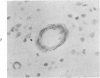
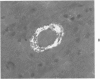
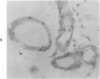
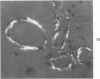
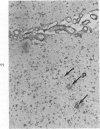
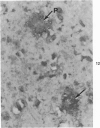
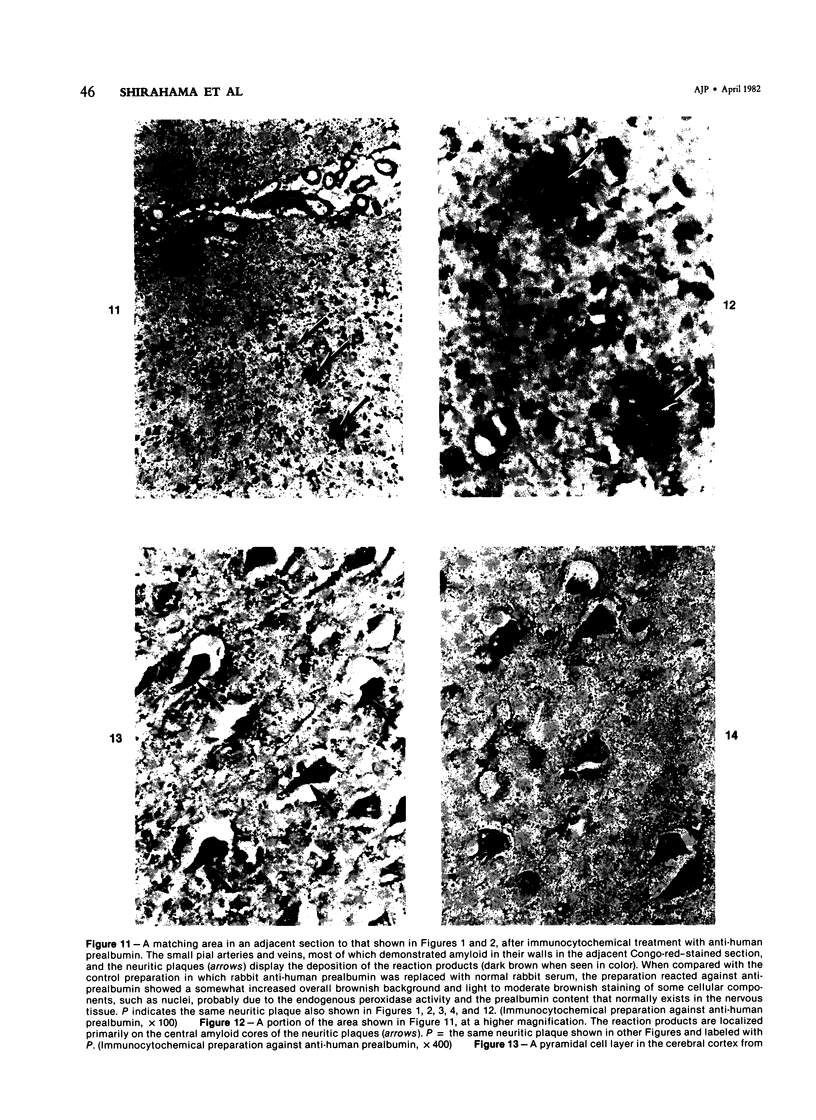
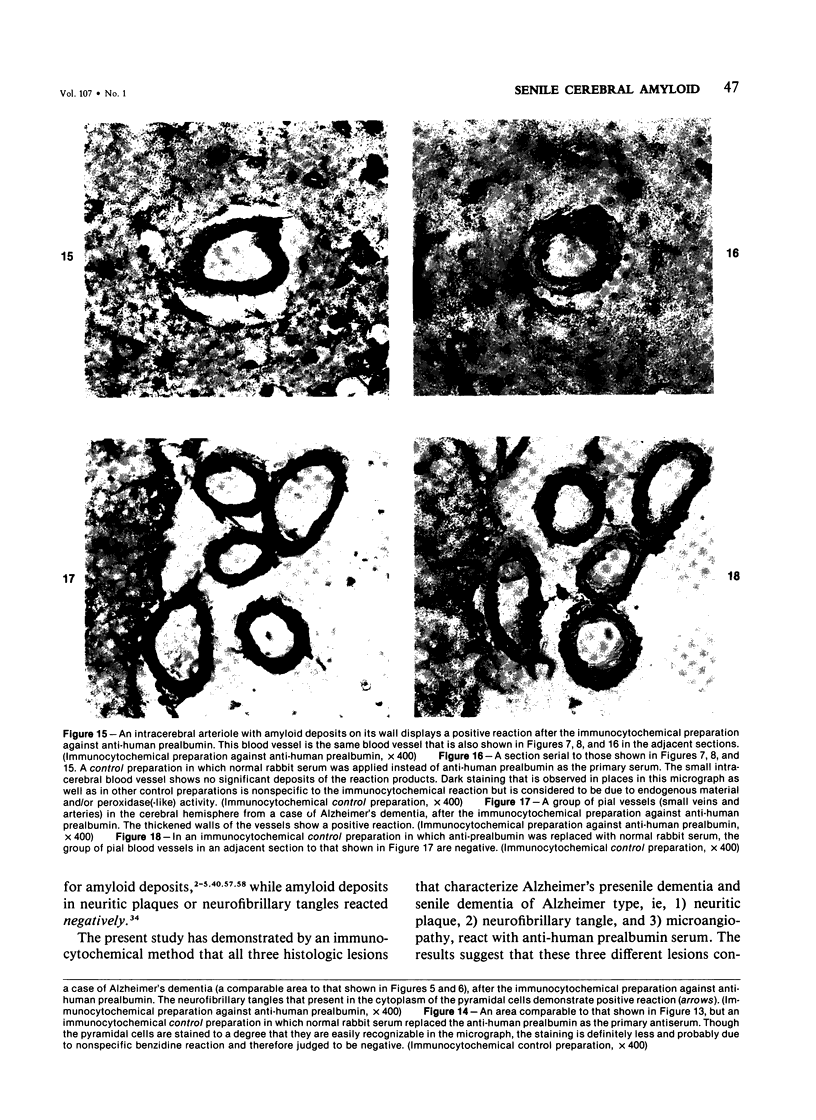
Three lesions that characterize the nosologic findings in the brain of Alzheimer's presenile dementia and senile dementia of Alzheimer type, ie, neuritic plaque, neurofibrillary tangle, and microangiopathy, all are frequently associated with amyloid deposition. There has been some question, however, as to whether these lesions share the same etiology. Moreover, the specific chemical nature of amyloid associated with these lesions has not yet been determined. In the present study, formalin-fixed paraffin sections of the affected brains were tested immunocytochemically for their reactivity against antiserum to prealbumin (recently disclosed as the major constituent of amyloid associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy as well as senile cardiac amyloid) and known components of other types of amyloid (AA, AP, etc.). The results demonstrated that amyloid deposits in all three lesions reacted with anti-prealbumin, suggesting that it is a common constituent of these lesions. Indeed, it is likely that prealbumin is the major constituent of amyloid associated with neuritic plaque, neurofibrillary tangle, and microangiopathy.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952 Sep;75(3):408–427. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders R. F., Nordstoga K., Natvig J. B., Husby G. Amyloid-related serum protein SAA in endotoxin-induced amyloidosis of the mink. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):678–683. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Chemical classes of amyloid substance. Am J Pathol. 1971 Oct;65(1):231–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D. Partial amino acid sequence homology between an heredofamilial amyloid protein and human plasma prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block P. J., Skinner M., Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Identity of a peritoneal fluid immunoglobulin light chain and the amyloid fibril in primary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jul-Aug;19(4):755–759. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197607/08)19:4<755::aid-art1780190416>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S. The constitution and genesis of amyloid. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1965;4:159–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Wegelius O. Classification of amyloid: 1979--1980. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):644–645. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. P., Figueira A. S., Bravo F. R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen N., Ericsson L. H., Pearsall N., Lagunoff D., Benditt E. P. Mouse amyloid protein AA: Homology with nonimmunoglobulin protein of human and monkey amyloid substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):964–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Terry W., Harada M., Isersky C., Page D. Amyloid fibril proteins: proof of homology with immunoglobulin light chains by sequence analyses. Science. 1971 Jun 11;172(3988):1150–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3988.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G., Offord R. E. The subunit structure of prealbumin. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):309–317. doi: 10.1042/bj1250309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein, prealbumin, and vitamin A transport. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1976;5:313–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Greenwald M., Frangione B., Pras M., Franklin E. C. The amino acid sequence of duck amyloid A (AA) protein. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1113–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Johnson A. B., Wisniewski H. M., Terry R. D., Iqbal K. Evidence that Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles originate from neurotubules. Lancet. 1979 Mar 17;1(8116):578–580. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Kuhn R. W., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Eriksen N., Benditt E. P. Amino acid sequence of monkey amyloid protein A. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):2934–2938. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Wisniewski H. M., Terry R. D. Chemical relationship of the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's dementia to normal human neurofilaments and neurotubules. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 24;142(2):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S., Canfield R. E., Morgan F. J. The amino acid sequence of human plasma prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6796–6805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Guyer R., Terry W. D., Glenner G. G. Chemical evidence for lambda-type amyloid fibril proteins. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):891–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Pras M. The amino acid sequence of a major nonimmunoglobulin component of some amyloid fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2773–2776. doi: 10.1172/JCI107098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Skinner M., Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Fractionation of primary amyloid fibrils. Characterization and chemical interaction of the subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang H. K. High-resolution electron microscopic analysis of the amyloid fibril in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Nov;39(6):621–631. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198011000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Austin J., Rinehart R., Trueb L., Hutchinson J., Stukenbrok H., Miles B. Studies in ageing of the brain. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Alzheimer plaques and cores. Arch Neurol. 1971 Sep;25(3):198–211. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490030024002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Ewen S. W., Polak J. M. The genesis of apudamyloid in endocrine polypeptide tumours: histochemical distinction from immunamyloid. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1972;10(2):93–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02899719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. M., Spicer S. S. Histochemical similarity of senile plaque amyloid to apudamyloid. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1977 Nov 17;376(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00432582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst A., Heitz P. U., Ulrich J. Histochemical analysis of senile plaque amyloid and amyloid angiopathy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1980;388(3):327–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00430862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahama T., Skinner M., Cohen A. S. Immunocytochemical identification of amyloid in formalin-fixed paraffin sections. Histochemistry. 1981;72(2):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00517130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Amyloid fibril protein related to immunoglobulin lambda-chains. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1433–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cathcart E. S., Cohen A. S., Benson M. D. Isolation and identification by sequence analysis of experimentally induced guinea pig amyloid fibrils. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):871–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S., Shirahama T., Cathcart E. S. P-component (pentagonal unit) of amyloid: isolation, characterization, and sequence analysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):604–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The prealbumin nature of the amyloid protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)-swedish variety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1326–1332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Shirahama T., Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Murine amyloid protein AA in casein-induced experimental amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1977 Apr;36(4):420–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Natvig J. B., Husby G., Juul J. The complete amino acid sequence of a prototype immunoglobulin-lambda light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein AR. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1950561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Westermark P., Natvig J. B. Characterization of amyloid fibril proteins from medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):993–998. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Westermark P., Natvig J. B. Senile cardiac amyloid is related to prealbumin. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(6):503–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D., Page D. L., Kimura S., Isobe T., Osserman E. F., Glenner G. G. Structural identity of Bence Jones and amyloid fibril proteins in a patient with plasma cell dyscrasia and amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1276–1281. doi: 10.1172/JCI107295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torack R. M. Congophilic angiopathy complicated by surgery and massive hemorrhage. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):349–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torack R. M., Lynch R. G. Cytochemistry of brain amyloid in adult dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(3):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00688021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Grimelius L., Polak J. M., Larsson L. I., Van Noorden S., Wilander E., Pearse A. G. Amyloid in polypeptide hormone-producing tumors. Lab Invest. 1977 Aug;37(2):212–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Johansson B., Natvig J. B. Senile cardiac amyloidosis: evidence of two different amyloid substances in the ageing heart. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(4):303–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Natvig J. B., Johansson B. Characterization of an amyloid fibril protein from senile cardiac amyloid. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):631–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Shirahama T., Skinner M., Norén P., Cohen A. S. Amyloid P-component (protein AP) in localized amyloidosis as revealed by an immunocytochemical method. Histochemistry. 1981;71(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00507821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. C., 2nd, Jacobson R. J., Binder R. A., Linke R. P., Glenner G. G. Immunoglobulin D myeloma and amyloidosis: immunochemical and structural studies of Bence Jones and amyloid fibrillar proteins. Blood. 1975 Nov;46(5):713–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Narang H. K., Terry R. D. Neurofibrillary tangles of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]