Abstract
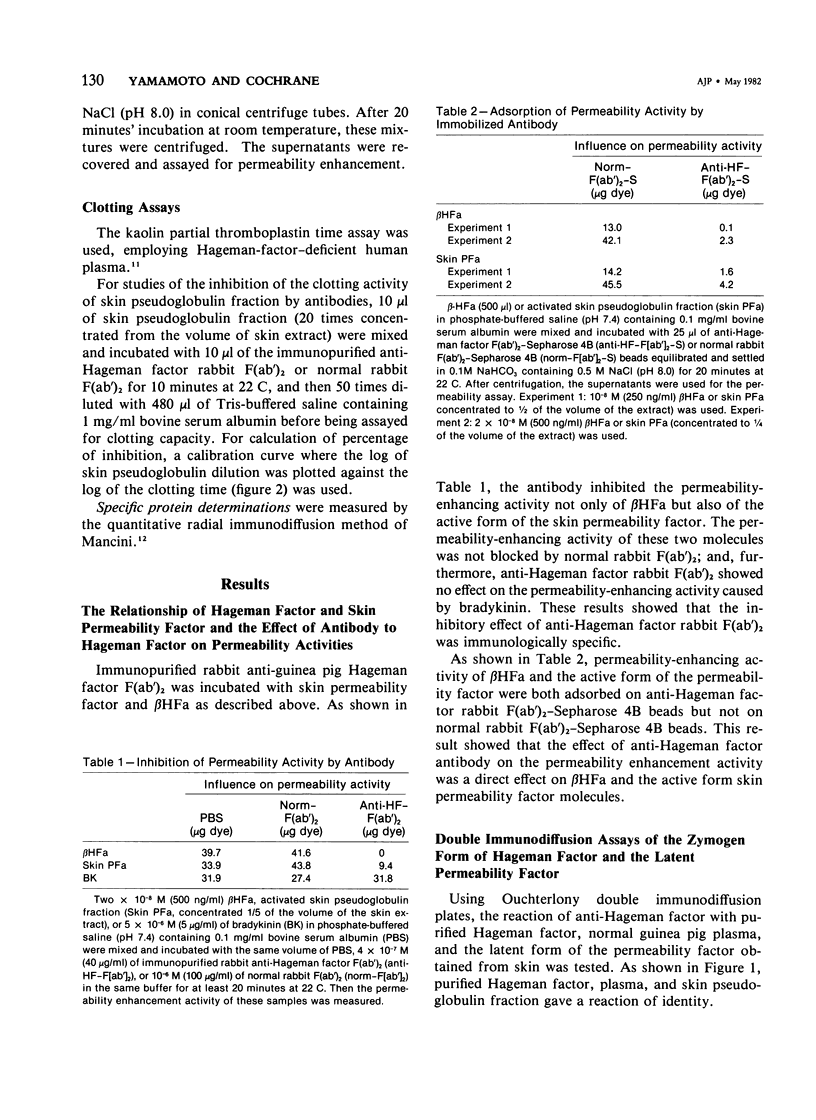
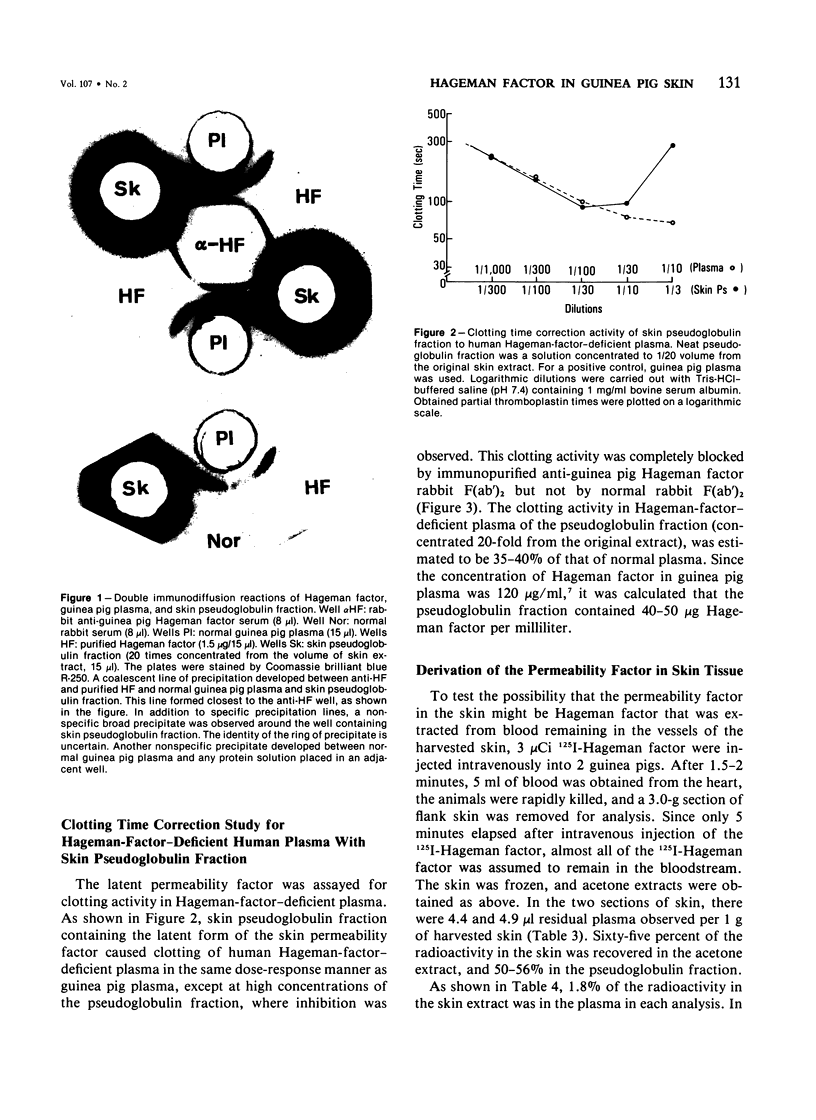
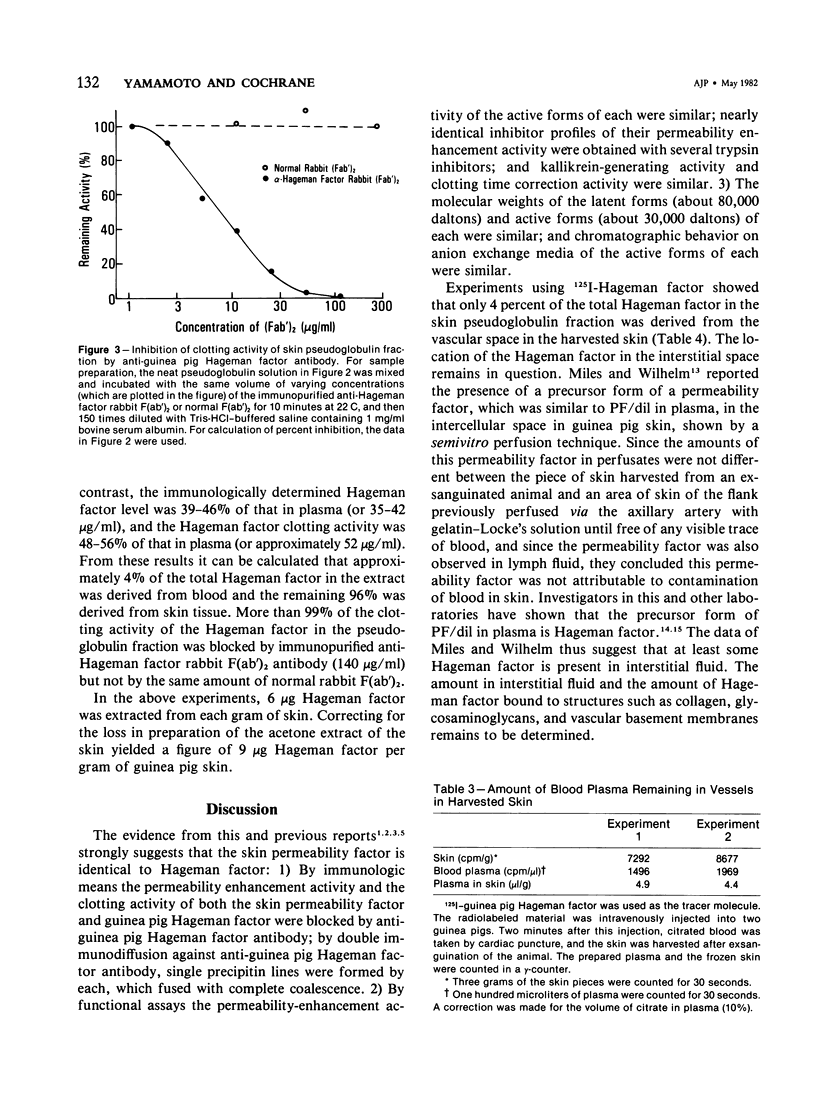
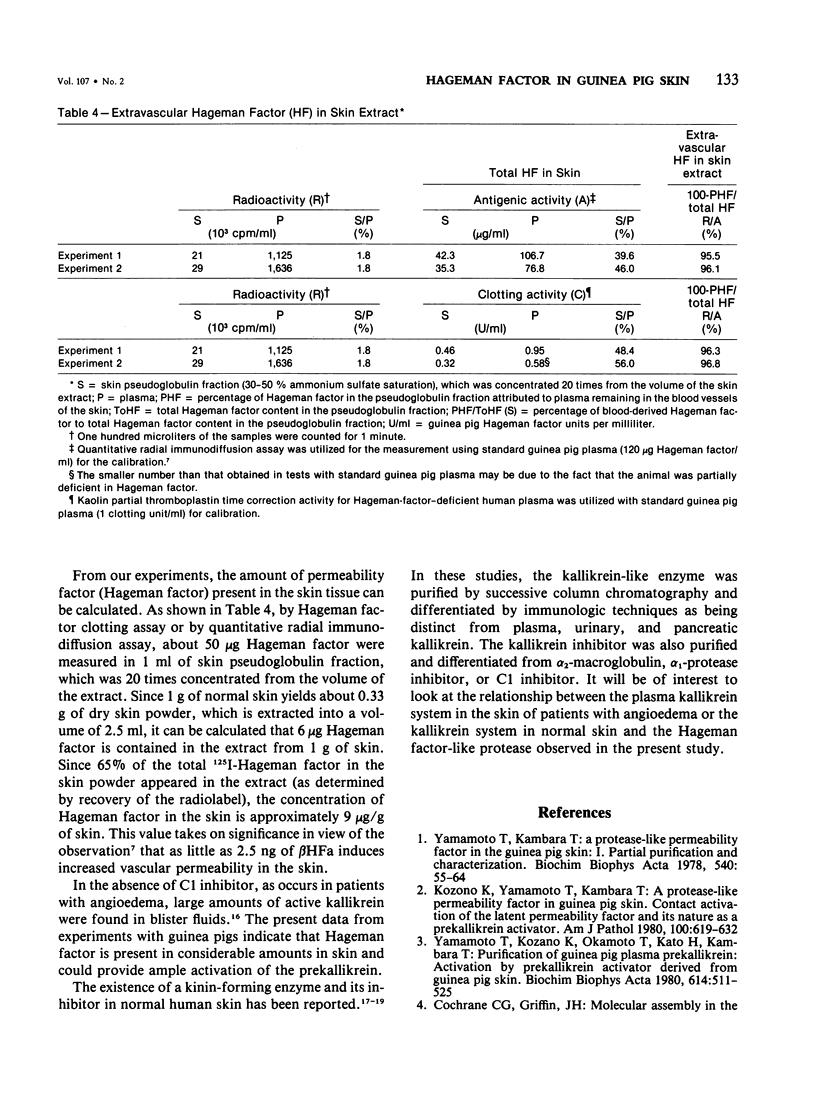
Vascular permeability enhancement activity of the protease-like permeability factor derived from guinea pig skin and of active guinea pig Hageman factor (beta HFa) were both inhibited by anti-guinea pig Hageman factor rabbit F(ab')2 antibody. The permeability activity of both factors was also absorbed on anti-Hageman factor F(ab')2-Sepharose beads. The latent form of the permeability factor derived from skin extracts produced a single immunoprecipitation line with anti-Hageman factor and gave a reaction of identity with a precipitation band developing between purified Hageman factor and anti-Hageman factor. The latent permeability factor in the fraction corrected the clotting activity of Hageman-factor-deficient human plasma. The clotting activity was also blocked by anti-Hageman factor F(ab')2 antibody. From these results, it was concluded that the skin permeability factor was immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from Hageman factor of plasma. Extracts were obtained from skin of guinea pigs given intravenous injections of 125I-guinea pig Hageman factor immediately before sacrifice to calculate the amount of Hageman factor in the extravascular tissue space of the skin. The pseudoglobulin fractions of the extracts containing a concentration of Hageman factor of approximately 9 microgram of Hageman factor per gram of skin. This was determined both by immunologic means and procoagulant activity. Only 4% of the Hageman factor in the extract was obtained from the intravascular plasma volume of the skin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. Molecular assembly in the contact phase of the Hageman factor system. Am J Med. 1979 Oct;67(4):657–664. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Prograis L. J., Jr, Cochrane C. G. Detection of active kallikrein in induced blister fluids of hereditary angioedema patients. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):742–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. R., Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. The relationship between PF-DIL and activated human Hageman factor. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozono K., Yamamoto T., Kambara T. A proteaselike permeability factor in guinea pig skin: contact activation of the latent permeability factor and its nature as a prekallikrein activator. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):619–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., WILHELM D. L. Distribution of globulin permeability factor and its inhibitor in the tissue fluid and lymph of the guinea pig. Nature. 1958 Jan 11;181(4602):96–98. doi: 10.1038/181096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi S., Webster M. E. Vascular permeability factors (PF/Nat and PF/Dil)--their relationship to Hageman factor and the kallikrein-kinin system. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 1;24(5):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MILES A. A. THE INDUCTION OF PERMEABILITY-INCREASING ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA BY ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:328–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toki N., Yamura T. Further studies on a new kallikrein inhibitor in human skin--its purification and characterization. Arch Dermatol Res. 1980;267(3):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00403851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toki N., Yamura T. Kinin-forming enzyme in human skin: the purification and characterization of a kinin-forming enzyme. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Oct;73(4):297–302. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toki N., Yamura T. Plasma-kinin-forming enzyme in human skin: extraction and column chromatographic separation of plasma-kinin-forming enzyme and its inhibitor. Acta Derm Venereol. 1978;58(5):395–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaka K., Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Simple method for quantitation of enhanced vascular permeability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1384–1387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Cochrane C. G. Guinea pig Hageman factor as a vascular permeability enhancement factor. Am J Pathol. 1981 Nov;105(2):164–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 1. Partial purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 19;540(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 2. In vitro activation of the latent form permeability factor by weakly acidic phosphate buffer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;542(2):222–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Okamoto T., Kato H., Kambara T. Purification of guinea-pig plasma prekallikrein. Activation by prekallikrein activator derived from guinea-pig skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 7;614(2):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



