Abstract
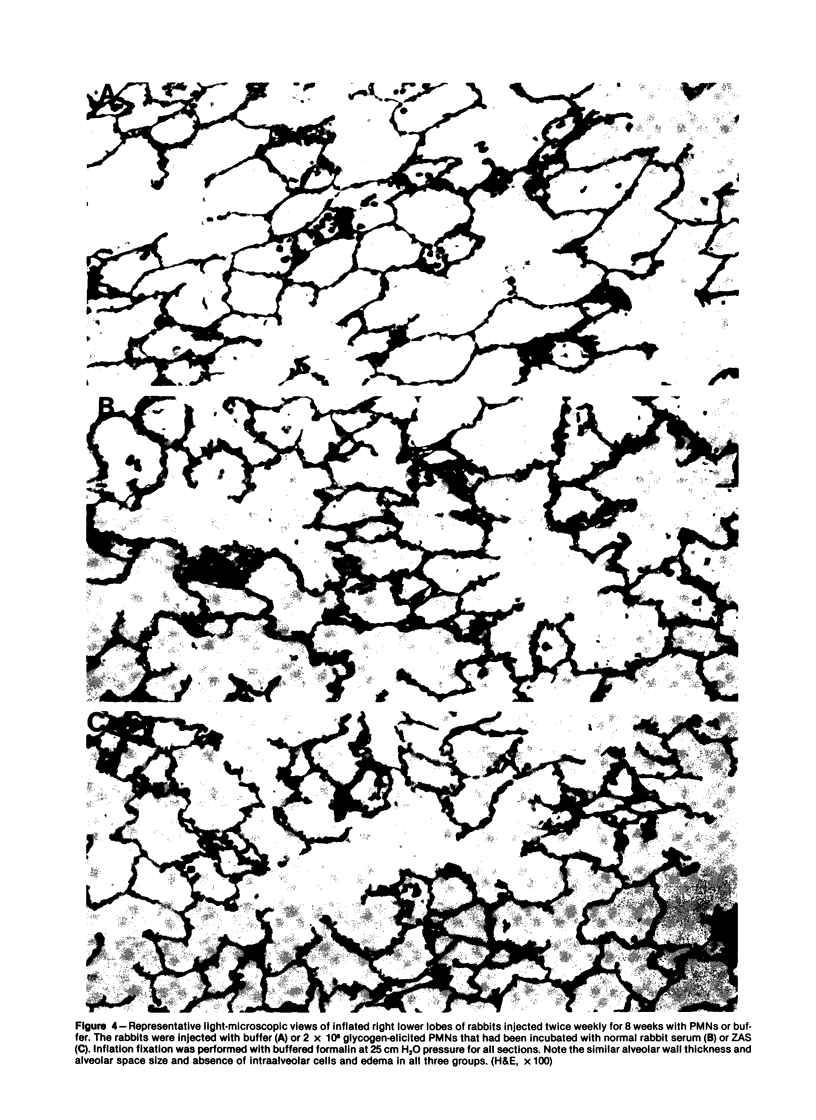
Rabbits were injected intravenously with glycogen-elicited allogenic peritoneal polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes (PMNs) for the study of the light-microscopic effects of acute and chronic sequestration of PMNs in the pulmonary vascular bed. Infusion of 51Cr-labeled PMNs demonstrated that approximately half of the cells were sequestered in the lung, with no difference observed between PMNs incubated with 10% normal rabbit serum and PMNs incubated with 10% zymosan-activated serum (ZAS) prior to infusion. Quantitative histologic studies demonstrated that the number of ZAS-activated PMNs present in the alveolar walls at 4 hours rapidly declined over the ensuing 20 hours and was back to buffer control values by 48 hours. No PMNs, red cells, or signs of edema were visible in the alveolar spaces. In rabbits injected chronically (twice weekly for 8 weeks) with 2 x 10(8) PMNs (ZAS-stimulated and unstimulated), no qualitative or quantitative (mean linear intercept) evidence for damage to alveolar walls was observed. These studies indicate that acute and chronic pulmonary sequestration of PMNs activated in vitro, infused in the absence of activated serum products, does not cause light-microscopic evidence of lung injury.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anuras J., Cheng F. H., Richerson H. B. Experimental leukocyte-induced pulmonary vasculitis with inquiry into mechanism. Chest. 1977 Mar;71(3):383–387. doi: 10.1378/chest.71.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN H. R., KELLY K. H., CORDES F. L. The sequestration and visceral circulation of leukocytes in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):850–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolanowski P. J., Bauer J., Machiedo G., Neville W. E. Prostaglandin influence on pulmonary intravascular leukocytic aggregation during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977 Feb;73(2):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai U., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H., Arroyave C. V., Ward P. A. Acute inflammatory pulmonary reactions induced by chemotactic factors. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Craddock P. R., McCullough F., Kronenberg R. S., Dalmasso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement activation and pulmonary leukotasis during nylon fiber filtration leukapheresis. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R., Scott J. L. Leukocyte labeling with 51-Chromium. I. Technic and results in normal subjects. Blood. 1968 Nov;32(5):738–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Effect of intravascular complement activation on granulocyte adhesiveness and distribution. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):731–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. W., Nissenson A. R., Miller J., Smith R. T., Narins R. G., Sullivan S. F. Hypoxemia and pulmonary gas exchange during hemodialysis. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Feb;50(2):259–264. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Butler C., Shaw J. O., Henson P. M. Intravascular aggregation and pulmonary sequestration of platelets during IgE-induced systemic anaphylaxis in the rabbit: abrogation of lethal anaphylactic shock by platelet depletion. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2185–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Henson P. M., Henson J., Webster R. O. Lung inflammation induced by complement-derived chemotactic fragments in the alveolus. Lab Invest. 1980 May;42(5):547–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. Measurement of pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 May;95(5):752–764. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittels E. H., Coalson J. J., Welch M. H., Guenter C. A. Pulmonary intravascular leukocyte sequestration. A potential mechanism of lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 May;109(5):502–509. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.109.5.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]