Abstract
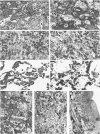
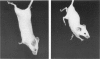
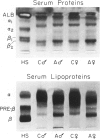
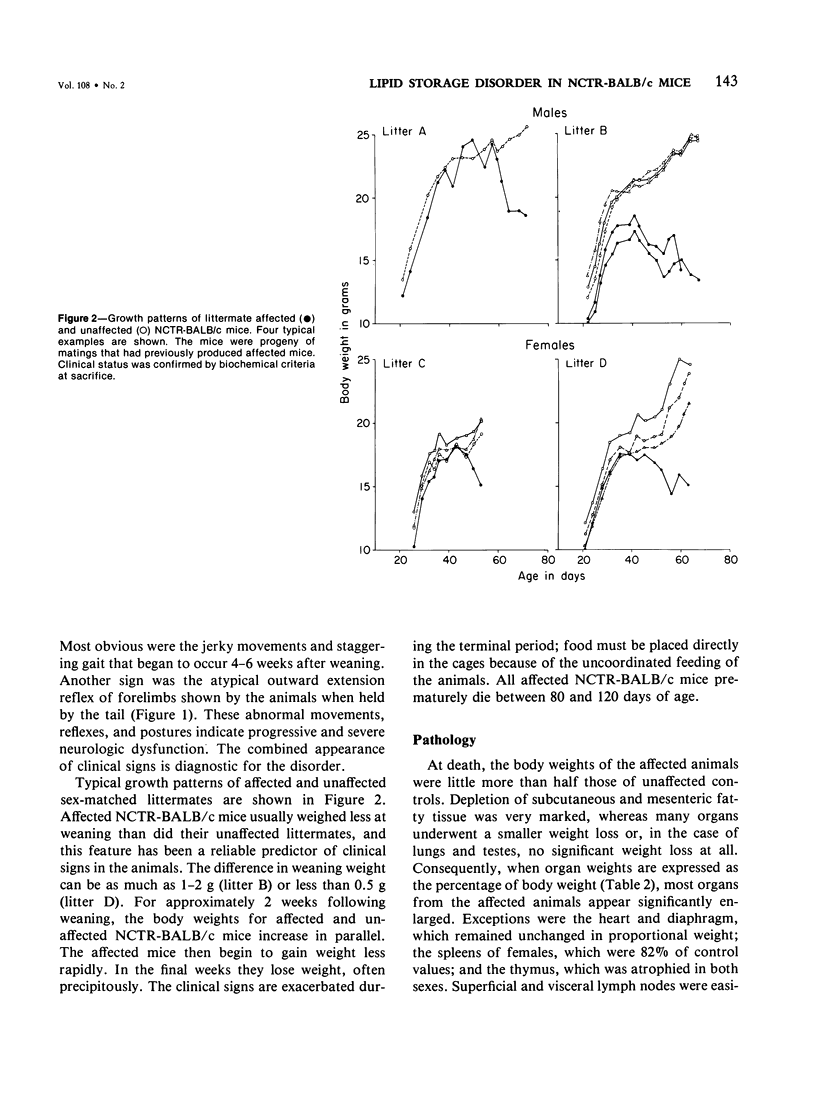
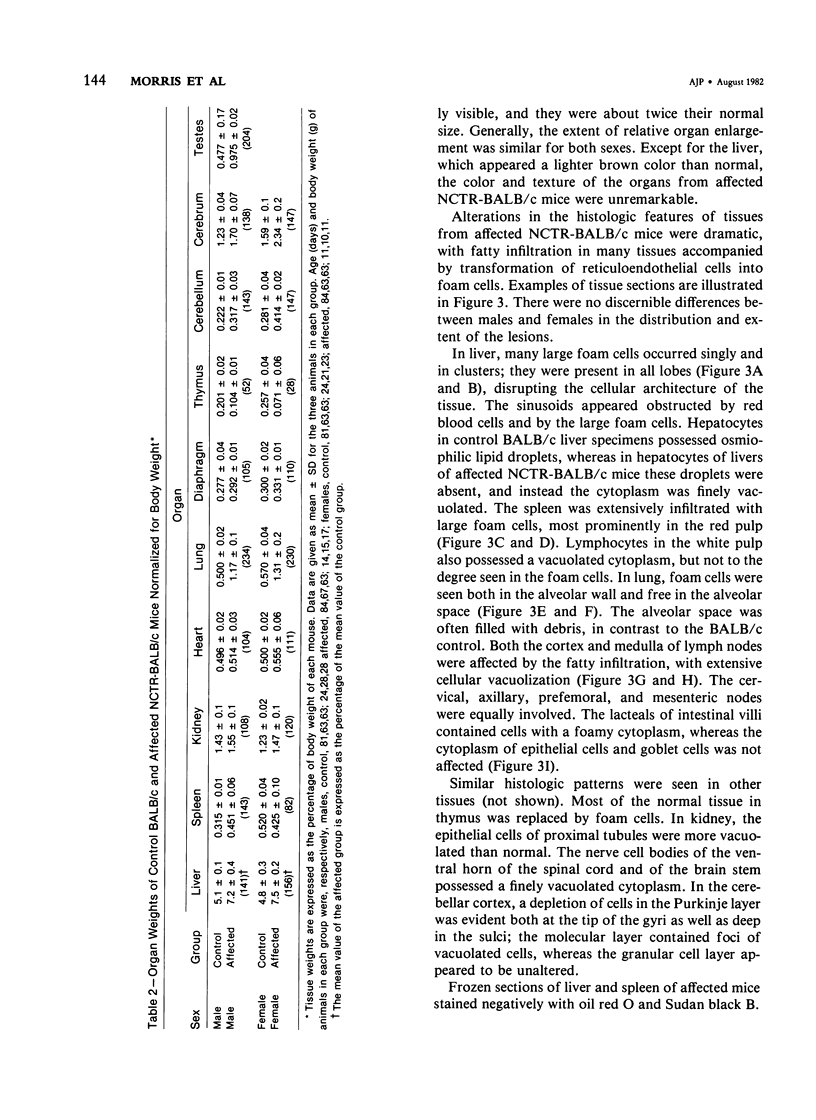
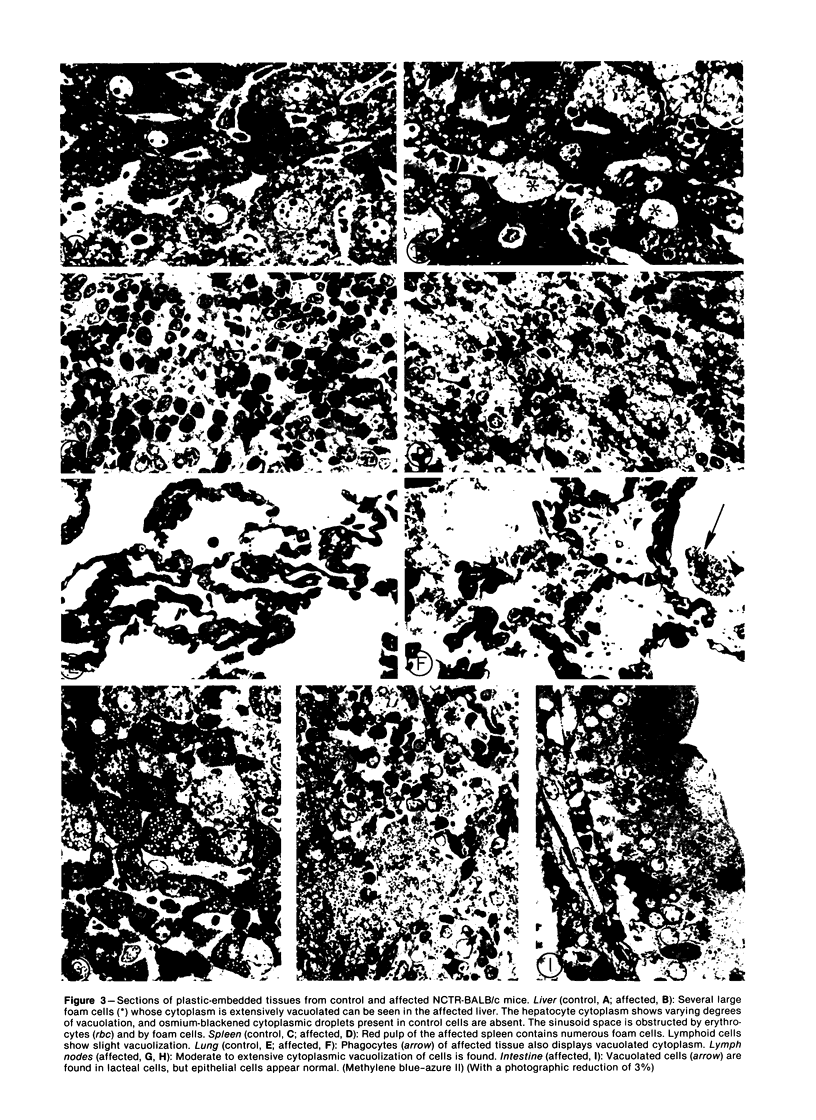
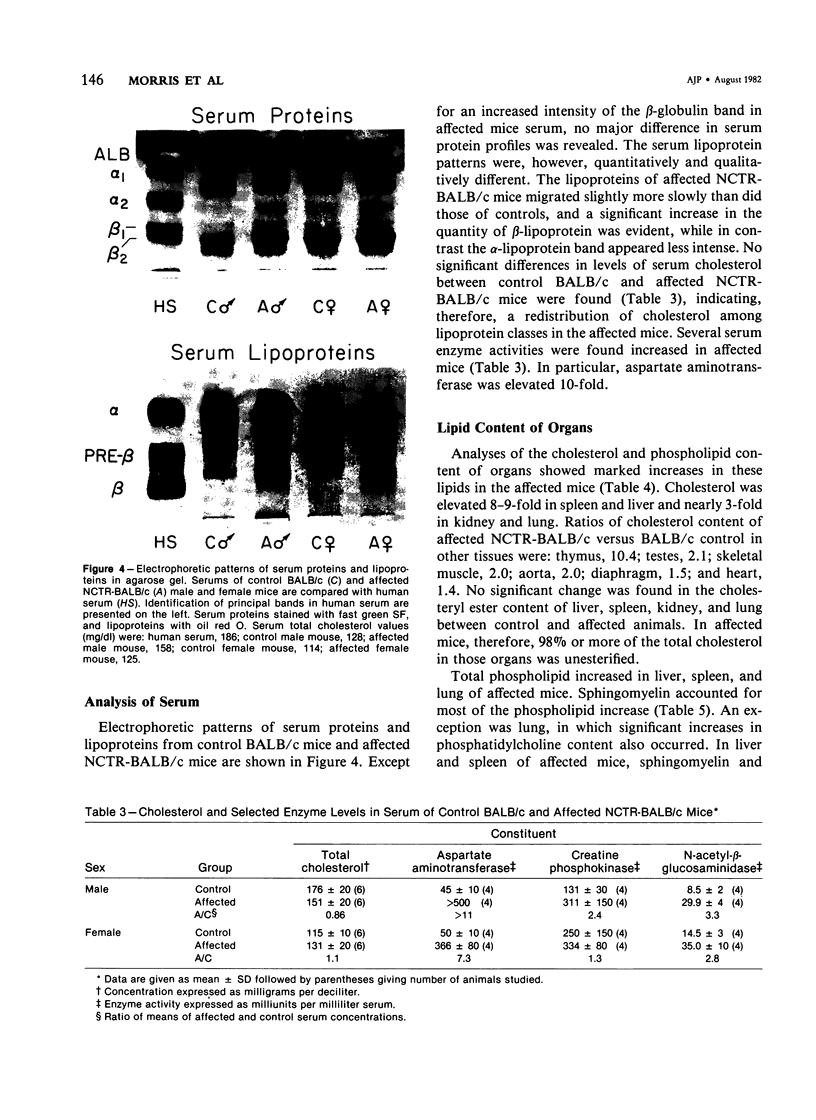
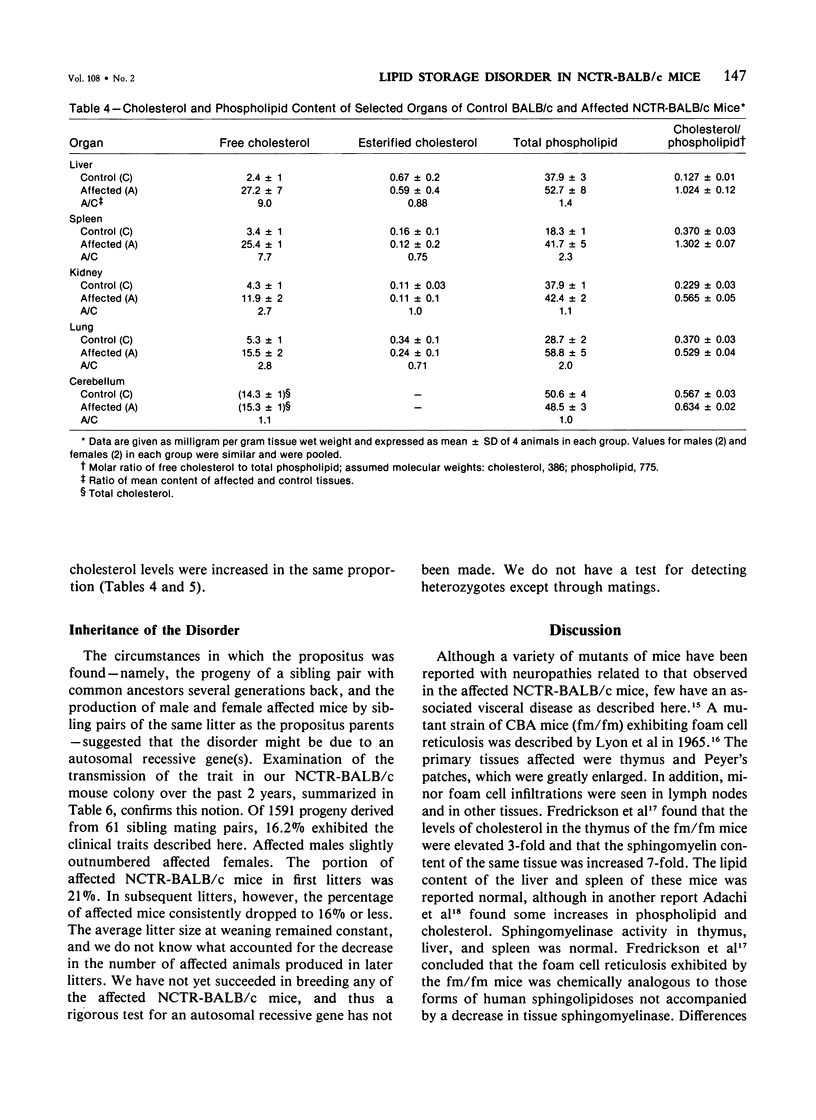
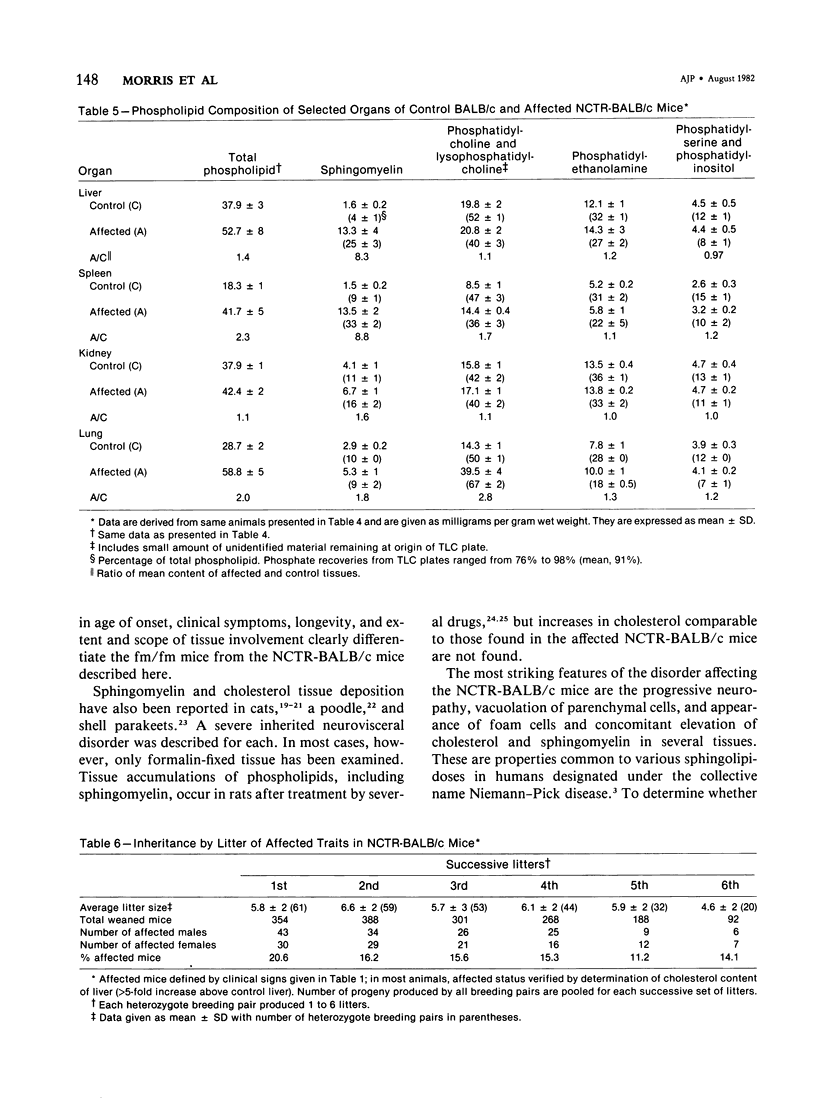
We describe a strain of BALB/c mice, designated NCTR-BALB/c, carrying a new genetic disorder characterized by excessive tissue deposition of cholesterol and phospholipid. The mice exhibit progressive incoordination, grow less rapidly, and die 80-120 days after birth. In comparison with control animals of the same age, organ weights in the affected animals are lower in absolute value but higher relative to body weight, except for the thymus, which is atrophied, and for the lung and testes, whose absolute weights are not changed. Vacuolated cells are found in many tissues, and large foam cells are present in reticuloendothelial system (RES)-rich organs. Compared with those of BALB/c controls, serum lipoproteins migrate more slowly on electrophoresis; the amount of beta-lipoproteins is increased, while alpha-lipoprotein content is decreased. Serum total cholesterol remains normal. The serum activities of aspartate aminotransferase, creatine phosphokinase, and N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase are elevated. Free cholesterol levels are increased 8-10-fold in liver, spleen, and thymus, and about 2-fold in other tissues; but esterified cholesterol levels are normal. The phospholipid content of several tissues is increased 50-100%, largely as a result of an increase in sphingomyelin content. Significant increases in phosphatidylcholine occur also in spleen and lung. The disorder is inherited, affecting both sexes equally, and appears to be transmitted as an autosomal recessive mutation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Tsai C. Y., Hoffman L. M., Schneck L., Volk B. W. The central nervous system, liver, and spleen of FM mice. Ultrastructural, histochemical, and biochemical studies. Arch Pathol. 1974 Apr;97(4):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswaran C., Morris M. D., Shio H., Fowler S. Lysosome lipid storage disorder in NCTR-BALB/c mice. III. Isolation and analysis of storage inclusions from liver. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):160–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundza A., Lowden J. A., Charlton K. M. Niemann-Pick disease in a poodle dog. Vet Pathol. 1979 Sep;16(5):530–538. doi: 10.1177/030098587901600504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrisp C. E., Ringler D. H., Abrams G. D., Radin N. S., Brenkert A. Lipid storage disease in a Siamese cat. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1970 Mar 1;156(5):616–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Sloan H. R., Hansen C. T. Lipid abnormalities in foam cell reticulosis of mice, an analogue of human sphingomyelin lipidosis. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):288–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F., HULSE E. V., ROWE C. E. FORM-CELL RETICULOSIS OF MICE: AN INHERITED CONDITION RESEMBLING GAUCHER'S AND NIERMANN-PICK DISEASES. J Med Genet. 1965 Jun;2(2):99–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leav I., Crocker A. C., Petrak M. L., Jones T. C. A naturally occurring lipidosis in shell parakeets, Melopsittacus undulatus. Lab Invest. 1968 Apr;18(4):433–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Morris M. D. Characterization of the serum low-density lipoproteins of normal and two rhesus monkeys with spontaneous hyperbeta-lipoproteinemia. Biochem Med. 1974 Jul;10(3):245–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Gal A. E., Booth A. D., Omodeo-Sale F., Fouks J., Neumeyer B. A., Quirk J. M., Dawson G., Brady R. O. A lysosomal storage disorder in mice characterized by a dual deficiency of sphingomyelinase and glucocerebrosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 8;619(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy D. H., Jortner B. S. Feline lipidosis. Light and electron microscopic studies. Arch Pathol. 1971 Aug;92(2):136–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudel L. L., Morris M. D. Determination of cholesterol using o-phthalaldehyde. J Lipid Res. 1973 May;14(3):364–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuragawa N., Sakuragaw M., Kuwabara T., Pentchev P. G., Barranger J. A., Brady R. O. Niemann-Pick disease experimental model: sphingomyelinase reduction induced by AY-9944. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):317–319. doi: 10.1126/science.66749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shio H., Fowler S., Bhuvaneswaran C., Morris M. D. Lysosome lipid storage disorder in NCTR-BALB/c mice. II. Morphologic and cytochemical studies. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):150–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szasz G., Gruber W., Bernt E. Creatine kinase in serum: 1. Determination of optimum reaction conditions. Clin Chem. 1976 May;22(5):650–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Sattler M., Kudoh T., Snyder S. P., Kingston R. S. Niemann-Pick disease: a genetic model in Siamese cats. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1471–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.7189903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Adachi S., Matsuzawa Y., Kitani T., Hiraoka A., Seki K. Studies on drug-induced lipidosis: VII. Effects of bis-beta-diethyl-aminoethylether of hexestrol, chloroquine, homochlorocyclizine, prenylamine, and diazacholesterol on the lipid composition of rat liver and kidney. Lipids. 1976 Aug;11(8):616–622. doi: 10.1007/BF02532875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]