Abstract
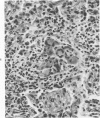
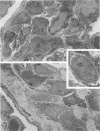
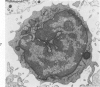
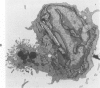
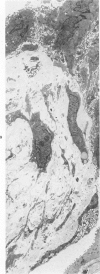
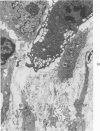
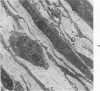
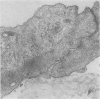
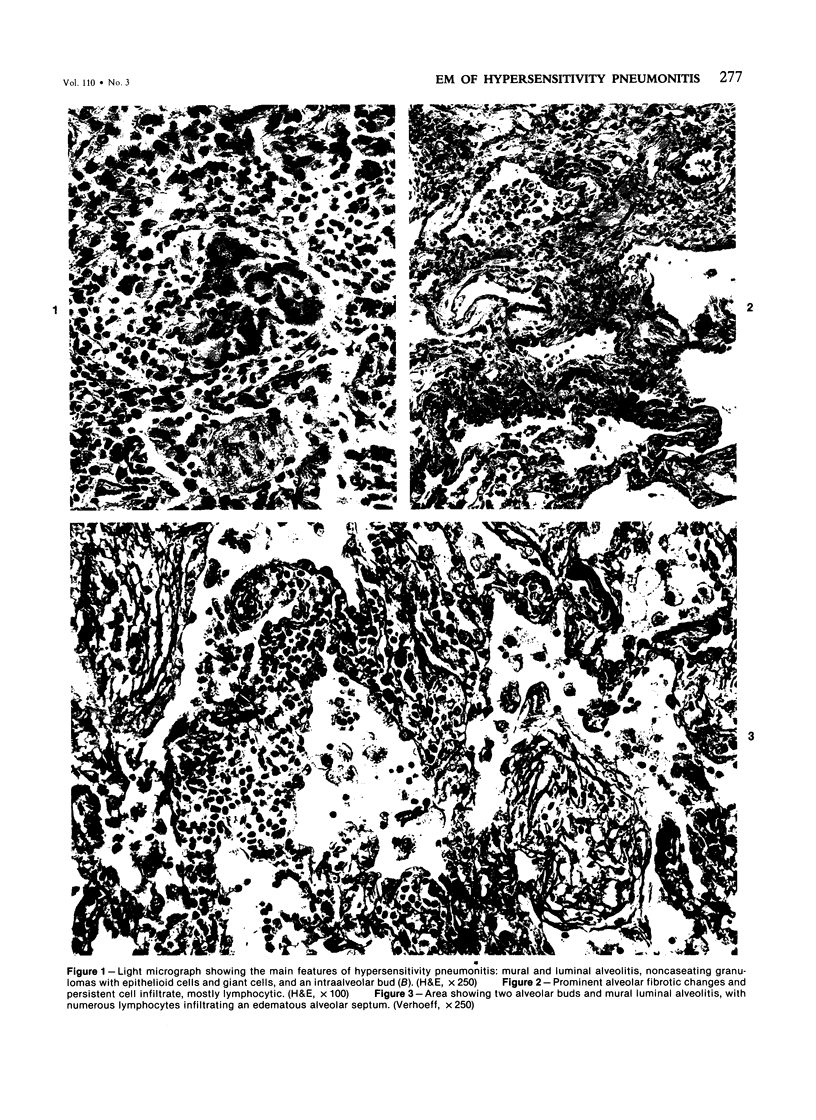
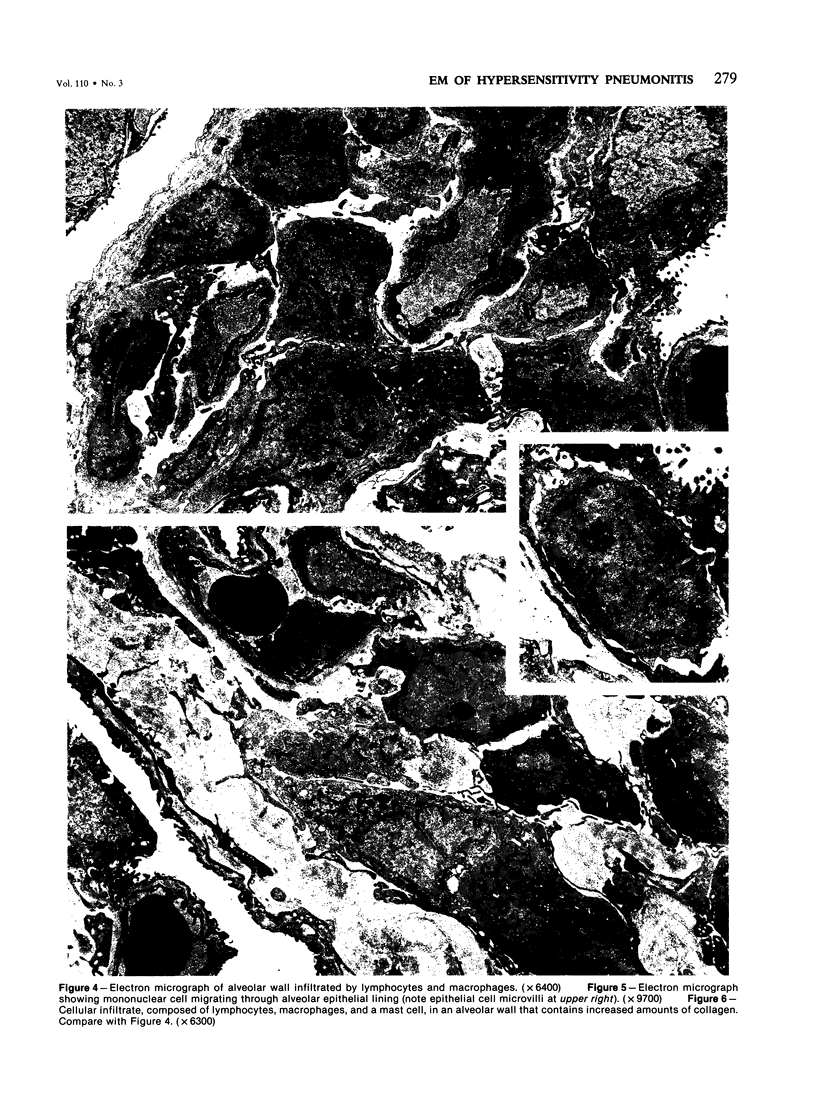
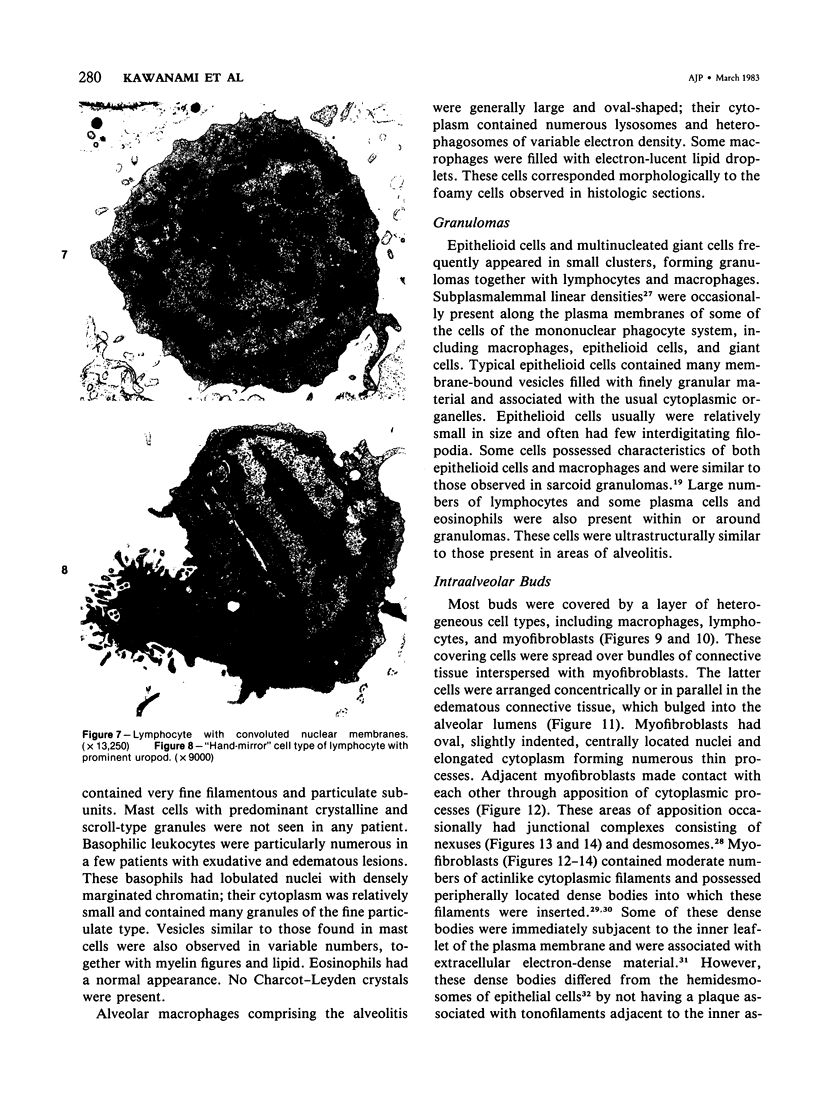
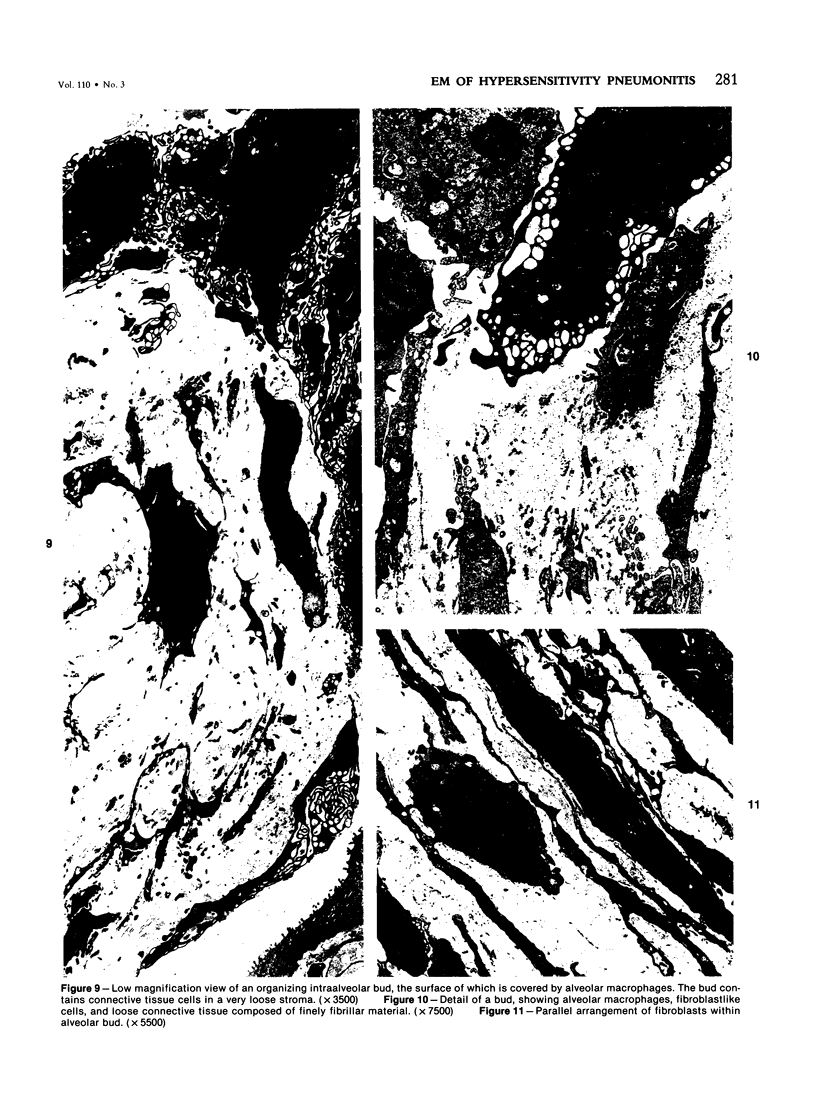
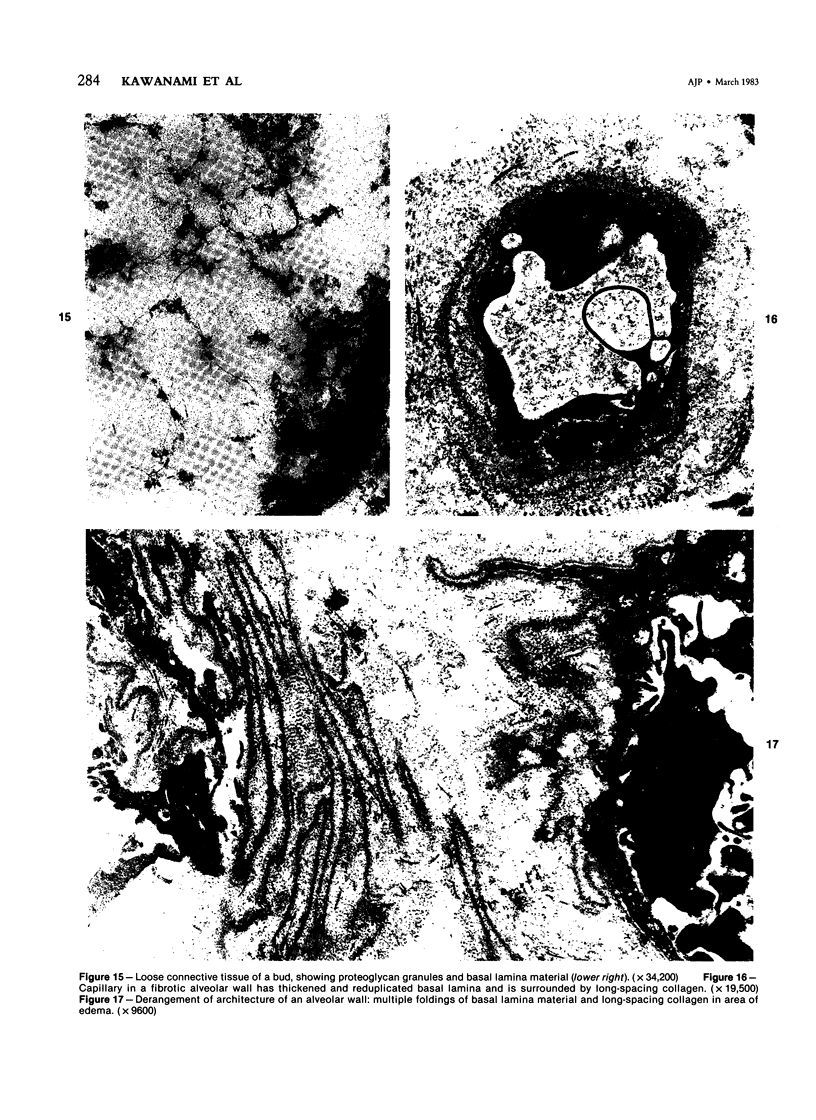
Light- and electron-microscopic changes produced by hypersensitivity pneumonitis were analyzed in open lung biopsies taken from 18 patients with chronic forms of the disease. The main changes observed were: alveolitis (both luminal and mural), granulomas, intraalveolar buds, and interstitial fibrosis. The cells infiltrating the alveolar walls were mainly lymphocytes. Occasionally these lymphocytes presented irregularities in the contours of the nuclear membranes and resembled Sézary cells. In one patient, a few lymphocytes were found that resembled "hand-mirror" cells. Intraalveolar macrophages often had a foamy appearance. Granulomas, present in two-thirds of the patients, differed in several respects from those in sarcoidosis: they were smaller, more loosely arranged, and poorly limited; they had a higher content of lymphocytes; and they were located more frequently in alveolar tissue than in the vicinity of bronchioles and vessels. Intraalveolar buds, also present in about two thirds of the patients, were composed mainly of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and macrophages in a loose connective tissue that was rich in proteoglycan material. Capillaries and epithelial cells were rarely seen in buds. Alveolar buds appear to develop by a process of disruption of the epithelial lining layer, due to alveolitis, followed by intraalveolar exudation and by subsequent intraalveolar migration of connective tissue cells interacting with macrophages. Severe fibrotic and alveolar epithelial changes were observed in four patients; milder changes were frequent in most other patients. It is concluded that hypersensitivity pneumonitis usually has distinctive morphologic features; these may help to distinguish the resultant pulmonary fibrosis from that due to other causes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfield W. G., Lee C. K., Lee C. W. Myocardial collagen of the fibrous long-spacing type. Arch Pathol. 1973 Apr;95(4):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliff D. F., Arblaster P. G. Farmer's lung: a study of an early acute fatal case. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):490–500. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Le Crom M., Decroix G. Etude ultrastructurale d'une biopsie pulmonaire au cours d'une maladie des éleveurs d'oiseaux. Pneumopathie interstitielle d'hypersensibilité. Presse Med. 1970 Mar 28;78(15):699–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo J., Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis: serial changes in lung lymphocyte subopulations after exposure to antigen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Nov;120(5):985–994. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.5.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P. Morphogenesis in blood lymphocytes stimulated with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA). A light and electron microscopic study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1971;223(Suppl):1–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice D. E., Salvaggio J., Hoffman E. Passive transfer of experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis with lymphoid cells in the rabbit. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Aug;58(2):250–262. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. The bentonite granuloma. Characterization of a model system for infectious and foreign body granulomatous inflammation using soluble mycobacterial, histoplasma and schistosoma antigens. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):511–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Interstitial associations of cells lining air spaces in human pulmonary fibrosis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1976 Nov 22;372(1):39–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00429715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee T. R., Murad T. M. Ultrastructure of mycosis fungoides. Cancer. 1970 Sep;26(3):686–698. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197009)26:3<686::aid-cncr2820260330>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. R., Pearce D. E., Spencer C., Leder R., Waldman R. H. Immunologic mechanisms in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. I. Evidence for cell-mediated immunity and complement fixation in pigeon breeders' disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Oct;52(4):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington C. B. Structure and function in sarcoidosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:265–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M. Basophils, mast cells, and cellular immunity in animals and man. Hum Pathol. 1972 Dec;3(4):454–456. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(72)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M., Simpson B. A., Richerson H. B., Leskowitz S., Karnovsky M. J. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity. II. A light and electron microscopic description. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):558–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Simpson B. A., Bast R. C., Jr, Leskowitz S. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity. 3. Participation of the basophil in hypersensitivity to antigen-antibody complexes, delayed hypersensitivity and contact allergy. Passive transfer. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMANUEL D. A., WENZEL F. J., BOWERMAN C. I., LAWTON B. R. FARMER'S LUNG: CLINICAL, PATHOLOGIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC STUDY OF TWENTY-FOUR PATIENTS. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:392–401. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson R. L., Kirkpatrick C. H., Shevach E. M., Schein P. S., Smith R. W., Green I., Lutzner M. Preferential cutaneous infiltration by neoplastic thymus-derived lymphocytes. Morphologic and functional studies. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jun;80(6):685–692. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson R. L., Lutzner M. A., Kirkpatrick C. H., Shevach E. M., Green I. Morphologic and functional properties of the atypical T lymphocytes of the Sezary syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Aug;49(8):558–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonck-Cussac Y., Delage J. Observations ultrastructurales sur un cas de poumon de fermier. Arch Anat Pathol (Paris) 1968 Jun;16(2):132–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. G., Paré J. A. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Semin Roentgenol. 1975 Jan;10(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0037-198x(75)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Le Lous M., Bailey A. J., Bazin S., Delaunay A. Collagen and myofibroblasts of granulation tissue. A chemical, ultrastructural and immunologic study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1976 Aug 11;21(2):133–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02899150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose T., Landrigan P., Killeen R., Dill J. Immunopathological studies in patients with farmer's lung. Clin Allergy. 1974 Jun;4(2):119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1974.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley G. T., Fink J. N., Barboriak J. J. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the monkey. Arch Pathol. 1974 Jan;97(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley G. T., Garancis J. C., Cherayil G. D., Fink J. N. Lung biopsies of pigeon breeders' disease. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jun;87(6):572–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Chapman W. E., Ward P. A. Immunopathology of the lung: a review. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jun;95(3):795–844. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabe J., Aoki Y., Miyamoto T. Antigenicity of fractions from extracts of Candida albicans. The immediate and delayed-type respiratory responses in guinea pigs. J Allergy. 1971 Feb;47(2):59–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Assimacopoulos A., Irle C., Zwahlen A., Gabbiani G. "Contractile interstitial cells" in pulmonary alveolar septa: a possible regulator of ventilation-perfusion ratio? Ultrastructural, immunofluorescence, and in vitro studies. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):375–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I. Recruitment of basophils in delayed hypersensitivity reactions. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jul;71(1):70–75. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12544415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Basset F., Ferrans V. J., Soler P., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary Langerhans' cells in patients with fibrotic lung disorders. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Structure of alveolar epithelial cells in patients with fibrotic lung disorders. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Subplasmalemmal linear densities in cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system in lung. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):131–150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D. Anchoring fibrils. A new connective tissue structure in fibrotic lung disease. Am J Pathol. 1978 Aug;92(2):389–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labaze J. J., Moscovic E. A., Pham T. D., Azar H. A. Histological and ultrastructural findings in a case of the Sézary syndrome. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Apr;25(4):312–319. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.4.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzner M. A., Jordan H. W. The ultrastructure of an abnormal cell in Sézary's syndrome. Blood. 1968 Jun;31(6):719–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Ichikawa K., Kabe J., Horiuchi Y. Delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in the lungs of guinea pigs due to potassium dichromate. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Dec;56(6):464–472. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Kabe J., Noda M., Kobayashi N., Miura K. Physiologic and pathologic respiratory changes in delayed type hypersensitivity reaction in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Apr;103(4):509–515. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Kabe J. The lungs as the site of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in guinea pigs. J Allergy. 1971 Mar;47(3):181–185. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(71)80296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. L., Hensley G. T., Fink J. N. An animal model of hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):937–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI108173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani H., Sasano N. Myofibroblasts and myoepithelial cells in human breast carcinoma. An ultrastructural study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1980;385(3):247–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00432535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J. Hypersensitivity diseases of the lungs due to fungi and organic dusts. Monogr Allergy. 1969;4:1–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J. Immunopathology of allergic lung disease. Clin Allergy. 1973 Mar;3(1):1–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED C. E., BARBEE R. A. PIGEON-BREEDERS' LUNG: A NEWLY OBSERVED INTERSTITIAL PULMONARY DISEASE. JAMA. 1965 Jul 26;193:261–265. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090040005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes C. N., Wenzel F. J., Lawton B. R., Emanuel D. A. The pulmonary pathology of farmer's lung disease. Chest. 1982 Feb;81(2):142–146. doi: 10.1378/chest.81.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Kazmierowski J. A., Roberts W. C., Frank M. M., Crystal R. G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B. Acute experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the guinea pig. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):745–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B., Dvorak H. F., Leskowitz S. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity. I. A new look at the Jones-Mote reaction, general characteristics. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):546–557. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Shevach E., Green I., Rosenthal A. S. The uropod-bearing lymphocyte of the guinea pig. Evidence for thymic origin. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1037–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvaggio J., Phanuphak P., Stanford R., Bice D., Claman H. Experimental production of granulomatous pneumonitis. Comparison of immunological and morphological sequelae with particulate and soluble antigens administered via the respiratory route. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Nov;56(5):364–380. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz M., Patterson R., Fink J. Immunopatholgenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Jul;60(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Robinson J. J., Creegan W. J., Pitts L. L., Stass S. A. Electron microscopy in hand-mirror-cell leukaemia. Lancet. 1977 Jun 4;1(8023):1214–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92764-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal R. M., Hapke E. J., Thomas G. O., Meek J. C., Hayes M. The pathology of the acute and chronic stages of farmer's lung. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):469–489. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. W., Stass S. A., Creegan W. J., Pitts L. L., Schumacher H. R. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, hand-mirror variant. A detailed ultrastructural study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;72(4):551–558. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler P., Basset F. Morphology and distribution of the cells of a sarcoid granuloma: ultrastructural study of serial sections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:147–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stass S. A., Perlin E., Jaffe E. S., Simon D. R., Creegan W. J., Robinson J. J., Holloway M. L., Schumacher H. R. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia--hand mirror cell variant: a detailed cytological and ultrastructural study with an analysis of the immunologic surface markers. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P., Weeks J. Antibodies in some chronic fibrosing lung diseases. II. Immunofluorescent studies. Clin Allergy. 1971 Jun;1(2):209–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Benacerraf B. Immunologic events in experimental hypersensitivity granulomas. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jun;71(3):349–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel F. J., Emanuel D. A., Gray R. L. Immunofluorescent studies in patients with farmer's lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Oct;48(4):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Ross R. Proteoglycans in primate arteries. I. Ultrastructural localization and distribution in the intima. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):660–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Properties of the Sezary lymphoid cell. An ultrastructural analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Aug;49(8):567–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Toorn D. W. Coffee worker's lung. A new example of extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Thorax. 1970 Jul;25(4):399–405. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]