Abstract
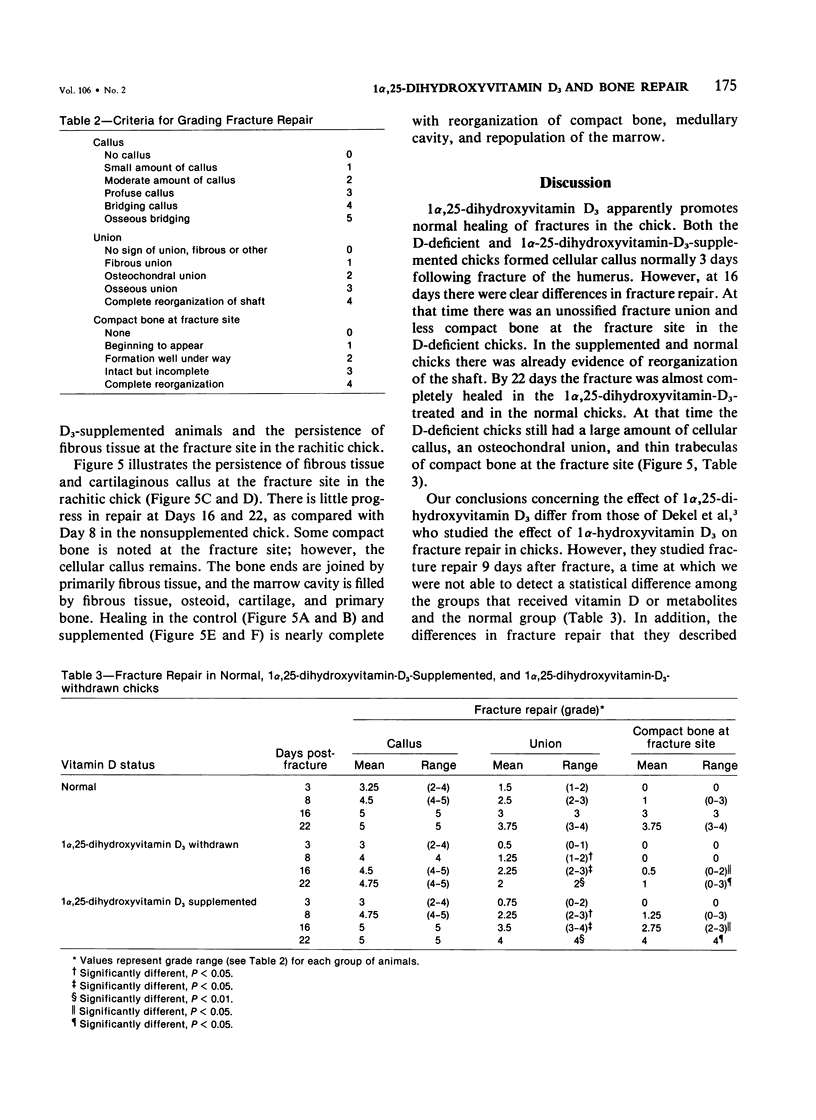
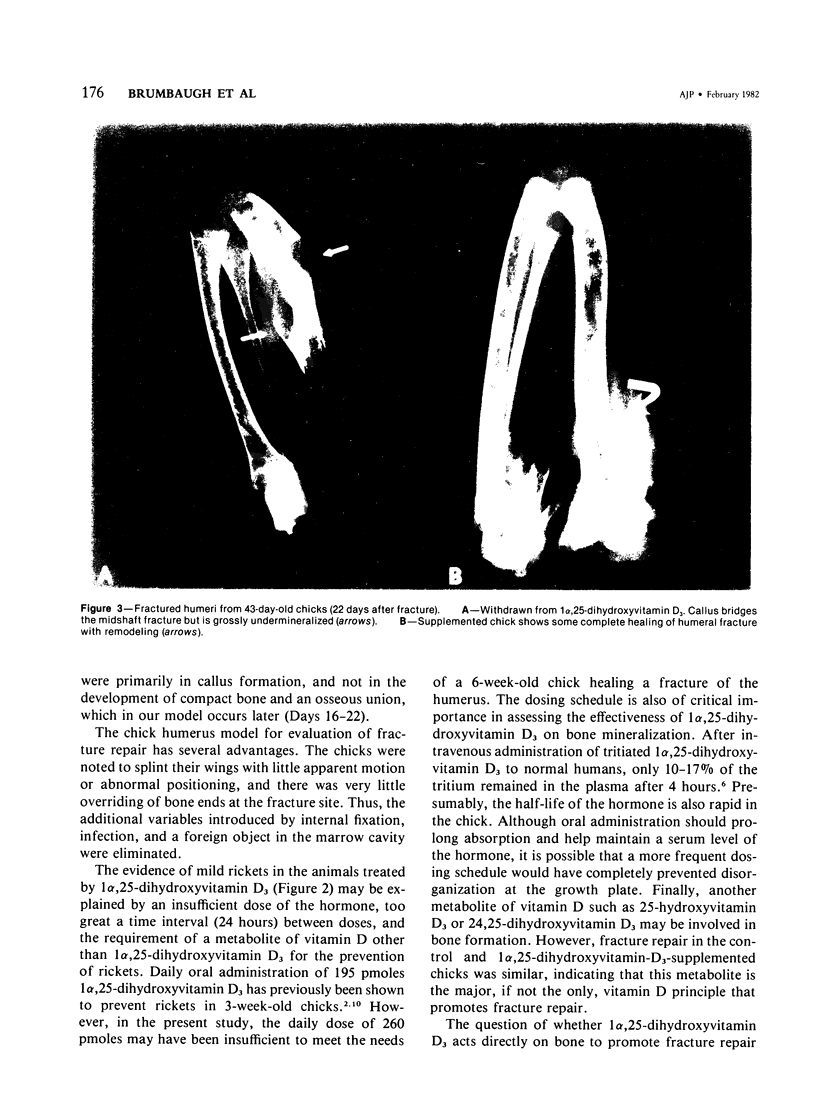
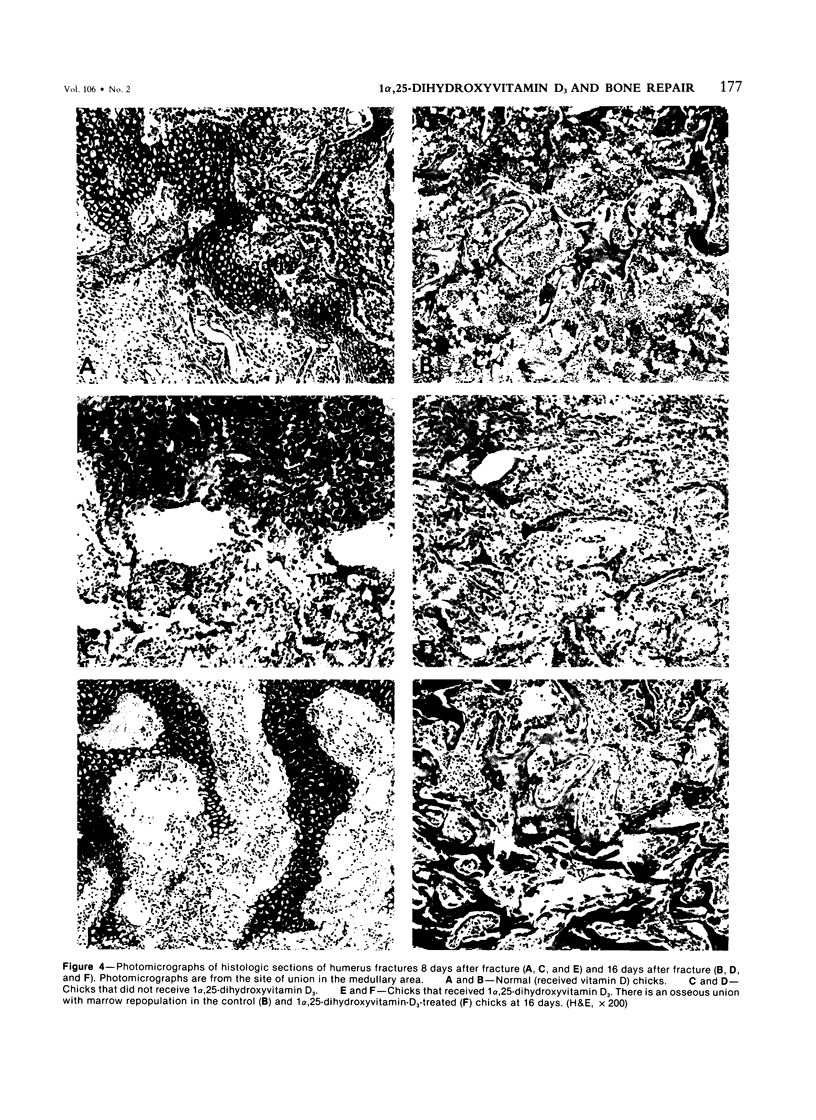
1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the hormonal form of vitamin D3 that mediates calcium translocation in intestine and bone, was tested for its ability to promote fracture repair. Chicks were raised on a vitamin D-deficient diet supplemented with 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 for 3 weeks. Following fracture of the humerus, those chicks that did not receive continued 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 supplementation showed prolonged fracture healing, abnormal enchondral bone formation delayed remodeling of woven bone and osseous union, but normal formation of callus. Fracture repair in chicks receiving 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 was normal. These data indicate that 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes bone repair in the absence of vitamin D3, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3.
Full text
PDF
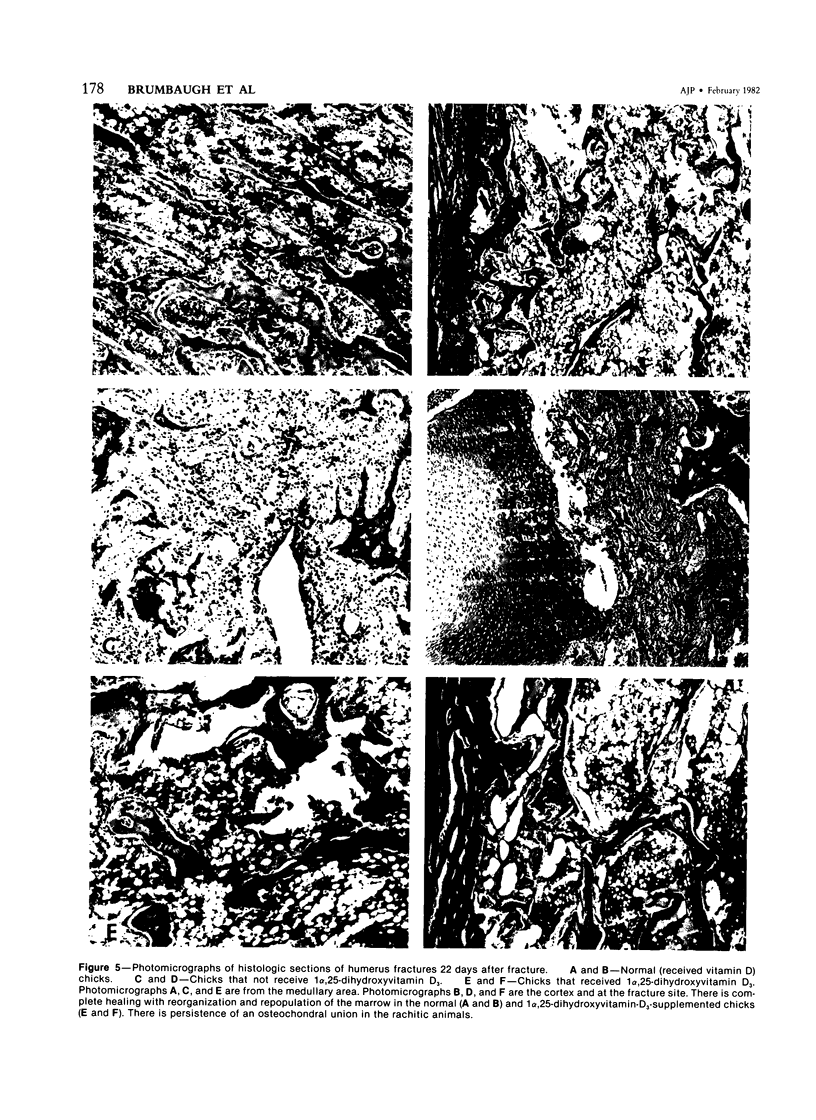



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christakos S., Norman A. W. Vitamin D3-induced calcium binding protein in bone tissue. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):70–71. doi: 10.1126/science.211584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork D. J., Haussler M. R., Pitt M. J., Rizzardo E., Hesse R. H., Pechet M. M. 1Alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3: a synthetic sterol which is highly active in preventing rickets in the chick. Endocrinology. 1974 May;94(5):1337–1345. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-5-1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Schnoes H. K. Metabolism and mechanism of action of vitamin D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:631–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekel S., Ornoy A., Sekeles E., Noff D., Edelstein S. Contrasting effects on bone formation and on fracture healing of cholecalciferol and of 1 alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol. Calcif Tissue Int. 1979 Nov 6;28(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02441243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R. Vitamin D: mode of action and biomedical applications. Nutr Rev. 1974 Sep;32(9):257–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1974.tb00970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makley J. T., Heiple K. G., Chase S. W., Herndon C. H. The effect of reduced barometric pressure on fracture healing in rats. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967 Jul;49(5):903–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNutt K. W., Haussler M. R. Nutritional effectiveness of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in preventing rickets in chicks. J Nutr. 1973 May;103(5):681–689. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrtle J. F., Norman A. W. Vitamin D: A cholecalciferol metabolite highly active in promoting intestinal calcium transport. Science. 1971 Jan 8;171(3966):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3966.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornoy A., Goodwin D., Noff D., Edelstein S. 24, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D is a metabolite of vitamin D essential for bone formation. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):517–519. doi: 10.1038/276517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Trummel C. L., Holick M. F., DeLuca H. F. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol: a potent stimulator of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):768–769. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steier A., Gedalia I., Schwarz A., Rodan A. Effect of vitamin D2 and fluoride on experimental bone fracture healing in rats. J Dent Res. 1967 Jul-Aug;46(4):675–680. doi: 10.1177/00220345670460040801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Fullmer C. S., Taylor A. N. Some aspects of vitamin D action; calcium absorption and the vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:299–324. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. L., Luben R. A., Cohn D. V. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol and parathormone: effects on isolated osteoclast-like and osteoblast-like cells. Science. 1977 Aug 12;197(4304):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.195343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]