Abstract
Popliteal and prefemoral lymphatics of sheep were cannulated, and lymph was collected before and during the course of responses to PPD and concanavalin A. Hyperemia-inducing activity (HIA) and phospholipase A2 (PLA2) were released into lymph in response to antigenic stimulation, whereas lymph plasma draining unstimulated lymph nodes had consistently little or no detectable HIA and PLA2 activity. HIA appeared in the lymph efferent to the stimulated node at a time when blood flow to the responding node was enhanced. While the appearance of HIA did not directly correlate with changes in lymphocyte output, lymph protein concentration, or lymph flow rates, there was, however, a statistically significant correlation between HIA and PLA2 levels in lymph plasma, suggesting that extracellular PLA2 may contribute to the vasoactivity in lymph and thereby modulate blood flow to areas of antigenic stimulation. Vasoactive lymph, injected into rabbits, induced hyperemia via an indomethacin-sensitive pathway, since the induction of hyperemia was abrogated by pretreatment of injection sites with indomethacin. The extracellular release of PLA2 in response to inflammatory stimuli may represent an amplification mechanism for the generation of high levels of prostaglandins found in lymph draining stimulated nodes.
Full text
PDF

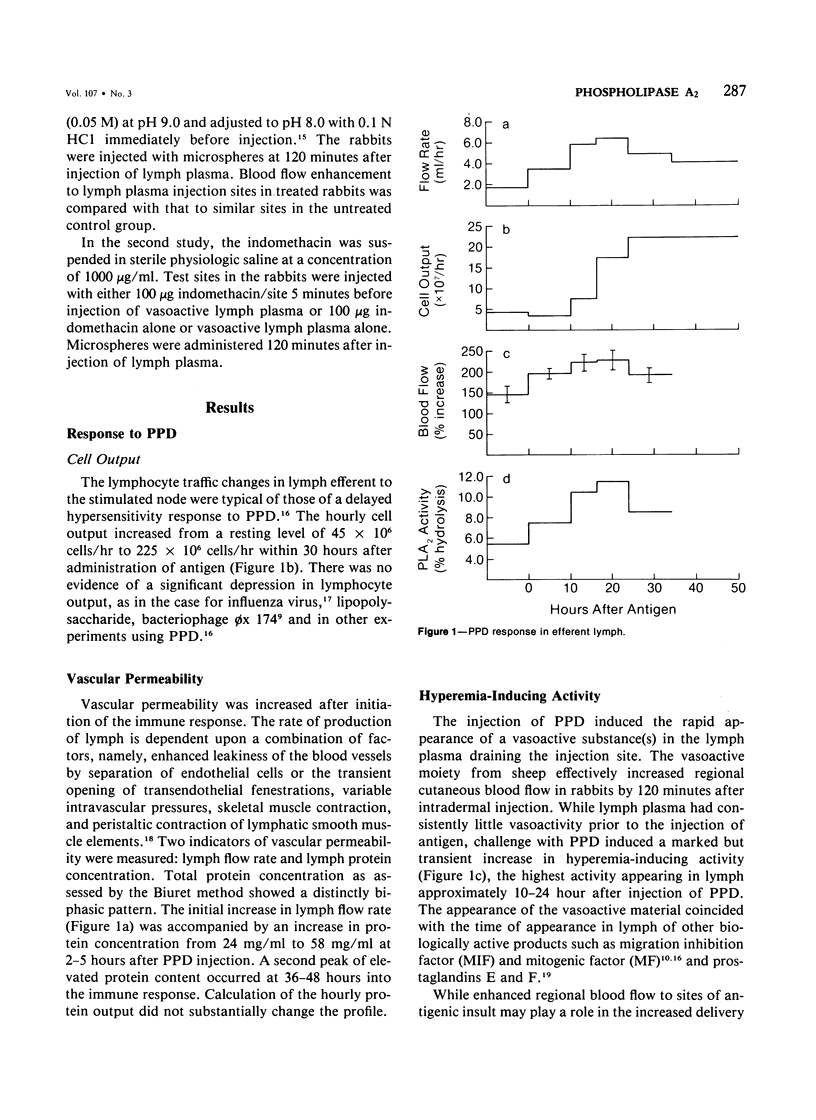
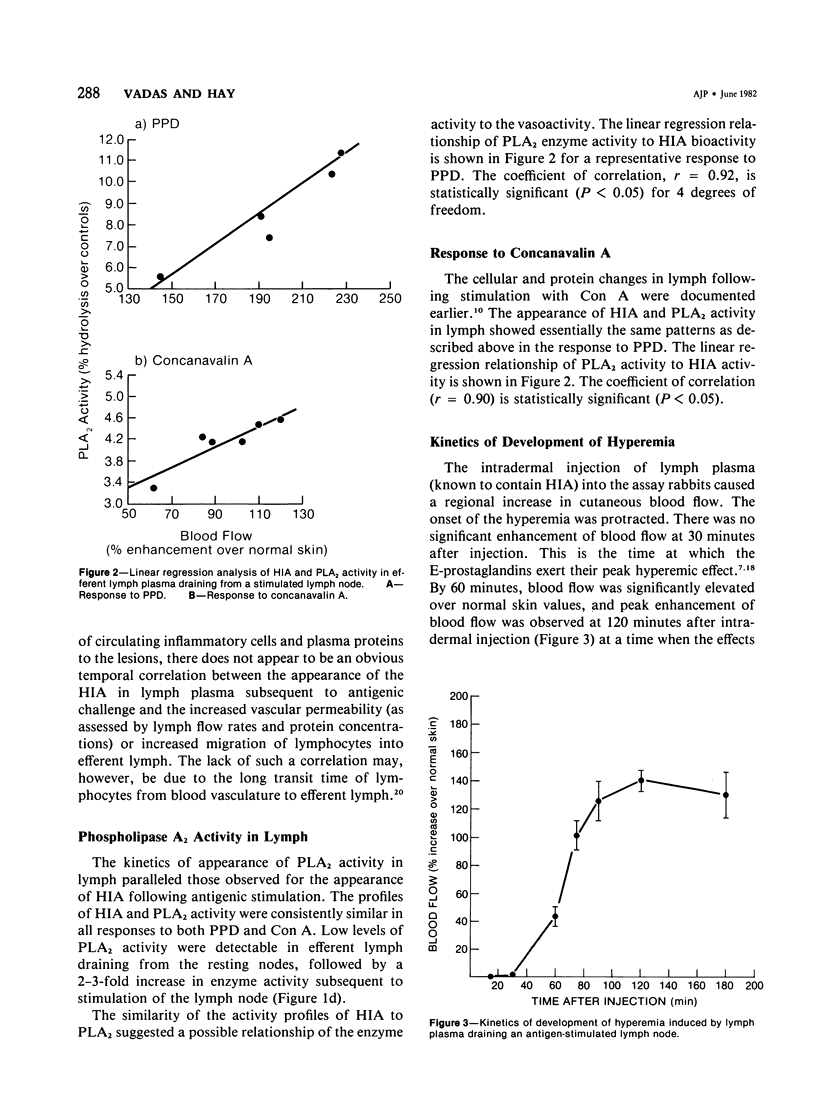
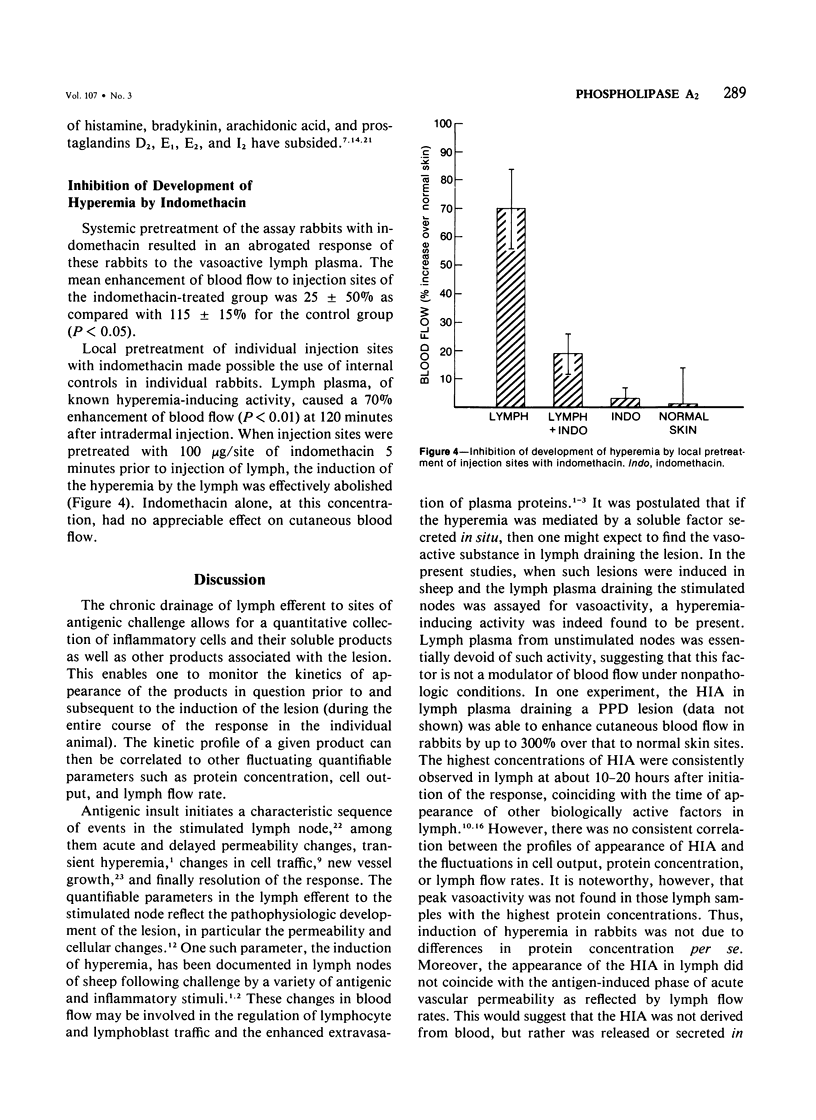


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cahill R., Hay J. B., Frost H., Trnka Z. Changes in lymphocyte circulation after administration of antigen. Haematologia (Budap) 1974;8(1-4):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl J. S., Chahl L. A. The role of prostaglandins in chemically induced inflammation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Dec;57(6):689–695. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Assouline G. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by corticosteroids requires RNA and protein synthesis. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):552–554. doi: 10.1038/273552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The lymph-borne cells of the immune response. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Jul;48:235–247. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The output of cells in lymph from the popliteal node of sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:360–369. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. B., Hobbs B. B., Johnston M. G., Movat H. Z. The role of hyperemia in cellular hypersensitivity reactions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):324–331. doi: 10.1159/000231943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. B., Hobbs B. B. The flow of blood to lymph nodes and its relation to lymphocyte traffic and the immune response. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):31–44. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. B. The production of biologically active factors in lymph following stimulation with concanavalin A. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(4):569–584. doi: 10.1159/000230962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. G. Microcirculation of organized lymphoid tissues. Monogr Allergy. 1980;16:126–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T. B., Chin W., Hay J. B. Lymphocyte traffic through granulomas: differences in the recovery of indium-111-labeled lymphocytes in afferent and efferent lymph. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 15;54(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. G., Hay J. B., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of prostaglandin production in various inflammatory lesions, measured in draining lymph. Am J Pathol. 1979 Apr;95(1):225–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. G., Hay J. B., Movat H. Z. The modulation of enhanced vascular permeability by prostaglandins through alterations in blood flow (hyperemia). Agents Actions. 1976 Nov;6(6):705–711. doi: 10.1007/BF02026092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopaniak M. M., Hay J. B., Movat H. Z. The effect of hyperemia on vascular permeability. Microvasc Res. 1978 Jan;15(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(78)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway C. A., Parrott D. M. Regional blood flow and its relationship to lymphocyte and lymphoblast traffic during a primary immune reaction. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):218–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., McIntosh G. H., Morris B. The traffic of cells through tissues: a study of peripheral lymph in sheep. J Anat. 1970 Jul;107(Pt 1):87–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Morris B. The response of the popliteal lymph node of the sheep to swine influenza virus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1970 Feb;48(1):33–46. doi: 10.1038/icb.1970.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Hay J. B. Cutaneous blood flow measurements: a standardization of the microsphere assay for vasoactive agents. Agents Actions. 1978 Oct;8(5):504–508. doi: 10.1007/BF02111437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Hay J. B. Secretion of a hyperemia-inducing moiety by mitogen or glycogen stimulated mononuclear inflammatory cells of sheep and rabbit. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(2):142–151. doi: 10.1159/000232506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Hay J. B. The release of phospholipase A2 from aggregated platelets and stimulated macrophages of sheep. Life Sci. 1980 May 19;26(20):1721–1729. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P. The efficacy of anti-inflammatory agents with respect to extracellular phospholipase A2 activity. Life Sci. 1982 Jan 11;30(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90647-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Wasi S., Movat H. Z., Hay J. B. A novel, vasoactive product and plasminogen activator from afferent lymph cells draining chronic inflammatory lesions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 May;161(1):82–85. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Wasi S., Movat H. Z., Hay J. B. Extracellular phospholipase A2 mediates inflammatory hyperaemia. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):583–585. doi: 10.1038/293583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee E., Gougat J., Navarro J., Delahayes J. F. Anti-inflammatory and platelet anti-aggregant activity of phospholipase-A2 inhibitors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;31(9):588–592. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


