Abstract
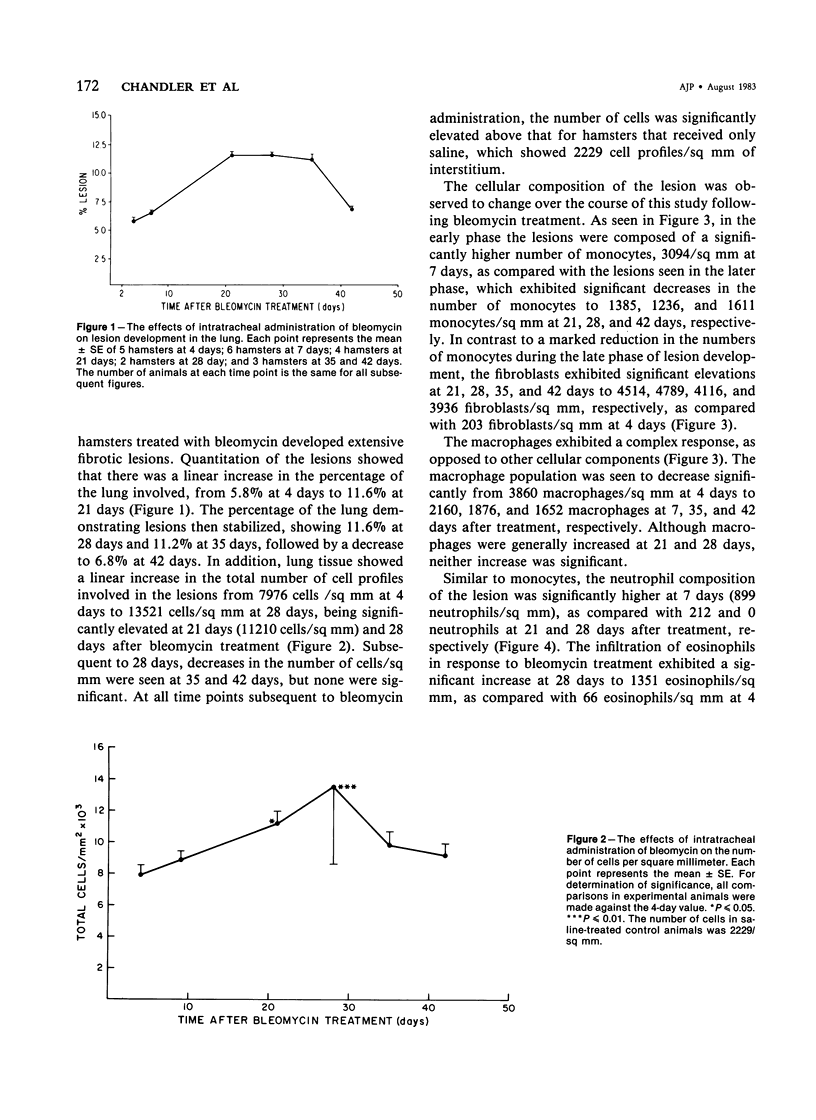
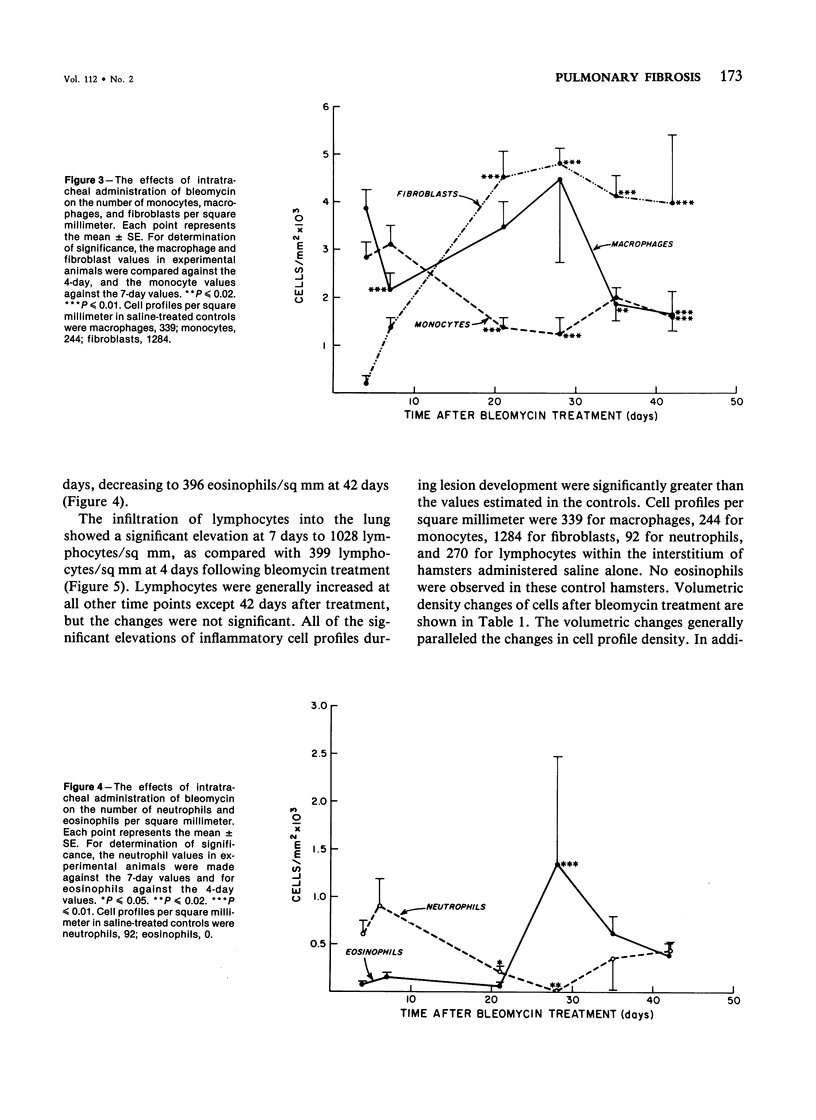
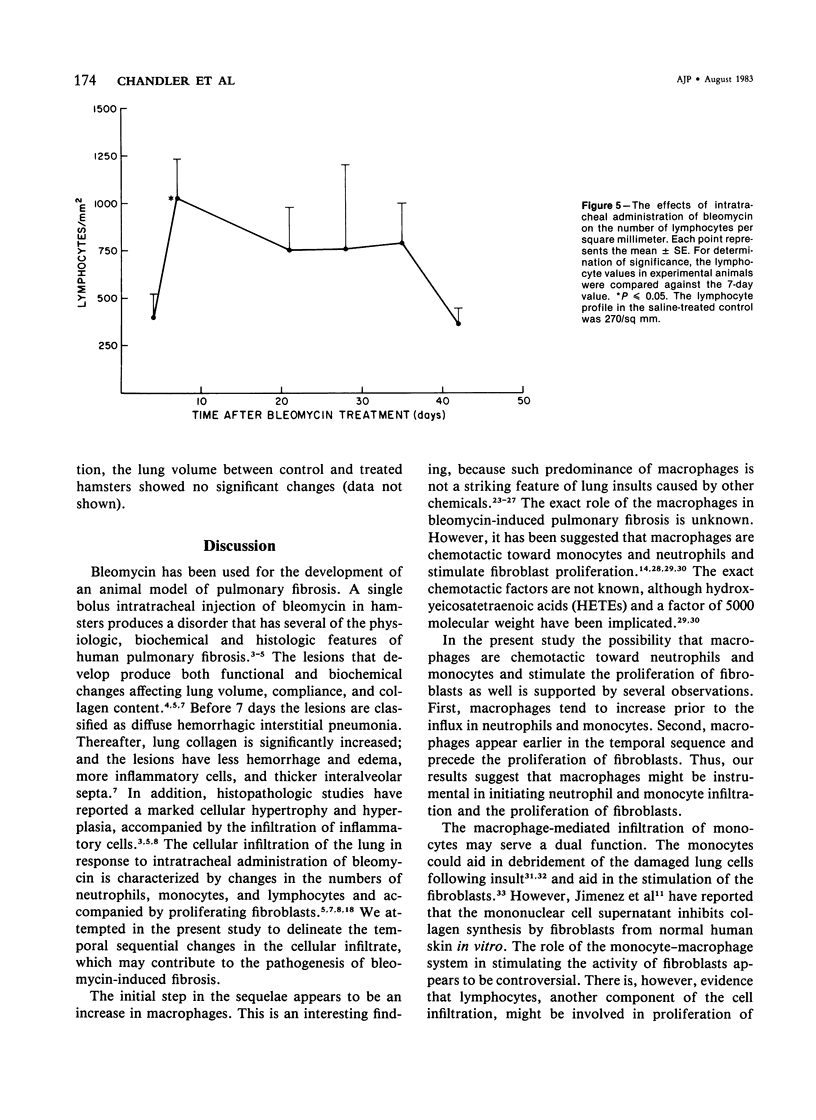
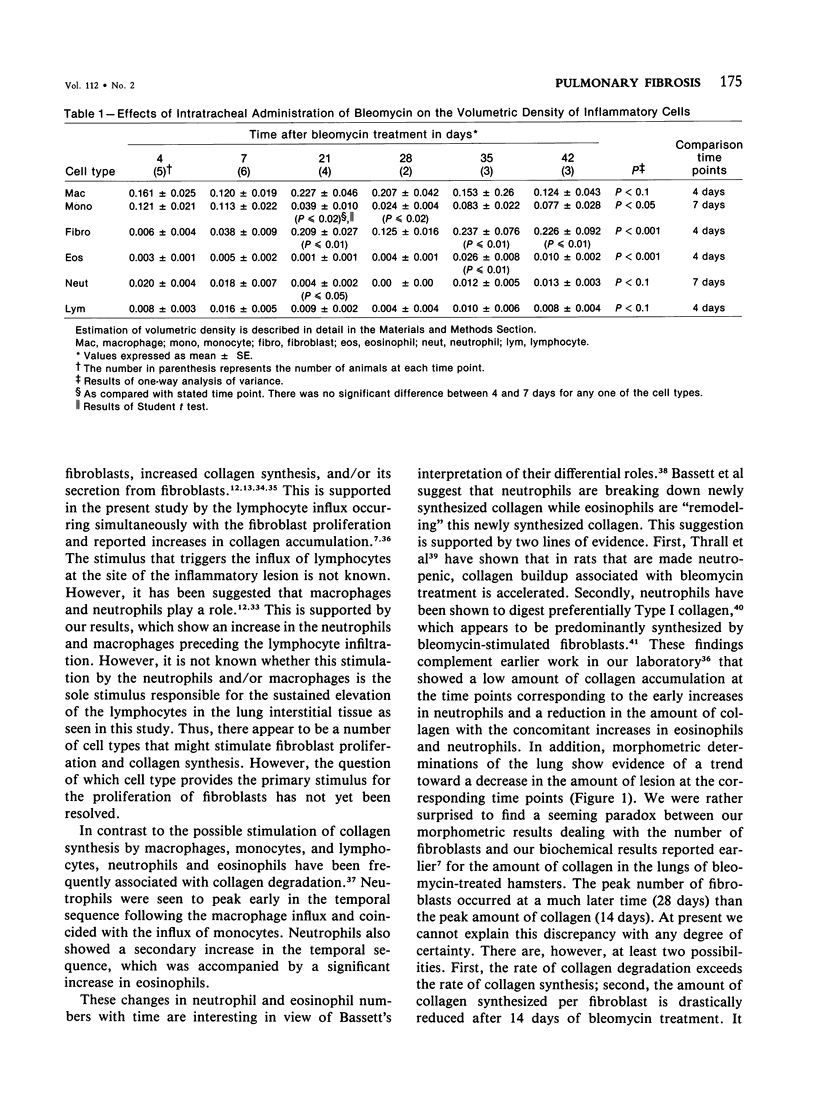
The sequence of cellular infiltration into interstitial lung tissue subsequent to intratracheal administration of bleomycin was examined in hamsters. Quantitation of lesions following bleomycin treatment showed a transient increase in the percentage of lung involved, which peaked at 21 days and decreased thereafter. Associated with these lesions was a significant increase in interstitial cell profile density at 21 and 28 days. The total number of cell profiles decreased after 28 days. The cellular composition of the lesion was dominated by monocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages in the initial phase of the fibrosis. Subsequently, monocytes were significantly decreased at 21, 28, and 42 days, as compared with the 7-day value. Similarly, neutrophils were significantly decreased at 21 and 28 days, as compared with the 7-day value. In contrast, macrophages were significantly decreased in the initial phase (7 days) of the cellular infiltration and the later phase at 35 and 42 days, as compared with the value at 4 days after treatment. Lesion composition in the later phase exhibited significant increases in fibroblasts and eosinophils, accompanied by a general increase in lymphocytes. It is concluded that bleomycin-induced inflammatory sequela exhibits temporally based changes in cellular composition of the infiltrate and that the temporal changes in cellularity might be one of the determinants in the pathophysiology of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett E. G., Baker J. R., BAKER P. A., MYERS D. B. Comparison of collagenase activity in eosinophil and neutrophil fractions from rat peritoneal exudates. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Oct;54(5):459–465. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum R. H., Carter S. K., Agre K. A clinical review of bleomycin--a new antineoplastic agent. Cancer. 1973 Apr;31(4):903–914. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197304)31:4<903::aid-cncr2820310422>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Starcher B. C., Uitto J. Bleomycin-induced synthesis of type I procollagen by human lung and skin fibroblasts in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Orive L. M., Weibel E. R. Sampling designs for stereology. J Microsc. 1981 Jun;122(Pt 3):235–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLustro F., Sherer G. K., LeRoy E. C. Human monocyte stimulation of fibroblast growth by a soluble mediator(s). J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Dec;28(6):519–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias H., Hyde D. M. An elementary introduction to stereology (quantitative microscopy). Am J Anat. 1980 Dec;159(4):412–446. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001590407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner C. S., 2nd, Connolly K. S. The ultrastructure of 60 Co radiation pneumonitis in rats. Lab Invest. 1973 May;28(5):545–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri S. N., Hyde D. M., Schwartz L. W., Younker W. R. The effect of alpha-difluoromethylornithine on the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):115–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri S. N., Schwartz L. W., Hollinger M. A., Freywald M. E., Schiedt M. J., Zuckerman J. E. Biochemical and structural alterations of hamster lungs in response to intratracheal administration of bleomycin. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Aug;33(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Fletcher K., Wyatt I. Changes in the composition of lung lipids and the "turnover" of dipalmitoyl lecithin in experimental alveolar lipo-proteinosis induced by inhaled quartz. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Aug;55(4):384–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg T. W., Last J. A. Ozone-induced acute pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Prevention of increased rates of collagen synthesis by methylprednisolone. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):47–52. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. L., Hance A. J., Crystal R. G. Granulocyte collagenase: selective digestion of type I relative to type III collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Immunologic reactivity of the lung: the in vivo and in vitro generation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):15–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., McArthur W., Rosenbloom J. Inhibition of collagen synthesis by mononuclear cell supernates. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Ziff M. Lymphokine stimulation of collagen accumulation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):240–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Weibel E. R., Kaplan H. P., Robinson F. R. Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierowski J. A., Gallin J. I., Reynolds H. Y. Mechanism for the inflammatory response in primate lungs. Demonstration and partial characterization of an alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor with preferential activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa Y., Suzuki K. Alteration of cellular and acellular alveolar and bronchiolar walls produced by hypocholesteremic drug AY9944. Lab Invest. 1972 Apr;26(4):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Lian J., Burleigh M. C. Role of granulocyte collagenase in collagen degradation. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):565–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. A macrophage-dependent factor that stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):501–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Jimenez S. A., Phillips S. M. Cell-mediated immunity in interstitial nephritis. III. T lymphocyte-mediated fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis: an immune mechanism for renal fibrogenesis. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1708–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S., Williams C. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Effects of steroid on lung collagen metabolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Oct;124(4):428–434. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. F. Experimental fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 May;105(5):776–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.5.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle W. A simple method for volumetry of organs in quantitative stereology. Mikroskopie. 1970 Jun;26(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Celli B. R., Goldstein R. H., O'Brien J. J., Lucey E. C. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin. Lung volumes, volume-pressure relations, carbon monoxide uptake, and arterial blood gas studied. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):289–297. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Hayes J. A., Korthy A. L. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin: pathology and stereology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jun;117(6):1099–1108. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.6.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. G., Willoughby D. A. The origin of mononuclear cells in chronic inflammation and tuberculin reactions in the rat. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(2):389–399. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcher B. C., Kuhn C., Overton J. E. Increased elastin and collagen content in the lungs of hamsters receiving an intratracheal injection of bleomycin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):299–305. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szapiel S. V., Elson N. A., Fulmer J. D., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):893–899. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., McCormick J. R., Jack R. M., McReynolds R. A., Ward P. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the rat: inhibition by indomethacin. Am J Pathol. 1979 Apr;95(1):117–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., Phan S. H., McCormick J. R., Ward P. A. The development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in neutrophil-depleted and complement-depleted rats. Am J Pathol. 1981 Oct;105(1):76–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKMAN A., GOWANS J. L. THE PRODUCTION OF MACROPHAGES IN THE RAT. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Feb;46:50–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Franklin M., Sun F. F., Goetzl E. J. Alveolar macrophage lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid: isolation and recognition as the predominant constituents of the neutrophil chemotactic activity elaborated by alveolar macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M., McCarthy J. B. Lymphocyte-mediated activation of fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):942–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki A., Rose G. G., Mahan C. J. Collagen degradation by human gingival fibroblasts. I. In vivo phagocytosis. J Periodontal Res. 1981 May;16(3):309–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman J. E., Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N. Evaluation of antifibrotic drugs in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


