Abstract
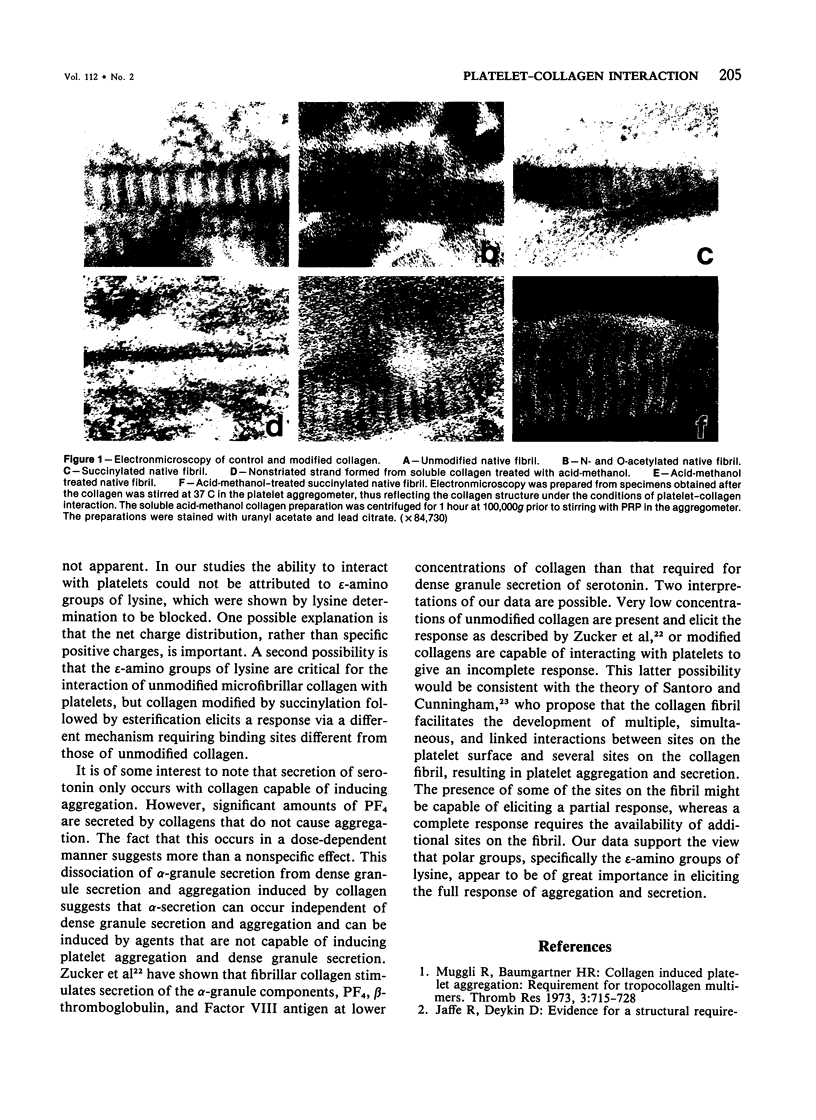
Chemical modification of collagen is a tool for exploring the platelet-collagen interaction. Since collagen must polymerize prior to the initiation of platelet aggregation and secretion, modification must be shown to affect platelet-collagen interaction and not collagen-collagen interaction. To address this point, the authors carried out the following chemical modifications on soluble monomeric collagen and preformed fibrillar collagen in parallel: 1) N-and O-acetylation, 2) esterification of the carboxyl groups, 3) succinylation of the free amino groups, 4) esterification of succinylated collagen. Intrinsic viscosity studies of the modified soluble collagens were consistent with normal triple helix conformation. Electron microscopy revealed all modified fibrillar collagen to maintain a fibrillar structure. Platelet aggregation and secretion of 14C-serotonin and platelet factor 4 by soluble and fibrillar collagen, respectively, were studied in human platelet-rich plasma. Neutralization of polar groups by 1) totally abolished aggregation and secretion by both collagens, while blocking acidic groups 2) resulted in enhanced aggregation and secretion by both soluble and fibrillar collagen. Blockage of amino groups by 3) abolished aggregation and secretion by both collagens. Esterified succinylated collagen 4) caused aggregation and secretion at relatively high collagen concentrations. These data support the theory that positive groups of collagen are important in platelet-collagen interaction.
Full text
PDF


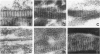
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V., CROSS M. J. THE AGGREGATION OF BLOOD PLATELETS. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:178–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Bensusan H. B. The role of collagen quaternary structure in the platelet: collagen interaction. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1480–1487. doi: 10.1172/JCI107896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. R., Gross J. High-resolution analysis of the modified quarter-stagger model of the collagen fibril. Biopolymers. 1974 May;13(5):931–941. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D. D., Dabbous M. K., Brinkley B. The role of the telopeptide region of collagen in the platelet-collagen interaction. Thromb Res. 1979 Feb-Mar;14(2-3):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper E., Simons E. R., Chesney C. M., Colman R. W. The effect of chemical or enzymatic modifications upon the ability of collagen to form multimers and to initiate platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe R., Deykin D. Evidence for a structural requirement for the aggregation of platelets by collagen. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):875–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI107628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerushalmy Z., Zucker M. B. Some effects of fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) on blood platelets. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakade M. L., Liener I. E. Determination of available lysine in proteins. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggli R. Collagen-induced platelet aggregation: native collagen quaternary structure is not an essential structural requirement. Thromb Res. 1978 Nov;13(5):829–843. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Wilner G. D., LeRoy E. C. Importances of polar groups for initiating blood coagulation and aggregating platelets. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):75–76. doi: 10.1038/221075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puett D., Wasserman B. K., Ford J. D., Cunningham L. W. Collagen-mediated platelet aggregation. Effects of collagen modification involving the protein and carbohydrate moieties. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2495–2506. doi: 10.1172/JCI107440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVEN F. S. THE NISHIHARA TECHNIQUE FOR THE SOLUBILIZATION OF COLLAGEN. APPLICATION TO THE PREPARATION OF SOLUBLE COLLAGENS FROM NORMAL AND RHEUMATOID CONNECTIVE TISSUE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Jul;23:300–301. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.4.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Cunningham L. W. Collagen-mediated platelet aggregation. Evidence for multivalent interactions of intermediate specificity between collagen and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1054–1060. doi: 10.1172/JCI108856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W., Kübler W., Gross R. Induction of blood platelet aggregation by cationic polypeptides. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):307–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons E. R., Chesney C. M., Colamn R. W., Harper E., Samberg E. The effect of the conformation of collagen on its ability to aggregate platelets. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):123–139. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., LeRoy E. C. Activation of Hageman factor by collagen. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2608–2615. doi: 10.1172/JCI105943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., LeRoy E. C. Aggregation of platelets by collagen. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2616–2621. doi: 10.1172/JCI105944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., Procupez T. L. Aggregation of platelets by collagen: polar active sites of insoluble human collagen. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1074–1079. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Broekman M. J., Kaplan K. L. Factor VIII-related antigen in human blood platelets: localization and release by thrombin and collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Nov;94(5):675–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]