Abstract
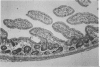
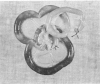
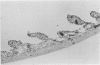
This report deals with the experimental production of ischemic bowel necrosis in rats by the administration of combined bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and platelet-activating factor (PAF). Neither LPS alone, nor PAF at a low dose, caused ischemic intestinal necrosis when administered intraaortically. With these two compounds in combination, necrotizing lesions of the gastrointestinal tract developed consistently. The lesions showed marked morphologic similarity to human necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). There were no thrombi in mesenteric arteries or necrotic lesions in other organs to which these bioactive compounds were delivered. These findings suggest a possible synergistic involvement of PAF and LPS in the pathogenesis of NEC and other forms of ischemic bowel necrosis. The authors further suggest that the pathogenesis of experimental NEC in rats is independent of platelet aggregation.
Full text
PDF




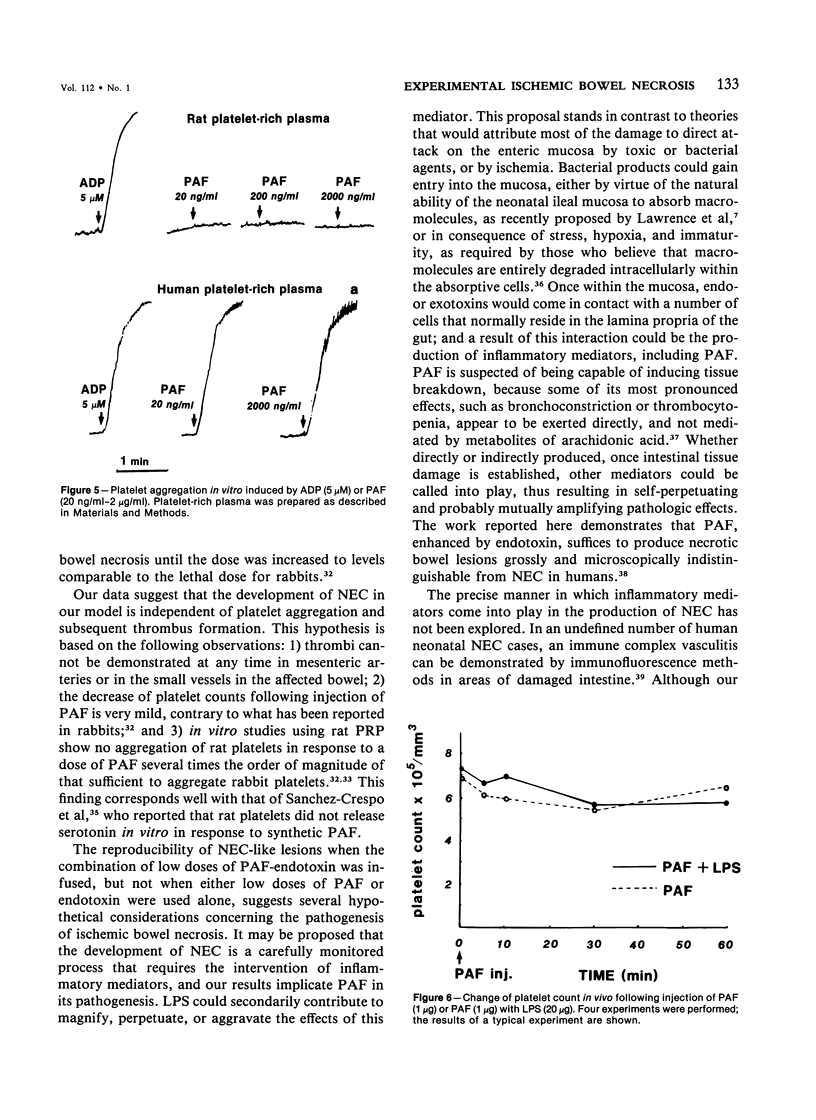


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow B., Santulli T. V., Heird W. C., Pitt J., Blanc W. A., Schullinger J. N. An experimental study of acute neonatal enterocolitis--the importance of breast milk. J Pediatr Surg. 1974 Oct;9(5):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Book L. S., Overall J. C., Jr, Herbst J. J., Britt M. R., Epstein B., Jung A. L. Clustering of necrotizing enterocolitis. Interruption by infection-control measures. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):984–986. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt L. G., Cheek R. C. Nonocclusive mesenteric vascular disease: clinical and experimental observations. Ann Surg. 1969 May;169(5):704–711. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196905000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashore W. J., Peter G., Lauermann M., Stonestreet B. S., Oh W. Clostridia colonization and clostridial toxin in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):308–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Areson P. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: absence of enteric bacterial toxins. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 24;299(8):424–424. doi: 10.1056/nejm197808242990814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignard M., Le Couedic J. P., Tence M., Vargaftig B. B., Benveniste J. The role of platelet-activating factor in platelet aggregation. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):799–800. doi: 10.1038/279799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack N. J. Platelet-activating factor. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):193–193. doi: 10.1038/285193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN P. M. INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE NEWBORN WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO TRANSIENT FUNCTIONAL ILEUS ASSOCIATED WITH RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME. Arch Dis Child. 1963 Oct;38:459–467. doi: 10.1136/adc.38.201.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSa D. J. The spectrum of ischemic bowel disease in the newborn. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1976;3:273–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Myers M. G. Clostridium difficile toxin in asymptomatic neonates. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):431–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Lewis R. A., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Comparative airway and vascular activities of leukotrienes C-1 and D in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIROR H. V., MYERS H. A. PERFORATING APPENDICITIS IN PREMATURE INFANTS. Surgery. 1964 Sep;56:581–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay S. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Contraction of guinea pig ileal smooth muscle by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):C130–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.3.C130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz I. D., 3rd, L'heureux P., Engel R. R., Hunt C. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. S., Lloyd D. J., Miller S. S., Davidson A. I., Balch N. J., Horne C. H. Evidence for an immune complex vasculitis in neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;34(7):759–763. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.7.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Acute immune complex disease in rabbits. The role of complement and of a leukocyte-dependent release of vasoactive amines from platelets. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):554–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Hunt C. E., Matsen J. M. Nosocomial colonization with Klebsiella, type 26, in a neonatal intensive-care unit associated with an outbreak of sepsis, meningitis, and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):415–419. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Induction of leukocytic infiltrates in rabbit skin by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. Lab Invest. 1982 Sep;47(3):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., McManus L. M., Satouchi K., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Vasoactive properties of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine and analogues. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Pulliam L. A., Upchurch H. F. The activity of partially purified leukocytic endogenous mediator in endotoxin-resistant C3H/HeJ mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Cerami A. Studies of endotoxin-induced decrease in lipoprotein lipase activity. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):631–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Hack M., Jones P., Fanaroff A. A. Epidemiologic study of necrotizing enterocolitis among low-birth-weight infants. Absence of identifiable risk factors. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):440–444. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: implications for an infectious disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1979 May;26(2):327–344. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosloske A. M. Necrotizing enterocolitis in the neonate. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Feb;148(2):259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravis T. C., Henson P. M. Accumulation of platelets at sites of antigen-antibody-mediated injury: a possible role for IgE antibody and mast cells. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1569–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence G., Bates J., Gaul A. Pathogenesis of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet. 1982 Jan 16;1(8264):137–139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livaditis A., Wallgren G., Faxelius G. Necrotizing enterocolitis after catheterization of the umbilical vessels. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1974 Mar;63(2):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1974.tb04796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. R. The etiology of gastrointestinal perforations in the newborn. J Pediatr Surg. 1969 Feb;4(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(69)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of endotoxin shock in rhesus monkeys. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 Oct;125(4):825–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of the effects of bacterial endotoxin on the blood-vascular system. Lab Invest. 1966 Dec;15(12):1815–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N. Pathobiology of the intravenous infusion of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC), a synthetic platelet-activating factor (PAF), in the rabbit. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2919–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathogenesis of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet. 1982 Feb 20;1(8269):451–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen E., Kaprio E., Rapola J., Soveri T., Oksanen H. Endothelial cell damage in piglet coronary artery after intravenous administration of E. coli endotoxin. A scanning and transmission electron-microscopic study. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Aug-Sep;40(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Farr R. S., Hanahan D. J. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IgE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IgE sensitized basophils. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1847–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman A. V., Gerber L. I., Balis J. U. Peritubular capillaries. A major target site of endotoxin-induced vascular injury in the primate kidney. Lab Invest. 1980 Oct;43(4):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Sarubbi F. A. The prevalence of Clostridium difficile and toxin in a nursery population: a comparison between patients with necrotizing enterocolitis and an asymptomatic group. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):435–439. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Ryan J. L., McAdam K. P., Rosenstreich D. L. Detection of a mediator derived from endotoxin-stimulated macrohpages that induces the acute phase serum amyloid A response in mice. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):597–606. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Anderson M. J. An ultrastructural study of endotoxin induced damage in rabbit mesenteric arteries. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Feb;52(1):75–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sántulli T. V., Schullinger J. N., Heird W. C., Gongaware R. D., Wigger J., Barlow B., Blanc W. A., Berdon W. E. Acute necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy: a review of 64 cases. Pediatrics. 1975 Mar;55(3):376–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touloukian R. J. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: an update on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Apr;56(2):281–298. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)40877-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touloukian R. J., Posch J. N., Spencer R. The pathogenesis of ischemic gastroenterocolitis of the neonate: selective gut mucosal ischemia in asphyxiated neonatal piglets. J Pediatr Surg. 1972 Apr;7(2):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(72)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Chignard M., Lefort J., Benveniste J. Platelet-tissue interaction: role of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether). Agents Actions. 1980 Dec;10(6):502–506. doi: 10.1007/BF02024151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]