Abstract
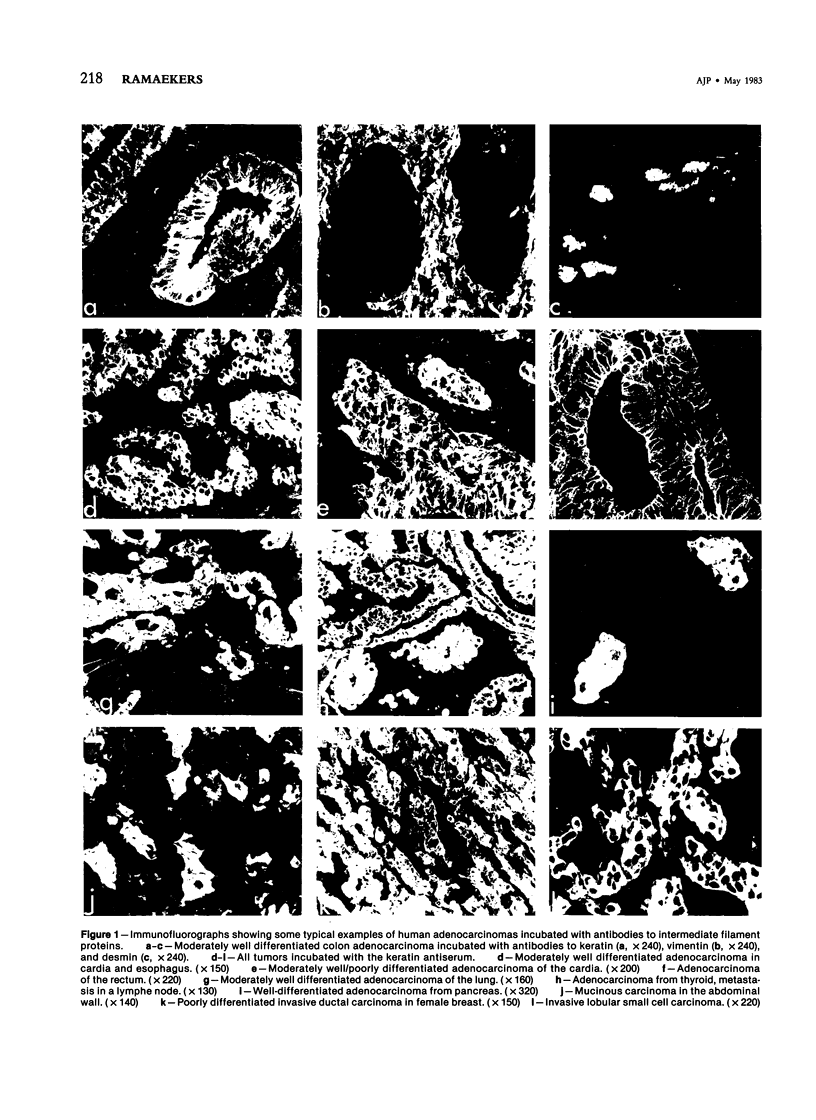
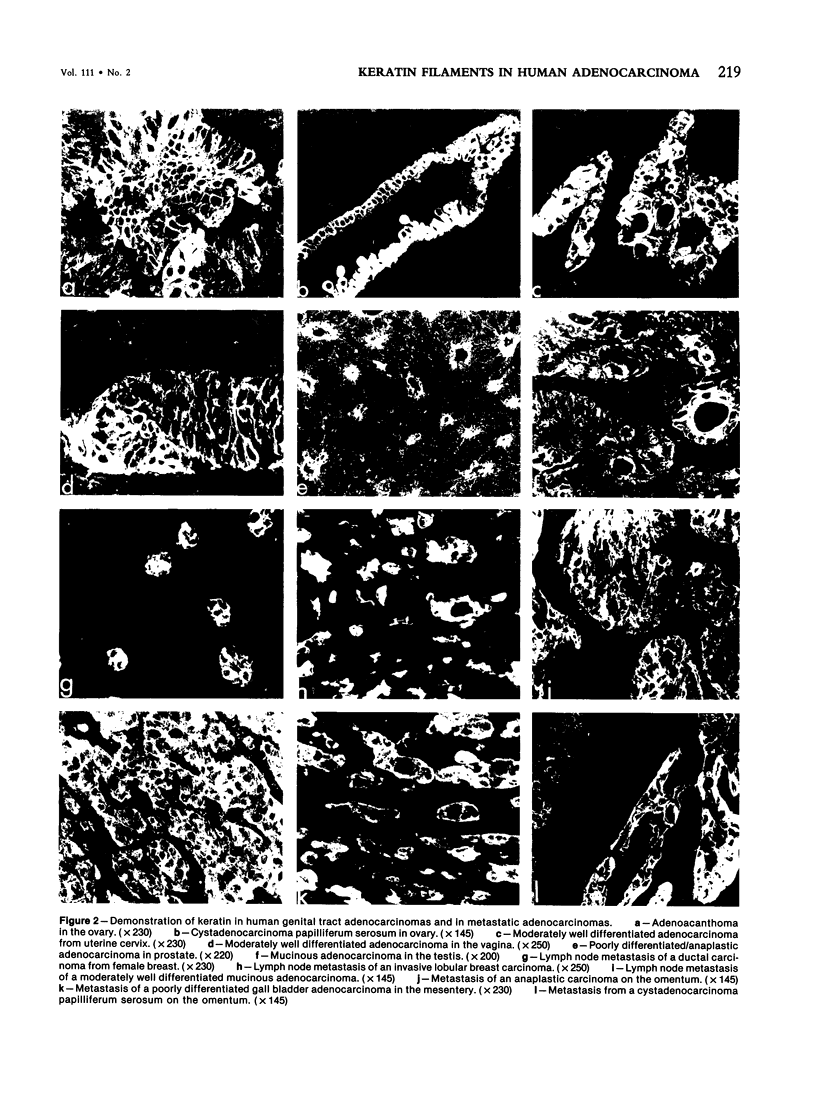
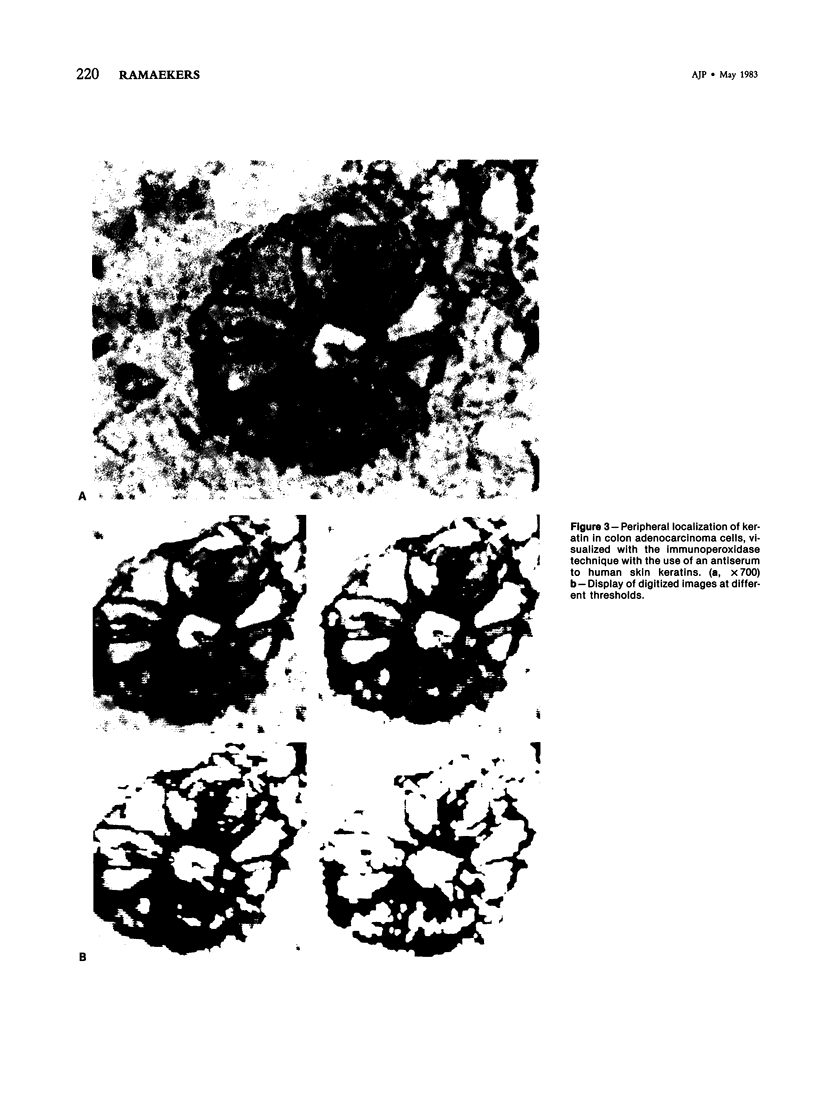
The occurrence and localization of intermediate-sized filaments in 85 cases of adenocarcinoma have been examined by the indirect immunofluorescence technique as well as by the immunoperoxidase technique. Frozen sections of human tumor tissue were incubated with antibodies to keratin, vimentin, and desmin. In contrast to earlier studies by Schlegel et al, this study demonstrates the presence of keratin in 64 cases of primary adenocarcinoma, including tumors of stomach, colon and rectum, lung, pancreas, bile ducts, ovary and uterus, female breast, and prostate, and in 21 cases of adenocarcinomatous metastases in lymph nodes, thoracic and abdominal wall, omentum, mesentery, testis, liver, and the pelvis. In order to establish the possibility of demonstrating intermediate filament proteins by immunohistochemical techniques in fixed, paraffin-embedded material, the authors tested seven fixation methods. It is concluded from the data that antibodies to intermediate filament proteins can be useful in the differential diagnosis of adenocarcinomas because they can distinguish them from tumors of nonepithelial origin in frozen sections.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Weber K. The distribution of keratin type intermediate filaments in human breast cancer. An immunohistological study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;37(3):277–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02892576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Schauer A., Weber K. Antibodies to different intermediate filament proteins. Cell type-specific markers on paraffin-embedded human tissues. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Treuner J., Hölscher A., Weber K., Shauer A. Diagnosis of human childhood rhabdomyosarcoma of antibodies to desmin, the structural protein of muscle specific intermediate filaments. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;39(2):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02892848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Weber K., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Osborn M. Antibodies to intermediate filaments as diagnostic tools: human gastrointestinal carcinomas express prekeratin. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asch B. B., Burstein N. A., Vidrich A., Sun T. T. Identification of mouse mammary epithelial cells by immunofluorescence with rabbit and guinea pig antikeratin antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5643–5647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Zerban H., Schmid E., Franke W. W. Characterization of cytoskeletal components in epithelial and mesenchymal liver tumors by electron and immunofluorescence microscopy. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;36(2-3):139–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02912063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Zerban H., Schmid E., Franke W. W. Liver tumors distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy with antibodies to proteins of intermediate-sized filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4948–4952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battifora H., Sun T. T., Bahu R. M., Rao S. The use of antikeratin antiserum as a diagnostic tool: thymoma versus lymphoma. Hum Pathol. 1980 Nov;11(6):635–641. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson J. M., Pinkus G. S. Mesothelioma: profile of keratin proteins and carcinoembryonic antigen: an immunoperoxidase study of 20 cases and comparison with pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jul;108(1):80–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Krepler R., Lackinger E., Artlieb U., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton in human hepatocellular carcinomas and in hepatic neoplastic nodules of mice. Lab Invest. 1982 Jun;46(6):584–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Appelhans B., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Osborn M., Weber K. Identification and characterization of epithelial cells in mammalian tissues by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to prekeratin. Differentiation. 1979;15(1):7–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Appelhans B., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Osborn M., Weber K. The organization of cytokeratin filaments in the intestinal epithelium. Eur J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;19(3):255–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Denk H., Kalt R., Schmid E. Biochemical and immunological identification of cytokeratin proteins present in hepatocytes of mammalian liver tissue. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):299–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Mayer D., Schmid E., Denk H., Borenfreund E. Differences of expression of cytoskeletal proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):345–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Appelhans B., Osborn M., Weber K., Keenan T. W. Intermediate-sized filaments of the prekeratin type in myoepithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):633–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Kapanci Y., Barazzone P., Franke W. W. Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized filaments in human neoplastic cells. A diagnostic aid for the surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol. 1981 Sep;104(3):206–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Purification of smooth-muscle desmin and a protein-chemical comparison of desmins from chicken gizzard and hog stomach. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guguen-Guillouzo C., Campion J. P., Brissot P., Glaise D., Launois B., Bourel M., Guillouzo A. High yield preparation of isolated human adult hepatocytes by enzymatic perfusion of the liver. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1982 Jun;6(6):625–628. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(82)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W. Vimentin and keratin intermediate filament systems in cultured PtK2 epithelial cells are interrelated. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):161–165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krepler R., Denk H., Artlieb U., Moll R. Immunocytochemistry of intermediate filament proteins present in pleomorphic adenomas of the human parotid gland: characterization of different cell types in the same tumor. Differentiation. 1982 May;21(3):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krepler R., Denk H., Weirich E., Schmid E., Franke W. W. Keratin-like proteins in normal and neoplastic cells of human and rat mammary gland as revealed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):242–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löning T., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J., Seifert G. Keratin polypeptides distribution in normal and diseased human epidermis and oral mucosa. Immunohistochemical study on unaltered epithelium and inflammatory, premalignant and malignant lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1980;388(3):273–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00430859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Barwick K. W. An immunohistochemical study of nasopharyngeal neoplasms using keratin antibodies: epithelial versus nonepithelial neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982 Mar;6(2):143–149. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198203000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Demonstration of the muscle type of intermediate filament protein, desmin, as a diagnostic aid. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):246–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Vartio T., Virtanen I. Epithelioid sarcoma. Ultrastructural and immunohistologic features suggesting a synovial origin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1982 Nov;106(12):620–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Keratin in the epithelial-like cells of classical biphasic synovial sarcoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF02932860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Franke W. W., Weber K. Visualization of a system of filaments 7-10 nm thick in cultured cells of an epithelioid line (Pt K2) by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Use of antibodies to intermediate filaments in the characterization of human tumors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):331–339. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F., Puts J., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P., Vooijs P. Differential diagnosis of human carcinomas, sarcomas and their metastases using antibodies to intermediate-sized filaments. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1982 Dec;18(12):1251–1257. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(82)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., Pinkus G. S. Immunohistochemical localization of keratin in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., van Blerkom J. Structural interaction of cytoskeletal components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):222–235. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieinski W., Dorsett B., Ioachim H. L. Identification of prekeratin by immunofluorescence staining in the differential diagnosis of tumors. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):452–458. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Shih C., Green H. Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhol M. J., Hickey W. F., Corson J. M. Malignant mesothelioma: ultrastructural distinction from adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982 Jun;6(4):307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Clawson C. C. Development of giant granules in platelets during prolonged storage. Am J Pathol. 1980 Dec;101(3):635–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]