Abstract
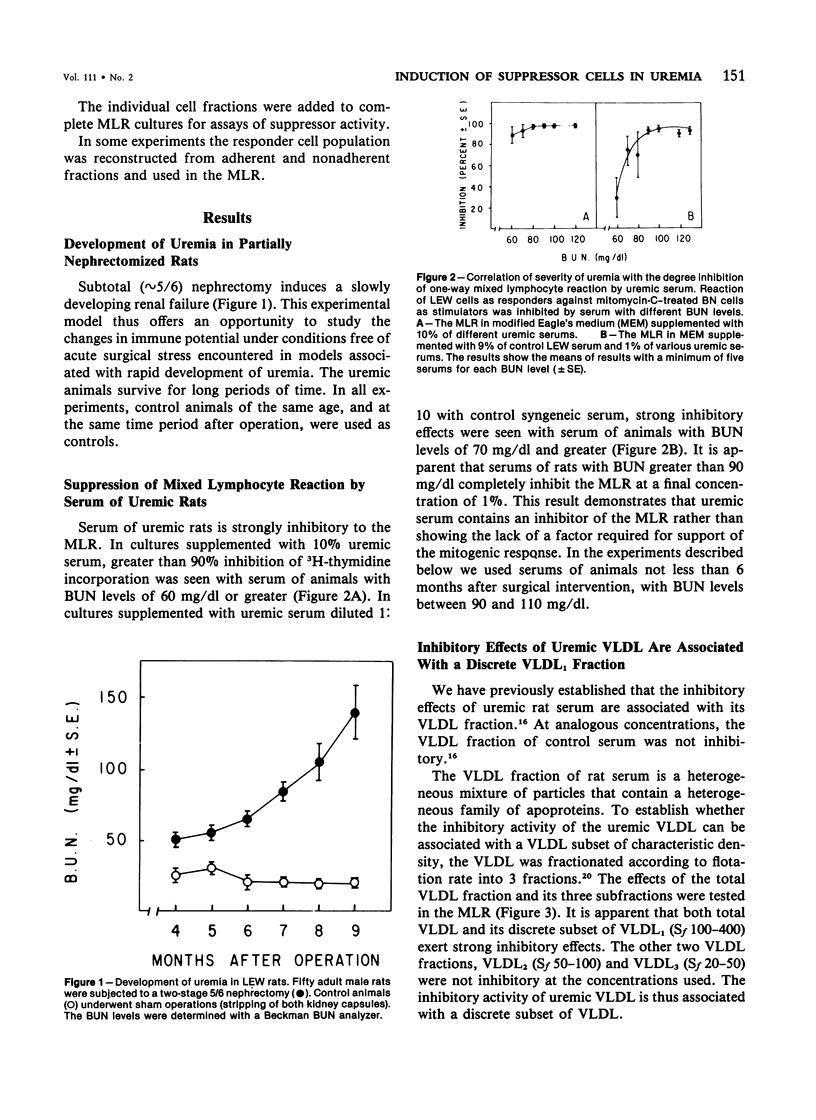
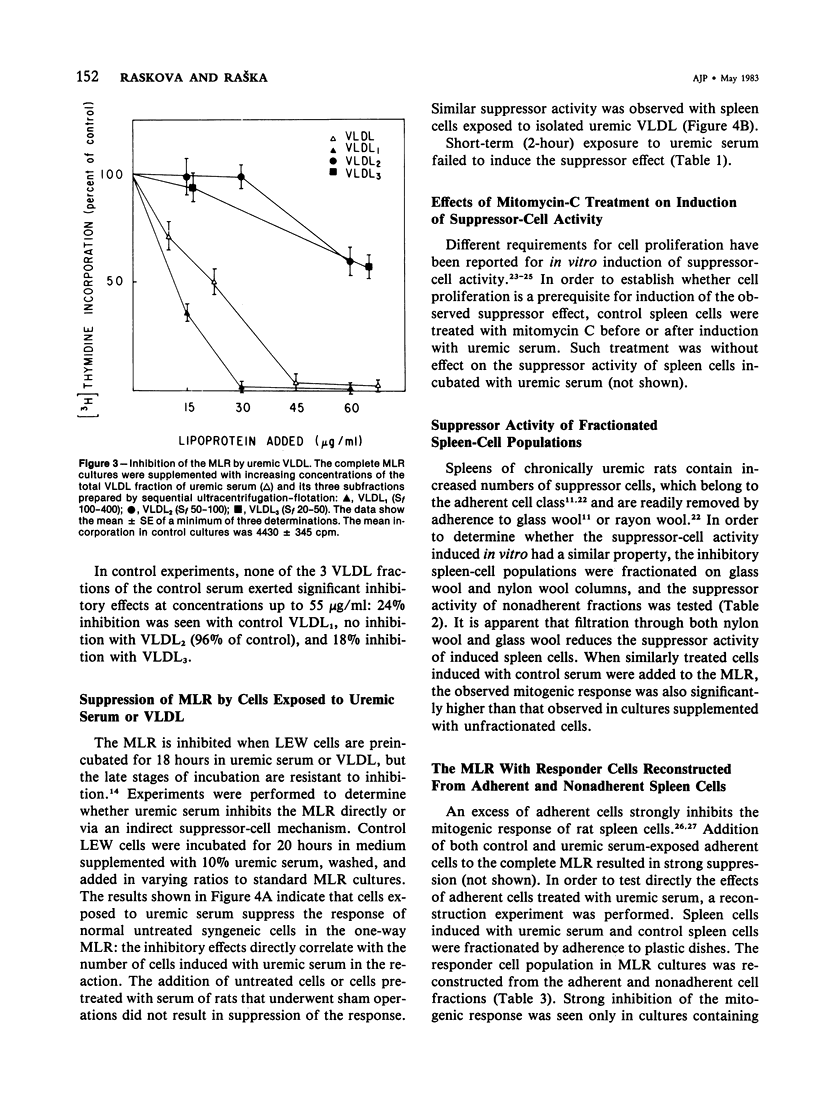
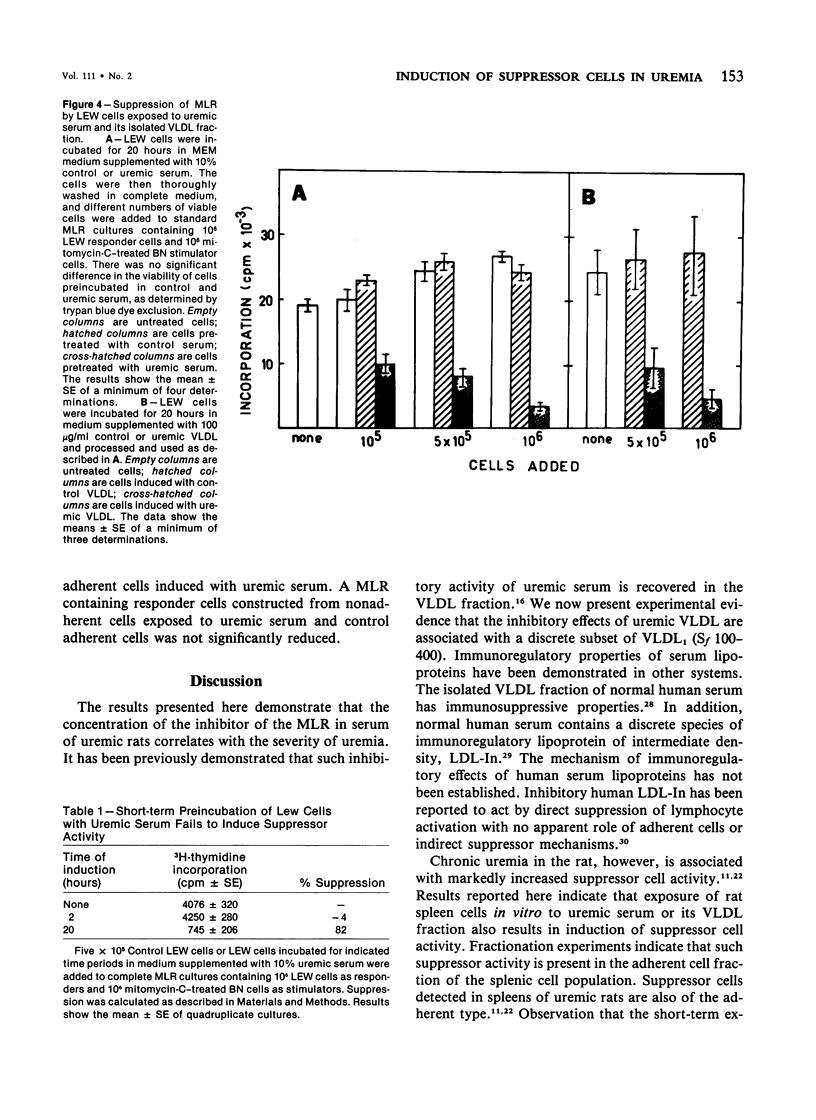
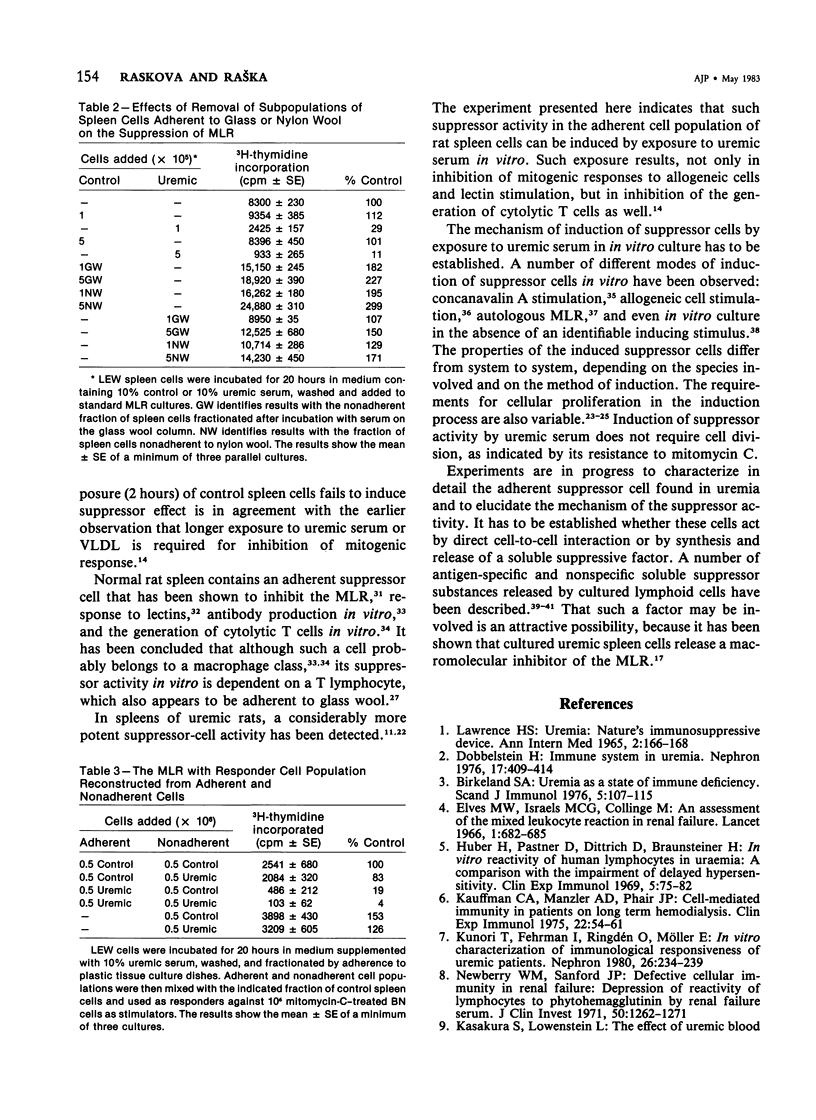
The mechanism of inhibition of mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) by serum of chronically uremic rats has been studied. The inhibitory activity of the serum has been associated with a discrete subset of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) of Sf 100-400. The degree of the inhibitory activity of uremic serum correlates with the severity of uremia. Spleen cells from normal rats incubated for 20 hours with uremic serum or its VLDL fraction suppress the response of control syngeneic cells in the MLR. Induction of such suppressor activity does not require cell proliferation because it is not inhibited by mitomycin C. although the exact identity of the induced suppressor cells has not been established, they may be macrophages. The suppressor activity of induced spleen cells can be markedly reduced by filtration of spleen cells on glass wool or on nylon wool columns. Reconstruction experiments show that the adherent cell fraction of spleen cells exposed to uremic serum suppresses the response of the nonadherent fraction of control spleen cells. These results indicate that the immunosuppressive effects of rat uremic serum in vitro involve the induction of suppressor cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alevy Y. G., Slavin R. G., Hutcheson P. Immune response in experimentally induced uremia. I. Suppression of mitogen responses by adherent cells in chronic uremia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Apr;19(1):8–18. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland S. A. Uremia as a state of immune deficiency. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(1-2):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb02997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V. Immunoregulatory properties of human plasma in very low density lipoproteins. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2129–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelstein H. Immune system to uremia. Nephron. 1976;17(6):409–414. doi: 10.1159/000180749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elves M. W., Israëls M. C., Collinge M. An assessment of the mixed leucocyte reaction in renal failure. Lancet. 1966 Mar 26;1(7439):682–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91628-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehrman I., Ringdén O., Bergström J. MLC-blocking factors in uremic sera. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Oct;14(4):183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. I. Activity of thymus-dependent adherent cells: changes with age and stress. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):127–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. II. Suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction by thymus-dependent adherent cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):140–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii D. K., Edgington T. S. Direct suppression of lymphocyte induction by the immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein, LDL-In. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):156–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSON A., ALAUPOVIC P., FURMAN R. H. STUDIES OF THE COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF SERUM LIPOPROTEINS: ISOLATION, PURIFICATION, AND CHARACTERIZATION OF VERY LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS OF HUMAN SERUM. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:596–605. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Layward L., Lydyard P. M., Moretta L., Dagg M., Lawton A. R. Fc-receptor heterogeneity of human suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herscowitz H. B., Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Heterogeneity of human suppressor cells induced by concanavalin A as determined in simultaneous assays of immune function. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1403–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Nordin A. A. Cell-mediated immune response in vitro. I. The development of suppressor cells and cytotoxic lymphocytes in mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1115–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Warner L. A., Mayrhofer G. Macrophages as effectors of T suppression: T-lymphocyte-dependent macrophage-mediated suppression of mitogen-induced blastogenesis in the rat. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Pastner D., Dittrich P., Braunsteiner H. In vitro reactivity of human lymphocytes in uraemia--a comparison with the impairment of delayed hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jul;5(1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Manzler A. D., Phair J. P. Cell-mediated immunity in patients on long-term haemodialysis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):54–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunori T., Fehrman I., Ringdén O., Möller E. In vitro characterization of immunological responsiveness of uremic patients. Nephron. 1980;26(5):234–239. doi: 10.1159/000181991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE H. S. UREMIA--NATURE'S IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE DEVICE. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Jan;62:166–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A., Murahata R., Terpenning M., Cantrell J., Zighelboim J. Activation and mechanism of action of suppressor macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Oct;64(1):150–161. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Hodes R. J. Regulatory mechanisms in cell-mediated immune responses. II. Comparison of culture-induced and alloantigen-induced suppressor cells in MLR and CML. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1886–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S. Production by stimulated macrophages of factors depressing lymphocyte transformation. Nature. 1973 Nov 30;246(5431):306–307. doi: 10.1038/246306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M., Sanford J. P. Defective cellular immunity in renal failure: depression of reactivity of lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin by renal failure serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1262–1271. doi: 10.1172/JCI106604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Herberman R. B., Campbell D. A., Jr, Djeu J. Y. Inhibition of rat mixed lymphocyte cultures by suppressor macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 15;29(2):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Role of the autologous rosette-forming T cells in the concanavalin A-induced suppressor cell function. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jul 1;61(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90375-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska K., Jr, Dougherty J., Gallimore P. H. Product of adenovirus type 2 early gene block E1 in transformed cells elicits cytolytic response in syngeneic rats. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska K., Jr, Morrison A. B., Raskova J. Humoral inhibitors of the immune response in uremia. III. The immunosuppressive factor of uremic rat serum is a very low density lipoprotein. Lab Invest. 1980 Jun;42(6):636–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskova J., Morrison A. B. A decrease in cell-mediated immunity in uremia associated with an increase in activity of suppressor cells. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskova J., Morrison A. B. Humoral inhibitors of the immune response in uremia. I. Effect of serum and of the supernatant of spleen cultures from uremic rats on the mixed lymphocyte reaction. Lab Invest. 1978 Jan;38(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskova J., Morrison A. B. Immunological responses to sheep red blood cells in experimentally induced chronic uremia of rats. Immunol Commun. 1973;2(6):607–614. doi: 10.3109/08820137309022831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskova J., Morrison A. B., Shea S. M., Raska K., Jr Humoral inhibitors of the immune response in uremia. II. Further characterization of an immunosuppressive factor in uremic serum. Am J Pathol. 1979 Nov;97(2):277–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskova J., Raska K., Jr Humoral inhibitors of the immune response in uremia. IV. Effects of serum and of isolated serum very low density lipoprotein from uremic rats on cellular immune reactions in vitro. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):410–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Specificity and suppressor function of human T cells responsive to autologous non-T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou L., Schwartz S. A., Good R. A. Suppressor cell activity after concanavalin A treatment of lymphocytes from normal donors. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1100–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Fitch F. W. Macrophages suppress CTL generation in rat mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):510–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Fitch F. W. Suppression of the plaque-forming cell response by macrophages present in the normal rat spleen. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):357–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


