Abstract
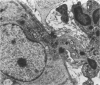
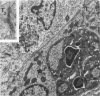
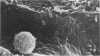
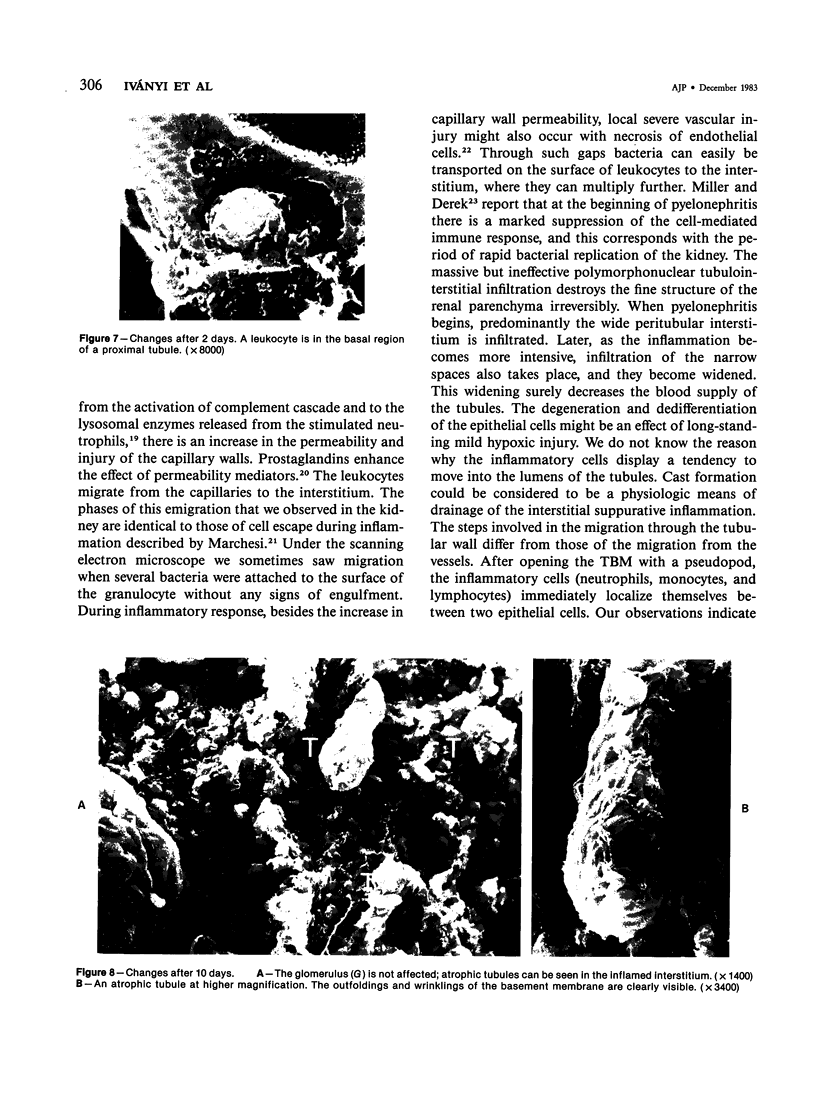
Some basic changes in experimental pyelonephritis were studied by transmission and scanning electron microscope. Initially, bacteria settled and multiplied in capillaries and venules. Leukocytes first marginated and then escaped from the capillaries, particularly to the wide peritubular interstitium. After opening the tubular basement membrane, the infiltrating leukocytes were immediately localized in the tubular wall between epithelial cells but were never seen between the epithelial cells and the underlying basement membrane. The inflammatory cells seemed not to be able to pass through the tight junctions of the nonnecrotic tubular epithelium. As a consequence of severe inflammatory injury, the tight junctions exhibited alterations of intermediate junction type. Where circumscribed necrosis of the tubular walls occurred, leukocytes appeared in the lumen. Thus, pus casts originated from these sites, apparently as drainage of interstitial abscesses. The secondary/regressive and regenerative/tubular changes were similar to those occurring after various tubular lesions.
Full text
PDF


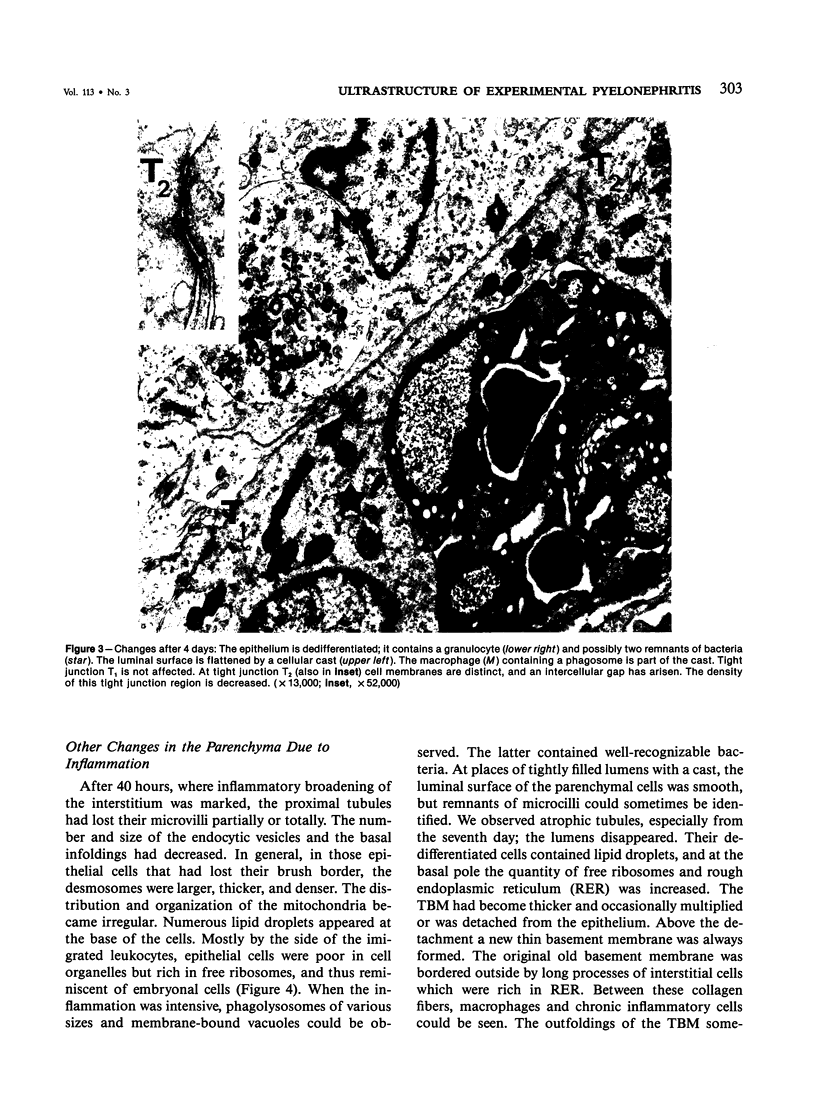
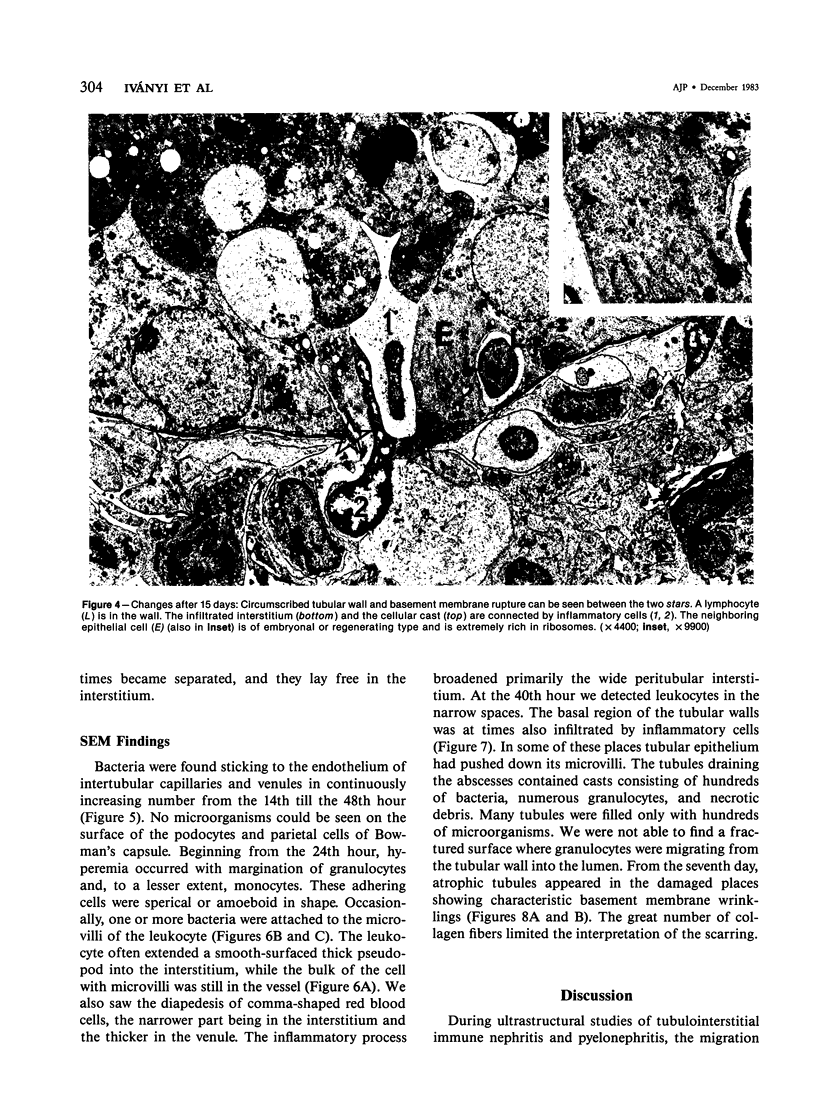



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G. A., Szymanski C., Albini B., Brentjens J., Milgrom M., Noble B., Ossi E., Steblay R. Structural observations on epithelioid and giant cells in experimental autoimmune tubulointerstitial nephritis in guinea pigs. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):21–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bille J., Glauser M. P. Protection against chronic pyelonephritis in rats by suppression of acute suppuration: effect of colchicine and neutropenia. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):220–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohman S. O., Maunsbach A. B. Effects on tissue fine structure of variations in colloid osmotic pressure of glutaraldehyde fixatives. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Jan;30(1):195–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTRAN R. S., MAJNO G. A LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC ANALYSIS OF VASCULAR INJURY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:750–764. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S. The renal lesion in chronic pyelonephritis: immunofluorescent and ultrastructural studies. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jul;120(1):109–118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppage F. E., Tate A. Repair of the nephron following injury with mercuric chloride. Am J Pathol. 1967 Sep;51(3):405–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauser M. P., Lyons J. M., Braude A. I. Prevention of chronic experimental pyelonephritis by suppression of acute suppuration. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI108951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Movat H. Z. The in vivo quantitation and kinetics of rabbit neutrophil leukocyte accumulation in the skin in response to chemotactic agents and Escherichia coli. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C. Vascular responses during acute neutrophilic inflammation. Their relationship to in vivo neutrophil emigration. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston W. H., Latta H. Acute hematogenous pyelonephritis in the rabbit. Electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli localization and early acute inflammation. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):439–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer K. H., Thoenes W. Characterization of cells involved in the formation of granuloma. An ultrastructural study on macrophages, epitheloid cells, and giant cells in experimental tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;36(2-3):177–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02912065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T. SOME ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON INTERACTIONS BETWEEN LEUKOCYTES, PLATELETS, AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS IN ACUTE INFLAMMATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:774–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T., North D. Immunobiologic factors in the pathogenesis of renal infection. Kidney Int. 1979 Dec;16(6):665–671. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T., Phillips S. Pyelonephritis: the relationship between infection, renal scarring, and antimicrobial therapy. Kidney Int. 1981 May;19(5):654–662. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. L., Bank H. L., Brissie N. T., Spicer S. S. Phagocytosis of bacteria by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A freeze-fracture, scanning electron microscope, and thin-section investigation of membrane structure. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):158–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos J., Csapó Z., Lantos J. Contributions to the development of experimental pyelonephritis. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung. 1968;16(1):85–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos J., Elemér G., Csapó Z. Ultrastructure of the proximal convoluted tubules during repair following hormonally induced necrosis in rat kidney. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1973 May 15;13(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02889292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos J., Mohácsi G., Kuthy E., Böti Z. Renal cortical tubules in experimental malakoplakia. Phagocytic alteration of tubular epithelium. Exp Pathol (Jena) 1979;17(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4908(79)80003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P., Pinto J., Hanifin J. M. Surface morphology of human mononuclear phagocytes during maturation and phagocytosis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Aug;48(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romen W., Mäder-Kruse I. The basement membrane of the atrophic kidney tubule. An electron microscopic study of changes in rats. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1978 Feb 14;26(4):307–319. doi: 10.1007/BF02889558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANFORD J. P., HUNTER B. W., DONALDSON P. Localization and fate of Escherichia coli in hematogenous pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:285–294. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T. Mechanisms of renal tissue destruction in an experimental acute pyelonephritis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Feb;34(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki T., Klassen J., Milgrom F., Andres G. A., McCluskey R. T. Immunopathologic study of an autoimmune tubular and interstitial renal disease in brown Norway rats. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):658–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan H. K., Heptinstall R. H. Experimental pyelonephritis. A light and electron microscopic study of the periodic acid-Schiff positive interstitial cell. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):62–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M. Release of inflammatory mediators from stimulated neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):27–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]