Abstract
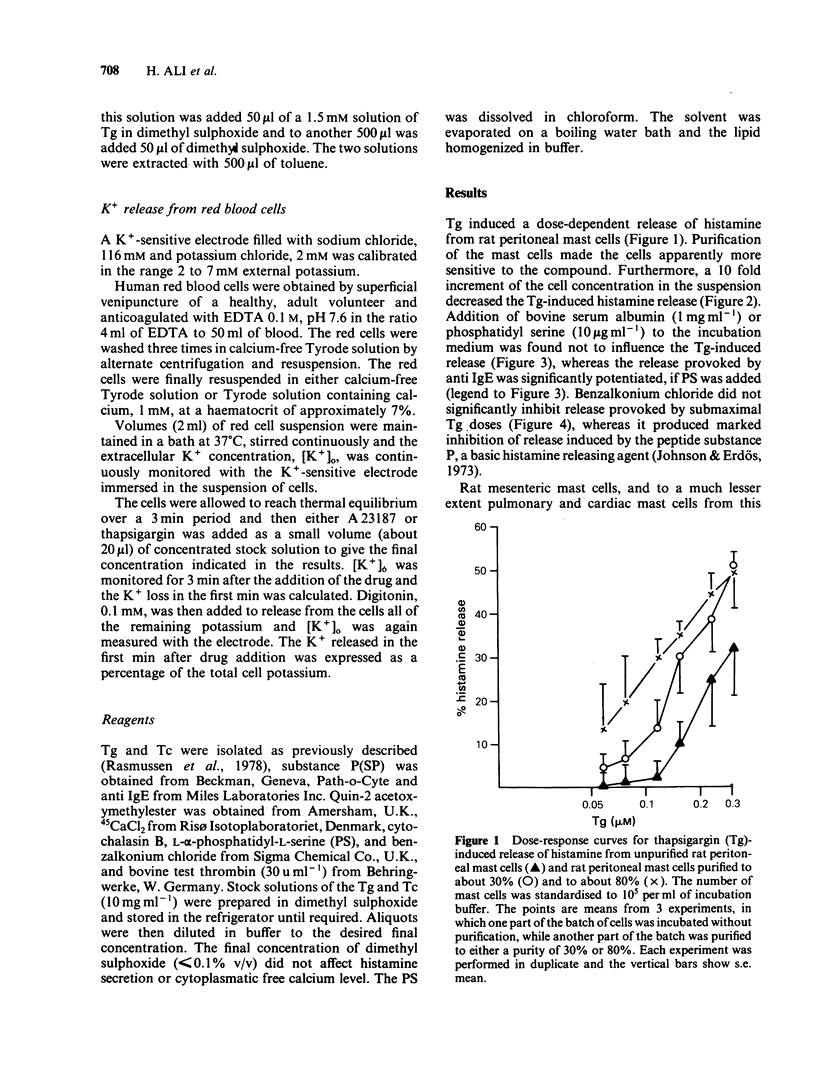
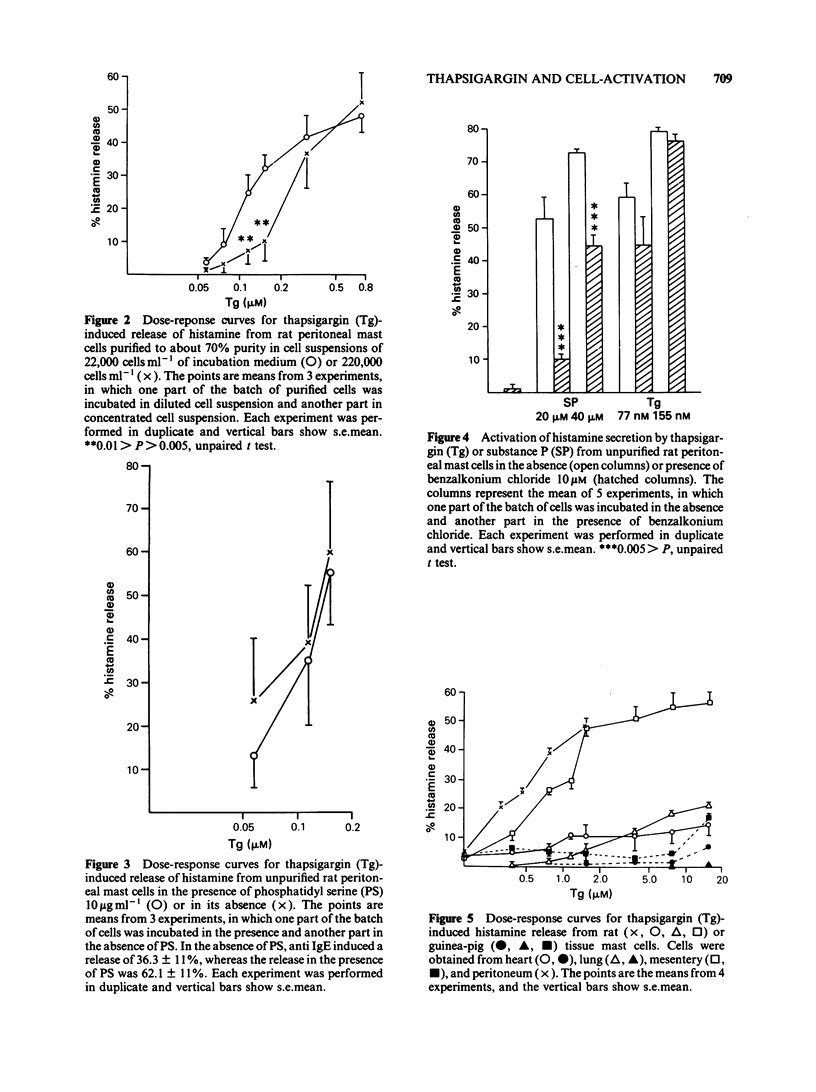
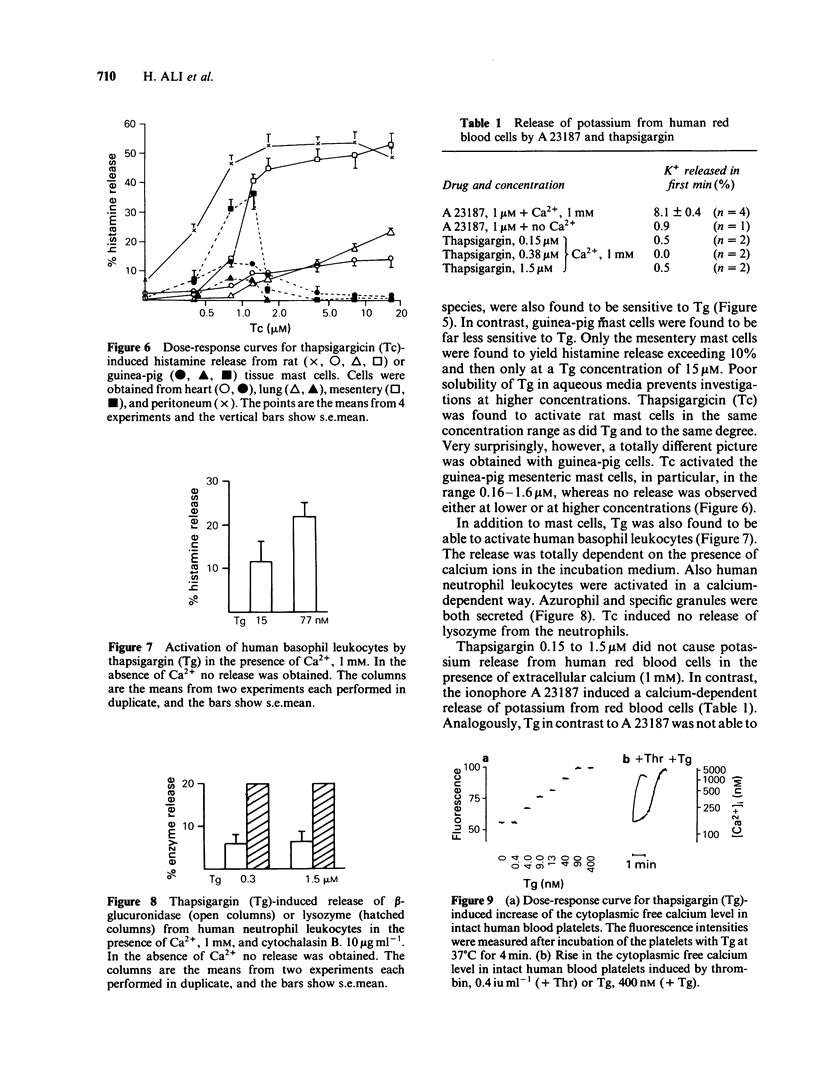
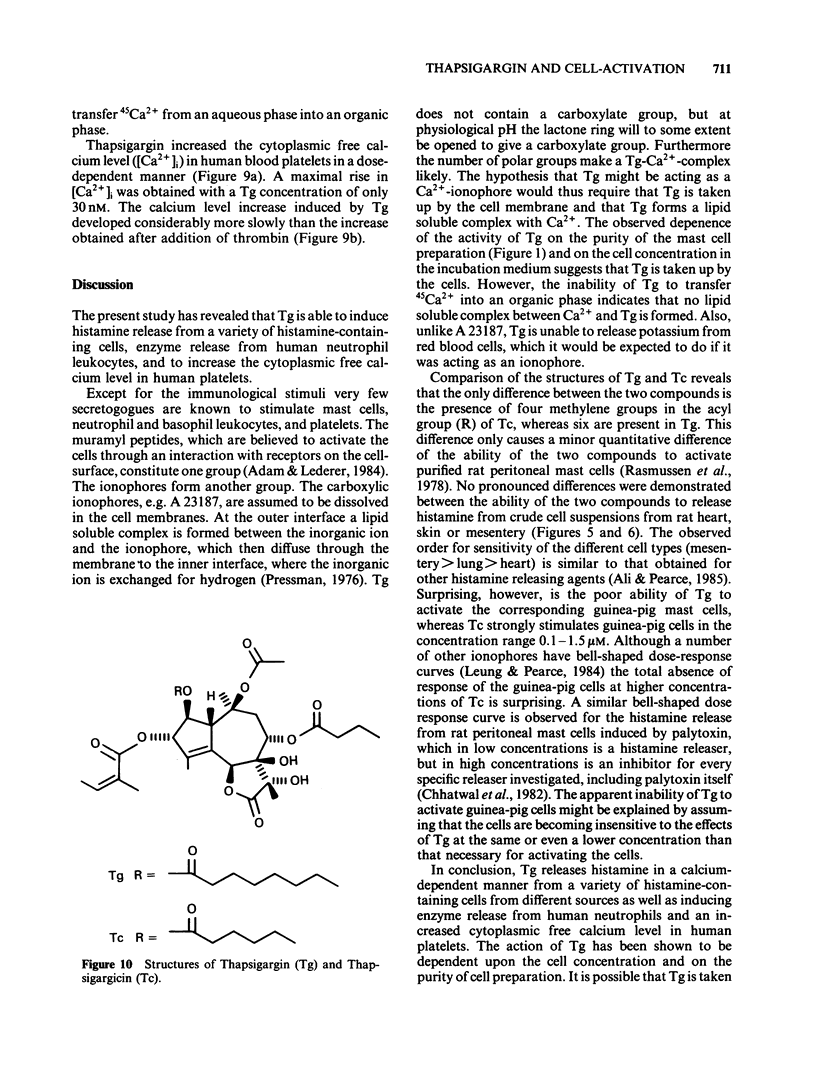
The ability of thapsigargin and thapsigargicin to activate mast cells and leukocytes has been investigated. The thapsigargin-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells was found to be dependent on the concentration of thapsigargin, the purity of the mast cell preparations, and the number of mast cells in suspension. Thapsigargin induced histamine release from human basophil leukocytes. Thapsigargin induced beta-glucuronidase and lysozyme release from human neutrophil leukocytes. Thapsigargin caused a release of histamine from mesentery, lung, and heart mast cells of the rat, but only to a minor extent from the corresponding guinea-pig cells. Thapsigargicin induced histamine release from mesentery, lung, and heart mast cells of the rat at concentrations from 0.1 microM but provoked only a release from the corresponding guinea-pig cells in the concentration-range 0.16 to 1.6 microM. Thapsigargin increased the cytoplasmic free calcium level in intact human blood platelets at concentrations from 3.0 nM.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam A., Lederer E. Muramyl peptides: immunomodulators, sleep factors, and vitamins. Med Res Rev. 1984 Apr-Jun;4(2):111–152. doi: 10.1002/med.2610040202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson G., Ennis M., Pearce F. L. The effect of alkaline earth cations on the release of histamine from rat peritoneal mast cells treated with compound 48/80 and peptide 401. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):395–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Ahnert-Hilger G., Beress L., Habermann E. Palytoxin both induces and inhibits the release of histamine from rat mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(2):97–100. doi: 10.1159/000233075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant B., Patkar S. A. The influence of hypertonicity on histamine release from isolated rat mast cells. Agents Actions. 1980 Apr;10(1 Pt 2):140–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02024197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M., Pearce F. L. Differential reactivity of isolated mast cells from the rat and guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 5;66(4):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Release of histamine from mast cells by vasoactive peptides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1252–1256. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K. B., Pearce F. L. A comparison of histamine secretion from peritoneal mast cells of the rat and hamster. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):693–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler L. J., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Effects of dibutyryl-3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphage, phosphodiesterase inhibitors and prostaglandin E1 on compound 48-80-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;20(9):2287–2297. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patkar S. A., Rasmussen U., Diamant B. On the mechanism of histamine release induced by thapsigargin from Thapsia garganica L. Agents Actions. 1979 Apr;9(1):53–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02024109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Ennis M. Isolation and some properties of mast cells from the mesentery of the rat and guinea pig. Agents Actions. 1980 Apr;10(1 Pt 2):124–131. doi: 10.1007/BF02024193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U., Brøogger Christensen S., Sandberg F. Thapsigargine and thapsigargicine, two new histamine liberators from Thapsia garganica L. Acta Pharm Suec. 1978;15(2):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


