Abstract
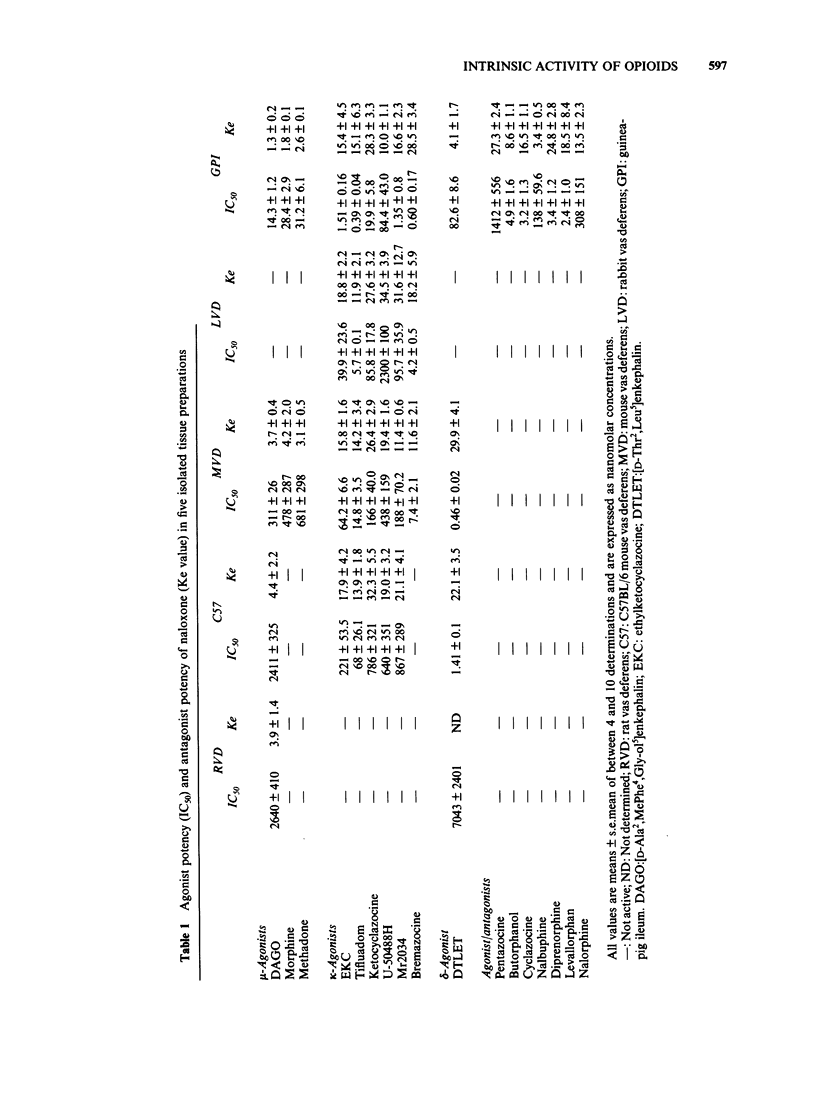
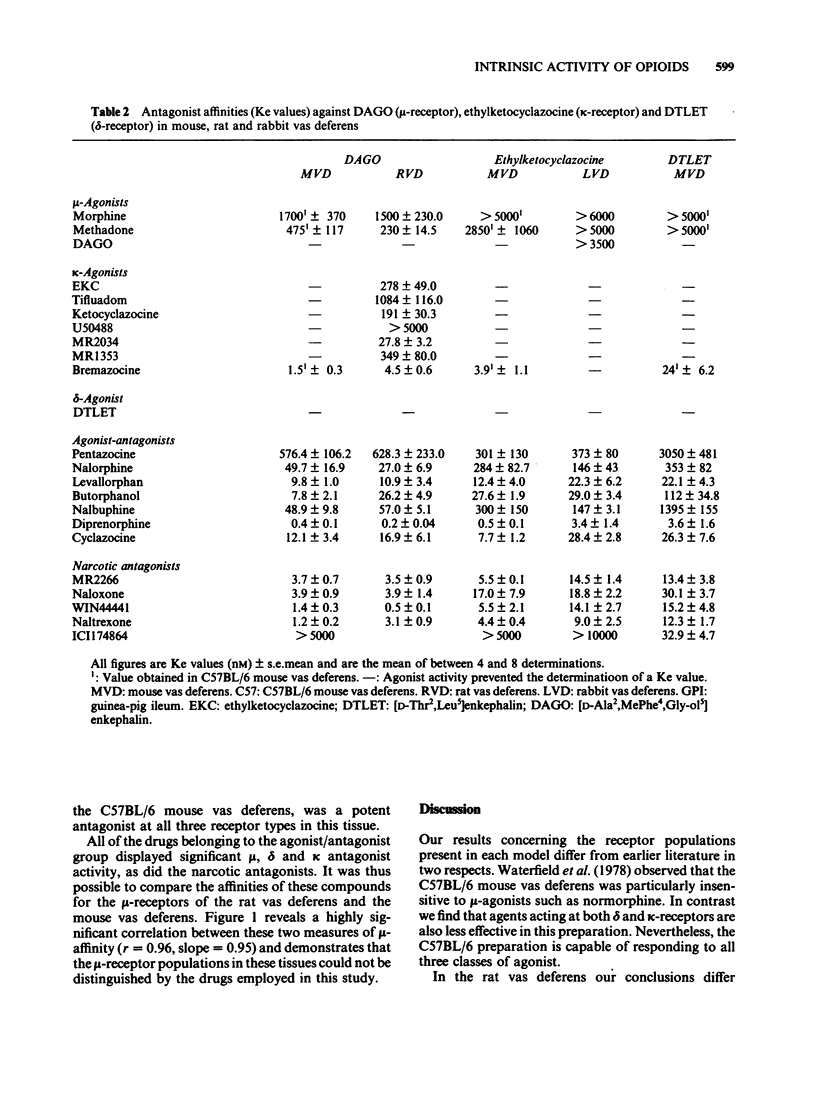
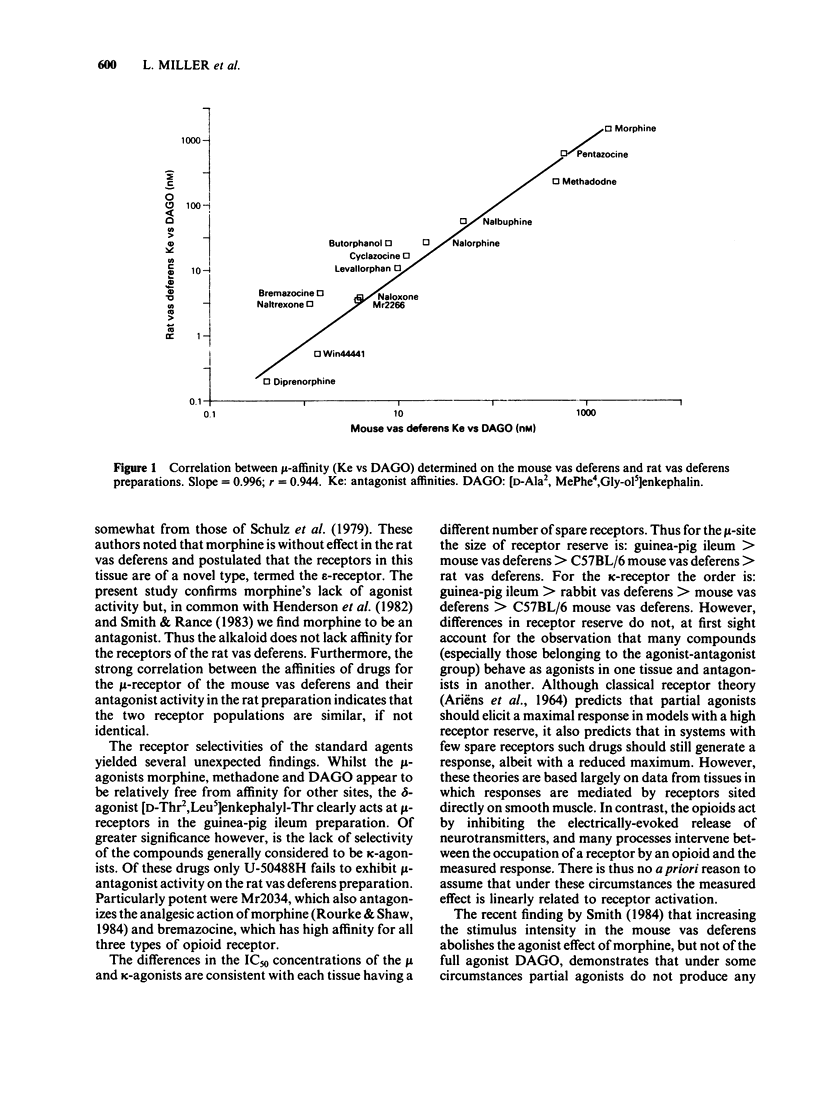
The effects of opioids were compared in five field-stimulated isolated tissue models, the guinea-pig ileum and vasa deferentia from rat, rabbit and mice of the Alderley Park and C57BL/6 strains. Although the mu-receptor agonist [D-Ala2, MePhe4, Gly-ol5] enkephalin appeared to act at similar receptors in the guinea-pig ileum, rat vas deferens, mouse vas deferens and C57BL/6 mouse vas deferens preparations, its potency varied considerably between these preparations. Similar potency differences were also observed with the kappa-agonist, ethylketocyclazocine. It is proposed that these variations in potency reflect differences in the number of spare receptors present in each model. The finding that some drugs which have agonist activity in the more sensitive preparations behave as antagonists in the less sensitive tissues supports this proposal and highlights the importance of intrinsic activity in determining the action of opioids. Many of the prototypic opioid agonists were found to be either partial agonists (eg. morphine and bremazocine) or to possess affinity for more than one receptor type (eg. ethylketocyclazocine, Mr 2034).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll J. A., Miller L., Shaw J. S., Downes C. P. Mu-receptor binding in physiological media: comparison with isolated tissue data. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M., Waterfield A. A. Assessment in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens of benzomorphans which have strong antinociceptive activity but do not substitute for morphine in the dependent monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. S., Day A. R., Freer R. J. Evidence for a single opioid receptor type on the field stimulated rat vas deferens. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2617–2622. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R. History and development of mixed opioid agonists, partial agonists and antagonists. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;7 (Suppl 3):273S–279S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Kosterlitz H. W. Increase in potencies of opioid peptides after peptidase inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Marcoli M., Kosterlitz H. W. Hamster vas deferens contains delta-opioid receptors. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Shaw J. S. Mu-receptors in the C57BL mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rourke J. D., Shaw J. S. Failure to demonstrate mu-isoreceptors. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Faase E., Wüster M., Herz A. Selective receptors for beta-endorphin on the rat vas deferens. Life Sci. 1979 Feb 26;24(9):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90368-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. F. Morphine, but not diacetyl morphine (heroin), possess opiate antagonist activity in the mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. F., Rance M. J. Opiate receptors in the rat vas deferens. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield A. A., Lord J. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Differences in the inhibitory effects of normorphine and opioid peptides on the responses of the vasa deferentia of two strains of mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan 15;47(2):249–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90399-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac J. M., Gacel G., Petit F., Dodey P., Rossignol P., Roques B. P. Deltakephalin, Tyr-D-Thr-Gly-Phe-Leu-Thr: a new highly potent and fully specific agonist for opiate delta-receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


