Abstract
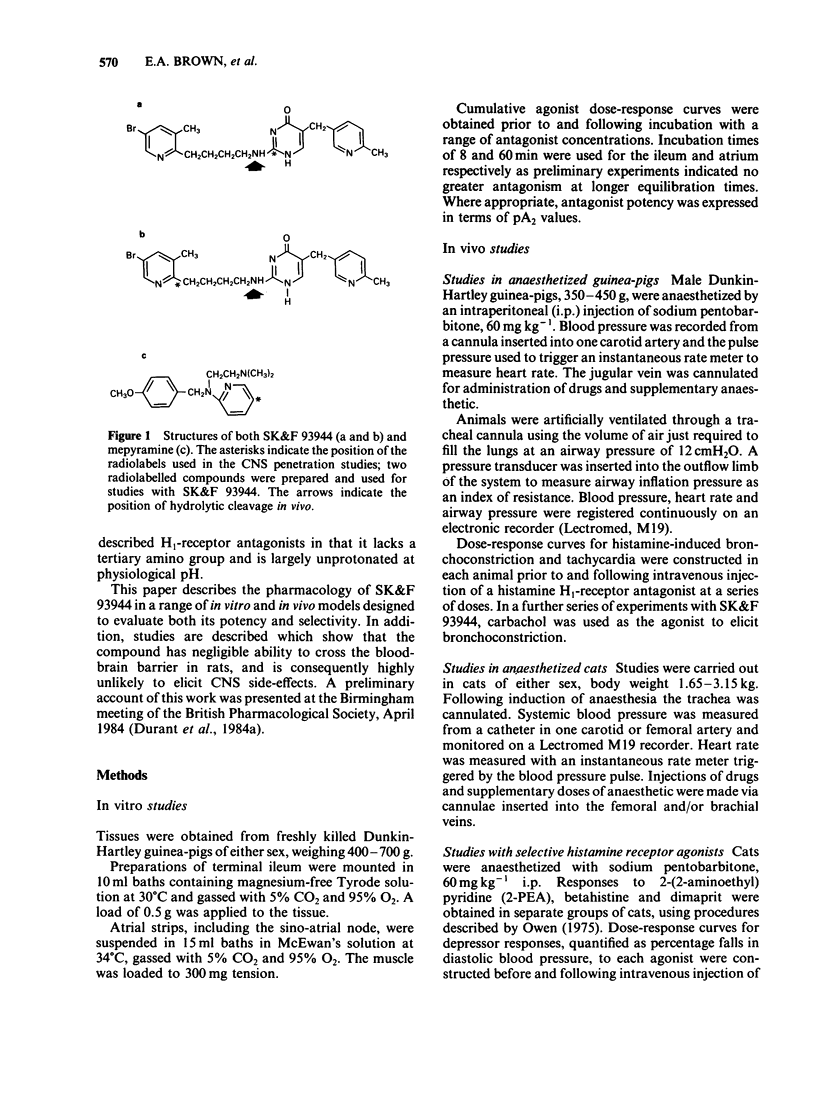
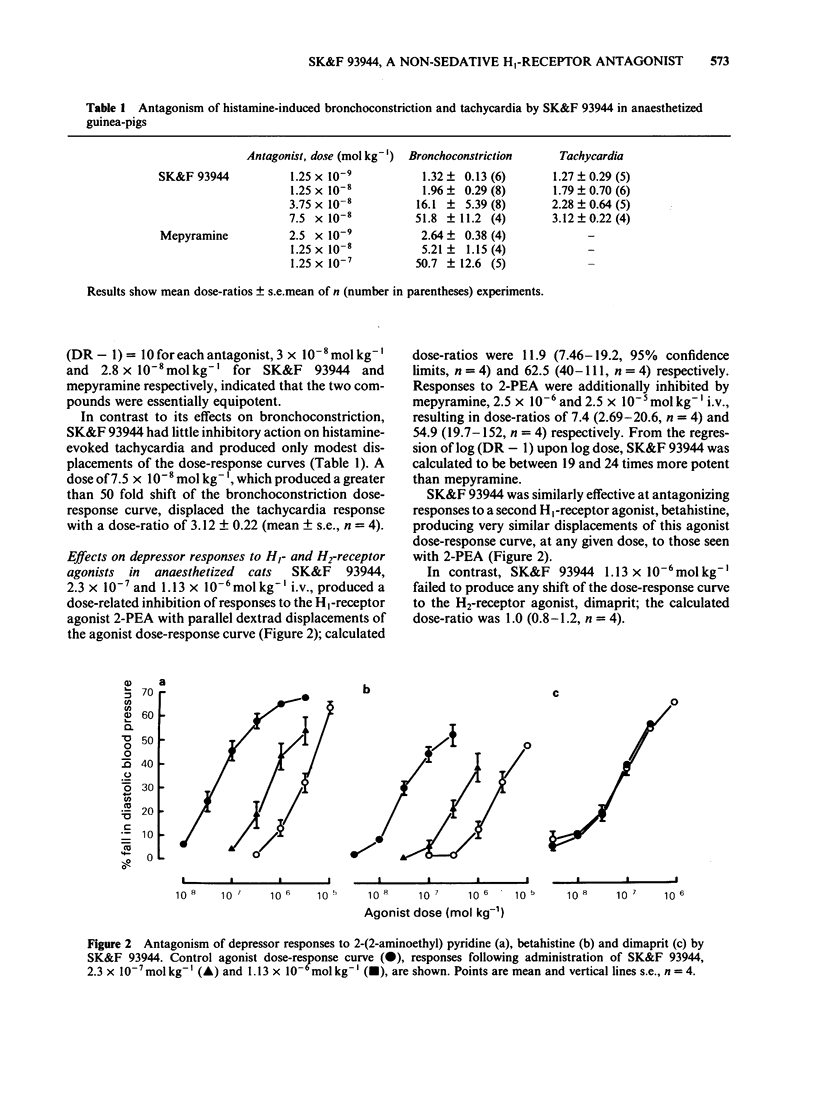
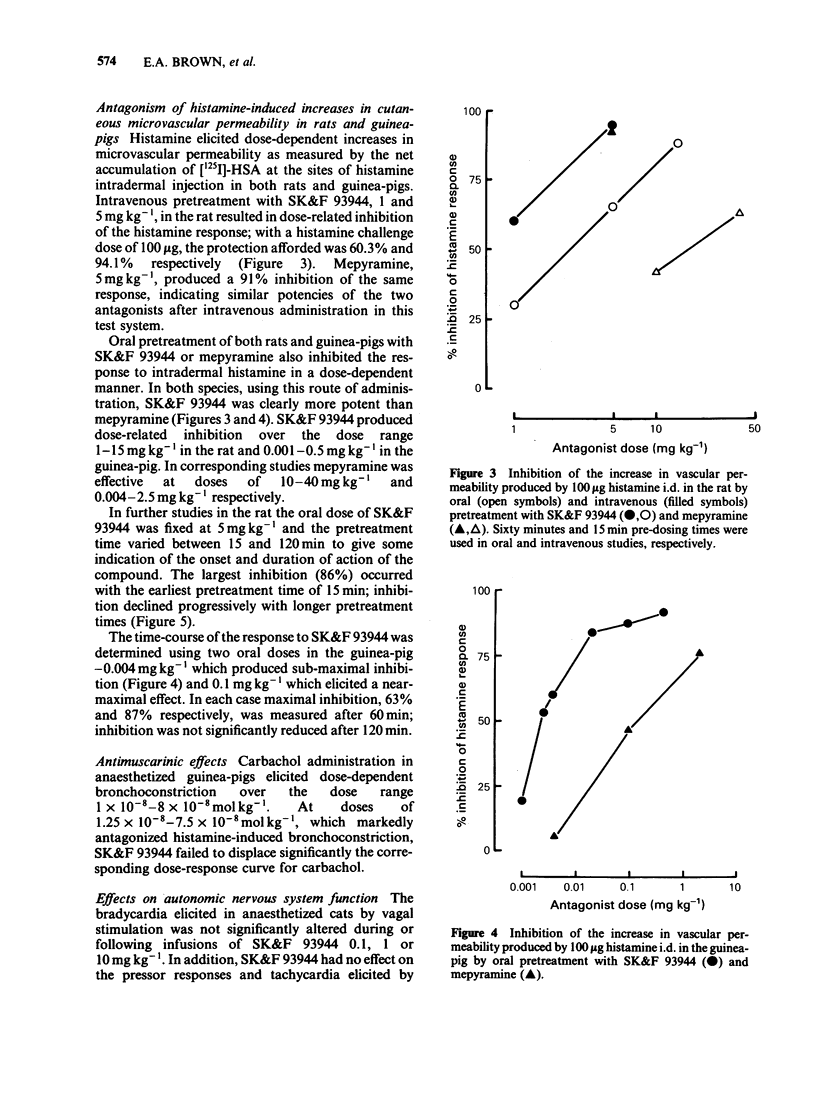
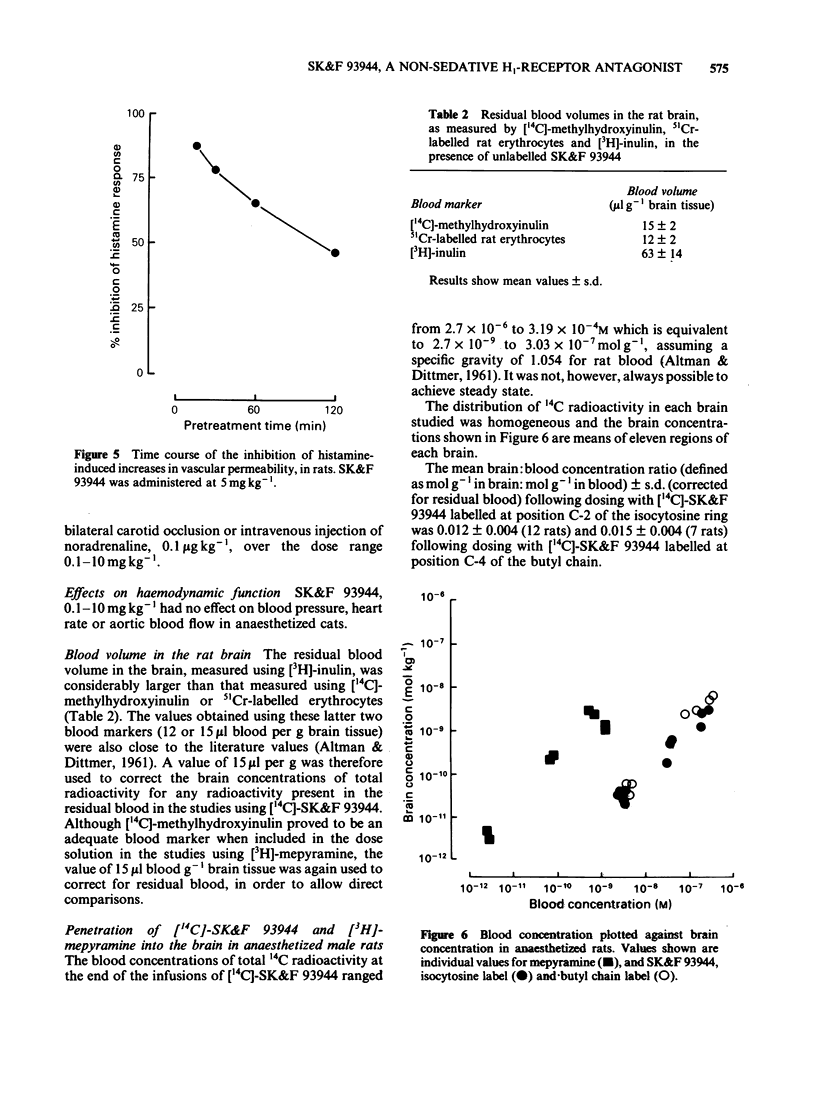
SK&F 93944 (temelastine), a novel histamine H1-receptor antagonist, has been studied in a variety of in vitro and in vivo test systems. SK&F 93944 was a competitive antagonist of histamine-induced contractions of guinea-pig ileum with a pA2 of 9.55 and a weak, non-competitive, inhibitor of the effects of histamine on guinea-pig atrium. In anaesthetized guinea-pigs SK&F 93944 displaced histamine bronchoconstriction dose-response curves at doses which had negligible effects on histamine tachycardia. In anaesthetized cats SK&F 93944 antagonized depressor responses to the histamine H1-receptor agonists, 2-(2-aminoethyl)pyridine and betahistine, at doses which had no effects on responses to the histamine H2-receptor agonist, dimaprit. Oral pretreatment with SK&F 93944 in conscious rats and guinea-pigs afforded protection versus the response to intradermal histamine injection. Comparative studies in each of the test systems showed that SK&F 93944 was of comparable or significantly greater potency than the standard compound, mepyramine. SK&F 93944 was found to be a weak, non-competitive antagonist of carbachol on the guinea-pig ileum but was devoid of measurable anticholinergic activity in vivo. Studies on the penetration of [14C]-SK&F 93944, labelled either in the isocytosine ring or in the butyl chain, showed that brain concentrations were very low when compared with the steady-state blood concentrations. In contrast, brain concentrations of [3H]-mepyramine exceeded blood concentrations by a factor of approximately 3. SK&F 93944 may have an advantage over classical histamine H1-receptor antagonists in that it is likely to be devoid of untoward effects on the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EBAUGH F. G., Jr, EMERSON C. P., ROSS J. F. The use of radioactive chromium 51 as an erythrocyte tagging agent for the determination or red cell survival in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1953 Dec;32(12):1260–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI102855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey C. A., Owen D. A. Cardiovascular studies with SK&F 93319, an antagonist of histamine at both H1- and H2-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):427–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fur G., Malgouris C., Uzan A. Effect of mequitazine a non sedative antihistamine on brain H1 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 10;29(6):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Pipkin M. A. A simple technique to simultaneously assess activity at histamine H1- and H2-receptors in vivo. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Jul;13(4):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Pipkin M. A., Woodward D. F. Studies on cutaneous vascular permeability in the rat: increases caused by histamine and histamine-like agents. Agents Actions. 1984 Jan;14(1):39–42. doi: 10.1007/BF01966830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A. The effects of histamine and some histamine-like agonists on blood pressure in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):173–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozzi S., Roth F. E., Tabachnick I. I. The pharmacology of azatadine, a potential antiallergy drug. Agents Actions. 1974 Oct;4(4):264–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01965229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J., Awouters F., Neimegeers C. J., Janssens F., Van Nueten J. M., Janssen P. A. In vivo pharmacology of astemizole, a new type of H1-antihistaminic compound. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 May;251(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


