Abstract
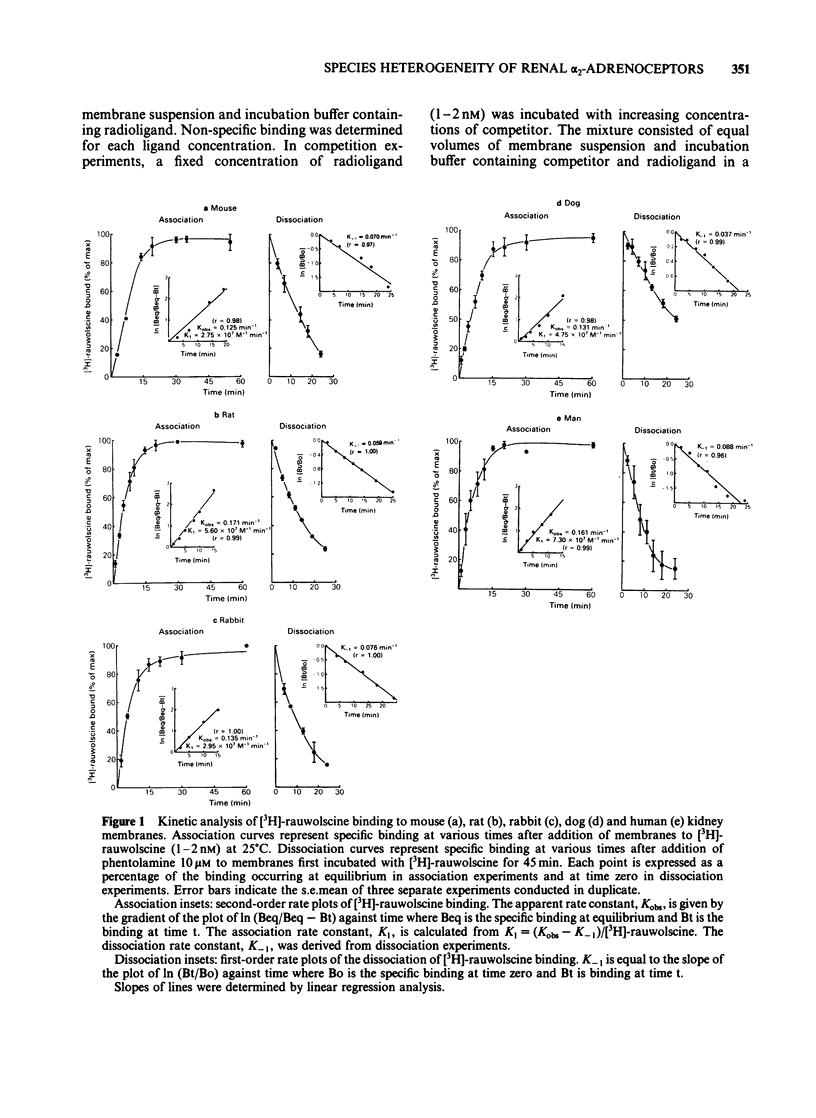
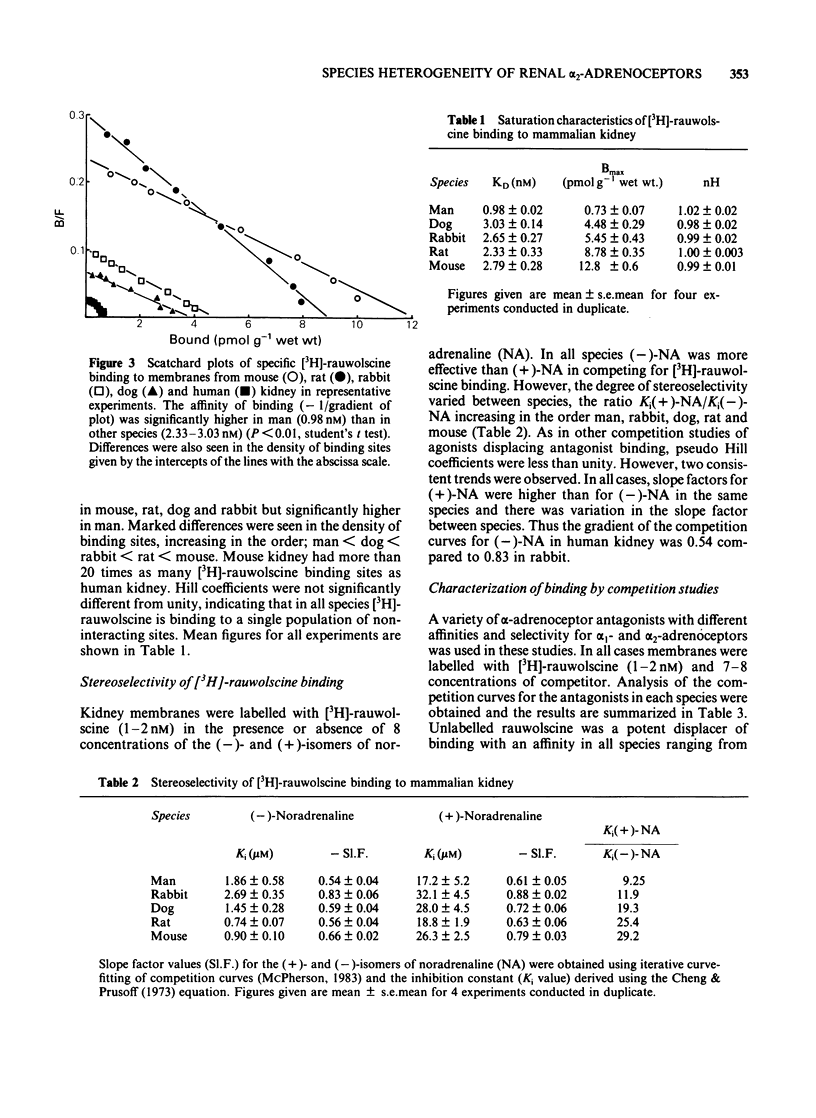
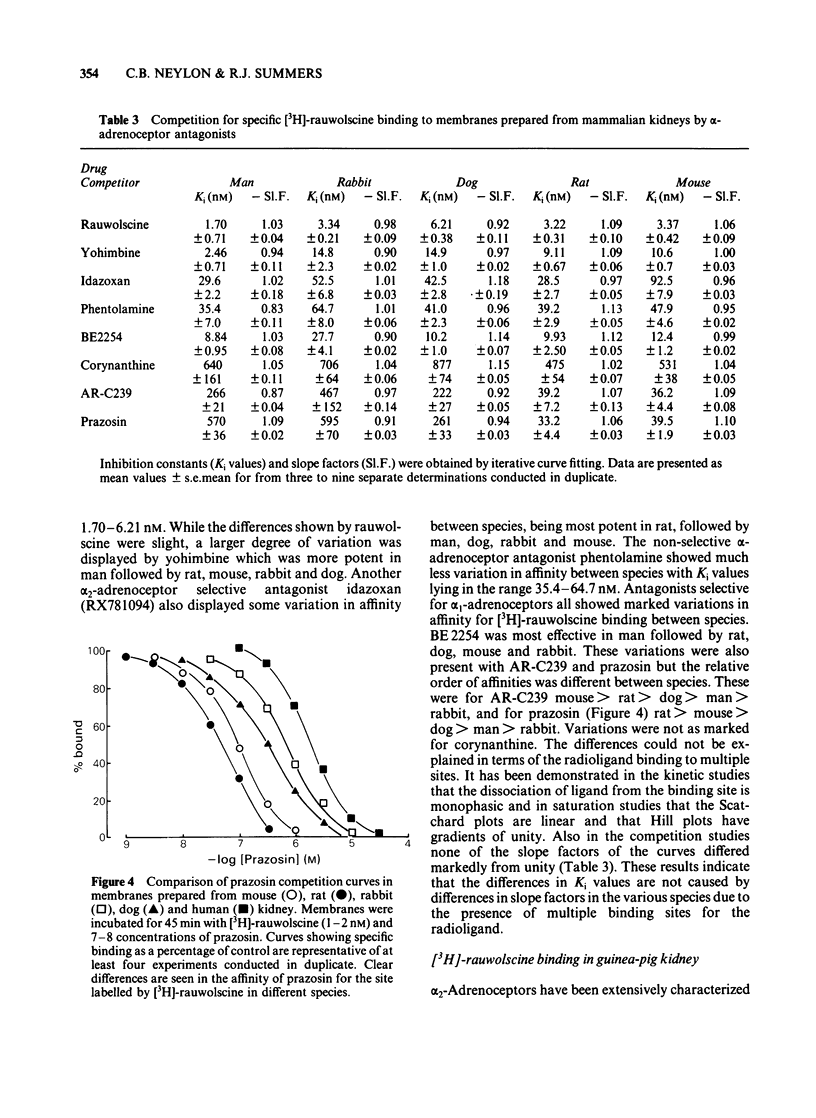
Binding of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist [3H]-rauwolscine was characterized in membrane preparations from the kidneys of mouse, rat, rabbit, dog, and man. In all species, binding reached equilibrium within 45 min and dissociated at a single exponential rate after addition of phentolamine 10 microM. Saturation studies showed that the affinity of [3H]-rauwolscine was similar in all species (2.33-3.03 nM) except man where it was significantly higher (0.98 nM). Marked differences were seen in the density of binding sites, increasing in the order: man less than dog less than rabbit less than rat less than mouse. In all cases, Hill coefficients were not significantly different from unity. [3H]-rauwolscine binds with low affinity (KD greater than 15 nM) to membranes prepared from guinea-pig kidney. The low affinity binding is not due to the absence of particular ions in the incubation medium or to receptor occupation by endogenous agonist. The binding in all species was found to be stereoselective with respect to the isomers of noradrenaline. However, differences were seen in the characteristics of agonist interactions with the binding site both between isomers and between species. Marked differences in affinity of particular alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists were observed for alpha 2-adrenoceptors labelled by [3H]-rauwolscine. These differences were most evident with the alpha 1-adrenoceptor selective antagonist prazosin which displayed inhibition constants (Ki values) of 33.2, 39.5, 261, 570 and 595 nM in rat, mouse, dog, man and rabbit, respectively. Differences are apparent in the characteristics of alpha 2-adrenoceptors labelled by [3H]-rauwolscine between species and it is suggested that the differences observed for alpha 1-selective antagonists such as prazosin may be related to binding to additional sites in the vicinity of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Jarrott B. Development of a radioiodinated ligand for characterising alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Life Sci. 1982 Mar 15;30(11):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90623-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariëns E. J., Simonis A. M. Physiological and pharmacological aspects of adrenergic receptor classification. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 May 15;32(10):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E., Eymer T., Arroyo J. 3H-yohimbine binding to guinea-pig kidney and calf cerebral cortex membranes: comparison with human platelets. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Dec;266(2):208–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Montégut M., Imbert-Teboul M., Morel F. Inhibition of alpha 2-adrenergic agonists on AVP-induced cAMP accumulation in isolated collecting tubule of the rat kidney. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Oct;37(3):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. Interactions of endogenous and exogenous norepinephrine with alpha 2 adrenoceptor binding sites in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1293–1298. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiguji M., Meltzer H. Y., U'Prichard D. C. Human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors: labeling with 3H-yohimbine, a selective antagonist ligand. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 15;28(24):2705–2717. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diop L., Dausse J. P., Meyer P. Specific binding of [3H]rauwolscine to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat cerebral cortex: comparison between crude and synaptosomal plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):710–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller D. J., Bylund D. B. Comparison of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and their regulation in rodent and porcine species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Nolte J., Weinheimer G. Preferential blockade of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors by BE 2254. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 5;70(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90429-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah J. A., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L. RX781094, a new potent alpha 2 adrenoceptor antagonist. In vivo and in vitro studies in the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;322(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00500769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Louis W. J., Summers R. J. The characteristics of [3H]-clonidine binding to an alpha-adrenoceptor in membranes from guinea-pig kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;65(4):663–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Summers R. J. Localisation of [3H]-clonidine binding in guinea pig kidney [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;64(3):418P–419P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. S., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. A quantitative analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor interactions: resolution of high and low affinity states of the receptor by computer modeling of ligand binding data. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):14–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerry R., Scrutton M. C., Wallis R. B. Mammalian platelet adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;81(1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latifpour J., Jones S. B., Bylund D. B. Characterization of [3H]yohimbine binding to putative alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in neonatal rat lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Dec;223(3):606–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Speck J. L., Smith S. K. Sodium ion modulates agonist and antagonist interactions with the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in membrane and solubilized preparations. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):609–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. A study of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat renal cortex: comparison of [3H]-prazosin binding with the alpha 1-adrenoceptor modulating gluconeogenesis under physiological conditions. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. Evidence from binding studies for alpha 2-adrenoceptors directly associated with glomeruli from rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 17;90(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90554-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine binding to alpha-adrenoceptors in membranes prepared from regions of rat kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Hoffman B. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Differential regulation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by Na+ and guanine nucleotides. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):709–711. doi: 10.1038/288709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Sanchez A., Saavedra J., Haywood J. R., Gandler T., Rodes T. Altered renal alpha 2-adrenergic receptor regulation in genetically hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3 Pt 2):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama A. I., Lin L. L., Repp L. D., U'Prichard D. C. Magnesium reduces affinities of antagonists at rat cortex alpha 2-adrenergic receptors labeled with 3H-clonidine: evidence for heterogeneity of alpha 2-receptor conformations with respect to antagonists. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 12;30(15):1305–1311. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90693-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snavely M. D., Insel P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes in the rat renal cortex. Differential regulation of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors by guanyl nucleotides and Na. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):532–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. The characteristics of adrenoceptors in homogenates of human cerebral cortex labelled by (3H)-rauwolscine. Life Sci. 1983 Sep 12;33(11):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90667-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J. Renal alpha adrenoceptors. Fed Proc. 1984 Nov;43(14):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ashida T., Deguchi F., Ikeda M. 3H-clonidine and 3H-rauwolscine binding to membranes from rat cerebral cortex and kidney. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;33(3):713–716. doi: 10.1254/jjp.33.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Qian J. Q., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, van Zwieten P. A. A study of the selectivity and potency of rauwolscine, RX 781094 and RS 21361 as antagonists of alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai B. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-specific effects of guanine nucleotides on alpha-adrenergic receptors in human platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUMJ DIFFERENT TYPES OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC ALPHA-RECEPTORS. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Apr;17:202–216. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological classification of adrenergic alpha receptors in the guinea pig. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):164–166. doi: 10.1038/273164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Johnston C. I. Characterization of adenylate cyclase-coupled alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in rat renal cortex using [3H]yohimbine. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. alpha 2-Adrenergic receptors are associated with renal proximal tubules. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 31;67(4):493–495. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



