Abstract
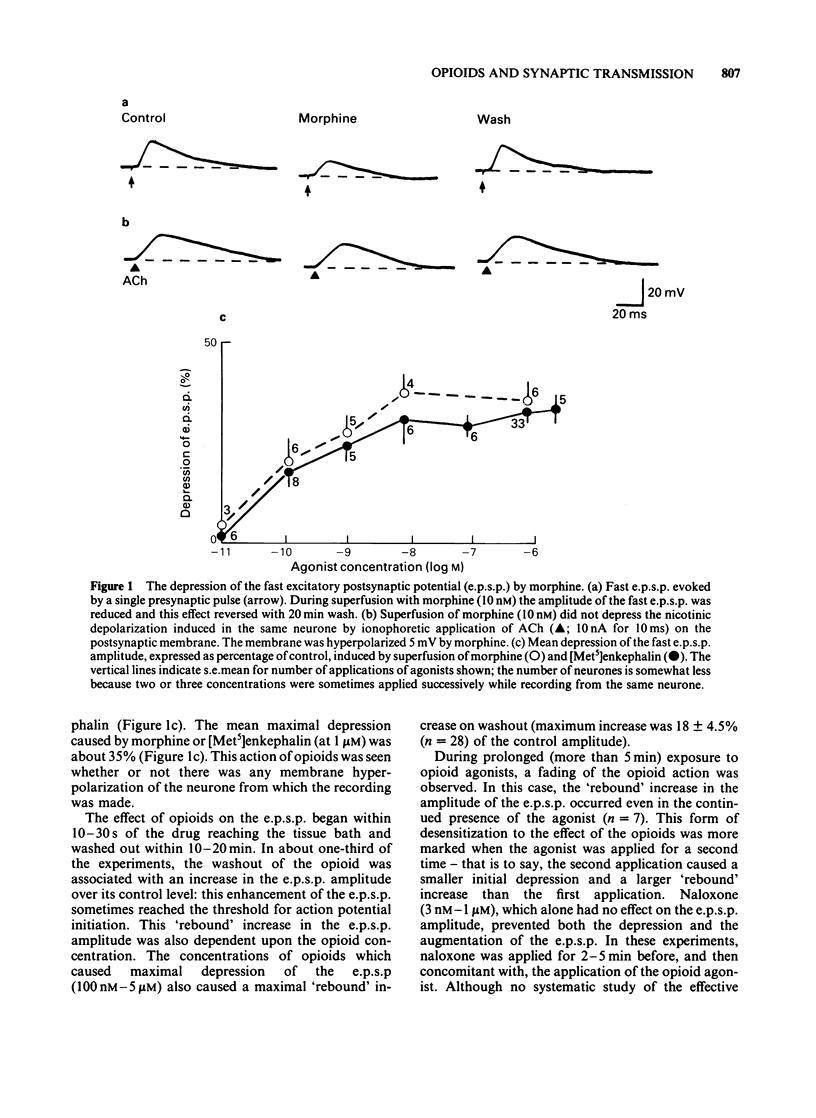
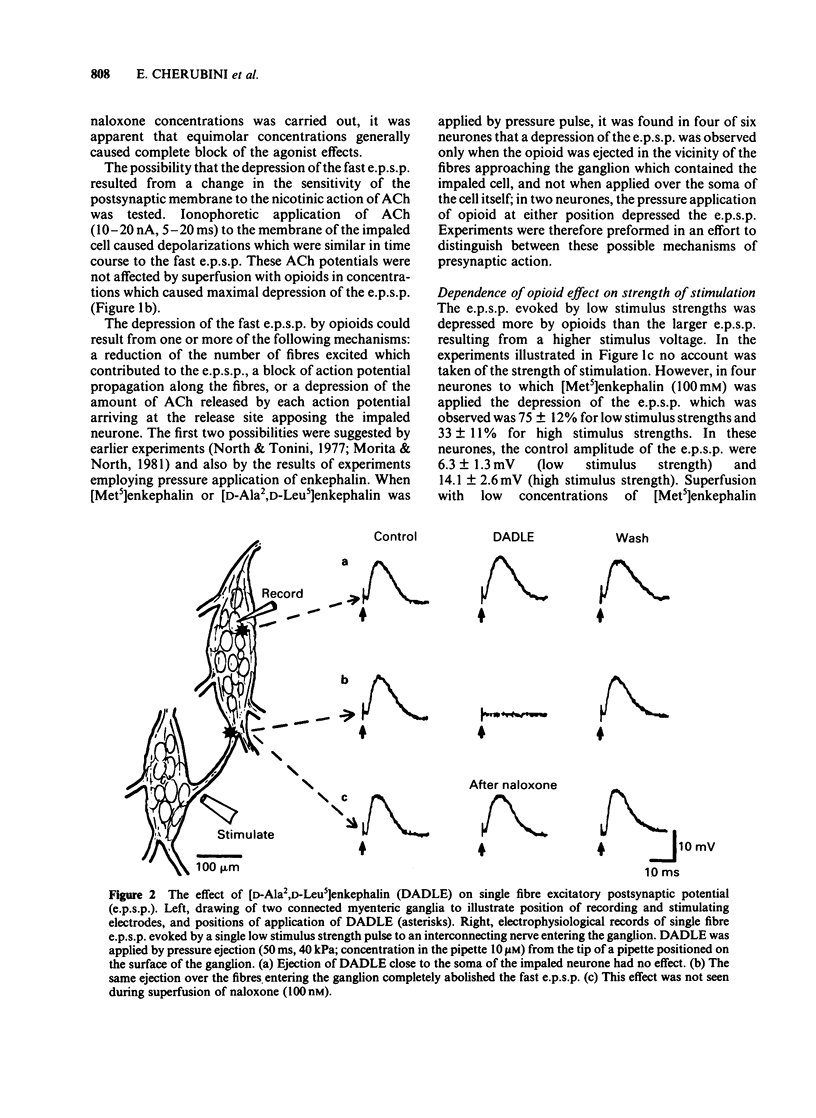
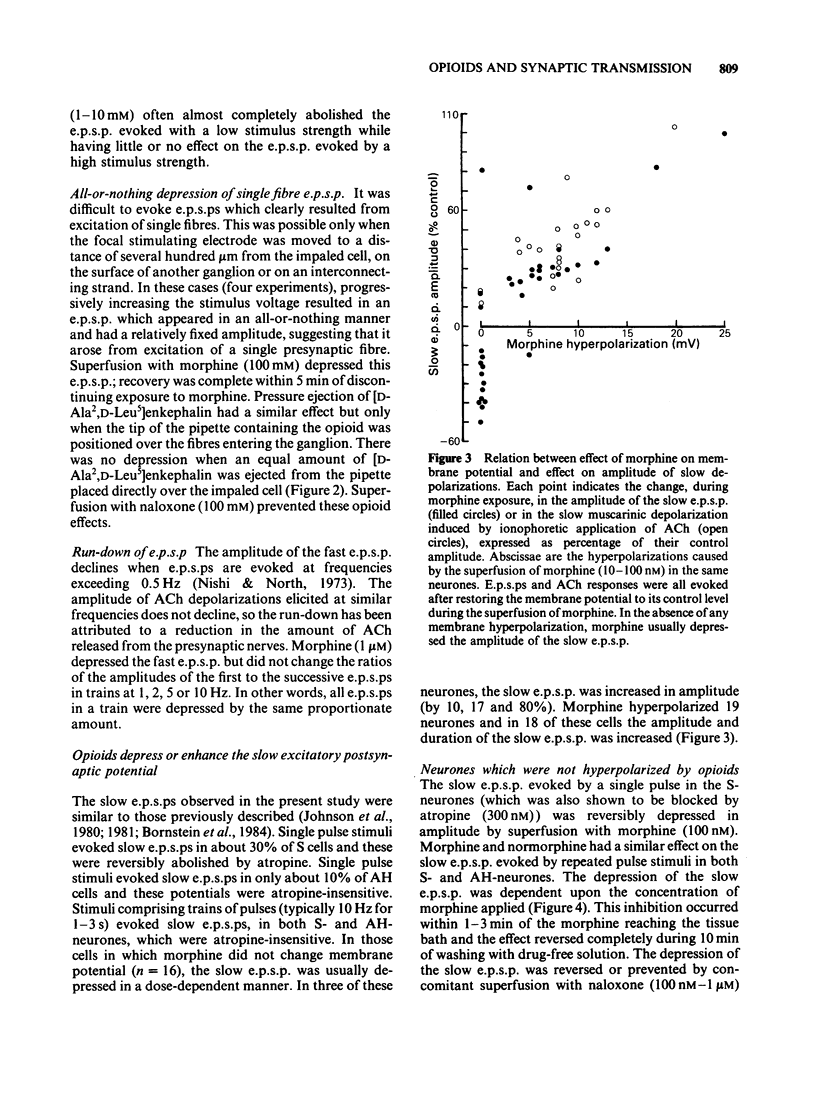
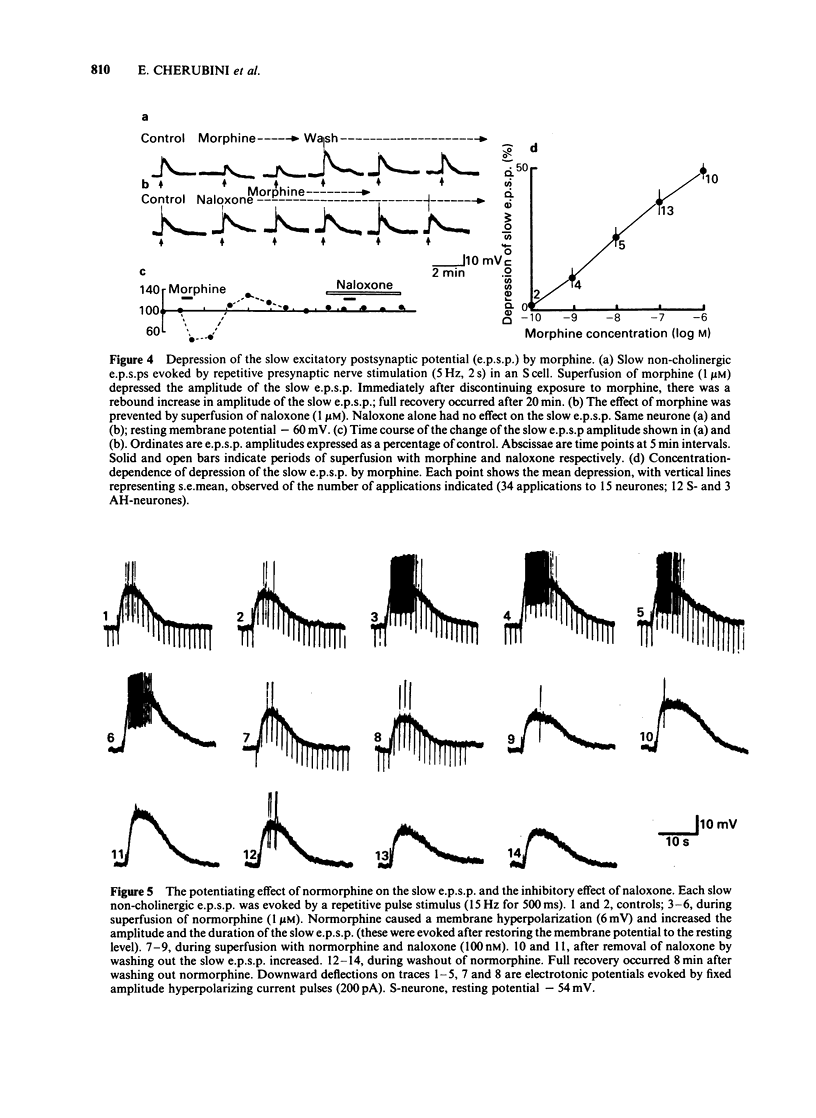
Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Presynaptic nerves were excited by a focal stimulating electrode on an interganglionic strand. Fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (e.p.s.ps) were depressed in amplitude by morphine and [Met5]enkephalin in the concentration range of 1 nM-1 microM. Nicotinic depolarizations evoked by exogenously applied acetylcholine (ACh) were not affected by these opioids. Hyperpolarization of the presynaptic fibres probably contributed to the depression of the fast e.p.s.p. because fast e.p.s.ps evoked by low stimulus voltages were more depressed than those evoked by high stimulus voltages and fast e.p.s.ps resulting from activation of a single presynaptic fibre were blocked in a non-graded manner. Opioids depressed the slow e.p.s.p. in those neurones in which they did not change the resting membrane potential. The slow e.p.s.p. was increased in amplitude in those neurones hyperpolarized by opioids. Depolarizations resulting from application of barium, substance P or ACh were also enhanced by opioids. Equivalent circuit models in which opioids increase, and substance P or ACh decrease, the same potassium conductance could account for this enhancement. The actions of opioids were prevented or reversed by naloxone (1 nM-1 microM). It is concluded that morphine and enkephalin inhibit the release of ACh and a non-cholinergic transmitter from fibres of the myenteric plexus, and that this may involve a hyperpolarization of presynaptic fibres. Additionally, opioids can interact postsynaptically with other substances which affect membrane potassium conductances.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bixby J. L., Spitzer N. C. Enkephalin reduces calcium action potentials in Rohon-Beard neurons in vivo. J Neurosci. 1983 May;3(5):1014–1018. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-01014.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Spitzer N. C. Enkephalin reduces quantal content at the frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):431–432. doi: 10.1038/301431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein J. C., North R. A., Costa M., Furness J. B. Excitatory synaptic potentials due to activation of neurons with short projections in the myenteric plexus. Neuroscience. 1984 Mar;11(3):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., Morita K., North R. A. Morphine augments calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., North R. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on neurones of guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., North R. A., Surprenant A. Quinine blocks a calcium-activated potassium conductance in mammalian enteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Who do barium ions imitate acetylcholine? Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Hirst G. D., Silinsky E. M. Interaction between inhibitory and excitatory synaptic potentials at a peripheral neurone. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):647–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Pinsky C. Morphine impairs acetylcholine release but facilitates acetylcholine action at a skeletal neuromuscular junction. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 19;231(20):93–94. doi: 10.1038/newbio231093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Miller R. J. Distribution and projections of nerves with enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1983 Apr;8(4):653–664. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Scalisi J. A. Effects of opioids on noncholinergic excitatory responses of the guinea-pig isolated ileum: inhibition of release of enteric substance P. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z. G., Simmons M. A., Dun N. J. Enkephalinergic modulation of non-cholinergic transmission in mammalian prevertebral ganglia. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 4;235(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., Morita K., North R. A. Mediators of slow synaptic potentials in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:175–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Slow synaptic potentials in neurones of the myenteric plexus. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:505–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Nishi S. Sites and mechanisms of actions of enkephalin in the feline parasympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:111–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A., Williams J. T. The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1163):191–208. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalin as a transmitter for presynaptic inhibition in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):80–82. doi: 10.1038/294080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalins presynaptically inhibit cholinergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):515–516. doi: 10.1038/282515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. In vitro models in the study of structure-activity relationships of narcotic analgesics. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:29–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Pumain R., Renaud L. The mechanism of excitation by acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):247–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Opiate activation of potassium conductance in myenteric neurons: inhibition by calcium ion. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 17;242(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90504-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Opiates and enkephalin reduce the excitability of neuronal processes. Neuroscience. 1981;6(10):1943–1951. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists inactivate potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:125–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. The calcium-activated potassium conductance in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:341–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Electrophysiology of the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Katayama Y., Williams J. T. On the mechanism and site of action of enkephalin on single myenteric neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic synaptic potentials in guinea-pig myenteric plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:151–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. The time course of muscarinic depolarization of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tonini M. The mechanism of action of narcotic analgesics in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. Opiate activation of potassium conductance inhibits calcium action potentials in rat locus coeruleus neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):225–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C. Correlation between acetylcholine release and neuronal activity in the guinea-pig ileum myenteric plexus; effect of morphine. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., MacDonald R. L. Opioid peptides selective for mu- and delta-opiate receptors reduce calcium-dependent action potential duration by increasing potassium conductance. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



