Abstract
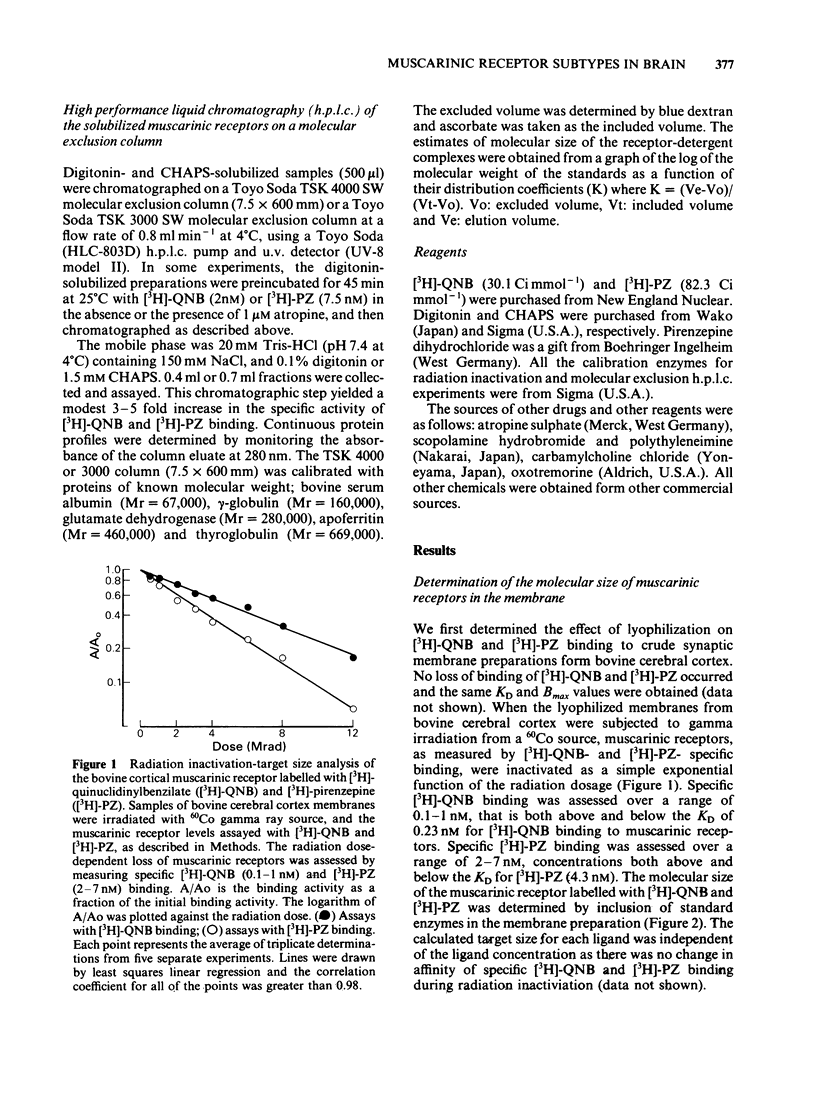
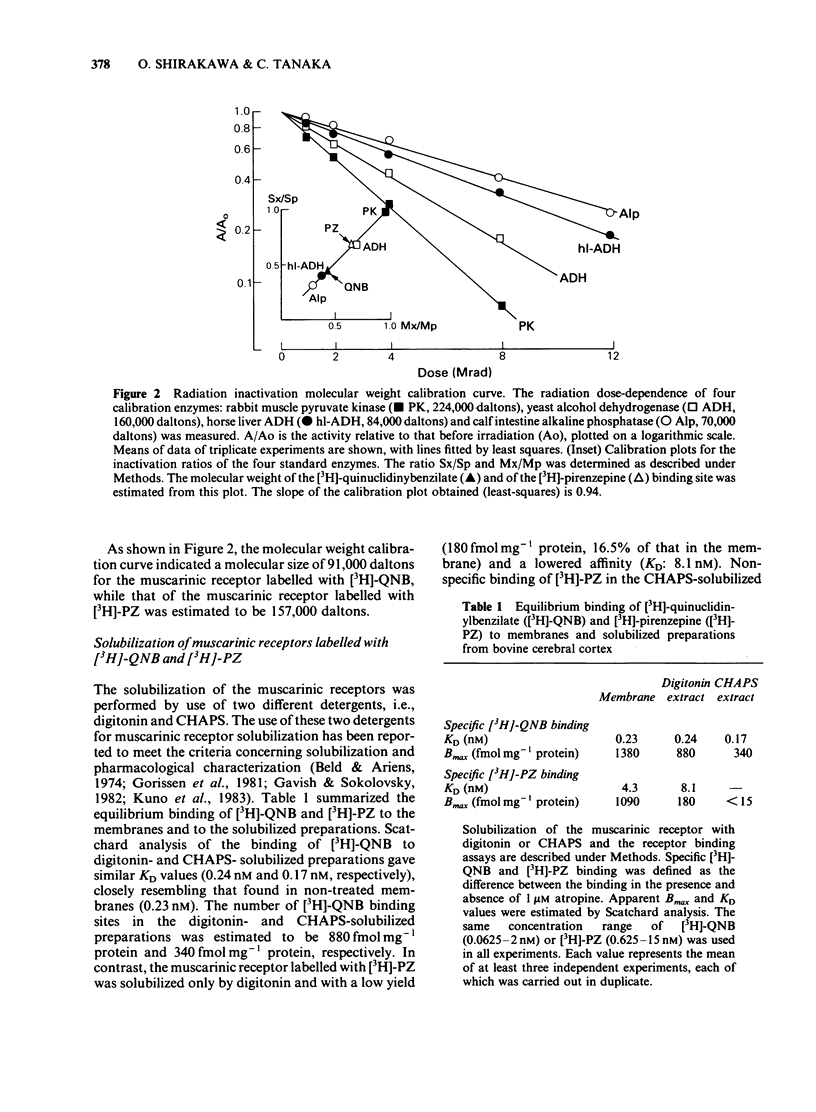
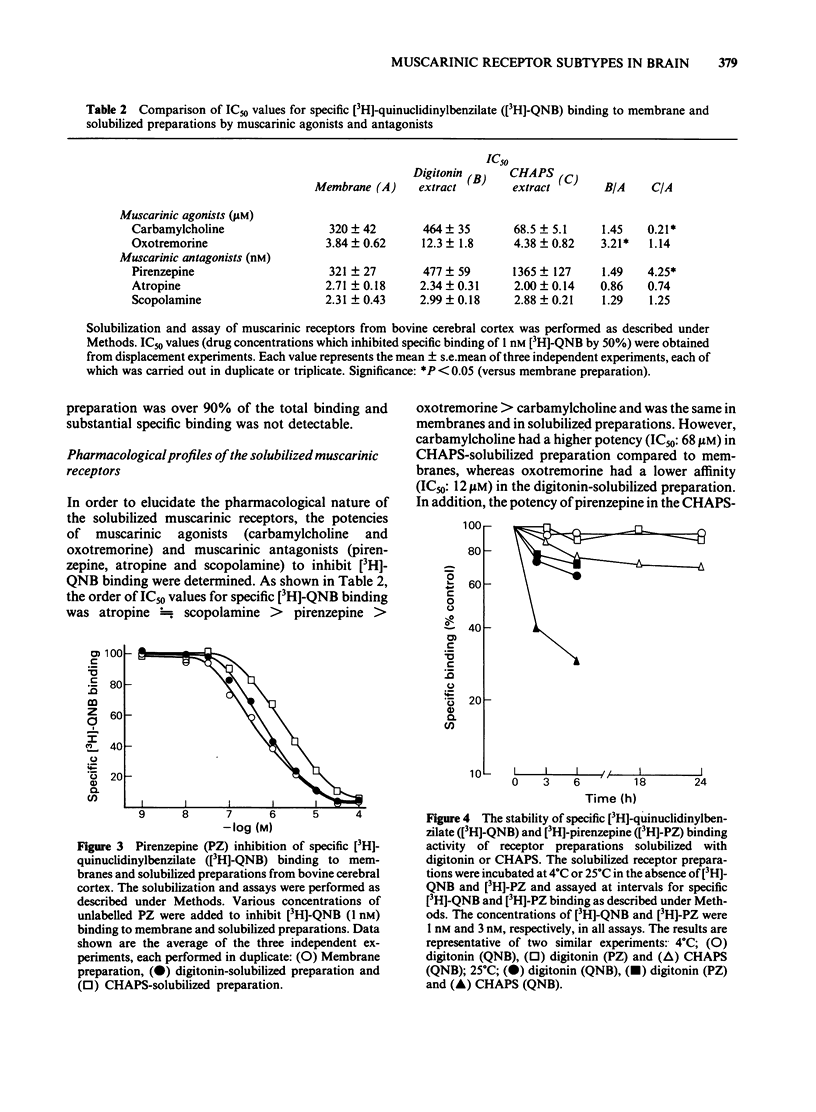
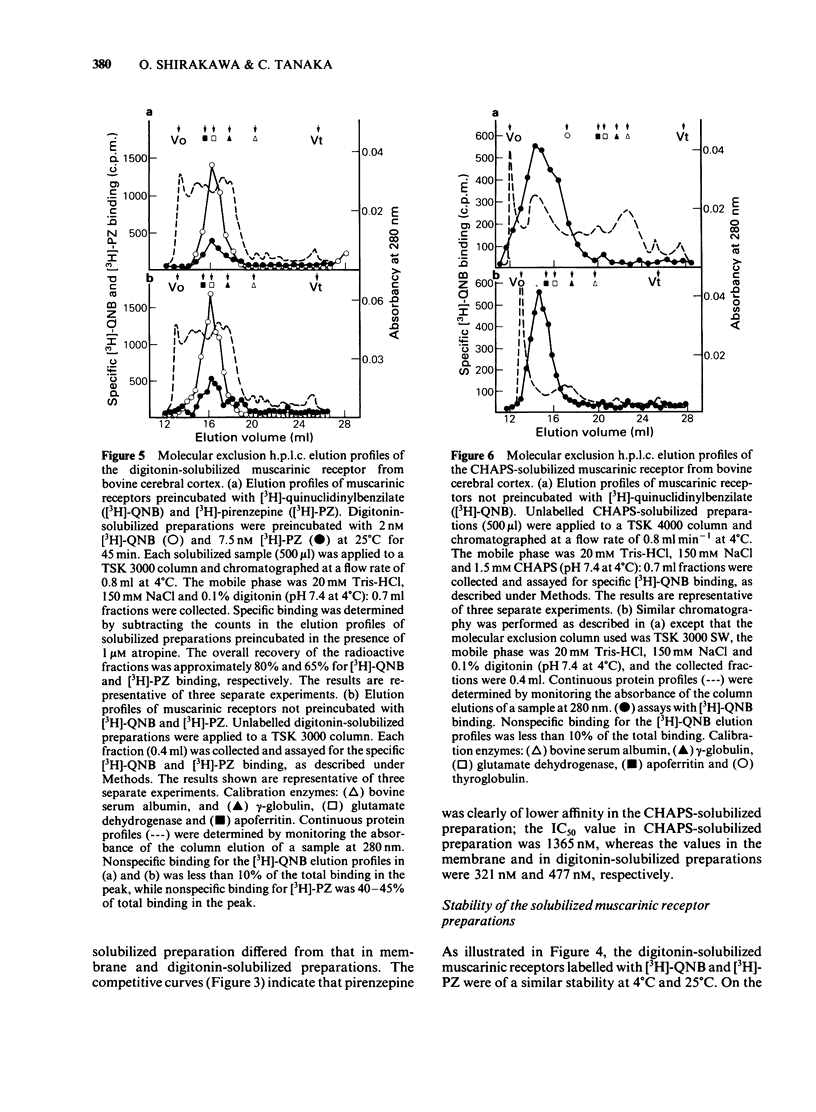
Muscarinic receptor subtypes in bovine cerebral cortex were investigated by means of radiation inactivation and molecular exclusion high performance liquid chromatography (h.p.l.c.). The functional molecular size of the muscarinic receptor in situ was determined by the radiation inactivation method. The value for the muscarinic receptor labelled with [3H]-quinuclidinylbenzilate ([3H]-QNB) was 91,000 daltons, while that labelled with [3H]-pirenzepine [( 3H]-PZ) was 157,000 daltons. The muscarinic receptor solubilized with digitonin could be labelled with [3H]-PZ as well as with [3H]-QNB. 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)-dimethylammonio] - propane sulphonate (CHAPS) solubilized the muscarinic receptor labelled with [3H]-QNB but not that labelled with [3H]-PZ, in agreement with the low affinity of pirenzepine for inhibiting [3H]-QNB binding in CHAPS-solubilized preparations. The size of the muscarinic receptor in solution was estimated by molecular exclusion h.p.l.c. The digitonin-solubilized muscarinic receptor had a molecular weight of 290,000 and the [3H]-QNB and [3H]-PZ binding activities behaved identically. The CHAPS-solubilized muscarinic receptor labelled with [3H]-QNB was apparently of high molecular weight (greater than 1,000,000 Mr), indicating the formation of aggregates and/or micelles. In the presence of digitonin this form was dissociated into a lower molecular weight species (580,000 Mr). These data indicate that the ligand binding component of the muscarinic receptor species labelled by both [3H]-QNB and [3H]-PZ exists on the same receptor protein, but that the [3H]-PZ binding component in situ is probably coupled to other components in the membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beld A. J., Ariëns E. J. Stereospecific binding as a tool in attempts to localize and isolate muscarinic receptors. Part II. Binding of (plus)-benzetimide, (minus)-benzetimide and atropine to a fraction from bovine tracheal smooth muscle and to bovine caudate nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;25(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Haga K., Haga T., Hulme E. C. Hydrodynamic properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors solubilized from rat forebrain. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug;82(4):839–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. A study of the muscarinic receptor by gel electrophoresis. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;66(2):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb13685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. The binding of agonists to brain muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;14(5):723–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lawson-Wendling K., Pugsley T. A. A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethylenimine-treated filters. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Sokolovsky M. Solubilization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor by zwitterionic detergent from rat brain cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 15;109(3):819–824. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorissen H., Aerts G., Ilien B., Laduron P. Solubilization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors from mammalian brain: an analytical approach. Anal Biochem. 1981 Feb;111(1):33–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Pirenzepine distinguishes between different subclasses of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):90–92. doi: 10.1038/283090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Giachetti A. Muscarinic receptor subtypes: M1 and M2 biochemical and functional characterization. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 27;31(26):2991–2998. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschowitz B. I., Fong J., Molina E. Effects of pirenzepine and atropine on vagal and cholinergic gastric secretion and gastrin release and on heart rate in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 May;225(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempner E. S., Schlegel W. Size determination of enzymes by radiation inactivation. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):2–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90617-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Shirakawa O., Tanaka C. Regulation of the solubilized bovine cerebral cortex muscarinic receptor by GTP and Na+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):948–953. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91709-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. M., Barnard E. A., Dolly J. O. Size of acetylcholine receptors in the membrane. An improved version of the radiation inactivation method. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):2210–2217. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruess K. P., Liefländer M. Action of detergents on covalently labelled, membrane bound muscarine acetylcholinreceptor of bovine nucleus caudatus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Matsumoto K., Takeyasu K., Higuchi H., Yoshida H. Molecular mechanism of the effects of guanine nucleotide and sulfhydryl reagent on muscarinic receptors in smooth muscles studied by radiation inactivation. Life Sci. 1982 Jul 19;31(3):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter J. C. Muscarinic cholinergic receptor structure. Receptor size, membrane orientation, and absence of major phylogenetic structural diversity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4842–4848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. [3h]pirenzepine selectively identifies a high affinity population of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 1;31(18):2019–2023. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


