Abstract
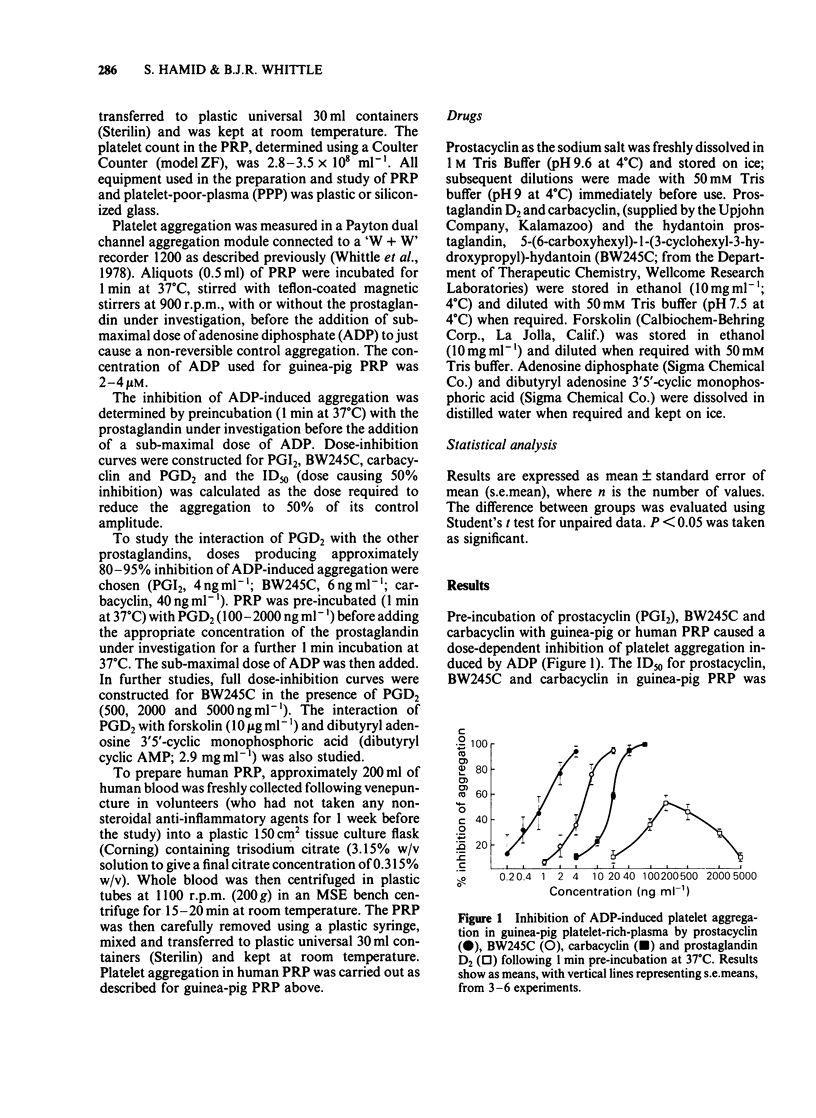
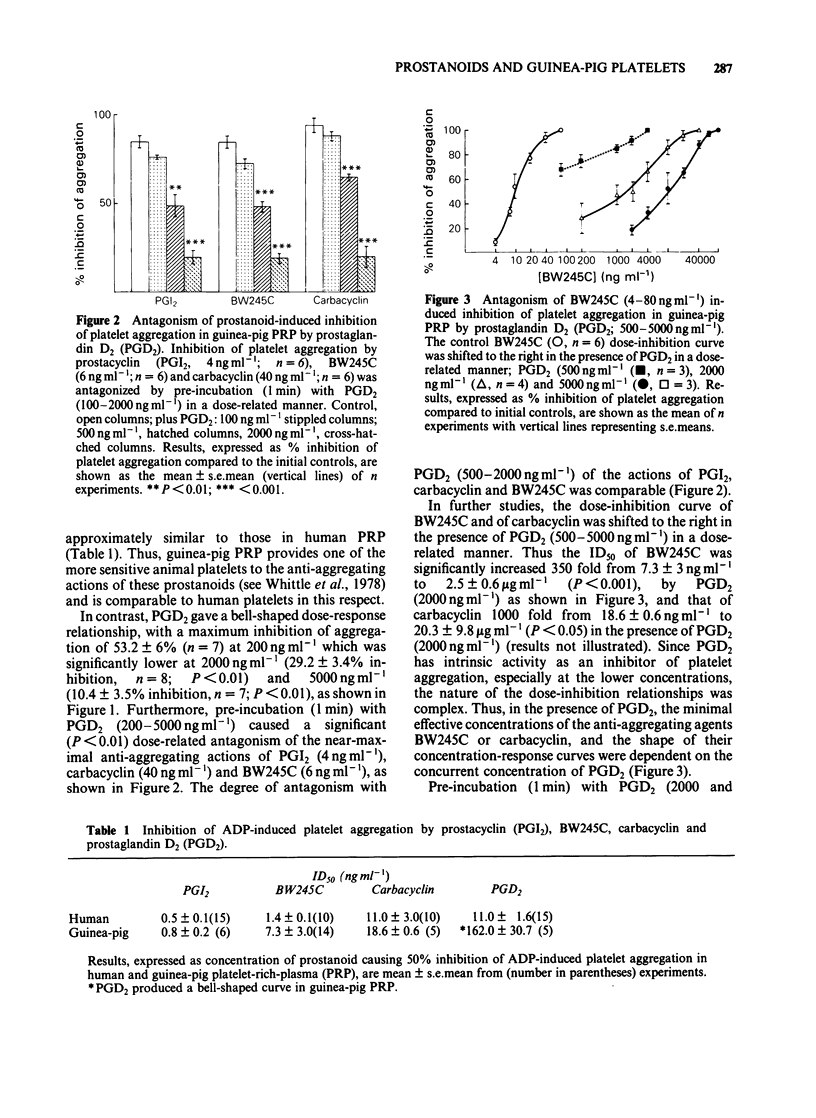
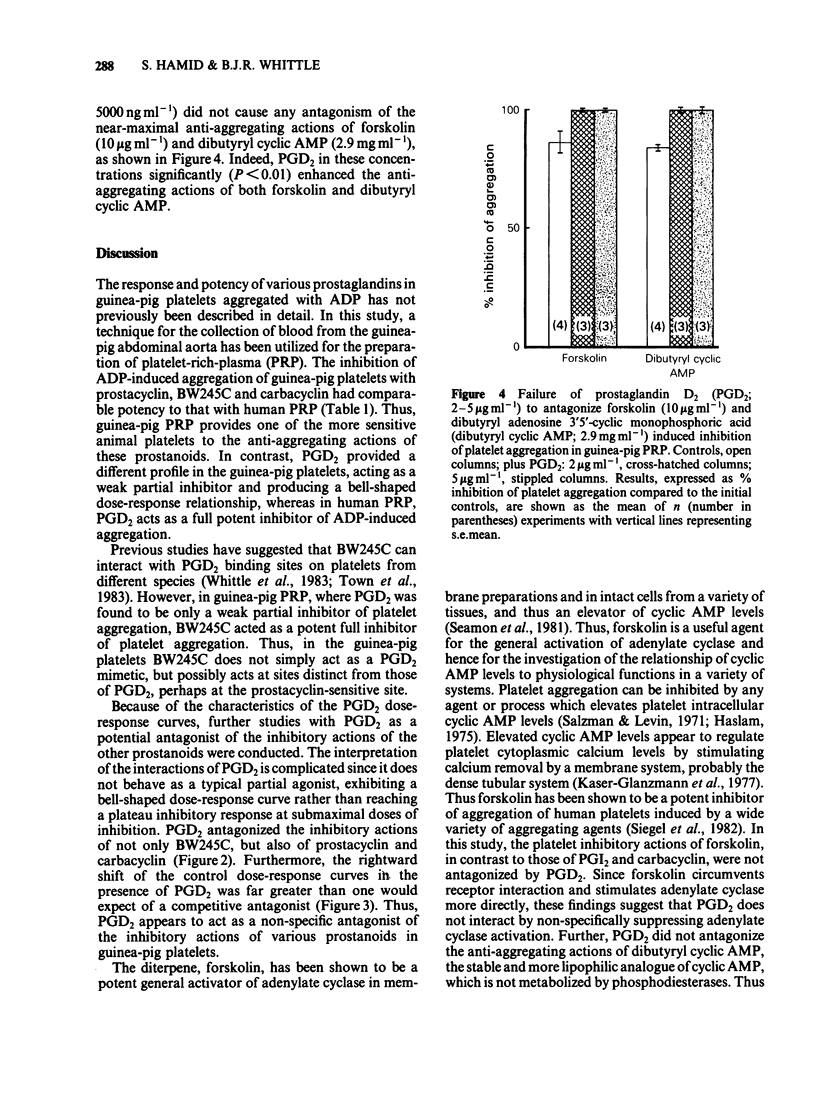
The anti-aggregating actions of prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) have been compared to prostacyclin (PGI2), its stable analogue carbacyclin and a hydantoin prostaglandin, BW245C, in guinea-pig PGI2, carbacyclin and BW245C were potent inhibitors of ADP-induced aggregation in guinea-pig platelets, with ID50 values comparable to those obtained in human platelet-rich-plasma. In contrast, PGD2 acted as a weak and partial inhibitor in guinea-pig platelet aggregation, producing a bell-shaped dose-response relationship. PGD2 induced a dose-related antagonism of the inhibitory actions of BW245C, prostacyclin and carbacyclin on guinea-pig platelets. However, PGD2 did not antagonize the inhibitory actions of either forskolin or dibutyryl cyclic AMP on this platelet preparation. The results suggest a non-specific interaction of PGD2 with these prostanoid binding sites on guinea-pig platelets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. A., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H. Ligand binding to thromboxane receptors on human platelets: correlation with biological activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):953–964. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair I. A., Leigh P. J., MacDermot J. Desensitization of prostacyclin receptors in a neuronal hybrid cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ-Hazelhof E., Nugteren D. H., Van Dorp D. A. Conversions of prostaglandin endoperoxides by glutathione-S-transferases and serum albumins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 20;450(3):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Fredholm B. B. Isomerization of prostaglandin H2 into prostaglandin D2 in the presence of serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):189–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J. Roles of cyclic nucleotides in platelet function. Ciba Found Symp. 1975;35:121–151. doi: 10.1002/9780470720172.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käser-Glanzmann R., Jakäbovä M., George J. N., Lüscher E. F. Stimulation of calcium uptake in platelet membrane vesicles by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. V., Gorman R. R. Evidence for distinct prostaglandin I2 and D2 receptors in human platelets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jul;210(1):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelz O., Oelz R., Knapp H. R., Sweetman B. J., Oates J. A. Biosynthesis of prostaglandin D2. 1. Formation of prostaglandin D2 by human platelets. Prostaglandins. 1977 Feb;13(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Levine L. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate in human blood platelets. II. Effect of N6-2'-o-dibutyryl cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate on platelet function. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):131–141. doi: 10.1172/JCI106467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Cooper B., O'Hara D., Handin R. I. Identification of platelet receptors for prostaglandin I2 and D2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2914–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl A. M., Daly J. W., Smith J. B. Inhibition of aggregation and stimulation of cyclic AMP generation in intact human platelets by the diterpene forskolin. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):680–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl A. M., Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Nicolaou K. C., Ahern D. Selective binding site for [3H]prostacyclin on platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):215–220. doi: 10.1172/JCI109292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Ingerman C. M., Kocsis J. J. Prostaglandin D2 inhibits the aggregation of human platelets. Thromb Res. 1974 Sep;5(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson J., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Prostaglandin endoperoxides IX. Characterization of rabbit aorta contracting substance (RCS) from guinea pig lung and human platelets. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Jun;94(2):222–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town M. H., Casals-Stenzel J., Schillinger E. Pharmacological and cardiovascular properties of a hydantoin derivative, BW 245 C, with high affinity and selectivity for PGD2 receptors. Prostaglandins. 1983 Jan;25(1):13–28. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Moncada S., Mullane K., Vane J. R. Platelet and cardiovascular activity of the hydantoin BW245C, a potent prostaglandin analogue. Prostaglandins. 1983 Feb;25(2):205–223. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Comparison of the effects of prostacyclin (PGI2), prostaglandin E1 and D2 on platelet aggregation in different species. Prostaglandins. 1978 Sep;16(3):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Moncada S., Whiting F., Vane J. R. Carbacyclin--a potent stable prostacyclin analogue for the inhibition of platelet aggregation. Prostaglandins. 1980 Apr;19(4):605–627. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(80)80010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


