Abstract
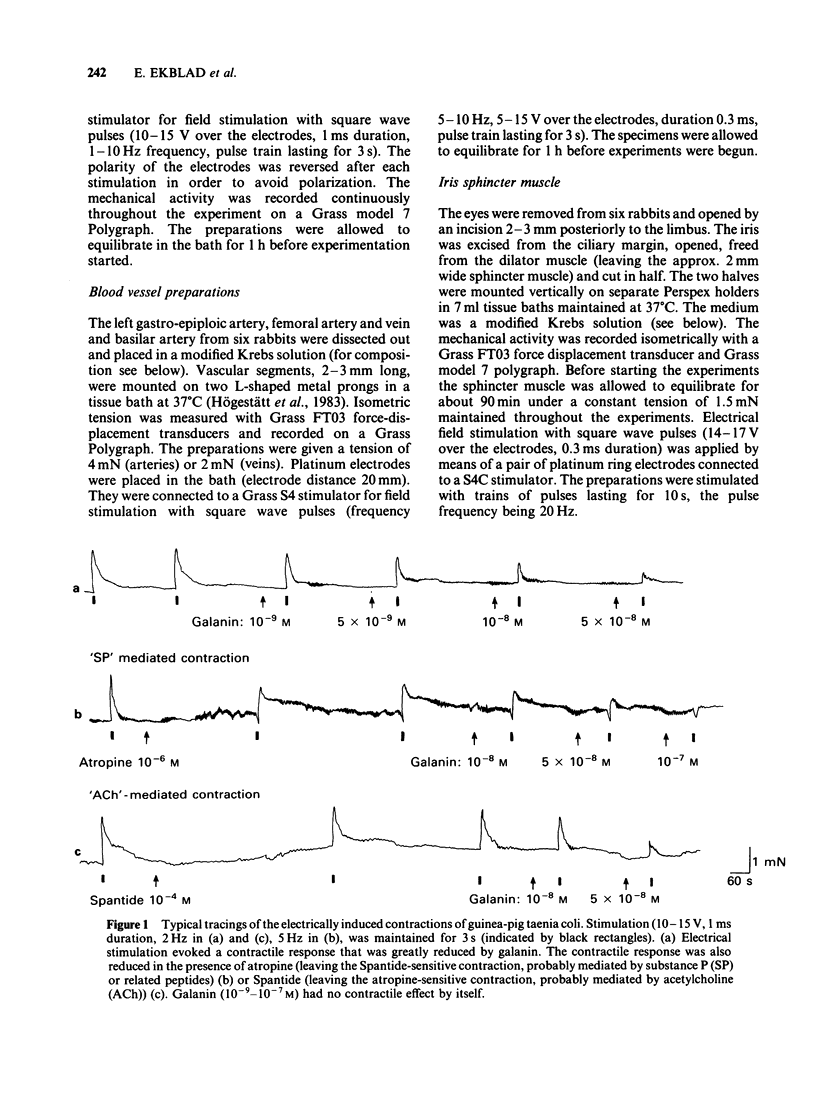
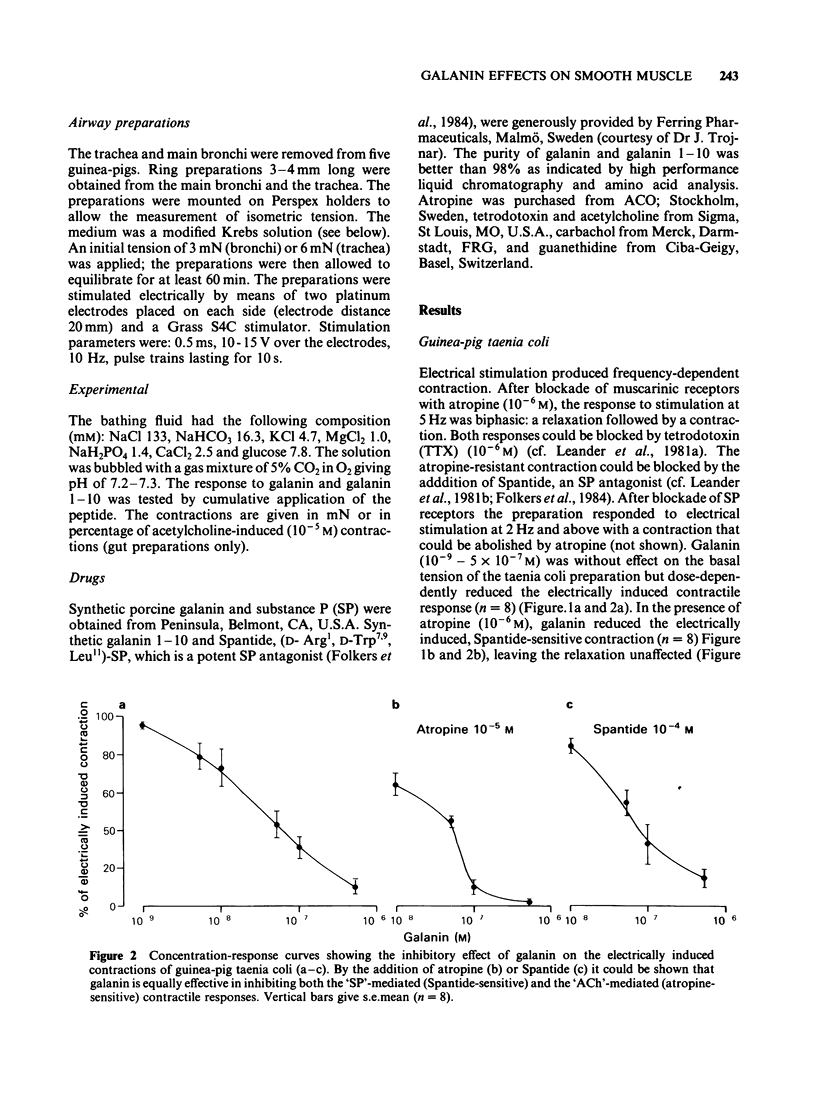
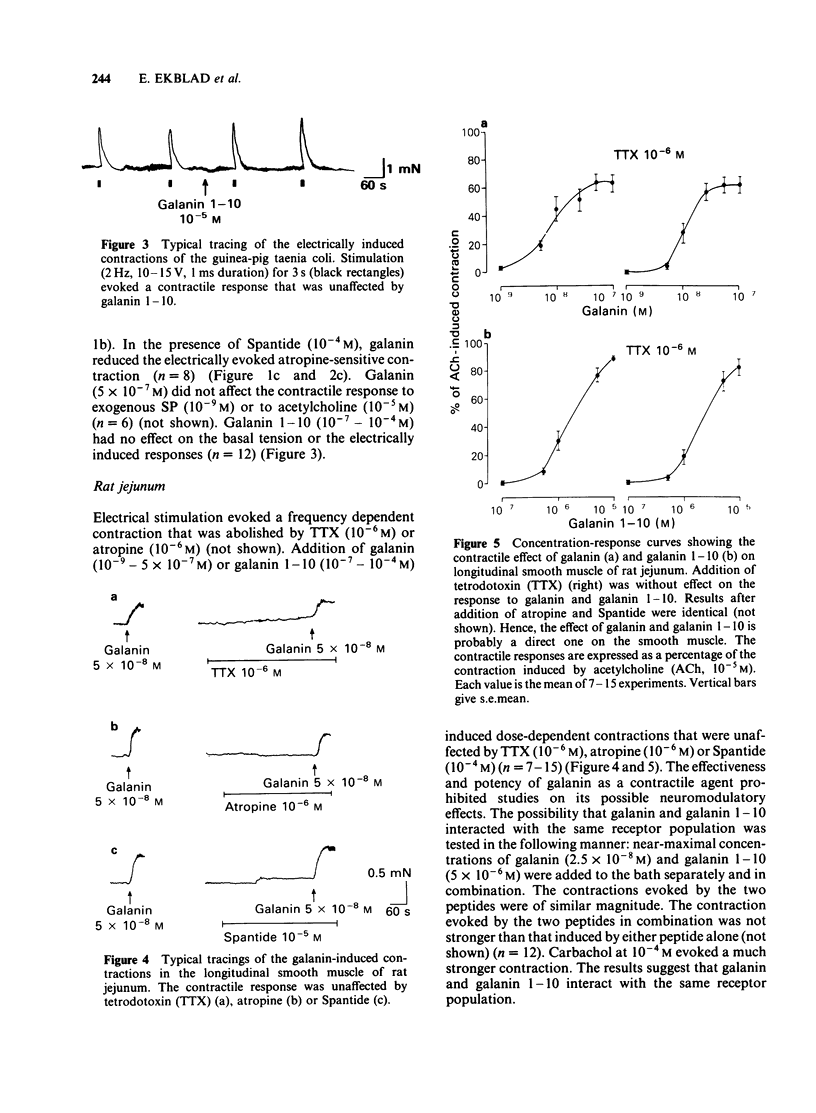
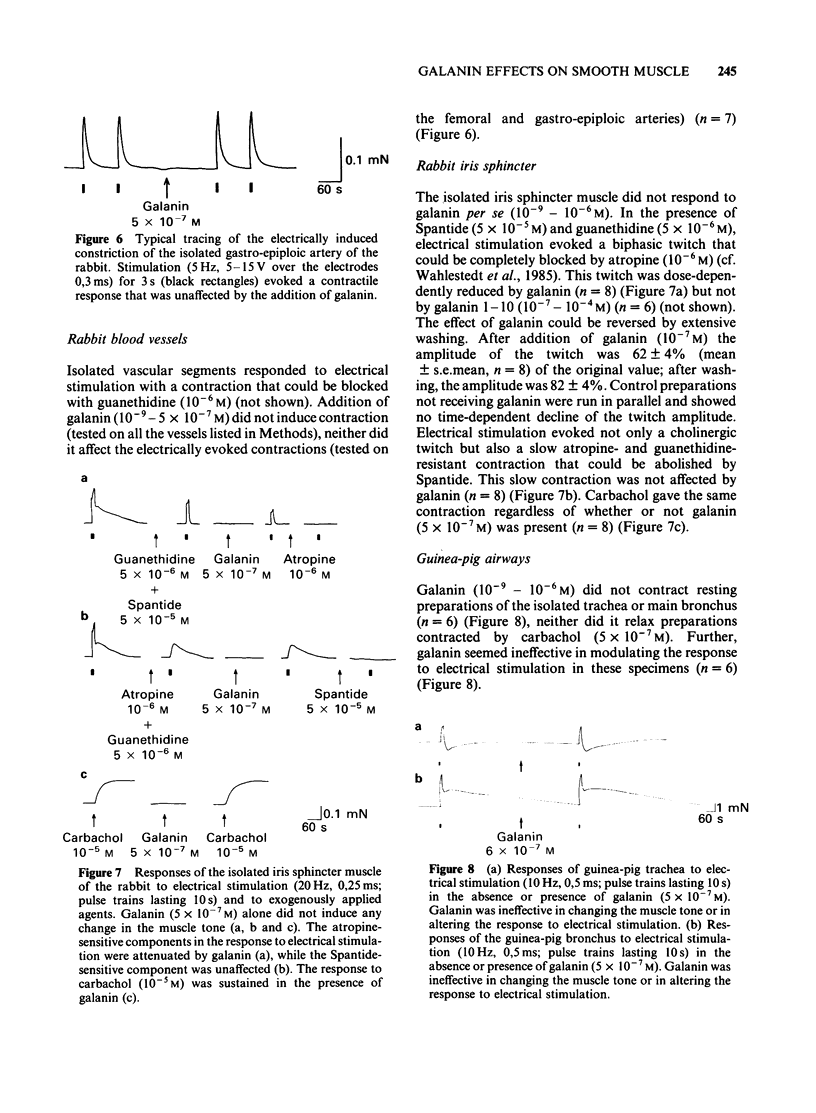
The effects of galanin, a newly isolated neuropeptide, and of a galanin fragment (galanin 1-10) were studied on various smooth muscle preparations in vitro. Direct motor effects as well as effects on electrically induced (neuronally mediated) responses (neuromodulatory effects) were observed. Both gatanin and galanin 1-10 evoked a strong contractile response in rat jejunal longitudinal muscle. This effect was a direct one on the smooth muscle. Addition of galanin to guinea-pig taenia coli inhibited the contractile response to electrical stimulation, mediated by endogenous substance P and acetylcholine. In the rabbit iris sphincter, galanin reduced the acetylcholine-mediated but not the substance P-mediated contraction evoked by electrical stimulation. The neuromodulatory effects seem to be presynaptic and require the whole or possibly only the C-terminal part of the galanin molecule, since galanin 1-10 was ineffective. Rabbit femoral artery and vein, gastroepiploic and basilar arteries and guinea-pig trachea and main bronchi did not respond to either galanin or galanin 1-10.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Rand M. J. The inhibitory innervation of the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):504–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkers K., Håkanson R., Hörig J., Xu J. C., Leander S. Biological evaluation of substance P antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):449–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högestätt E. D., Andersson K. E., Edvinsson L. Mechanical properties of rat cerebral arteries as studied by a sensitive device for recording of mechanical activity in isolated small blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jan;117(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Urakawa N. Isometric and isotonic spontaneous contractions of guinea-pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;24(6):925–927. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander S., Håkanson R., Rosell S., Folkers K., Sundler F., Tornqvist K. A specific substance P antagonist blocks smooth muscle contractions induced by non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nerve stimulation. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):467–469. doi: 10.1038/294467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rökaeus A., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. A galanin-like peptide in the central nervous system and intestine of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 15;47(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tervo K., Tervo T., Eränkö L., Eränkö O., Valtonen S., Cuello A. C. Effect of sensory and sympathetic denervation on substance P immunoreactivity in nerve fibres of the rabbit eye. Exp Eye Res. 1982 Apr;34(4):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


