Abstract
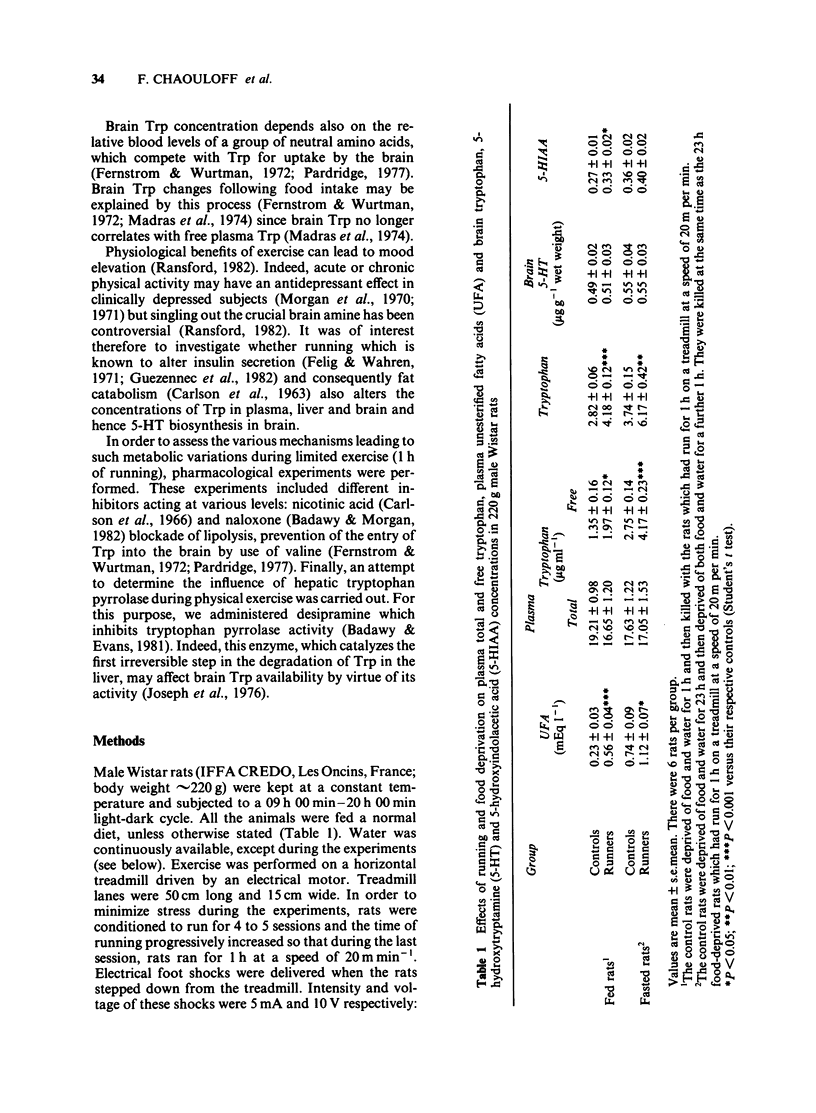
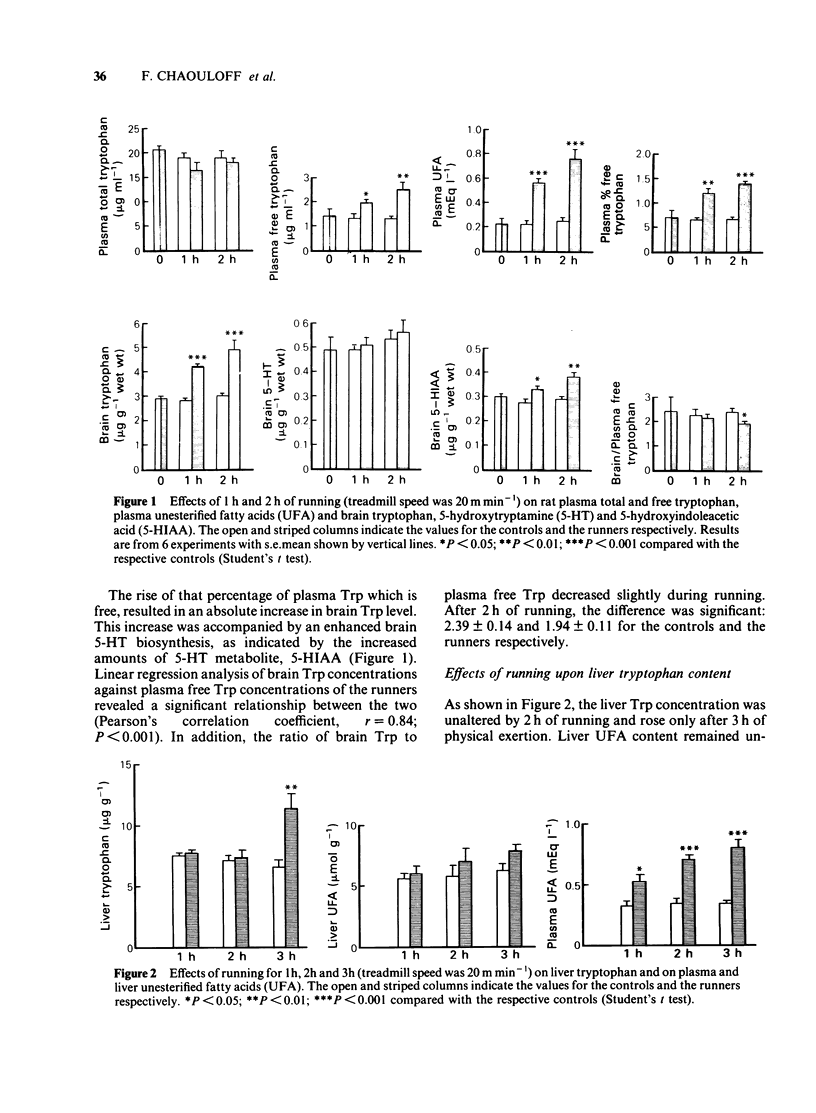
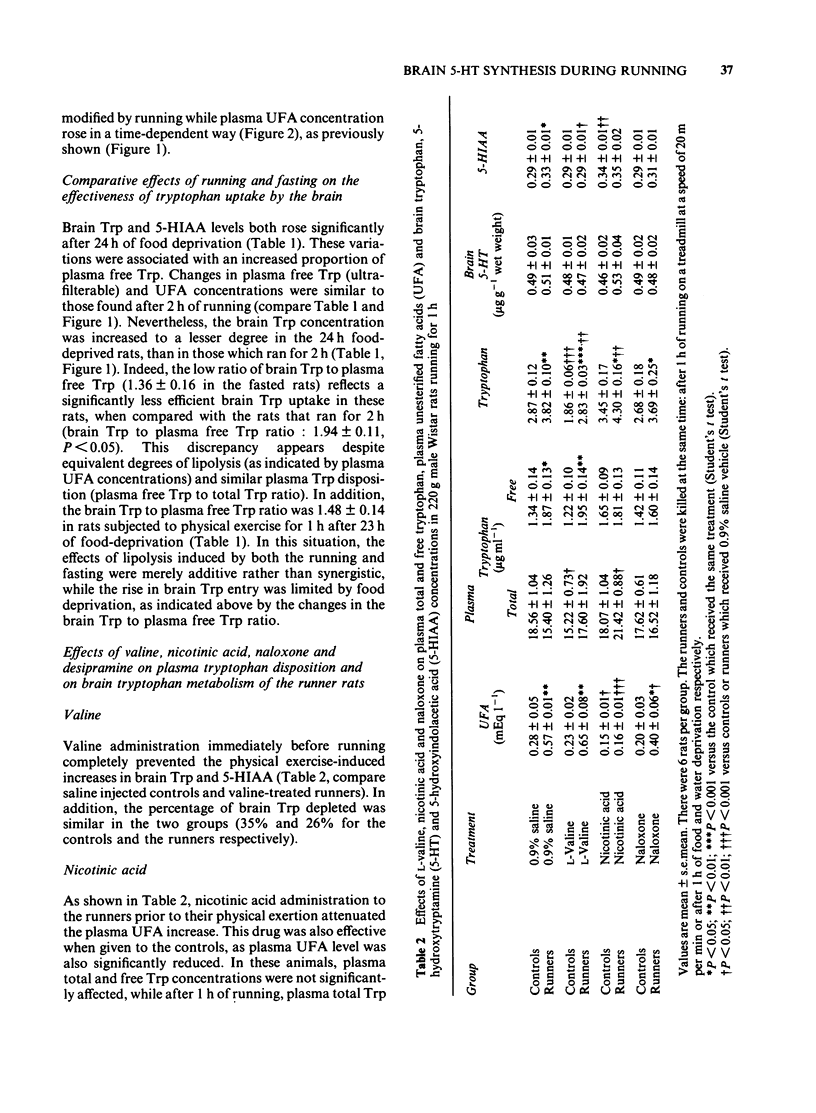
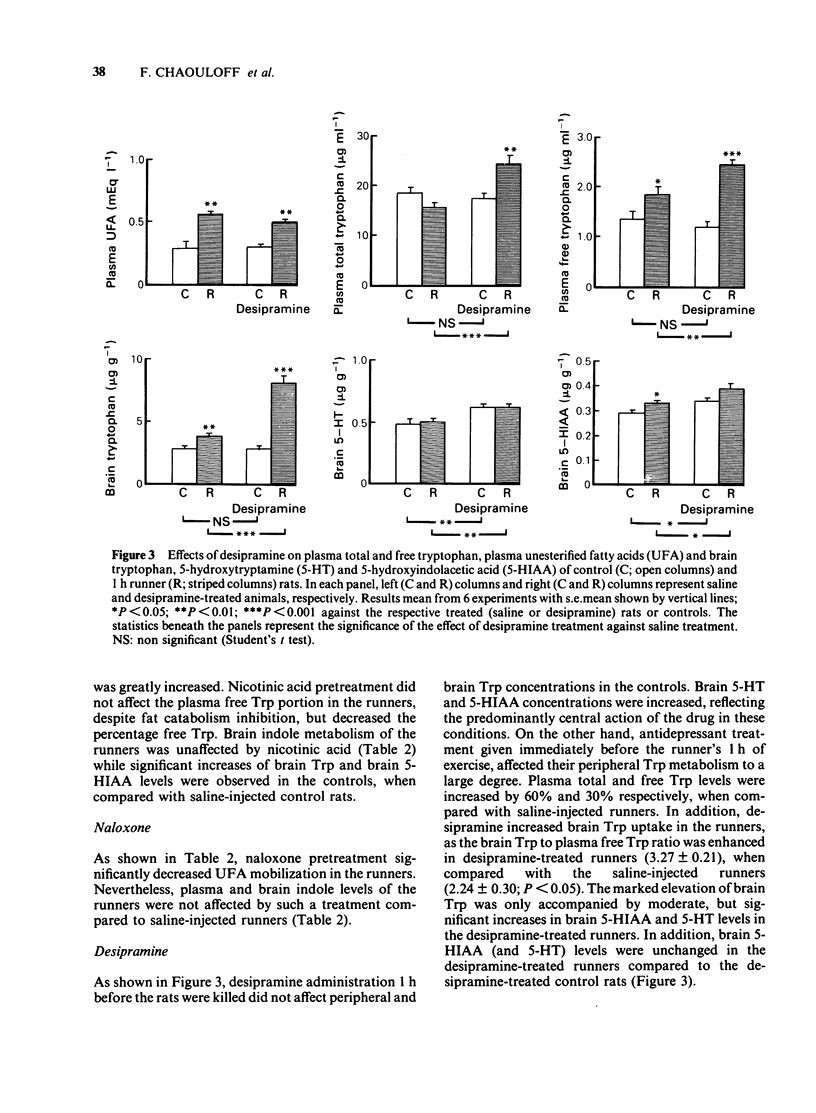
An investigation was made into the effects of conditioned running (1 h and 2 h at 20 m min-1), which accelerates lipolysis, on the concentrations of tryptophan (Trp) in plasma, liver and brain and on 5-hydroxytrptamine (5-HT) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) levels in brain. Running caused time-dependent increases in plasma free Trp and brain Trp of the rat, leading to increased brain 5-HT turnover as revealed by higher amounts of its metabolite, 5-HIAA. The ratio of brain Trp to plasma free Trp was decreased after 2 h of running. Liver Trp content rose only after 3 h of running, while liver unesterified fatty acid (UFA) concentrations remained unmodified. A comparison between food deprivation and running (both of which promote lipolysis) was performed. Running for 2 h affected to the same extent plasma Trp disposition when compared with 24 h food deprivation. Nevertheless, the ratio of brain Trp to plasma free Trp was decreased in the food-deprived rats, when compared to the runners. Nicotinic acid, which inhibits fat catabolism, completely abolished the plasma UFA increase induced by 1 h of running. The drug did not affect plasma free Trp, brain Trp, 5-HT or 5-HIAA but enhanced plasma total Trp level. Naloxone, an opiate antagonist, which decreased running-induced lipolysis, did not alter plasma Trp disposition. Desipramine, an antidepressant compound, affected only peripheral Trp concentrations of the runners.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Inhibition of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity and elevation of brain tryptophan concentration by administration of antidepressants. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 1;30(11):1211–1216. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Morgan C. J. Tryptophan and tryptophan pyrrolase in haem regulation. The role of lipolysis and direct displacement of serum-protein-bound tryptophan in the opposite effects of administration of endotoxin, morphine, palmitate, salicylate and theophylline on rat liver 5-aminolaevulinate synthase activity and the haem saturation of tryptophan pyrrolase. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):451–460. doi: 10.1042/bj2060451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banister E. W., Griffiths J. Blood levels of adrenergic amines during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Nov;33(5):674–676. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.5.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barakat H. A., Kasperek G. J., Dohm G. L., Tapscott E. B., Snider R. D. Fatty acid oxidation by liver and muscle preparations of exhaustively exercised rats. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2080419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Faivre-Bauman A., Benda P., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Plasma tryptophan and 5-HT metabolism in the CNS of the newborn rat. J Neurochem. 1974 Aug;23(2):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSON L. A., EKELUND L. G., ORO L. Studies on blood lipids during exercise. IV. Arterial concentration of plasma free fatty acids and glycerol during and after prolonged exercise in normal men. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:724–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Fröberg S. O., Nye E. R. Acute effects of nicotinic acid on plasma, liver, heart and muscle lipids. Nicotinic acid in the rat. II. Acta Med Scand. 1966 Nov;180(5):571–579. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A., Lindqvist M. Effects of antidepressant agents on the synthesis of brain monoamines. J Neural Transm. 1978;43(2):73–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01579067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Friedel J., Knott P. J. The effect of fatty acids on the binding of tryptophan to plasma protein. Nature. 1973 Mar 16;242(5394):198–200. doi: 10.1038/242198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Knott P. J. Effects on plasma and brain tryptophan in the rat of drugs and hormones that influence the concentration of unesterified fatty acid in the plasma. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in rat brain. A study of intermediate metabolism using the technique of tryptophan loading. II. Applications and drug studies. J Neurochem. 1965 Jun;12(6):493–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2703–2714. doi: 10.1172/JCI106771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando J. C., Knott P. J., Curzon G. The relevance of both plasma free tryptophan and insulin to rat brain tryptophan concentration. J Neurochem. 1976 Jul;27(1):343–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. Science. 1972 Oct 27;178(4059):414–416. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4059.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorelli G., Piolanti P., Forti G., Serio M. Determination of plasma corticosteroids and urinary cortisol by a competitive protein-binding method using dextran-coated charcoal. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:179–187. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kappelman A. H., Kaufman S. Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4165–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Holst J. J., Christensen N. J. Glucagon and plasma catecholamine responses to graded and prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):70–76. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guezennec C. Y., Ferre P., Serrurier B., Merino D., Pesquies P. C. Effects of prolonged physical exercise and fasting upon plasma testosterone level in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1982;49(2):159–168. doi: 10.1007/BF02334064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph M. H., Young S. N., Curzon G. The metabolism of a tryptophan load in rat brain and liver. The influence of hydrocortisone and allopurinol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Dec 1;25(23):2599–2604. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90515-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX W. E., AUERBACH V. H. The hormonal control of tryptophan peroxidase in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett G. A., Joseph M. H. The functional importance of increased brain tryptophan in the serotonergic response to restraint stress. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Jan;20(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott P. J., Curzon G. Free tryptophan in plasma and brain tryptophan metabolism. Nature. 1972 Oct 20;239(5373):452–453. doi: 10.1038/239452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Pogson C. I. Characteristics of tryptophan accumulation by isolated rat forebrain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):663–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Raisman R., Briley M. High-affinity [3H] DMI binding is associated with neuronal noradrenaline uptake in the periphery and the central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):423–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90592-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassers B. W., Wahlqvist M. L., Kaijser L., Carlson L. A. Effect of nicotinic acid on myocardial metabolism in man at rest and during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Jul;33(1):72–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Quan-Bui K. H., Elghozi J. L., Devynck M. A., Meyer P. Rapid liquid chromatographic determination of 5-hydroxyindoles and dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madras B. K., Cohen E. L., Messing R., Munro H. N., Wurtman R. J. Relevance of free tryptophan in serum to tissue tryptophan concentrations. Metabolism. 1974 Dec;23(12):1107–1116. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamy R. H. Binding of indole analogues to human serum albumin. Effects of fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4235–4243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. P., Roberts J. A., Brand F. R., Feinerman A. D. Psychological effect of chronic physical activity. Med Sci Sports. 1970 Winter;2(4):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. P., Roberts J. A., Feinerman A. D. Psychologic effect of acute physical activity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1971 Sep;52(9):422–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson J. A., Glaser G. H. Identification of beta-adrenergic-sensitive adenylate cyclase in intracranial blood vessels. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):567–569. doi: 10.1038/278567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M. Kinetics of competitive inhibition of neutral amino acid transport across the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem. 1977 Jan;28(1):103–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransford C. P. A role for amines in the antidepressant effect of exercise: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(1):1–10. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198201000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliamonte A., Biggio G., Vargiu L., Gessa G. L. Free tryptophan in serum controls brain tryptophan level and serotonin synthesis. Life Sci II. 1973 Mar 22;12(6):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90361-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


