Abstract
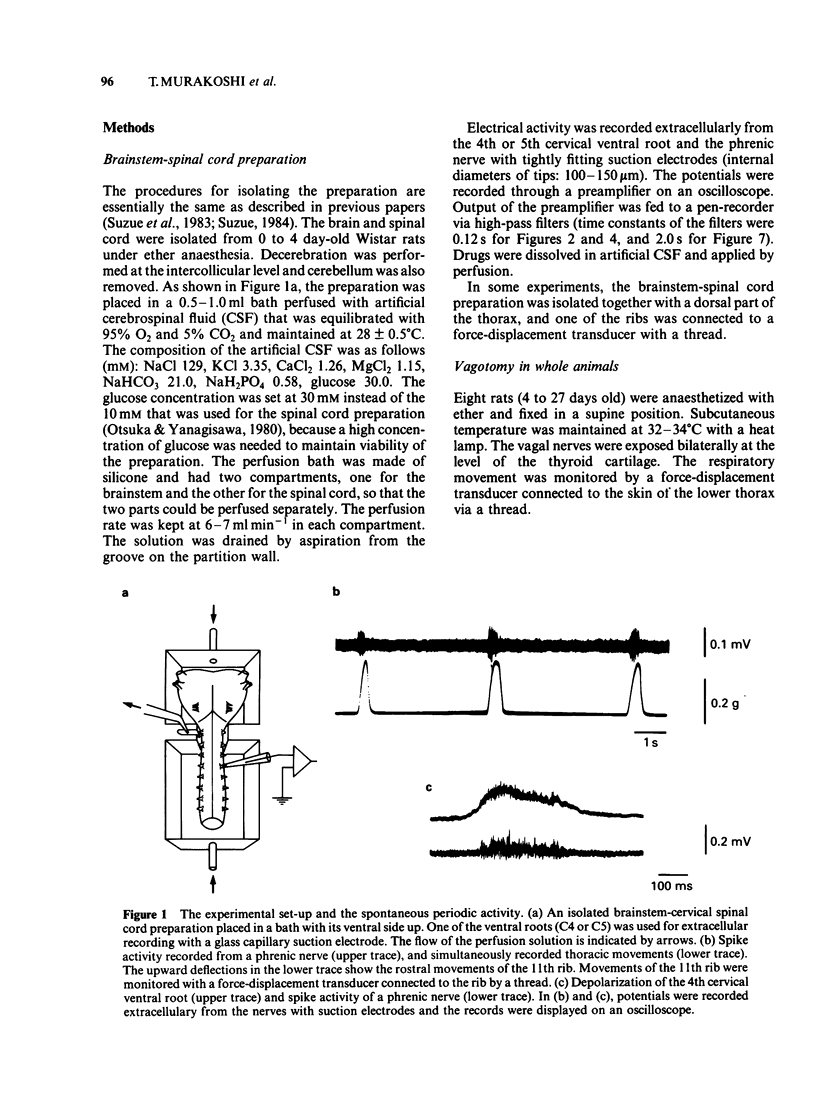
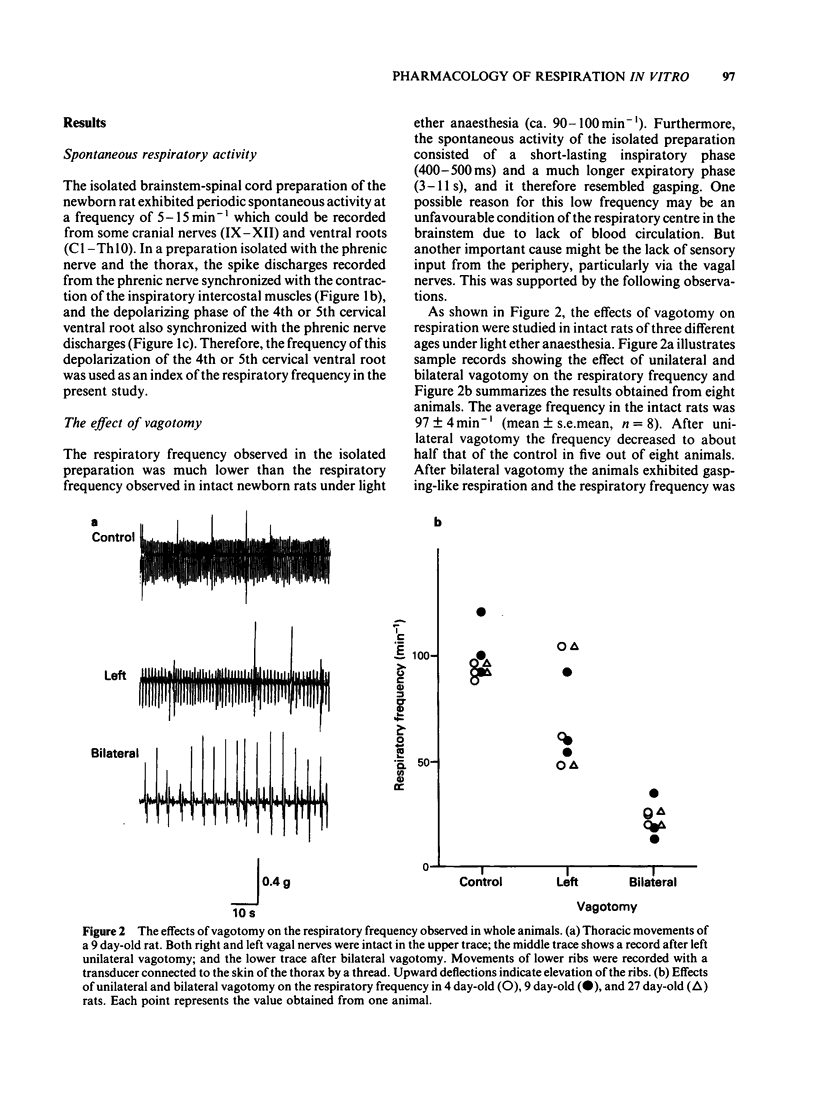
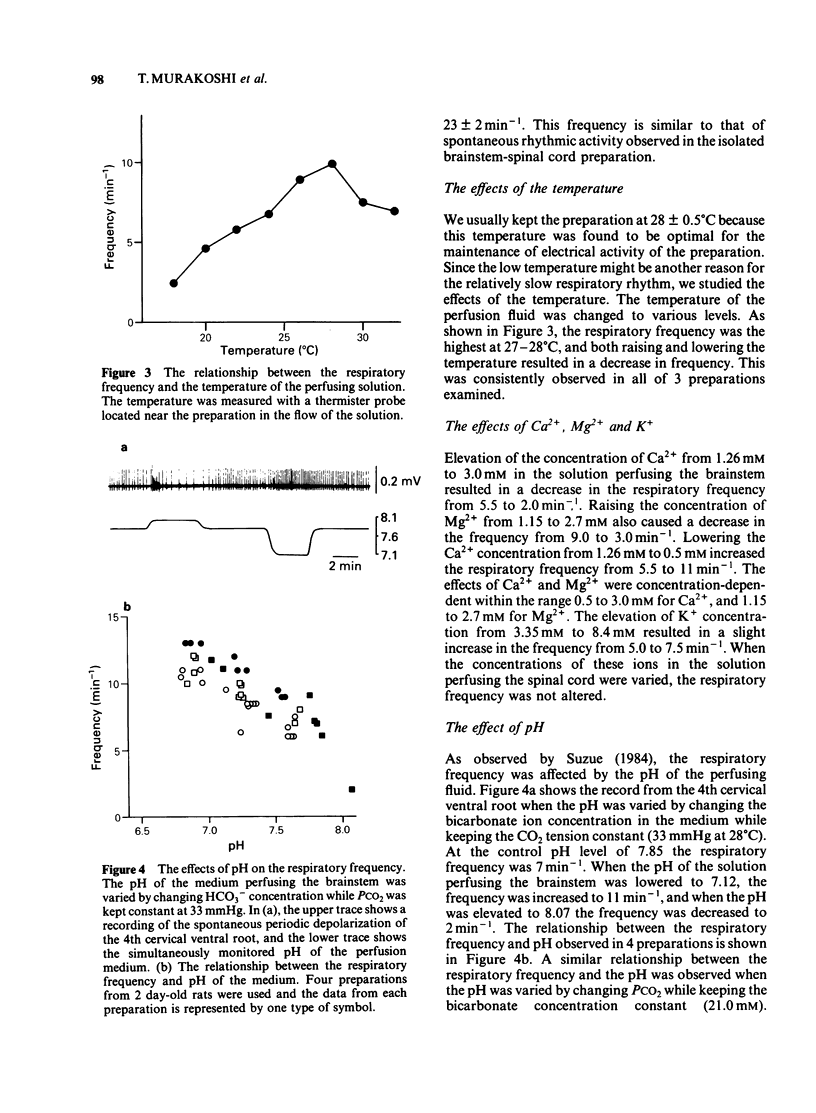
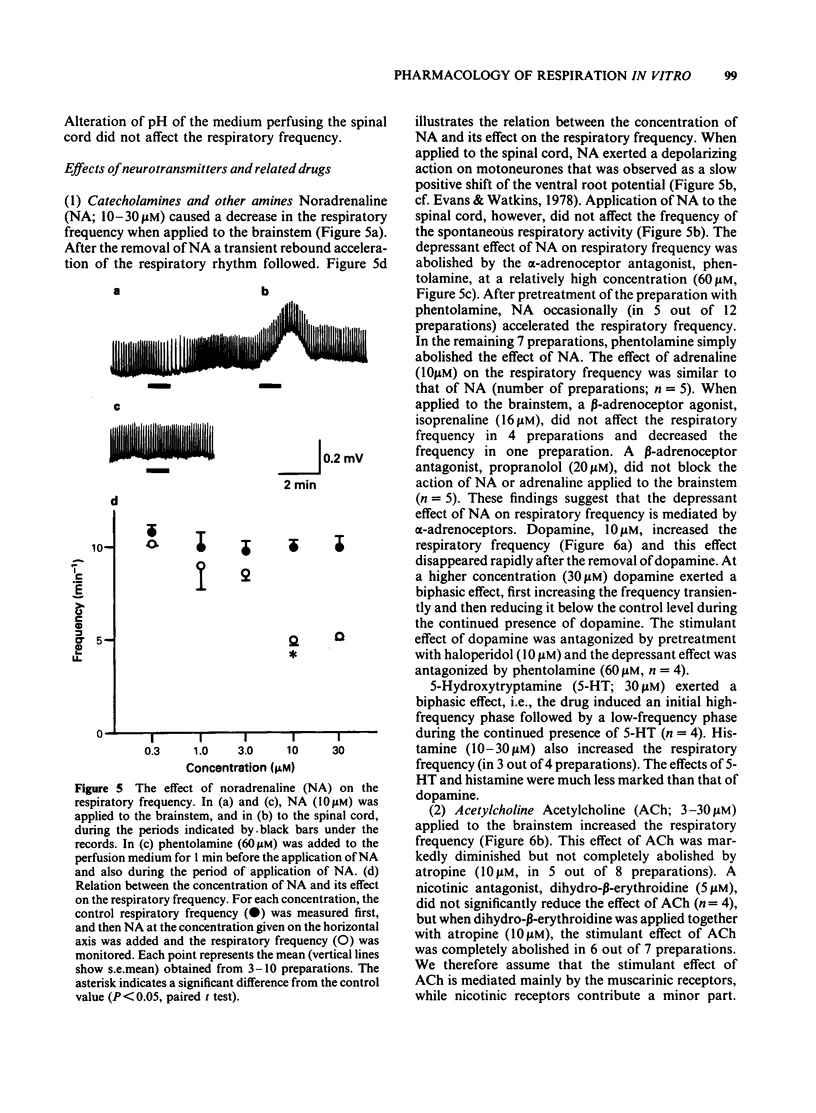
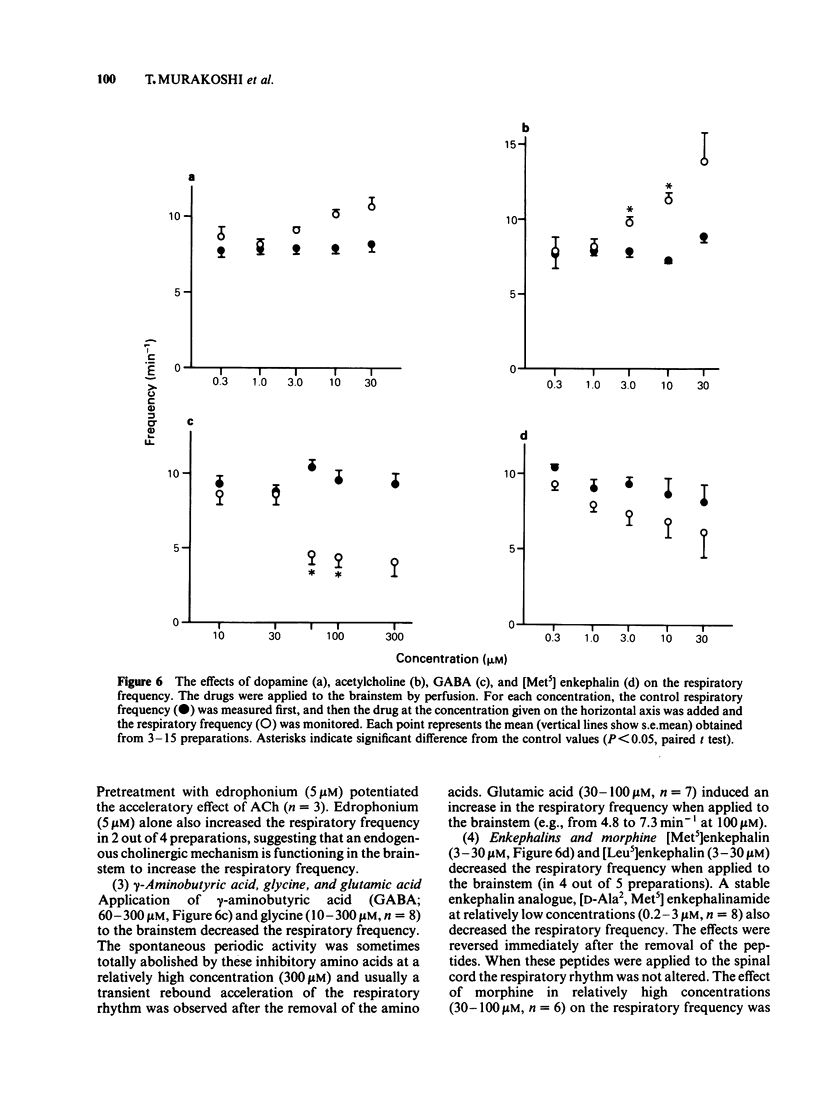
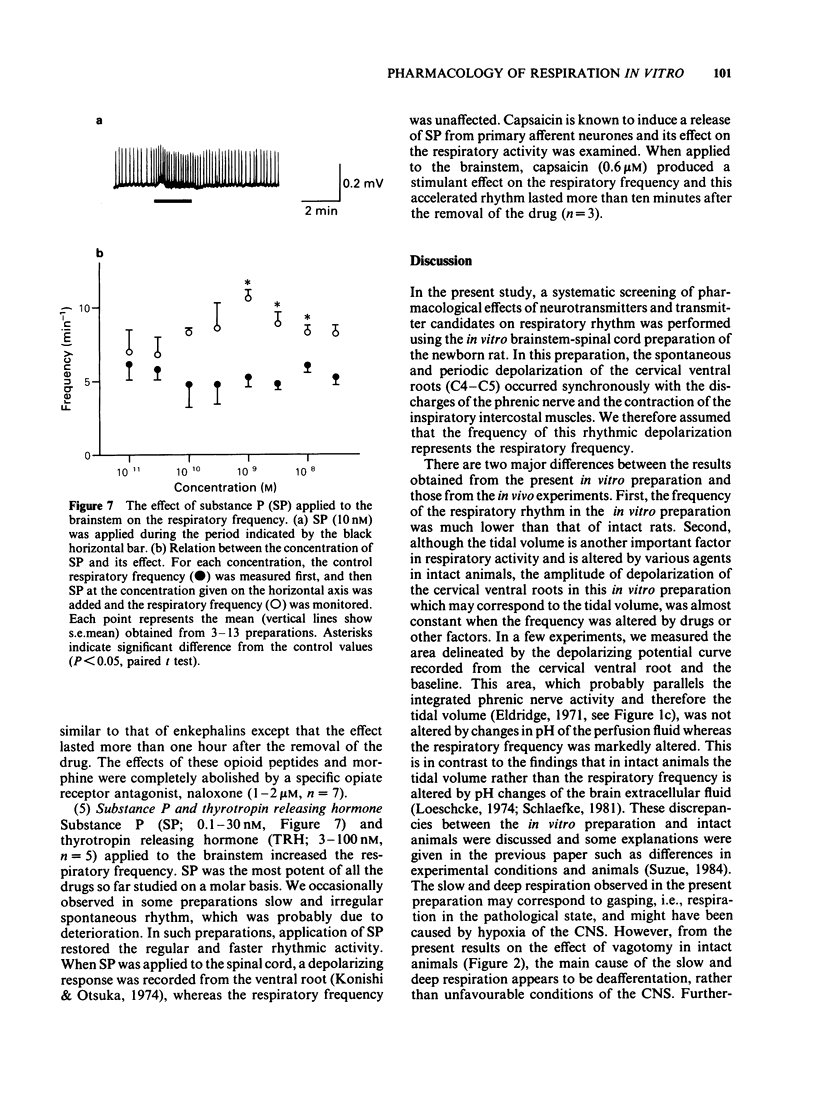
An in vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparation of the newborn rat was used to examine the effects of neurotransmitters and transmitter candidates on respiratory frequency. Spontaneous periodic depolarization of the spinal ventral roots of the 4th or 5th cervical segment was observed at a frequency of 5-15 min-1 constantly for more than 5 h. The frequency of this depolarization was monitored as an index of the respiratory frequency. An elevation of the concentration of Ca2+ or Mg2+ caused a decrease in the respiratory frequency, whereas an elevation of K+ concentration caused an increase. The frequency was also increased by a reduction of pH. The highest frequency was observed at 27-28 degrees C. Dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine, acetylcholine, glutamic acid, substance P, and thyrotropin releasing hormone accelerated the respiratory frequency when applied by perfusion to the brainstem, whereas noradrenaline, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glycine, and [Met5] enkephalin and [Leu5] enkephalin slowed the frequency. Experiments with antagonists suggested that the stimulant effect of acetylcholine on respiratory frequency was mediated mainly by muscarinic receptors and the depressant effect of noradrenaline was mediated by alpha-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolme P., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. Studies on the role of dopamine in cardiovascular and respiratory control: central versus peripheral mechanisms. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1977;16:281–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolme P., Fuxe K. Pharmacological studies on a possible role of central noradrenaline neurons in respiratory control. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;25(4):351–352. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. I. Neurogenesis of respiratory rhythm in the mammal. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):1105–1173. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Kanazawa I. The distribution of substance P immunoreactive fibers in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 1;178(1):129–156. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E. Central regulation of respiration by endogenous neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:121–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L. Relationship between phrenic nerve activity and ventilation. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):535–543. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. Specific antagonism of excitant amino acids in the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul 15;50(2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. Injections of drugs into the lateral ventricle of the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):148–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. IV. DISTRIBUTION OF MONOAMINE NERVE TERMINALS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965:SUPPL 247–247:37+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flórez J., Mediavilla A. Respiratory and cardiovascular effects of met-enkephalin applied to the ventral surface of the brain stem. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 23;138(3):585–900. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90699-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Molnar A., Lembeck F. Substance P release from spinal cord slices by capsaicin. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 13;25(7):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner J., Hedner T., Jonason J., Lundberg D. Central respiratory stimulant effect by thyrotropin in releasing hormone in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 25;25(3):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90411-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner J., Hedner T., Jonason J., Lundberg D. Evidence for a dopamine interaction with the central respiratory control system in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner J., Hedner T., Jonason J., Lundberg D. GABA-ergic mechanisms in central respiratory control in the anesthetized rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981;317(4):315–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00501312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., McGeer P. L., Peng J. H., McGeer E. G. The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Aug 1;200(2):151–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Otsuka M. Excitatory action of hypothalamic substance P on spinal motoneurones of newborn rats. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):734–735. doi: 10.1038/252734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson E. E., Waldrop T. G., Eldridge F. L. Naloxone enhances respiratory output in cats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Nov;47(5):1105–1111. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.5.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leusen I. Regulation of cerebrospinal fluid composition with reference to breathing. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl A., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G. Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat--I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience. 1978;3(10):861–943. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg D. B., Mueller R. A., Breese G. R. An evaluation of the mechanism by which serotonergic activation depresses respiration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Mar;212(3):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maley B., Elde R. Immunohistochemical localization of putative neurotransmitters within the feline nucleus tractus solitarii. Neuroscience. 1982 Oct;7(10):2469–2490. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mediavilla A., Feria M., Fernández J. F., Cagigas P., Pazos A., Flórez J. The stimulatory action of d-amphetamine on the respiratory centre, and its mediation by a central alpha-adrenergic mechanism. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Feb;18(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. A., Lundberg D. B., Breese G. R., Hedner J., Hedner T., Jonason J. The neuropharmacology of respiratory control. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Sep;34(3):255–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Yanagisawa M. The effects of substance P and baclofen on motoneurones of isolated spinal cord of the newborn rat. J Exp Biol. 1980 Dec;89:201–214. doi: 10.1242/jeb.89.1.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Jacobowitz D. M. Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. II. Hindbrain (mesencephalon, rhombencephalon). J Comp Neurol. 1974 Sep 1;157(1):29–42. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Flórez J. Interaction of naloxone with mu- and delta-opioid agonists on the respiration of rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 18;87(2-3):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez de la Mora M., Possani L. D., Tapia R., Teran L., Palacios R., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A. Demonstration of central gamma-aminobutyrate-containing nerve terminals by means of antibodies against glutamate decarboxylase. Neuroscience. 1981;6(5):875–895. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaefke M. E. Central chemosensitivity: a respiratory drive. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;90:171–244. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaragli G., Pavan F. Effects of amino acid compounds injected into cerebrospinal fluid spaces, on colonic temperature, arterial blood pressure and behaviour of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1972 Jan;11(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(72)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzue T. Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Hartman B. K. The central adrenergic system. An immunofluorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine-beta-hydroxylase as a marker. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Oct 15;163(4):467–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.901630406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriault E., Otsuka M., Jessell T. Capsaicin-evoked release of substance P from primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 6;170(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90957-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., PERNOW B. Neurotropic effects of substance P. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 May 18;36(3):265–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessberg P., Hedner J., Hedner T., Jonason J. Central respiratory and cardiovascular effects in the rat of some putative neurotransmitter amino acids. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;323(1):58–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00498829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. G., Dockray G. J. Distribution of enkephalin-related peptides in rat brain: immunohistochemical studies using antisera to met-enkephalin and met-enkephalin Arg6Phe7. Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):563–586. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. A., Norman W. P., Hamosh P., Gillis R. A. Medullary ventral surface GABA receptors affect respiratory and cardiovascular function. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 23;248(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Lagercrantz H., von Euler C. Effects of substance P and TRH on ventilation and pattern of breathing in newborn rabbits. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):541–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


