Abstract
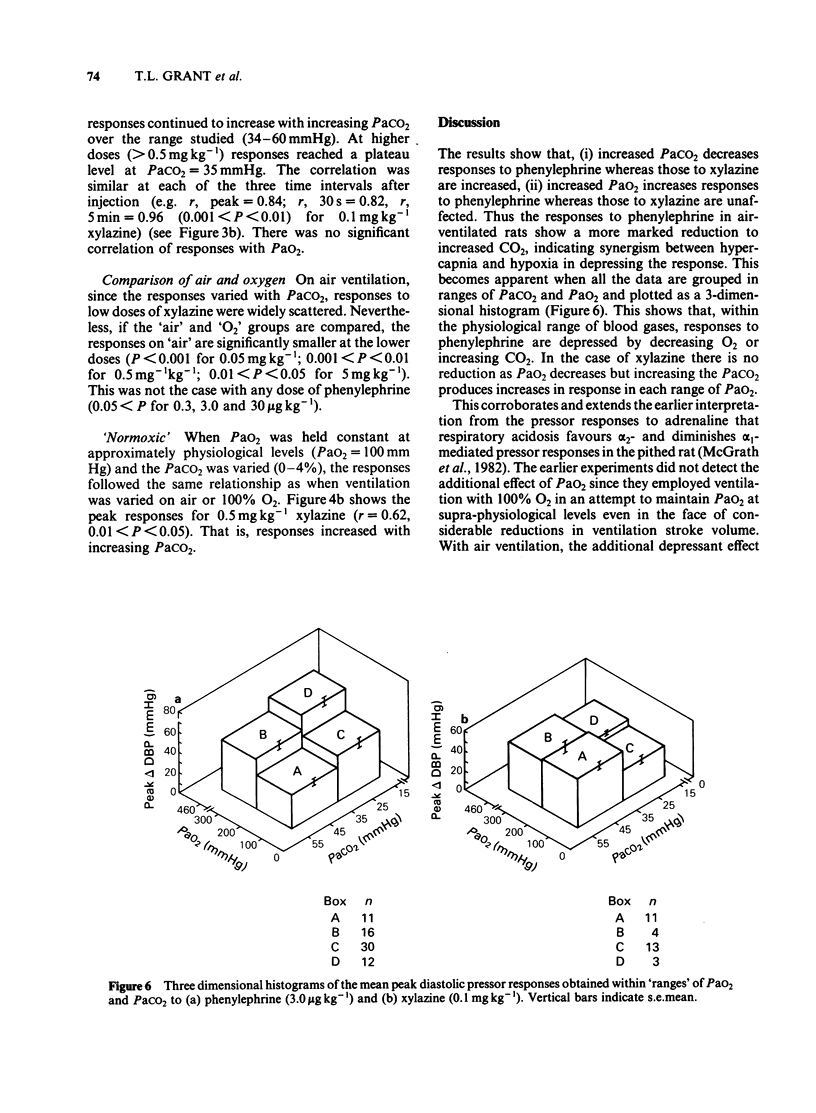
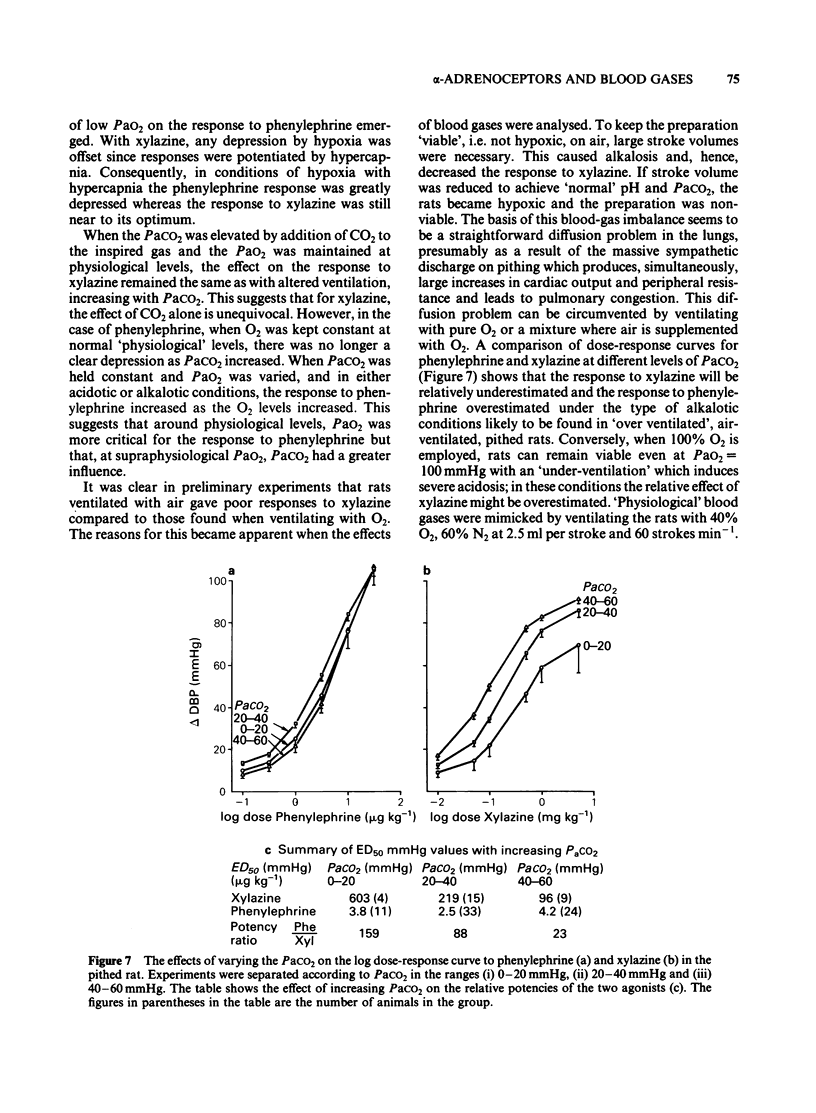
The influence of blood gases on alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses was studied in the pithed rat by varying the inspired gas mixture or the ventilation stroke volume. Acidosis favoured the peak responses to the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, xylazine, while alkalosis favoured the peak responses to the alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonist, phenylephrine. A combination of hypoxia and hypercapnia greatly depressed the alpha 1 response to phenylephrine whereas the alpha 2 response to xylazine remained relatively unaffected. When Pao2 was varied in either acidotic or alkalotic conditions the response to the phenylephrine increased as Pao2 increased. To prevent hypoxia in air ventilated rats, large stroke volumes were required. This caused alkalosis and hence decreased responsiveness to xylazine. Consequently, air ventilated pithed rats gave poorer responses to xylazine than did those ventilated on 100% O2. The results show that alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses can be differentially affected by blood gases. The relative contribution of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors to vascular tone may be either under- or over-estimated depending on the arterial blood gases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. An examination of factors influencing adrenergic transmission in the pithed rat, with special reference to noradrenaline uptake mechanisms and post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):101–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00498564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. The factors influencing the time course of drug action at alpha-adrenoceptors: an investigation of the effects of clonidine in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Maclaren A., Pollock D. A method of stimulating different segments of the autonomic outflow from the spinal column to various organs in the pithed cat and rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):257–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C., Flavahan N. A., McKean C. E. alpha 1- and alpha 2-Adrenoceptor-mediated pressor and chronotropic effects in the rat and rabbit. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982;4 (Suppl 1):S101–S107. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198200041-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. W., Flavahan N. A., Grant T. L., McGrath J. C., Marshall R. J. Influence of blood gases, Ca2+-entry blockade and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on pressor responses to alpha-adrenoceptor agonists: evidence in vivo for subtypes of response independent of receptor subtype? Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):99s–104s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


