Abstract
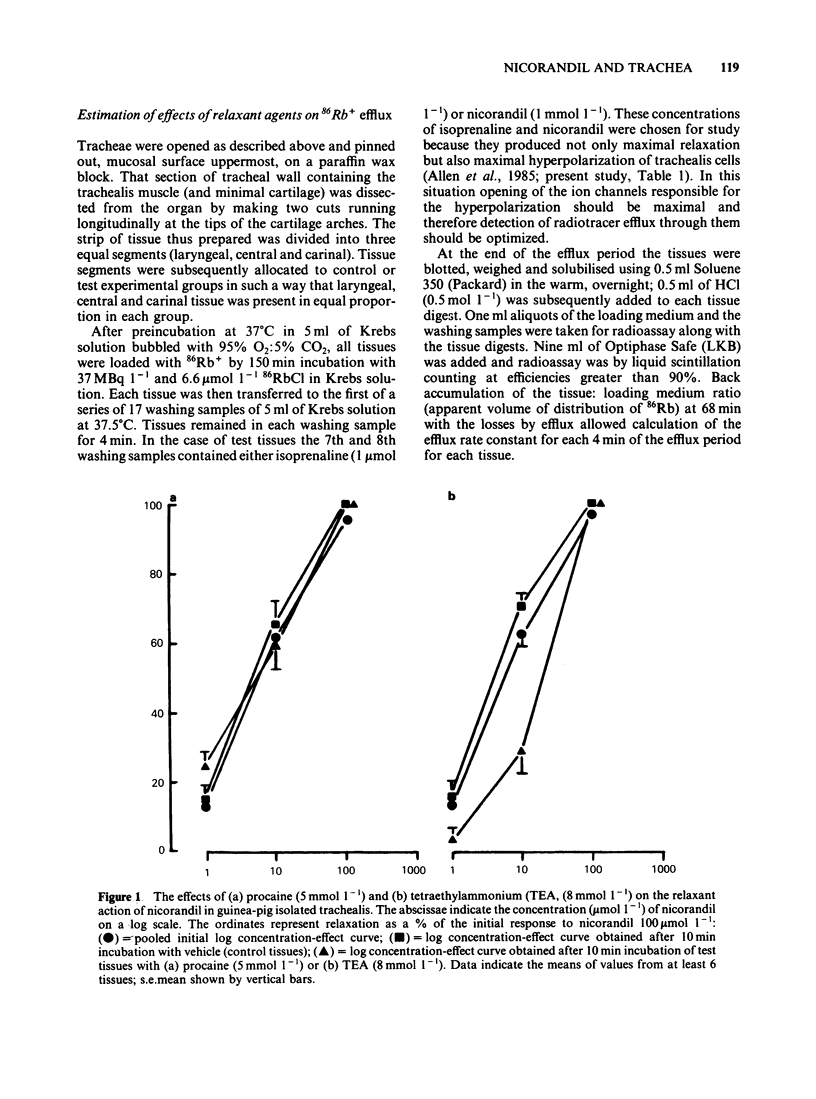
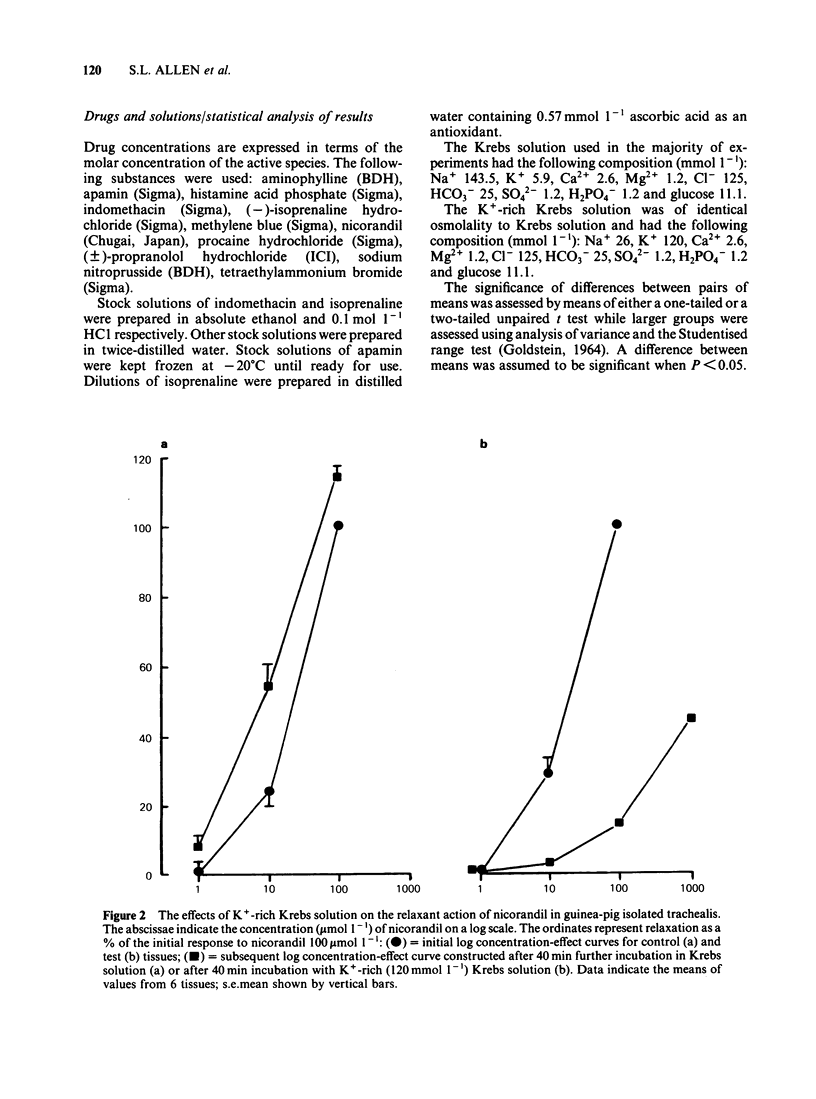
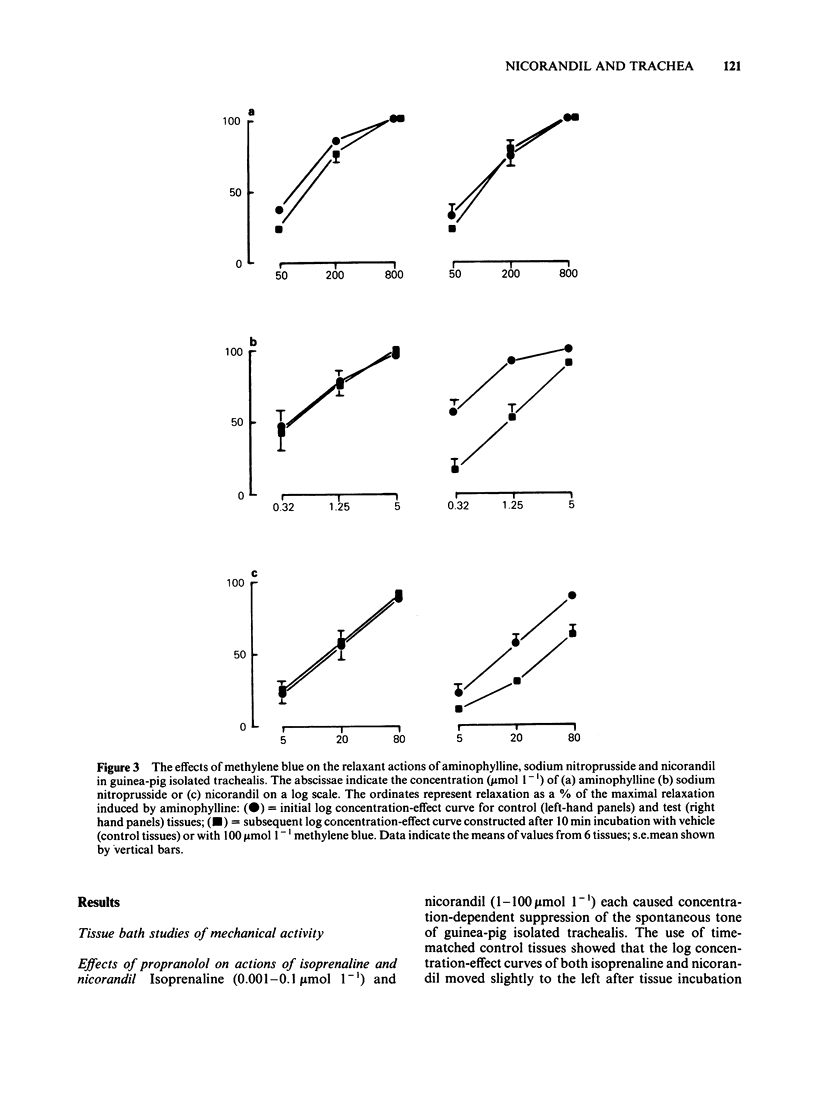
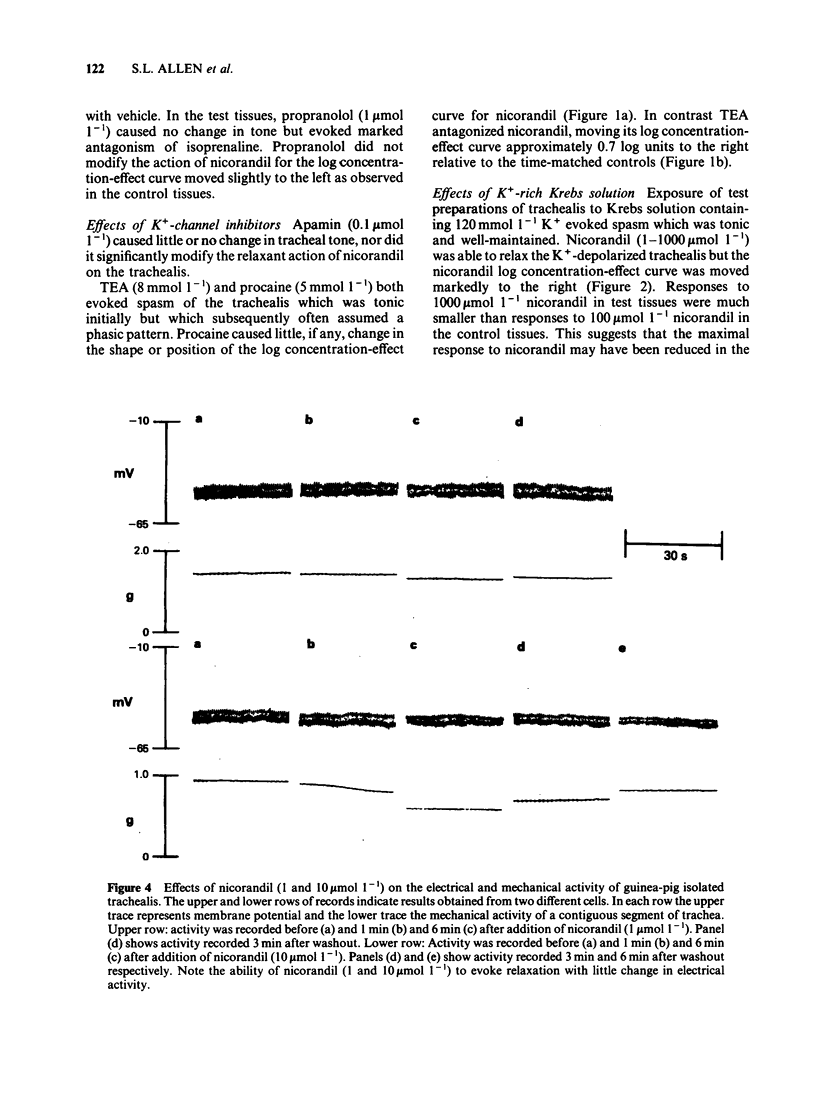
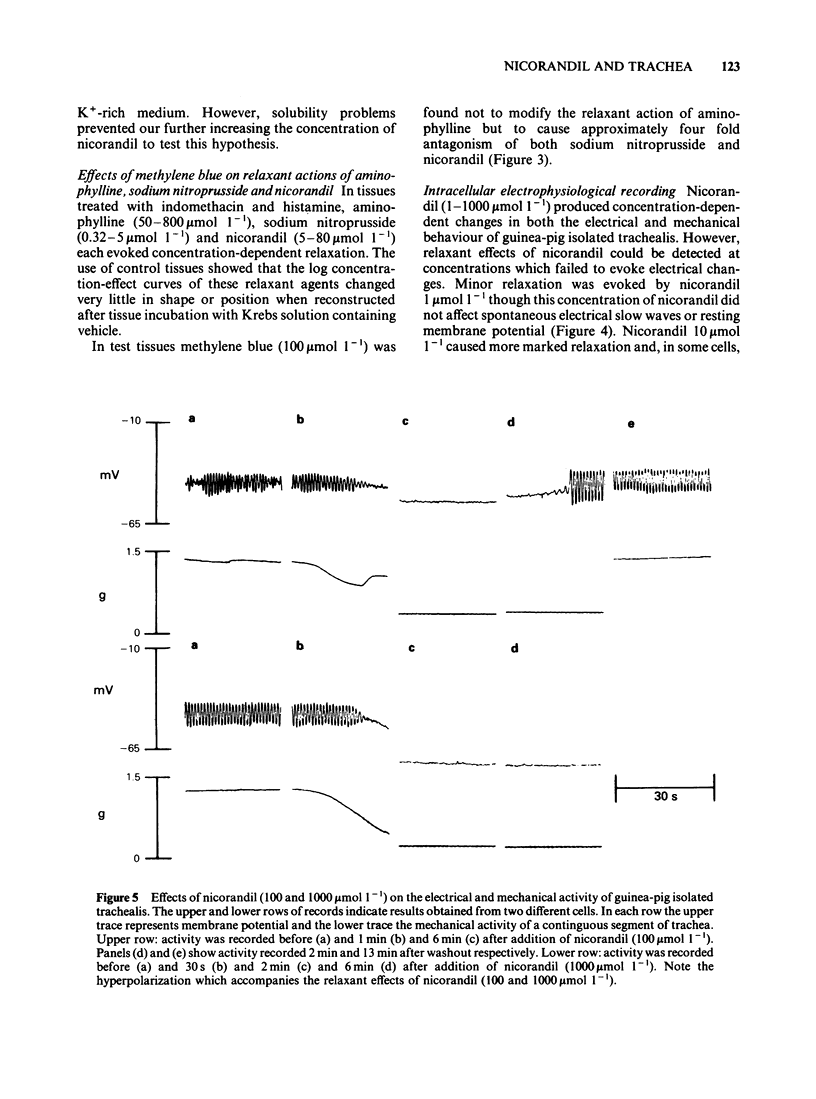
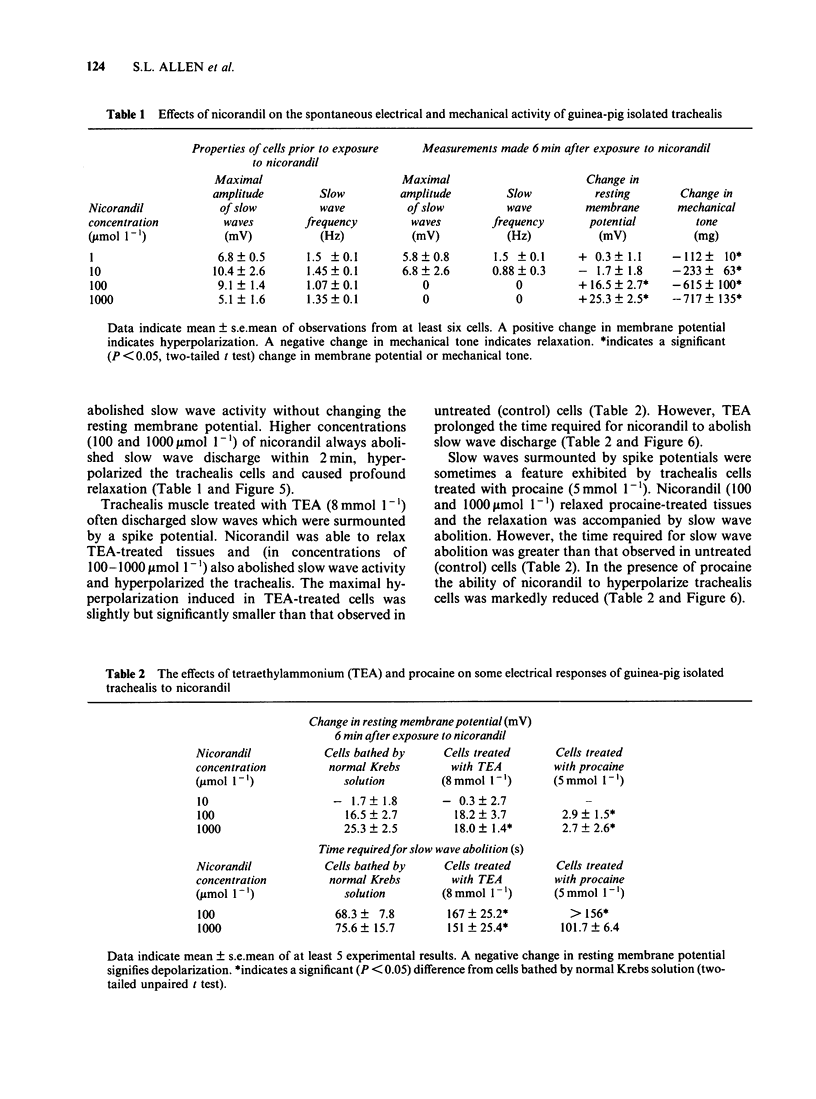
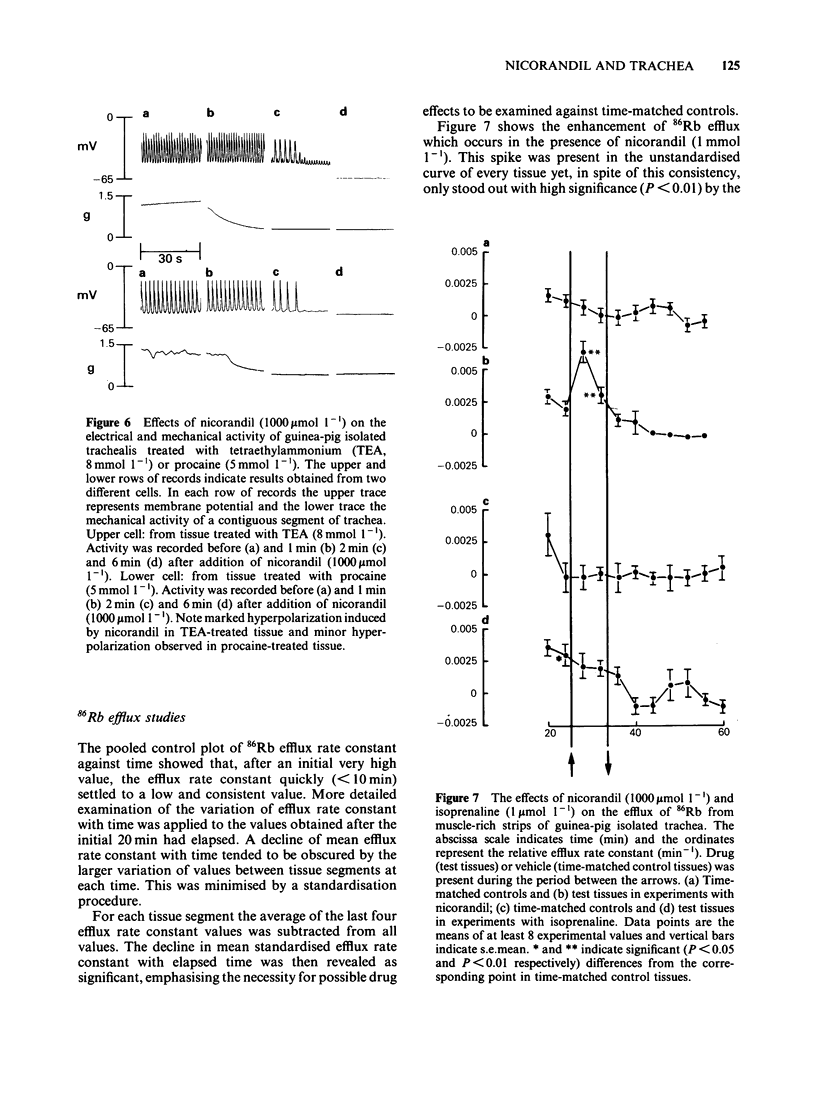
Nicorandil (1-1000 mumol l-1) caused concentration-dependent relaxation of guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Propranolol (1 mumol l-1) did not modify the relaxant action of nicorandil but antagonized isoprenaline. Among K+-channel inhibitors tested, apamin (0.1 mumol l-1) and procaine (5 mmol l-1) did not modify the relaxant action of nicorandil. In contrast, tetraethylammonium (TEA, 8 mmol l-1) caused five fold antagonism. Trachealis exposed to K+-rich (120 mmol l-1) Krebs solution developed near-maximal tension. Nicorandil relaxed the K+-depolarized tissue though its concentration-effect curve was shifted markedly to the right. In tissues in which tone was induced by histamine, methylene blue (100 mumol l-1) antagonized nicorandil and sodium nitroprusside but did not modify the relaxant action of aminophylline. Intracellular electrophysiological recording showed that nicorandil (1 mumol l-1) could evoke some relaxation in the absence of electrical changes. Higher concentrations (10-1000 mumol l-1) reduced the amplitude and frequency of spontaneous electrical slow waves. Nicorandil also caused concentration-dependent hyperpolarization and relaxation. When the hyperpolarization was sufficiently pronounced slow wave activity was abolished. TEA (8 mmol l-1) induced slow waves which were surmounted by a spike potential. TEA slightly reduced the maximal hyperpolarization induced by nicorandil and increased the time required for nicorandil to abolish slow wave discharge. Procaine (5 mmol l-1) induced slow waves of relatively low frequency. Sometimes these were surmounted by a spike potential Procaine markedly reduced the hyperpolarization induced by nicorandil and increased the time required for abolition of slow waves. In studies of the efflux of 86Rb+ from muscle-rich strips of trachea, nicorandil (1000 mumol l-1) increased the efflux rate constant, whereas isoprenaline (1 mumol l-1) was without effect. It is concluded that nicorandil-induced relaxation does not involve the activation of beta-adrenoceptors but is partly attributable to the formation of nitric oxide from the nitrate moiety in its molecular structure. Nicorandil can evoke relaxation in the absence of membrane potential change but towards the upper end of its effective concentration range, nicorandil increases membrane K+ conductance and thereby evokes hyperpolarization of trachealis cells. The K+ channels opened by nicorandil are permeable to 86Rb, insensitive to apamin and TEA but may be inhibited by procaine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron A. R., Johnston C. F., Kirkpatrick C. T., Kirkpatrick M. C. The quest for the inhibitory neurotransmitter in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Jul;68(3):413–426. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Small R. C. Evidence of poor conduction of muscle excitation in the longitudinal axis of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Evidence that the spasmogenic action of tetraethylammonium in guinea-pig trachealis is both direct and dependent on the cellular influx of calcium ion. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Barry B. K., McNamara D. B., Gruetter D. Y., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. Relaxation of bovine coronary artery and activation of coronary arterial guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide, nitroprusside and a carcinogenic nitrosoamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;5(3):211–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. J. Methylene blue inhibits coronary arterial relaxation and guanylate cyclase activation by nitroglycerin, sodium nitrite, and amyl nitrite. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;59(2):150–156. doi: 10.1139/y81-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. The effect of tetraethylammonium chloride on potassium permeability in the smooth muscle cell membrane of canine trachea. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Ito Y., Takeda K. The effects of 2-nicotinamidoethyl nitrate on smooth muscle cells of the dog mesenteric artery and trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;80(3):459–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Tajima K. Dual effects of catecholamines on pre- and post-junctional membranes in the dog trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;75(3):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Satoh K., Taira N. Effects of nicorandil and its congeners on musculature and vasculature of the dog trachea in situ. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Aug;258(2):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Shiraki Y., Nabata H., Sakai K. Comparative effects of nicorandil and nitroglycerin on tracheal and vascular smooth muscle in the dog, in vivo and in vitro. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;34(3):269–276. doi: 10.1254/jjp.34.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


