Abstract
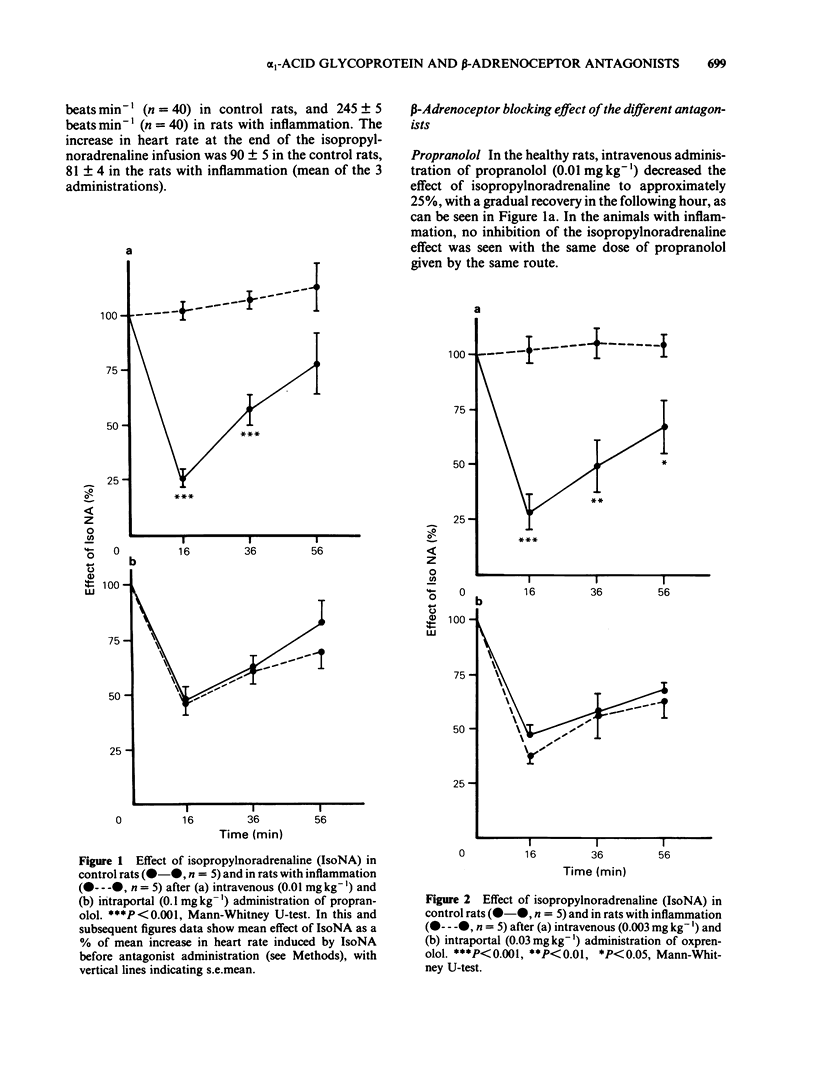
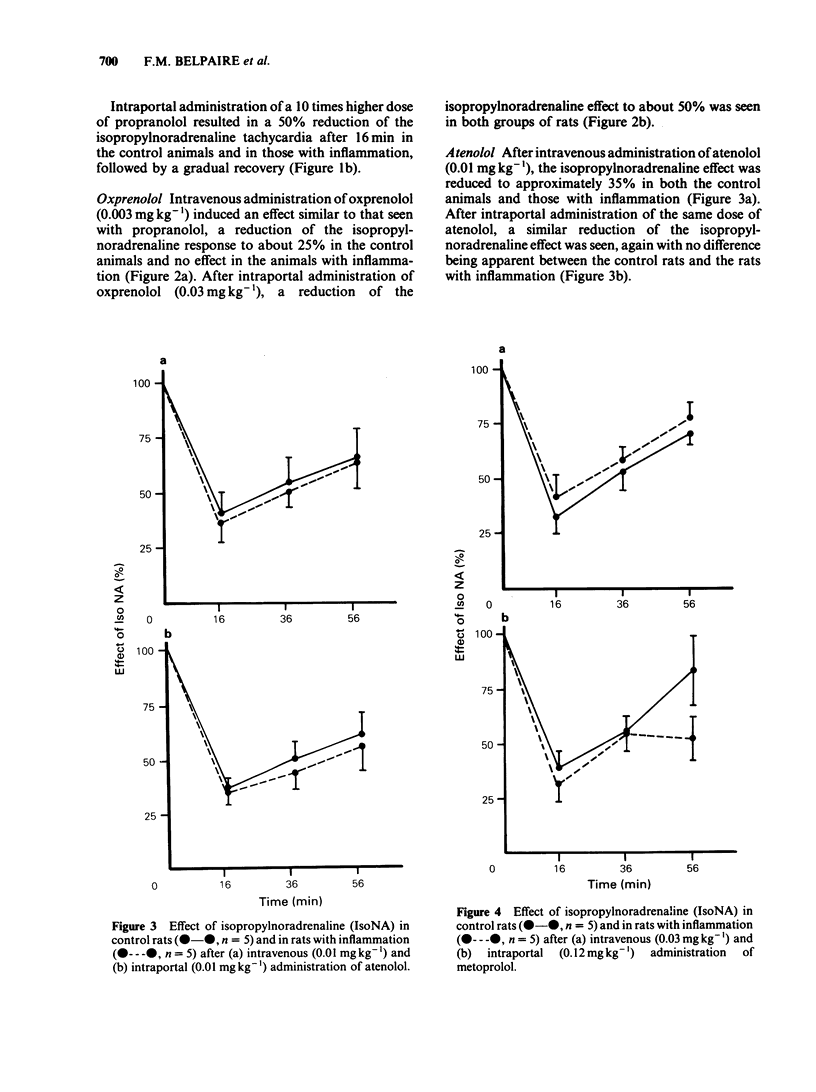
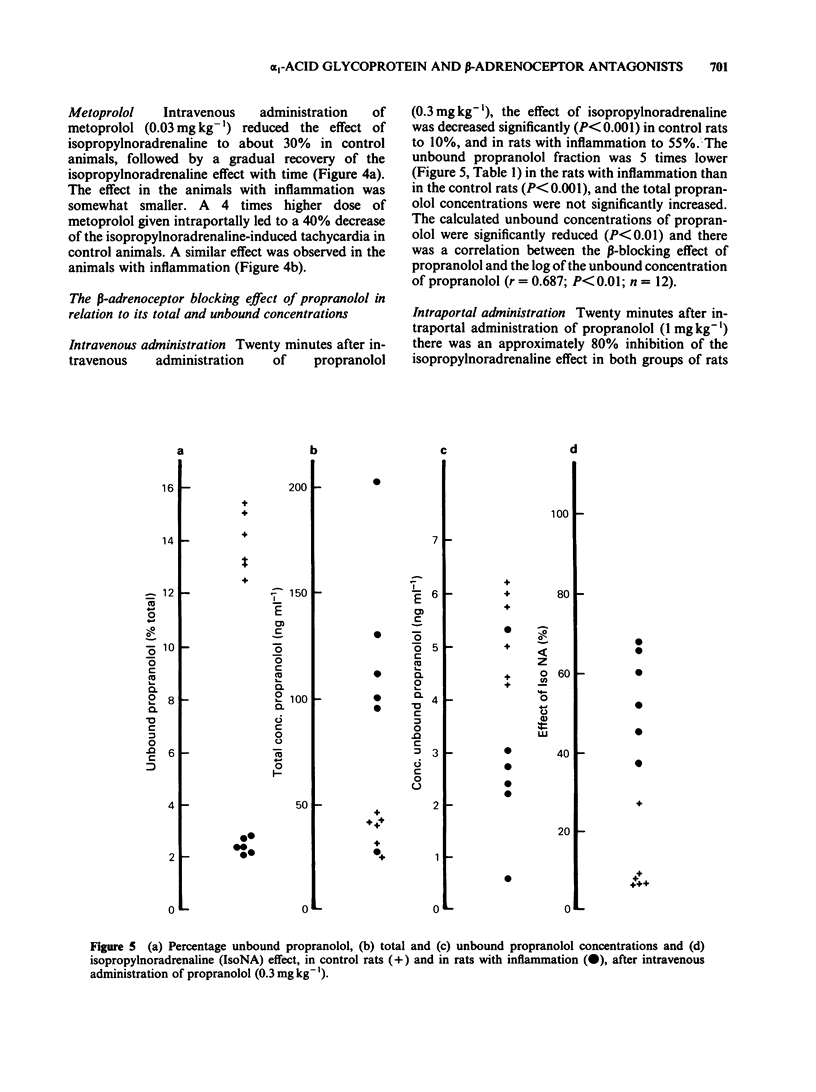
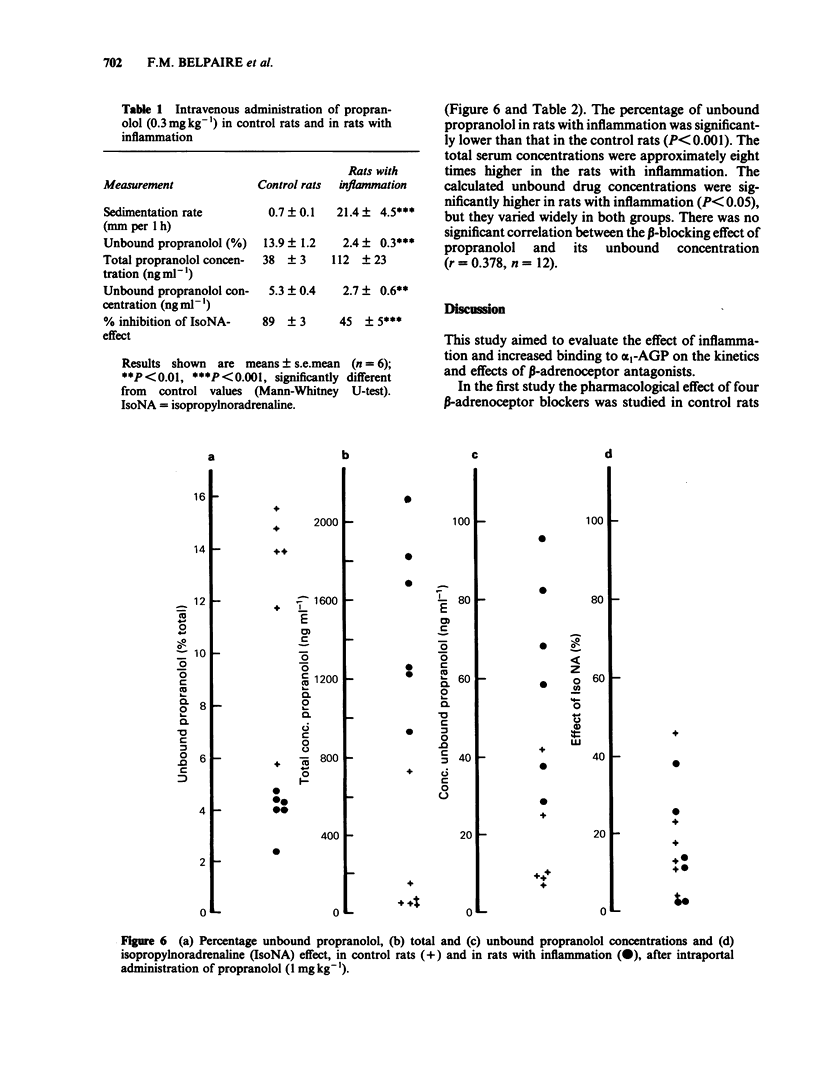
The beta-blocking effect of 4 beta-adrenoceptor antagonists with different pharmacokinetic properties was studied after intravenous and intraportal administration to control rats and to rats with experimental inflammation. In rats with inflammation the effects of propranolol and oxprenolol, which are mainly bound to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (alpha 1-AGP), were significantly less after intravenous administration, but not after intraportal administration. In contrast, for metoprolol and atenolol, which are only negligibly serum bound, no difference was observed between control rats and rats with inflammation for either route of administration. Total and unbound serum concentrations of propranolol were measured 20 min after intravenous and intraportal administration. After intravenous administration, in the rats with inflammation total concentrations of propranolol were more than twice, and unbound concentrations less than half those of control rats. After intraportal administration the total concentrations were 8 times, and the unbound concentrations 3 times higher in the rats with inflammation. There was a significant correlation between the beta-blocking effect and the unbound concentrations of propranolol after intravenous administration, but not after intraportal administration. The latter finding is probably because the unbound concentrations were supramaximal.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bai S. A., Abramson F. P. Interaction of phenobarbital with propranolol in the dog. 3. Beta blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belpaire F. M., Bogaert M. G., Rosseneu M. Binding of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs to human serum albumin, to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and to human serum. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;22(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00545224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop H., Schneider R. E., Welling P. G. Plasma propranolol concentrations in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1981 Jul-Sep;2(3):291–297. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510020310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. C., Ashton F. E., Friesen A. D., Chou B. Studies on acute phase proteins of rat serum. II. Determination of the contents of 1 -acid glycoprotein, 2-macroglobulin, and albumin in serum from rats suffering from induced inflammation. Can J Biochem. 1972 Aug;50(8):871–880. doi: 10.1139/o72-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Quarterman C. P., Bishop H., Schneider R. E. Effects of inflammatory disease on plasma oxprenolol concentrations. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 25;2(6188):465–468. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6188.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt D. G., Frisk-Holmberg M., Hollifield J. W., Shand D. G. Plasma binding and the affinity of propranolol for a beta receptor in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Aug;20(2):152–157. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976202152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel M. T., Bogaert M. G. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of propranolol and 4-hydroxypropranolol in plasma. J Pharm Sci. 1981 Jun;70(6):688–689. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600700631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. E., Babb J., Bishop H., Mitchard M., Hoare A. M. Plasma levels of propranolol in treated patients with coeliac disease and patients with Crohn's disease. Br Med J. 1976 Oct 2;2(6039):794–795. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6039.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. E., Bishop H., Hawkins C. F. Plasma propranolol concentrations and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. E., Bishop H. beta-blocker plasma concentrations and inflammatory disease: clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jul-Aug;7(4):281–284. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. G., Smith C. L., Renwick A. G., George C. F. Intravenous propranolol in patients with inflammation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;13(4):577–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse M. W., Beck F. J. Impaired drug metabolism in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis: a brief review. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Jan-Feb;1(1):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


